Chapter 8: Gene Mutations Molecular Diagnostic Lela Buckingham
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What characteristic of the genetic code facilitates identification of open reading frames in DNA sequence
Out of frame or chance consecutive codons tend to be short and often end in a stop codon
Compare and contrast EIA with western blots for the detection of protein targets
The EIA includes liquid handling and is more easily automated when compared to the Western blot
On a size-exclusion column, large molecules will elute _____________ small molecules
after
MALDI methods separate ions by:
a. molecular volume
b. mass
c. charge
d. mass and charge
D
What is a heteroduplex?
A double-stranded nucleic acid with one or more noncomplementary bases
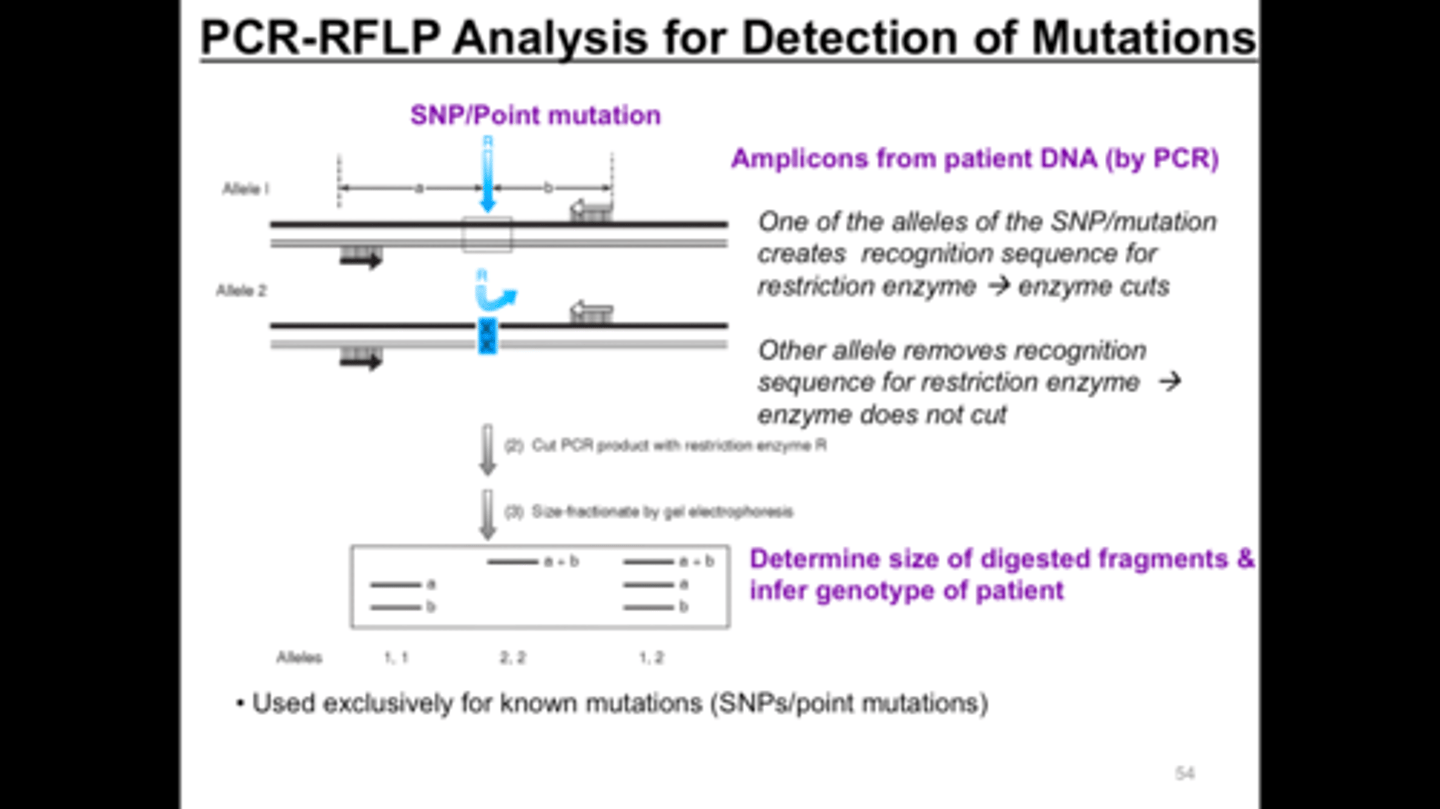
Exon 4 of the HFE gene from a patient suspected of having hereditary hemachromatosis was amplified by PCR. The G to A mutation, frequently found in hemachromatosis, creates an Rsa1 site in exon 4. When the PCR products are digested with Rsa1, what results (how many bands) would you expect to see if the patient has the mutation if no other RSA sites are naturally present in the PCR product
2
Which of the following methods identifies the presence of a mutation but not the mutant sequence
A.SSP-PCR
B.SSCP
C.PCR-RFLP
D. NGS
B
What is the effect on the protein when a codon sequence is changed from TCT to TCC
No effect. Both codons encode for Serine. Translation efficiency might be affected though
A Reference sequence ATGCCCTCTGGC is mutated in malignant cells. The Following mutations in this sequence has been described. Express these mutations using the accepted gene nomenclature (A= nucleotide position 1)
ATGCGCTCTGGC
5C>G
A Reference sequence ATGCCCTCTGGC is mutated in malignant cells. The Following mutations in this sequence has been described. Express these mutations using the accepted gene nomenclature (A= nucleotide position 1)
ATGCCCTC--GC
9_10del or 9_10delTG
A Reference sequence ATGCCCTCTGGC is mutated in malignant cells. The Following mutations in this sequence has been described. Express these mutations using the accepted gene nomenclature (A= nucleotide position 1)
ATAGCCTCTGGC
3_4delGCinsAG or 3_4delinsAG
A Reference sequence ATGCCCTCTGGC is mutated in malignant cells. The Following mutations in this sequence hterm-16as been described. Express these mutations using the accepted gene nomenclature (A= nucleotide position 1)
ATGTCTCCCGGC
4_9inv6
A reference peptide, MPSGCWR, is subject to inherited alterations., The following peptide sequences have been reported. Express these mutations using the accepted nomenclature. (M= amino acid position 1)
MPS(T is underlined)GCWR
s3_g4insT or s3_g4ins1
A reference peptide, MPSGCWR, is subject to inherited alterations., The following peptide sequences have been reported. Express these mutations using the accepted nomenclature. (M= amino acid position 1)
MPSG(X Is underlined)
c5x
A reference peptide, MPSGCWR, is subject to inherited alterations., The following peptide sequences have been reported. Express these mutations using the accepted nomenclature. (M= amino acid position 1)
MPSGCW(LVTGX is underlined)
r7*, r7ins5 or r7lfsx5
A reference peptide, MPSGCWR, is subject to inherited alterations., The following peptide sequences have been reported. Express these mutations using the accepted nomenclature. (M= amino acid position 1)
MPSG(R is underlined)
c5rdel2
A reference peptide, MPSGCWR, is subject to inherited alterations., The following peptide sequences have been reported. Express these mutations using the accepted nomenclature. (M= amino acid position 1)
MPSGCW(GCW Is underlined)R
w6_r7insgcw or w6_r7ins3
What are gene mutations?
