Surgery EOR: Cardiovascular (Smarty PANCE)
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
Acute Arterial Occlusion
What is acute arterial occlusion?
Sudden loss of blood flow to an extremity due to an embolus or thrombus
What is the classic presentation of acute arterial occlusion?
The 6 Ps: Pain, Pallor, Pulselessness, Paresthesia, Paralysis, Poikilothermia
What is the most common cause of acute arterial occlusion?
Embolism from atrial fibrillation or recent myocardial infarction
What imaging is used to confirm acute arterial occlusion?
Duplex ultrasound or CT angiography
What is the first-line treatment for acute arterial occlusion?
Immediate anticoagulation with heparin
What is the definitive treatment for acute arterial occlusion?
Surgical thrombectomy or embolectomy
What is a complication of untreated acute arterial occlusion?
Irreversible limb ischemia and potential amputation
What is the role of thrombolytics in acute arterial occlusion?
Considered if surgery is not immediately available or for distal occlusions
How does compartment syndrome relate to acute arterial occlusion?
It can develop after reperfusion, requiring fasciotomy
What are the risk factors for acute arterial occlusion?
Atrial fibrillation, peripheral artery disease, recent cardiac events
Aortic Aneurysm
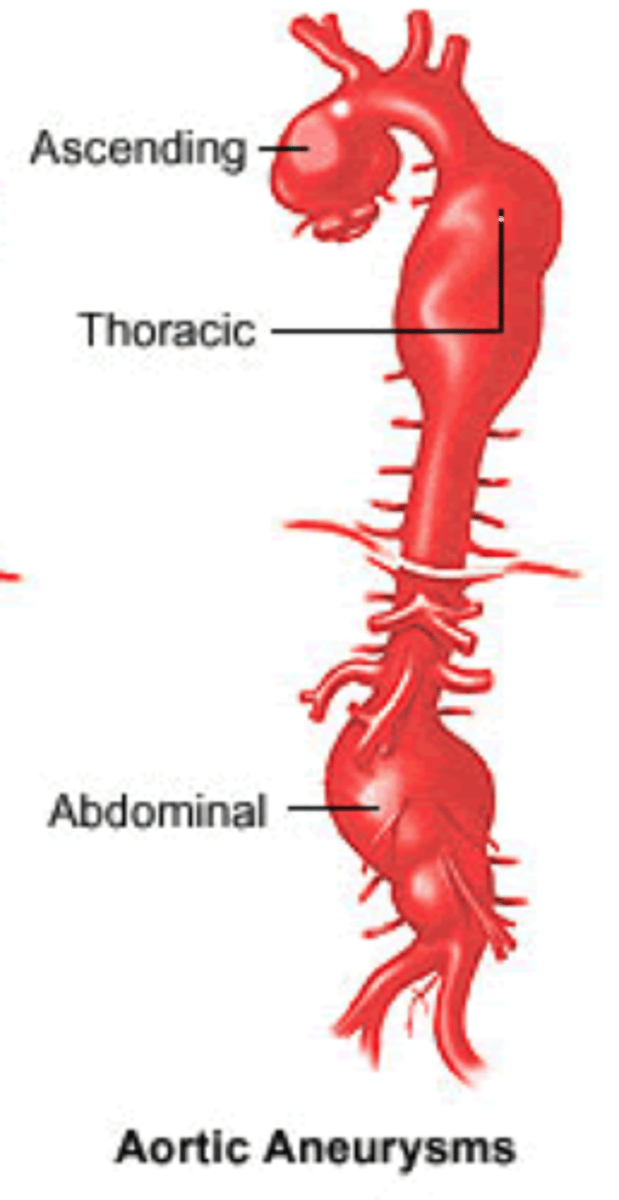
What is an aortic aneurysm?
Abnormal dilation of the aorta, typically >3 cm
What is the most common location for an aortic aneurysm?
Abdominal aorta
What are the risk factors for developing an aortic aneurysm?
Smoking, hypertension, family history, male gender
What imaging is used to screen for an aortic aneurysm?
Abdominal ultrasound
What is the threshold for elective repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
>5.5 cm or rapid expansion (>0.5 cm/year)
What is the typical presentation of a ruptured aortic aneurysm?
Sudden onset of severe abdominal or back pain with hypotension
What is the treatment for a ruptured aortic aneurysm?
Emergent surgical repair
What are the complications of untreated aortic aneurysm?
Rupture, thrombosis, embolism
What is the role of CT angiography in aortic aneurysms?
To assess the size and extent of the aneurysm and plan surgical repair
What is the mortality rate of ruptured aortic aneurysms?