any deletions, insertions, inversions, translocations and any other changes that can affect base pairs/DNA sequences
Point mutations
alteration of a single or few base pairs, may or may not affect amino acid codon
What does gene sequencing detect
the mutated base or bases and provides the context of neighboring bases. Can also provide % of variant alleles compared to normal sequence
phenotypic alterations in protein sequence can only be predicted from what
nucleotide sequence
silent mutation
1 nucleotide substitution will not change the amino acid sequence.
Conservative mutation
Results in an amino acid change, but the properties of the amino acid are the same; will not drastically alter protein function (think leucine for valine)
non-conservative mutation
replacement amino acid substitution has vastly different biochemical properties. Changes biochemical nature of protein (Valine for glutamate at position 6 of beta chain in SCA)
nonsense mutation
terminates proteins prematurely when a nucleotide substitution produces a stop codon instead of amino acid codon. 11% of disease related lesions are related to these
frameshift mutations
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide. Throws triplet code out of frame. 3' end may be more minimal than 5' end. Just finding a change in the test DNA also may not guarantee a change
What are some examples of inherited genes/diseases that occur at the same genetic location
Factor V Leiden and Hemochromatosis occurring at C282Y, H63D, S65C mutations
CTFR gene
codes transmembrane regulator protein; moves ions in and out of cells. Aka Cystic Fibrosis Regulator Gene
BRCA1 and BRCA2
breast cancer 1 and 2 - genetic mutations associated with increased risk for breast cancer
Describe the biochemical methods used to detect gene mutations
used to directly analyze the change in protein structure or function--instead of point mutations.
Include immunoassays that can detect the presence of: hormones, drugs, antibodies, cancer biomarkers, metabolites in blood urine/other fluids, can also use immunohistochemistry and GC/MS
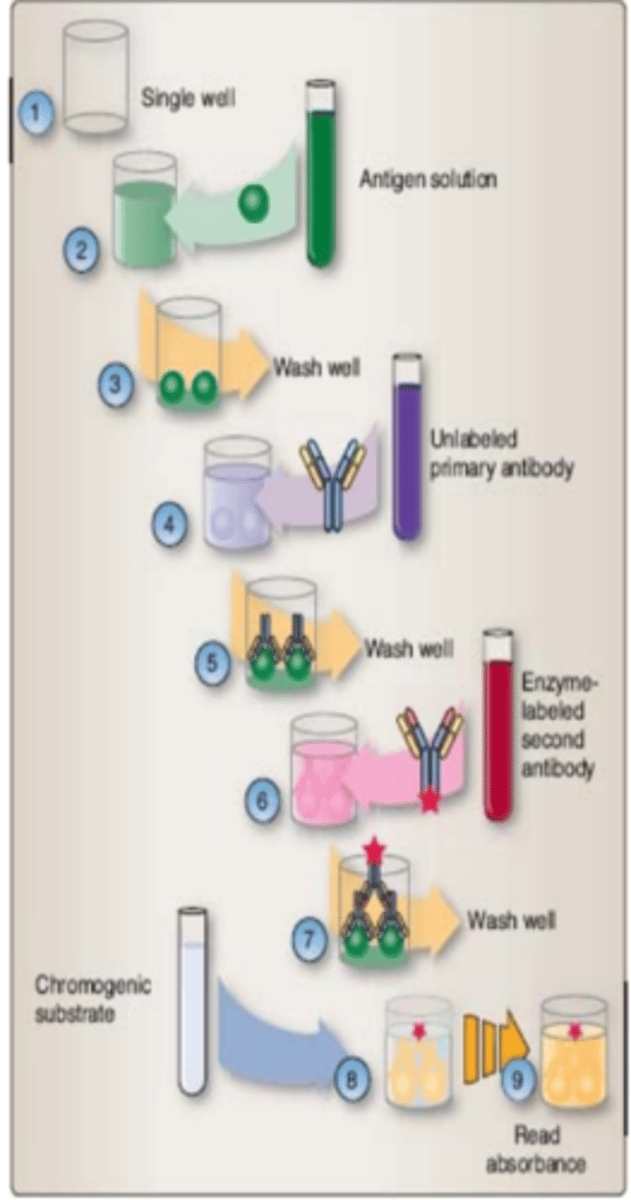
How does a Enzyme Immunoassay occur
plate wells are coated with capture antibodies exposed to test serum diluted in buffer--> bind to antibody-wash-> conjugate antibody is introduced -wash-> substrate added will chemiluminesce if analyte is present.