High, up to 90% if not treated promptly
Aortic Dissection
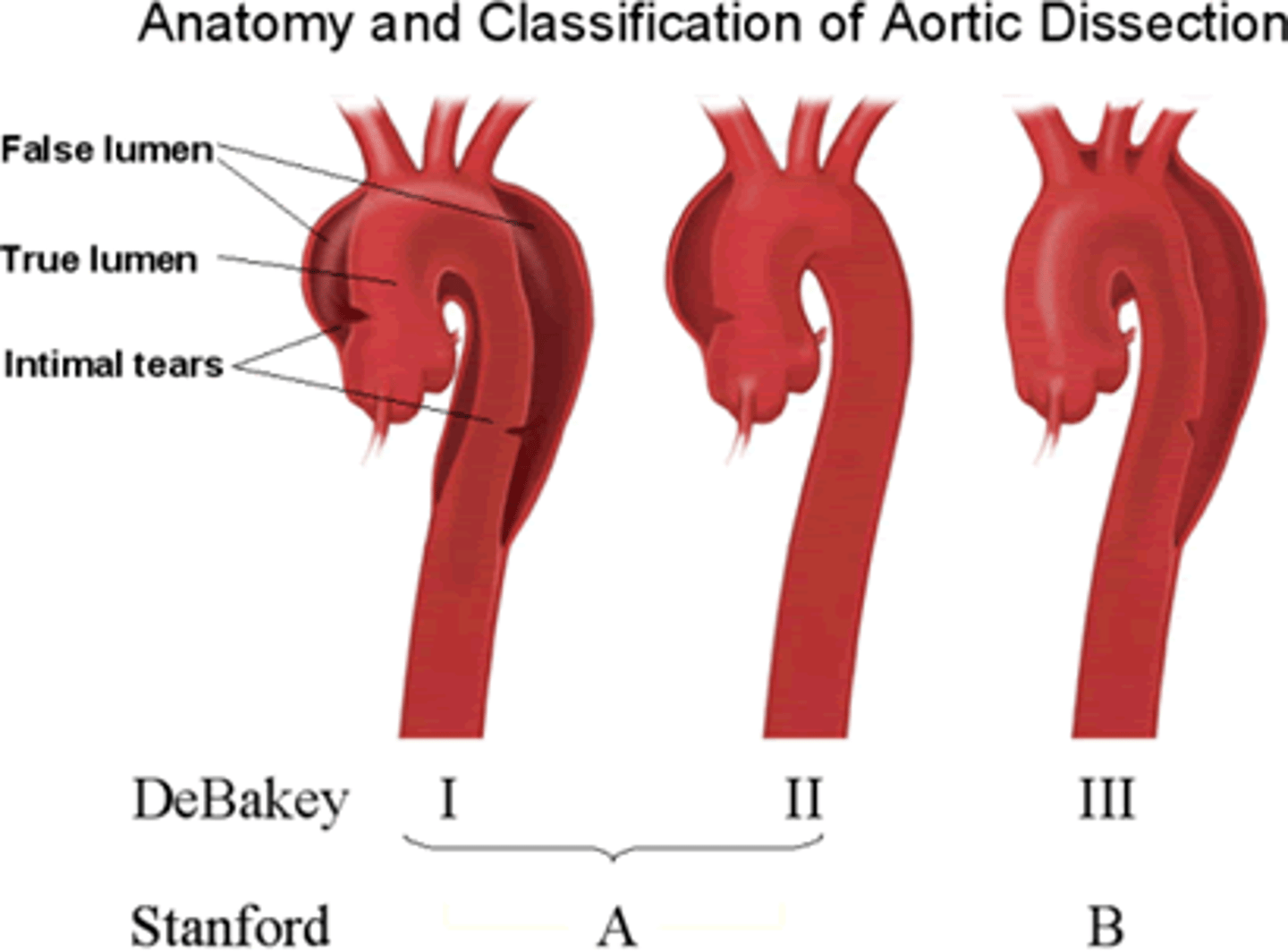
What is an aortic dissection?
A tear in the intimal layer of the aorta leading to blood flow between the layers of the aortic wall
What are the risk factors for aortic dissection?
Hypertension, connective tissue disorders (e.g., Marfan syndrome), aortic aneurysm
What is the typical presentation of aortic dissection?
Sudden onset of severe, tearing chest or back pain
What is the classification system for aortic dissection?
Stanford Type A (ascending aorta) and Type B (descending aorta)
What imaging is used to diagnose aortic dissection?
CT angiography is the gold standard
What is the initial management of aortic dissection?
Blood pressure control with IV beta-blockers (e.g., labetalol)
What is the definitive treatment for Stanford Type A dissections?
Emergent surgical repair
How are Stanford Type B dissections typically managed?
Medical management unless complicated by malperfusion or rupture
What is the major complication of untreated aortic dissection?
Aortic rupture or organ ischemia
What is the mortality rate for untreated aortic dissection?
High, especially for Type A dissections
Chronic Arterial Insufficiency
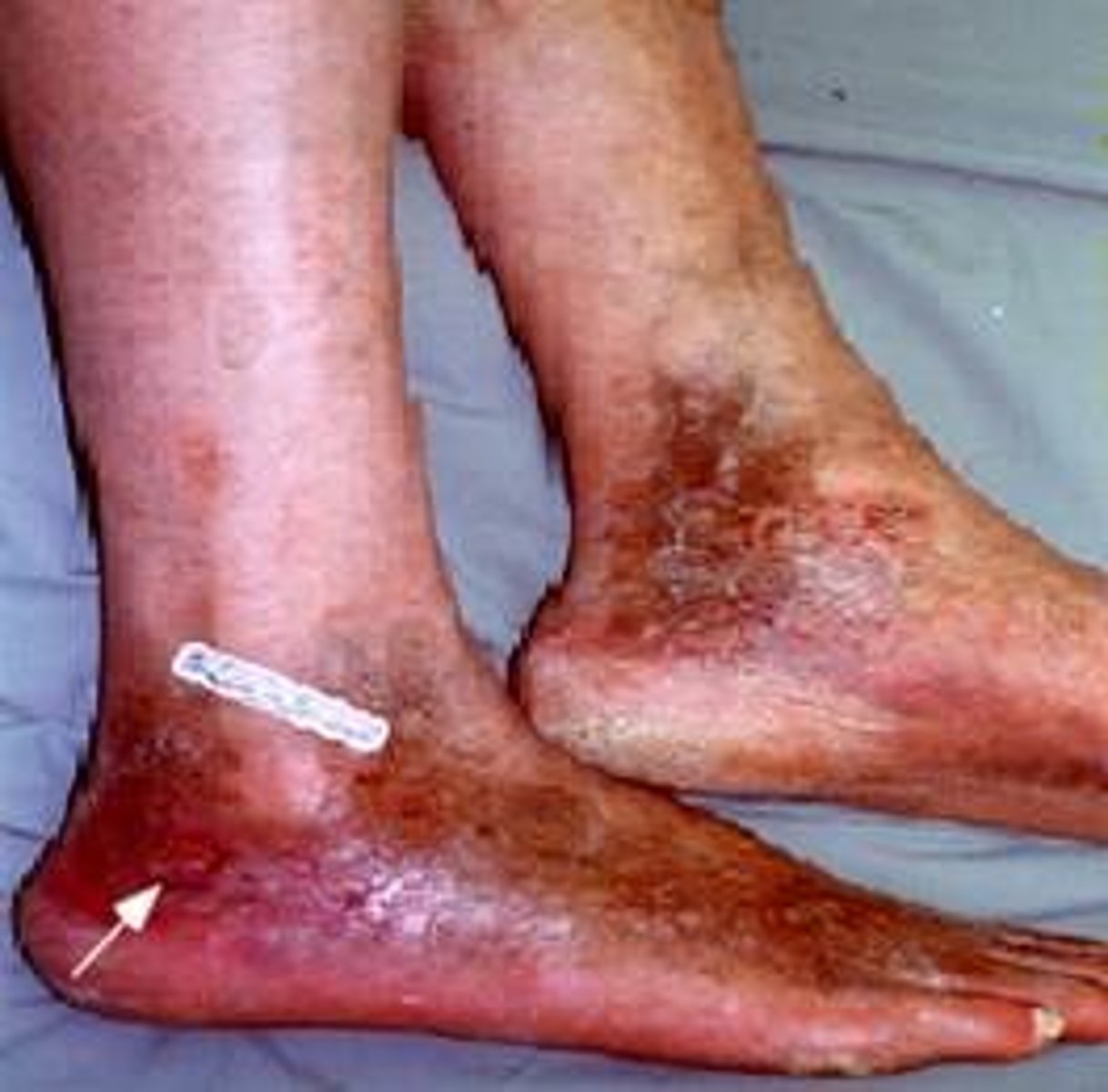
What is chronic arterial insufficiency?
A condition caused by progressive narrowing of the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the limbs
What are the classic symptoms of chronic arterial insufficiency?
Intermittent claudication, rest pain, and non-healing ulcers
What is the most common cause of chronic arterial insufficiency?
Atherosclerosis
What is the ankle-brachial index (ABI) cutoff for diagnosing chronic arterial insufficiency?
ABI <0.9
What imaging is used to assess chronic arterial insufficiency?
Duplex ultrasound or CT/MR angiography
What is the first-line treatment for chronic arterial insufficiency?
Lifestyle modifications (smoking cessation, exercise), antiplatelet therapy, statins
What medications are used to improve walking distance in chronic arterial insufficiency?
Cilostazol
What is the definitive treatment for severe chronic arterial insufficiency?
Revascularization via angioplasty or bypass surgery
What is a major complication of untreated chronic arterial insufficiency?
Critical limb ischemia, gangrene
What lifestyle changes can help prevent the progression of chronic arterial insufficiency?