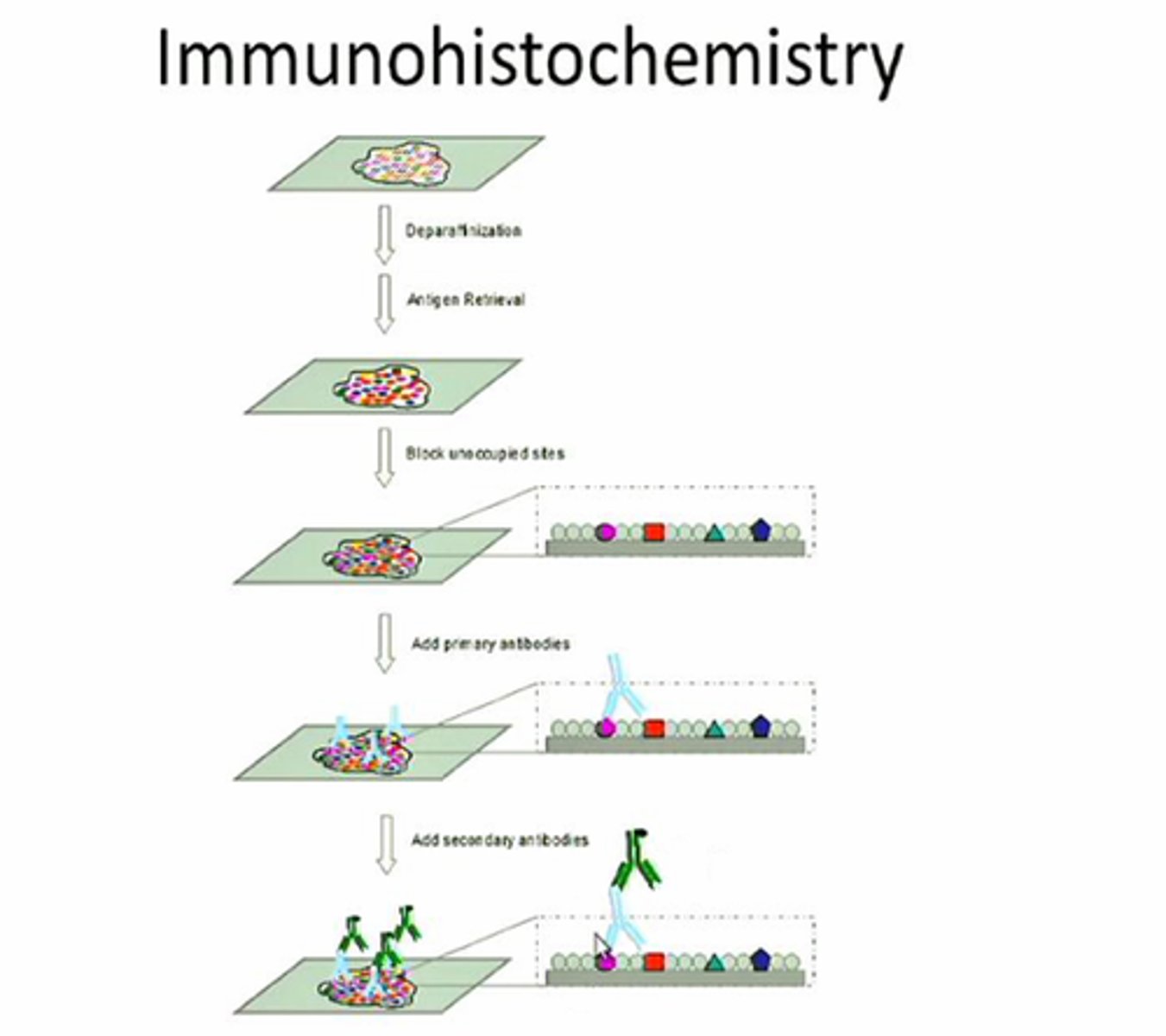
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Test to detect antigens (e.g., proteins) in cells of tissue by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding to specific antigens. uses thin <5 micron sheets thick of fixed tissues 5-15 micron sections in length. Fixed tissues may alter epitopes, may need to be treated with enzymes or heated with water (antigen retrieval). Can be fixed in acetone or cryostat instead of formalin. Endogenous peroxidase, fluoresence, non-specific antibody may interfere with IHC results. Standard in pathology to integrate target detection, localization, and quantify tissue morphology.
Describe Enzyme immunoassays
Flexible, potentially high though-put methods for detecting analytes that can be automated. Positive results have color or antibody fluorescence. Only binding with primary antibody causes limited signal intensity; binding with secondary antibodies increase signal intensity and sensitivity.