Smoking cessation, control of hypertension, and diabetes management
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
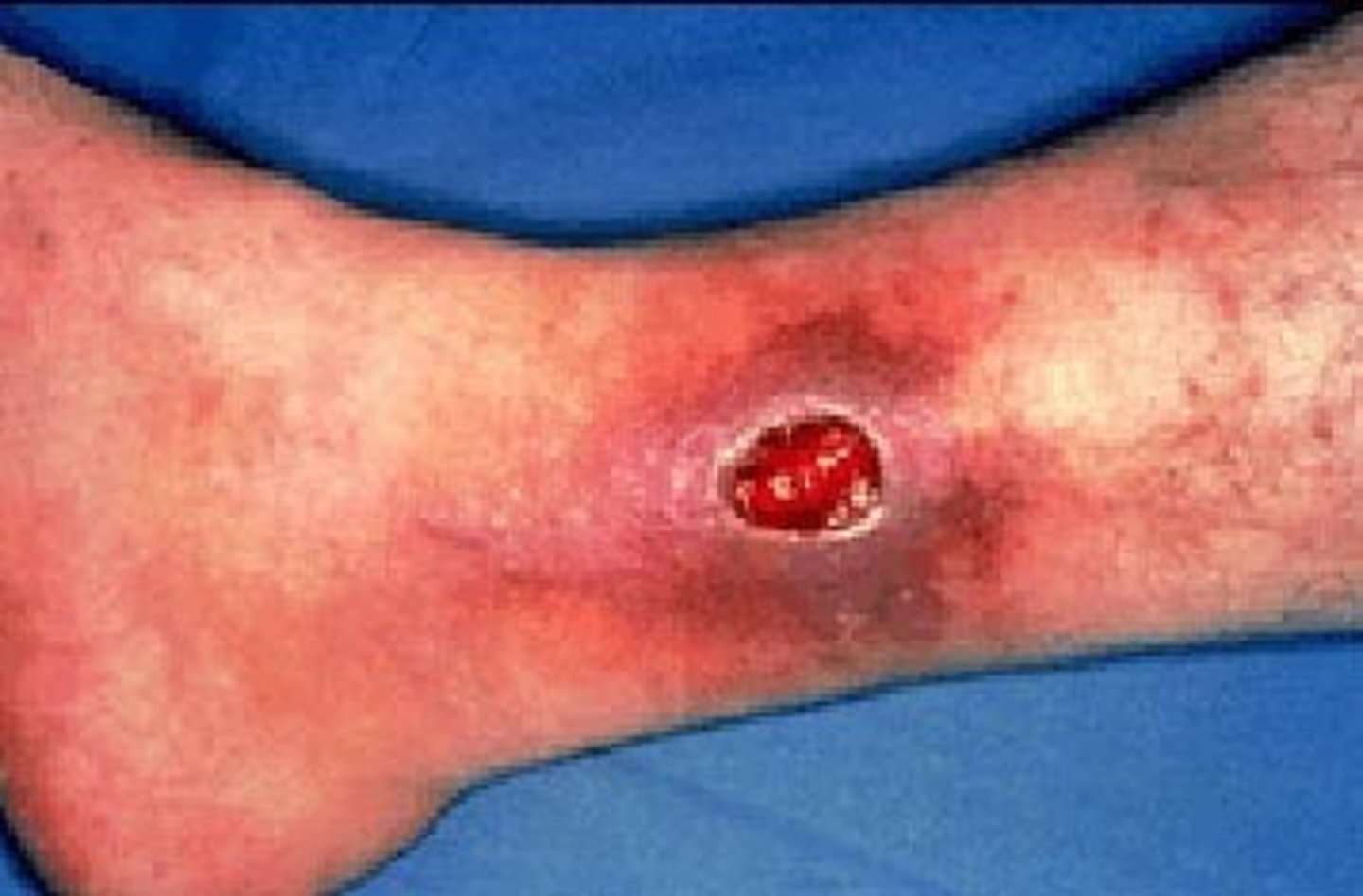
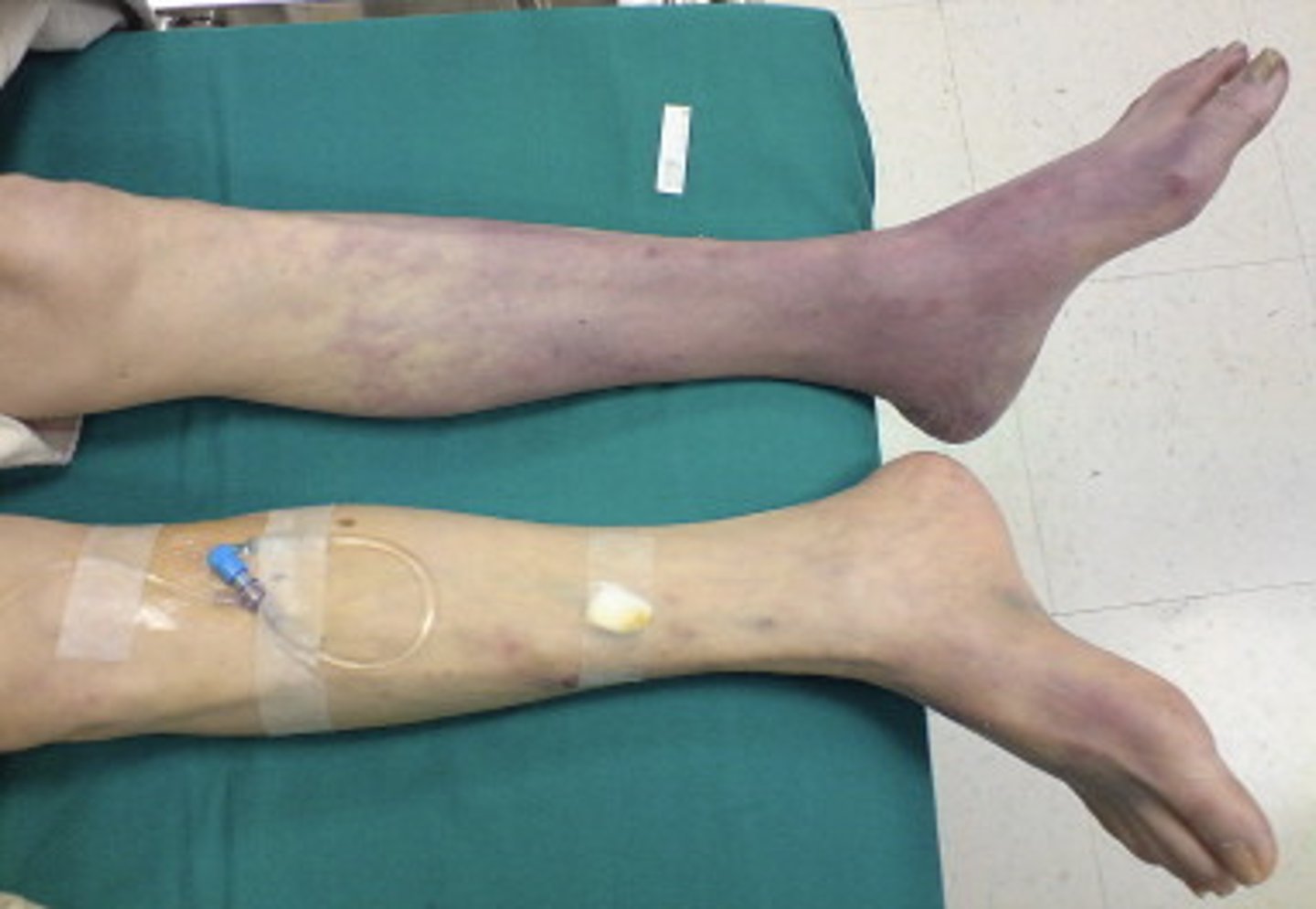
What is chronic venous insufficiency?
A condition where the veins in the legs are unable to return blood effectively to the heart
What are the typical symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency?
Leg swelling, varicose veins, skin changes, and venous ulcers
What is the most common cause of chronic venous insufficiency?
Venous valve incompetence
How is chronic venous insufficiency diagnosed?
Duplex ultrasound to assess venous reflux and obstruction
What is the first-line treatment for chronic venous insufficiency?
Compression stockings and leg elevation
What lifestyle modifications can help manage chronic venous insufficiency?
Weight loss, regular exercise, avoiding prolonged standing
What is the role of surgery in chronic venous insufficiency?
Vein stripping or ablation for severe or refractory cases
What is a common complication of untreated chronic venous insufficiency?
Venous stasis ulcers
What are the skin changes associated with chronic venous insufficiency?
Hyperpigmentation, lipodermatosclerosis, and eczema
How are venous ulcers treated?
Compression therapy, wound care, and sometimes surgery
Compartment Syndrome
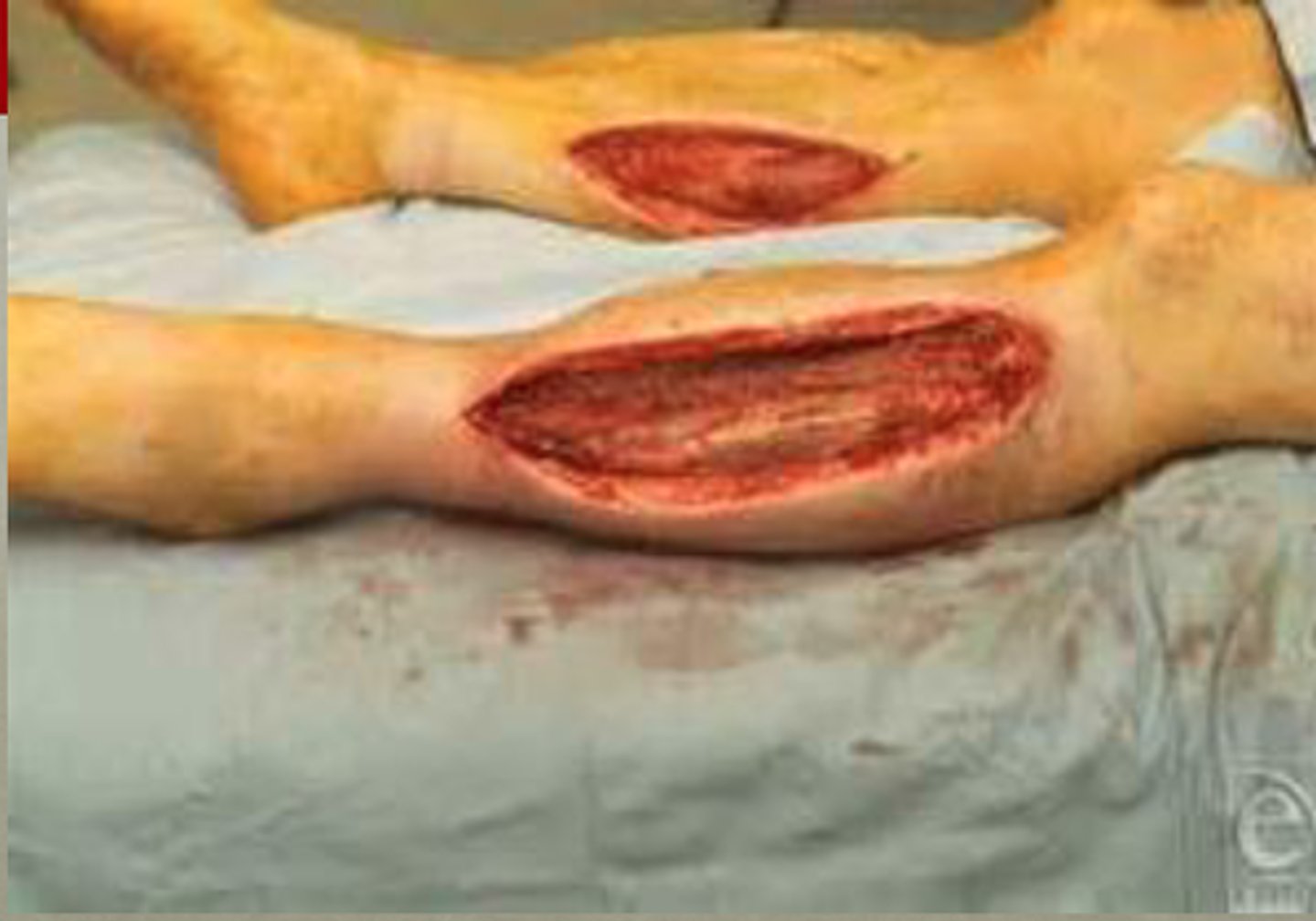
What is compartment syndrome?
Increased pressure within a closed muscle compartment leading to reduced blood flow and tissue damage
What is the most common cause of compartment syndrome?
Trauma, fractures, or crush injuries
What are the early signs of compartment syndrome?
Pain out of proportion to injury, pain with passive stretch
What is the definitive treatment for compartment syndrome?
Emergent fasciotomy
What is the normal compartment pressure
and when does compartment syndrome occur?, Normal pressure is <10 mmHg; compartment syndrome occurs when pressures exceed 30 mmHg
What are the potential complications of untreated compartment syndrome?
Muscle necrosis, nerve damage, limb loss
What imaging is used to diagnose compartment syndrome?
Compartment pressure measurement; imaging is typically not needed
What is the time window for preventing permanent damage in compartment syndrome?
Within 6 hours of symptom onset
What is the role of physical exam in diagnosing compartment syndrome?
Palpable firmness, decreased pulses, and increased pain with passive movement
What are the risk factors for developing compartment syndrome?
Trauma, tight casts or dressings, severe burns
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
What is coronary artery disease?
A condition caused by atherosclerosis leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle
What are the classic symptoms of CAD?
Angina pectoris (chest pain), shortness of breath, and fatigue
What are the major risk factors for CAD?
Smoking, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, family history
What is the initial diagnostic test for suspected CAD?
Stress test or coronary angiography
What is the first-line treatment for stable CAD?
Lifestyle modification, aspirin, beta-blockers, statins, and nitrates
What is the role of coronary angioplasty in CAD?
To open blocked arteries and restore blood flow, often with stent placement
What is the difference between stable angina and unstable angina?
Stable angina occurs with exertion and is relieved by rest, while unstable angina occurs at rest and is more severe
What is the role of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) in CAD?
For patients with severe multivessel disease or left main coronary artery disease
What is the target LDL level in patients with CAD?
LDL <70 mg/dL
What are the complications of untreated CAD?