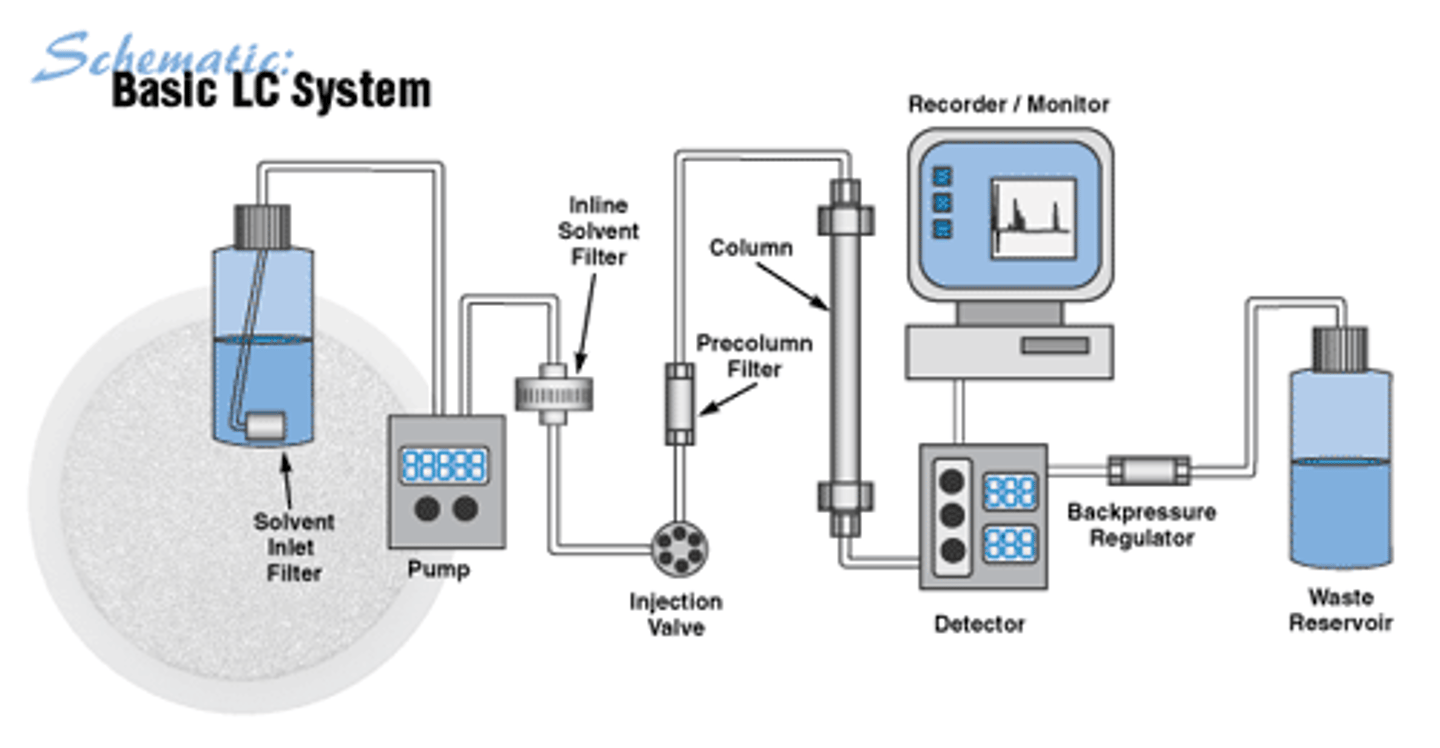
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
A form of chromatography in which a small sample is put into a column that can be manipulated with sophisticated solvent gradients to allow very refined separation and characterization; Basis for seperation/analysis instruments (amino acid analyzers). 1 phases: mobile and solvent that flows through a stationary phase and solid support (isocratic or gradient). Molecules can be identified from normal migration patterns. Stationary phases differ depending upon application.
Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC)
higher resolution, decreased separation time, and uses less solvent when compared to normal HPLC
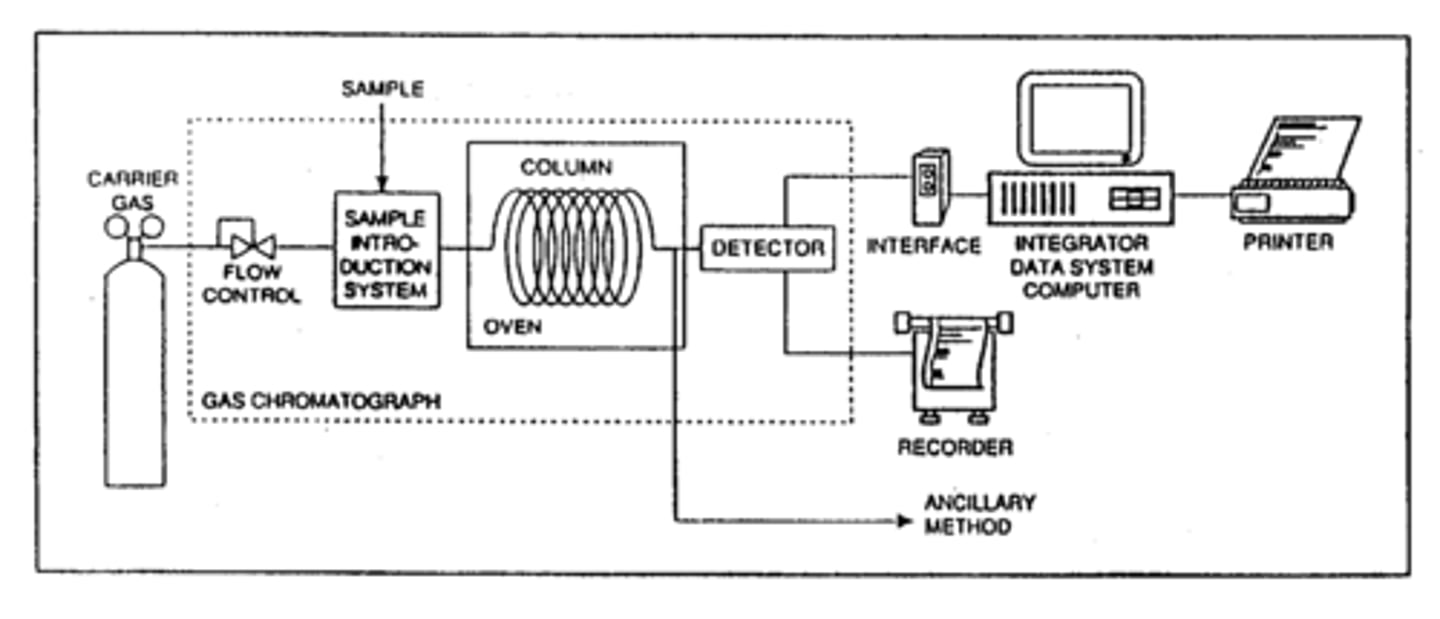
Gas chromatography