Myocardial infarction, heart failure, arrhythmias
Carotid Artery Stenosis
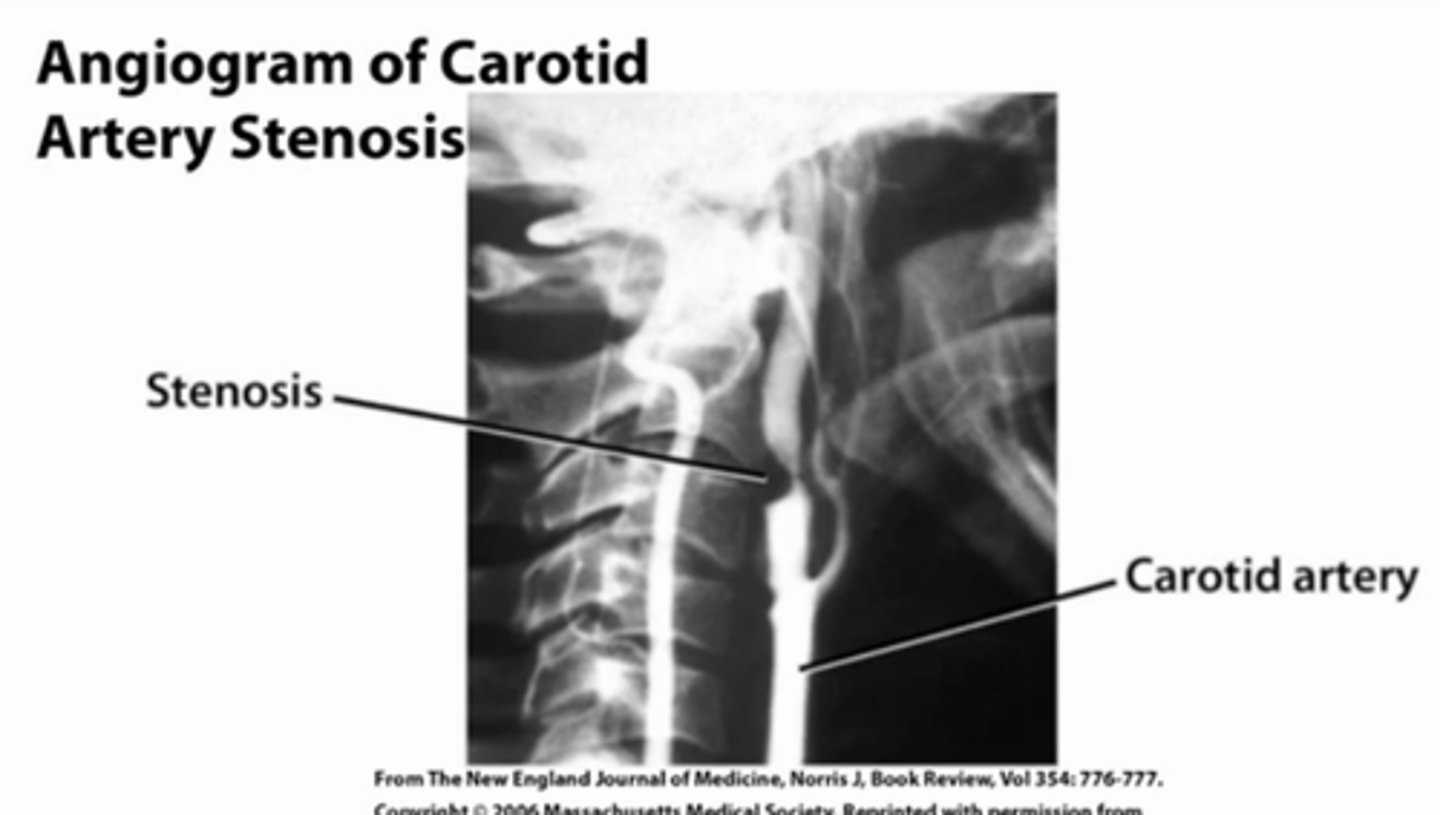
What is carotid artery stenosis?
Narrowing of the carotid arteries due to atherosclerosis
What is the most common presentation of carotid artery stenosis?
Asymptomatic or transient ischemic attack (TIA) symptoms
What is the diagnostic test of choice for carotid artery stenosis?
Duplex ultrasound
What is the treatment for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis?
Antiplatelet therapy (aspirin), statins, and lifestyle modifications
What is the indication for carotid endarterectomy (CEA) in asymptomatic carotid stenosis?
Stenosis >70% with low surgical risk
What is the role of carotid artery stenting in carotid artery stenosis?
An alternative to CEA for high surgical risk patients
What are the risk factors for carotid artery stenosis?
Smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes
What is the risk of stroke in untreated carotid artery stenosis?
Higher in patients with >70% stenosis
What are the complications of carotid endarterectomy?
Stroke, nerve injury, bleeding
What is the typical follow-up for patients after carotid endarterectomy?
Regular duplex ultrasound to monitor for restenosis
Intestinal Ischemia
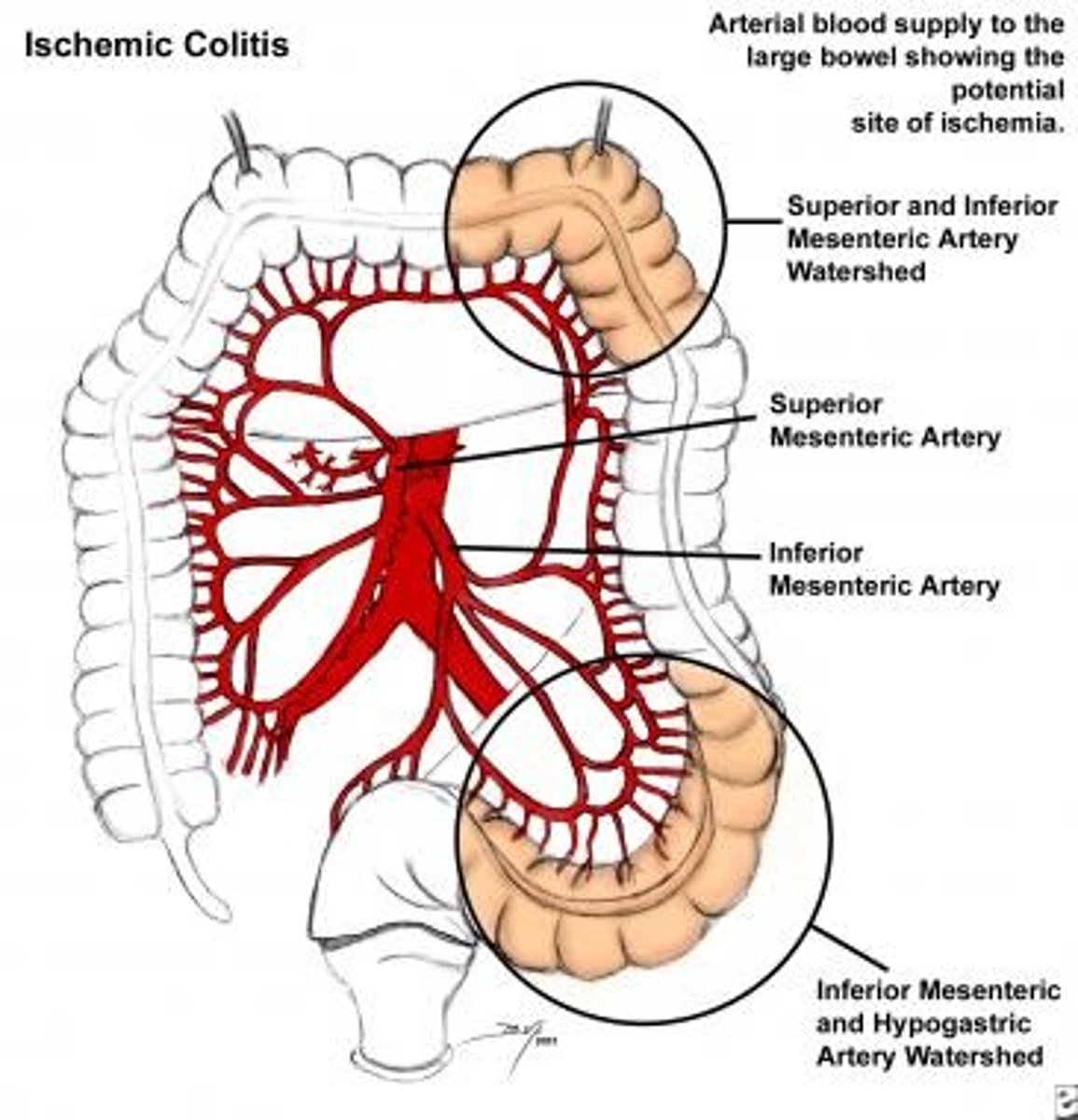
What is intestinal ischemia?
Reduced blood flow to the intestines leading to tissue damage
What are the two main types of intestinal ischemia?
Acute mesenteric ischemia and chronic mesenteric ischemia
What is the typical presentation of acute mesenteric ischemia?
Sudden onset of severe abdominal pain, out of proportion to physical findings
What imaging is used to diagnose acute mesenteric ischemia?
CT angiography
What is the initial management for acute mesenteric ischemia?
Fluid resuscitation, anticoagulation, and sometimes surgical revascularization
What are the common causes of acute mesenteric ischemia?
Embolism, thrombosis, low-flow states (e.g., heart failure)
What is the typical presentation of chronic mesenteric ischemia?
Postprandial abdominal pain and weight loss
What is the definitive treatment for chronic mesenteric ischemia?
Angioplasty or surgical revascularization
What are the complications of untreated intestinal ischemia?
Bowel necrosis, sepsis, death
What is the role of bowel resection in intestinal ischemia?
Required if bowel necrosis occurs
Renal Vascular Disease