automated mobile phase is an inert gas, stationary phase is a high boiling point liquid that is observed to an inert solid support in the column. Strength of the interaction/dissolution of sample into the liquid phase will result in varying retention times in column. Couple with MS to identify biomarkers of disease
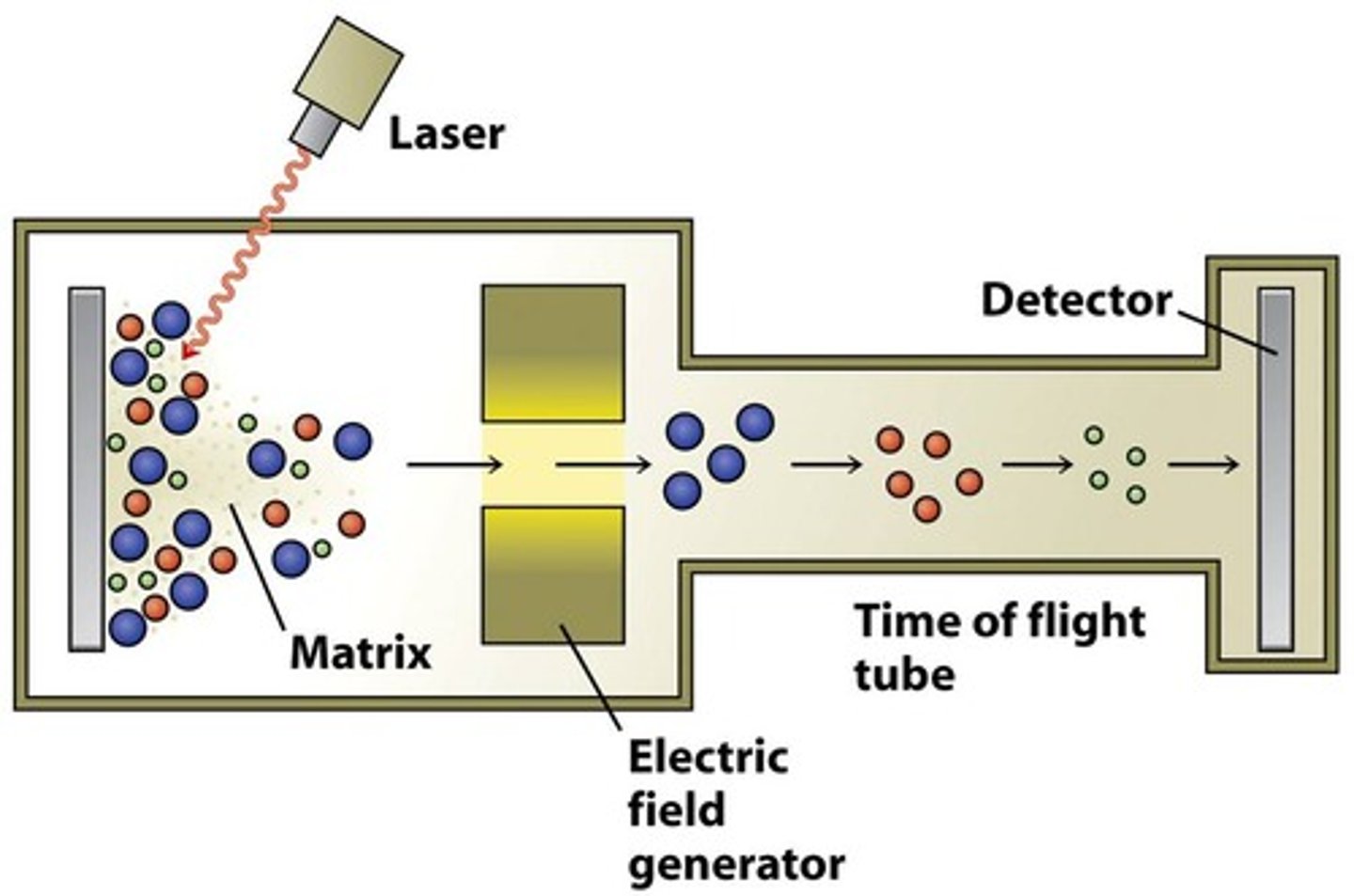
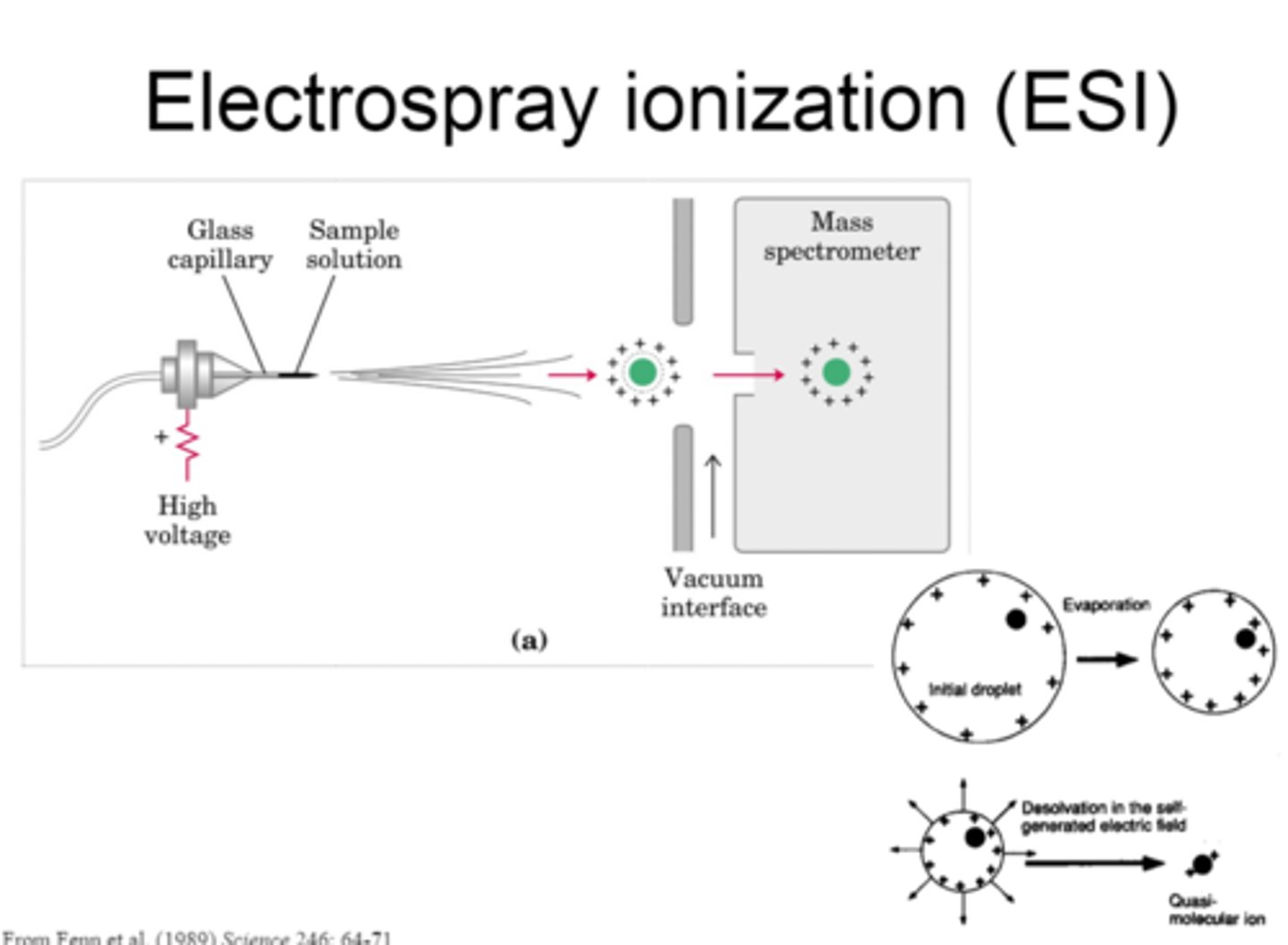
Mass spectrometry
coverts molecules to ions that can be moved in a magnetic field based on their charge and mass. There are two methods to identify large biomolecules such as proteins: Electrospray ionization (ESI) and MALDI. MALDI-TOF ID High Molecular weight molecules, SELDI-TOF identify and quantifies peptides. Nucleic acids can also be measured by mass spec, single BC changes can be identified by primer extension
Nucleic acid analysis
Inherited mutations are detected from blood/buccal cells. Somatic mutations use PCR+ techniques that minimize excess mutations being added. Mutation scanning just sees if there is a mutation present, needs confirmation and characterization. Classified based on 3 broad approaches: Hybridization based methods, polymerization-sequence based methods, Enzymatic/Cleavage based sequencing methods
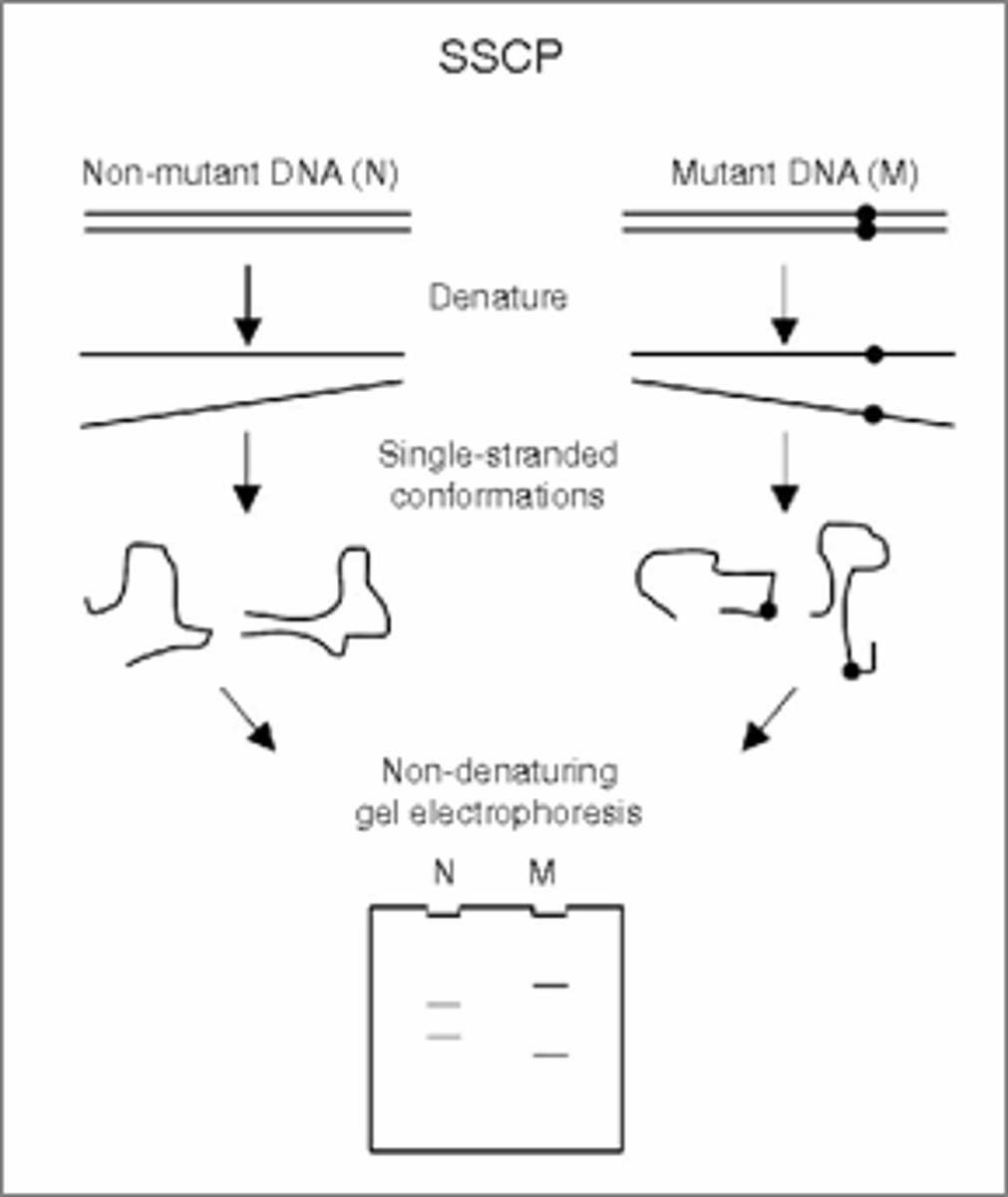
Hybridization based methods: Single-stranded confirmation polymerization (SSCP)
Based on preference of DNA and RNA to exist in double strand state (not single strand state). If the double strand is not available, single strands will fold over into a 3D conformer based on primary structure. Migration of conformers in polyacrylic gel under controlled conditions distinguishes sequence variants. Speed of migration depends on shape and size of conformer(Differences in shape are caused by nucleotide sequence differences in DNA). Detects 35-100% of mutations, sensitive enough to detect a mutation if 5% is present in sample but 30% is recommended.
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: Sequencing
Target BP >1000 Accuracy 100% Specificity 100% Sensitivity 10-20%
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: SSCP
Target BP 70-100 Accuracy 70-100 Specificity 80-100 Sensitivity 5-20
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: ASO
Target BP defined Accuracy 100 Specificity 90-100 Sensitivity 5-20
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: HR-MCA
Target BP defined Accuracy95-100 Specificity 95-100 Sensitivity 1-5
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: DHPLC
Target BP Accuracy 95-100 Specificity85-100 Sensitivity 5-20
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: Array Technology
Target BP defined, multiplex Accuracy 95-100 Specificity 80-100 Sensitivity 1-5
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: SSP
Target BP defined Accuracy 98-100 Specificity 95-100 Sensitivity .0005
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: Allelic Discrimination
Target BP defined Accuracy 95-100 Specificity 90-100 Sensitivity 0.0001
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: PCR-RFLP
Target BP Defined Accuracy 100 Specificity 100 Sensitivity .01-1
Summary of Mutation detection methodologies: Cleavage
Target BP defined/multiplex Accuracy 100 Specificity 100
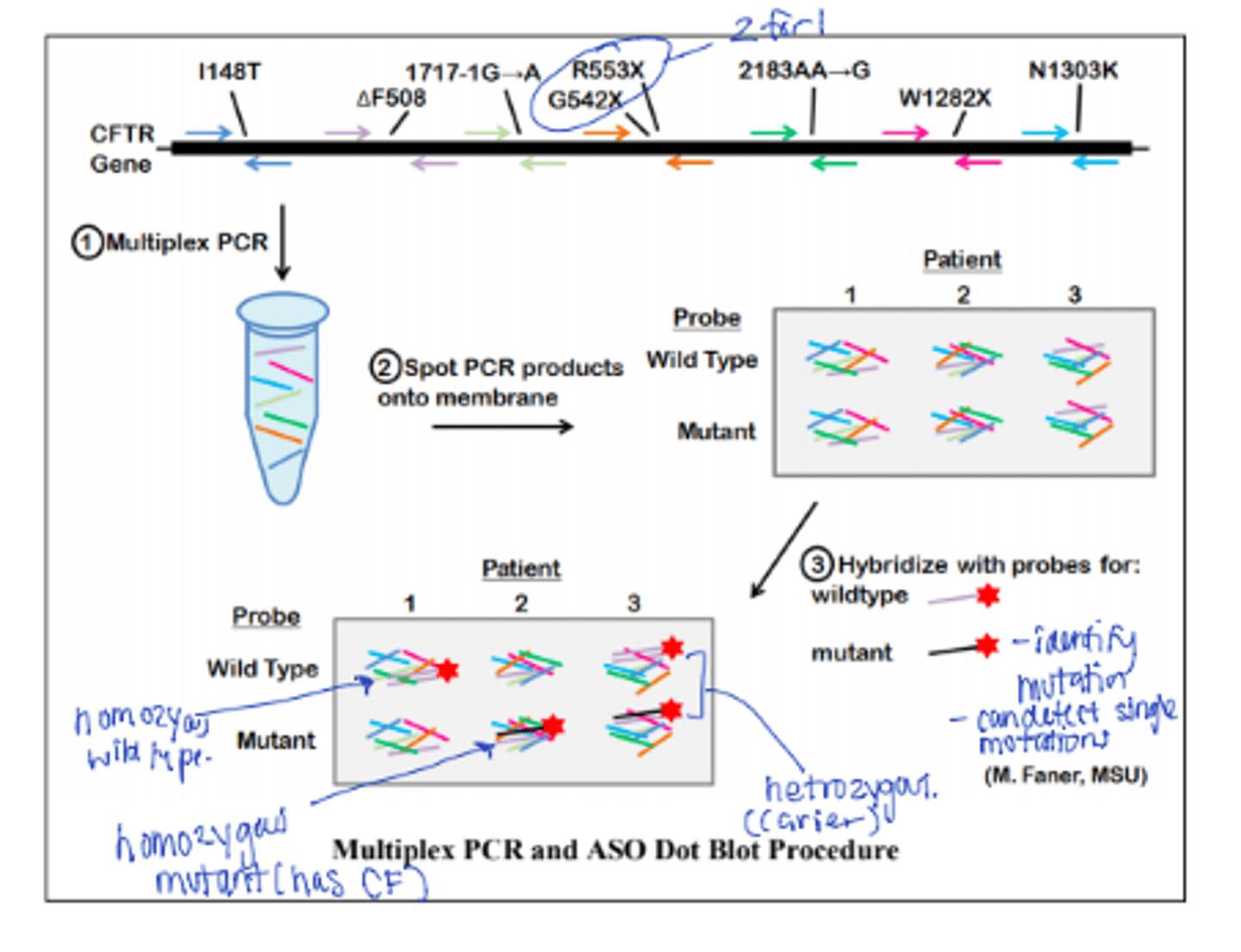
Allele specific Oligomer hybridization (ASO)
AKA Allele specific hybridization. Utilizes differences in the melting temperatures of short sequences of about 20 bp with 1 or 2 mismatches and those with no mismatches. Uses immobilized target + labeled probe ID--BRCA 1 and 2 mutations p16 in familial melanoma. Cause use reverse dot blot for MTB and C trachomatis. Been applied to HLA antigen typing, replaced with Bead microarray and NGS
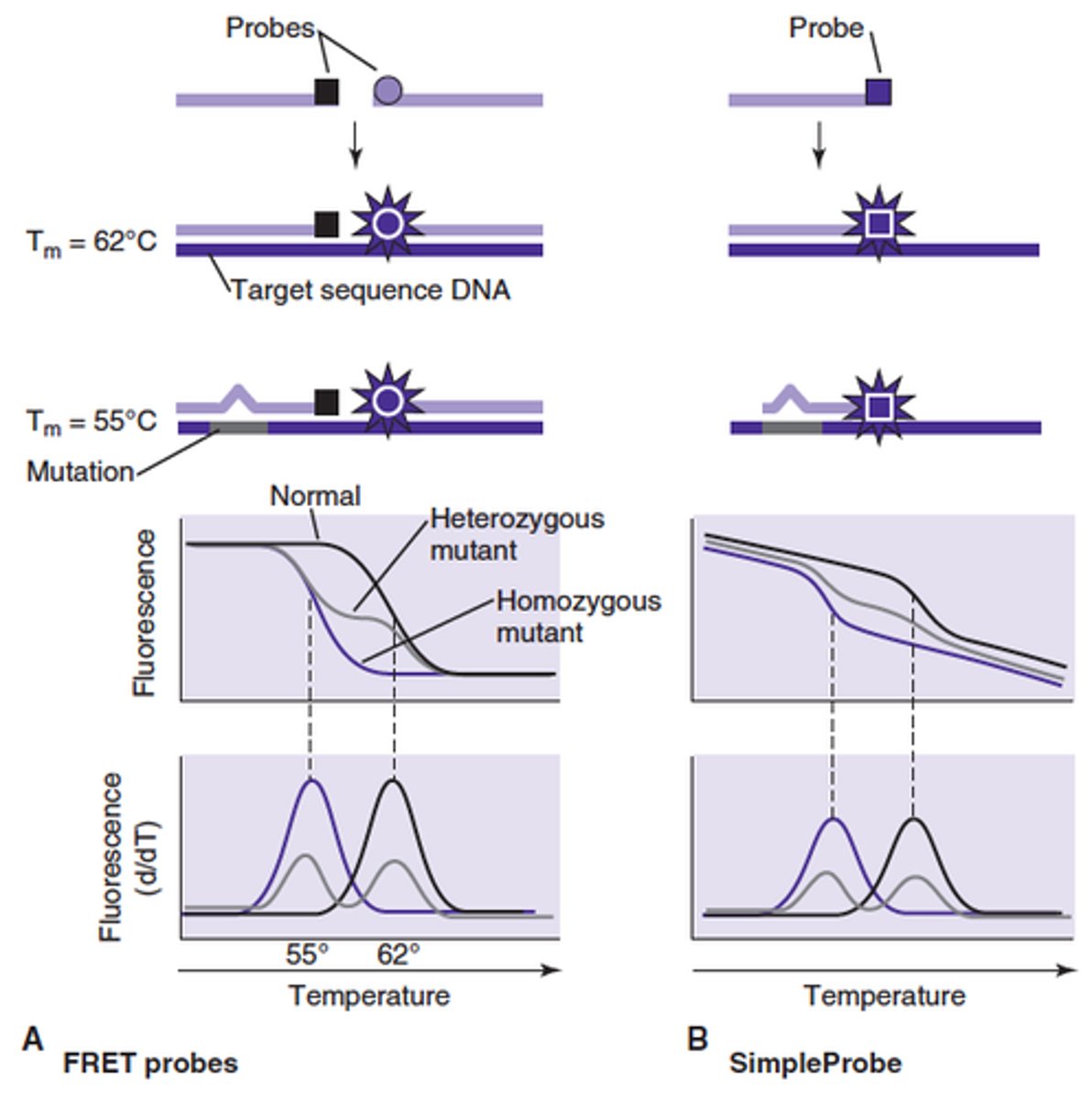
Melt Curve Analysis (MCA)
exploits the sequence and stacking directed denaturation characteristics of DNA duplexes. Post amplification step of real time PCR. Sequence differences result in different melting characteristics and Tm for each sequence. Non specific dues are not sequence specific and do not distinguish between target and junk.
Specificity can be increased greatly using HR-MCA. How is this different from normal MCA
HR-MCA uses FRET probes that hybridize next to one another across sequence positions that are being analyzed. If the Tm in this run is lower than the normal Tm, the probe+ complement indicates that there is a mutation or sequence that is different than the reference probe+ test sequence. Mostly done with 2 probes. Requires special instrumentation, detects DNA polymorphology and can microtype organisms. Natural sequence variation can cause false positives.
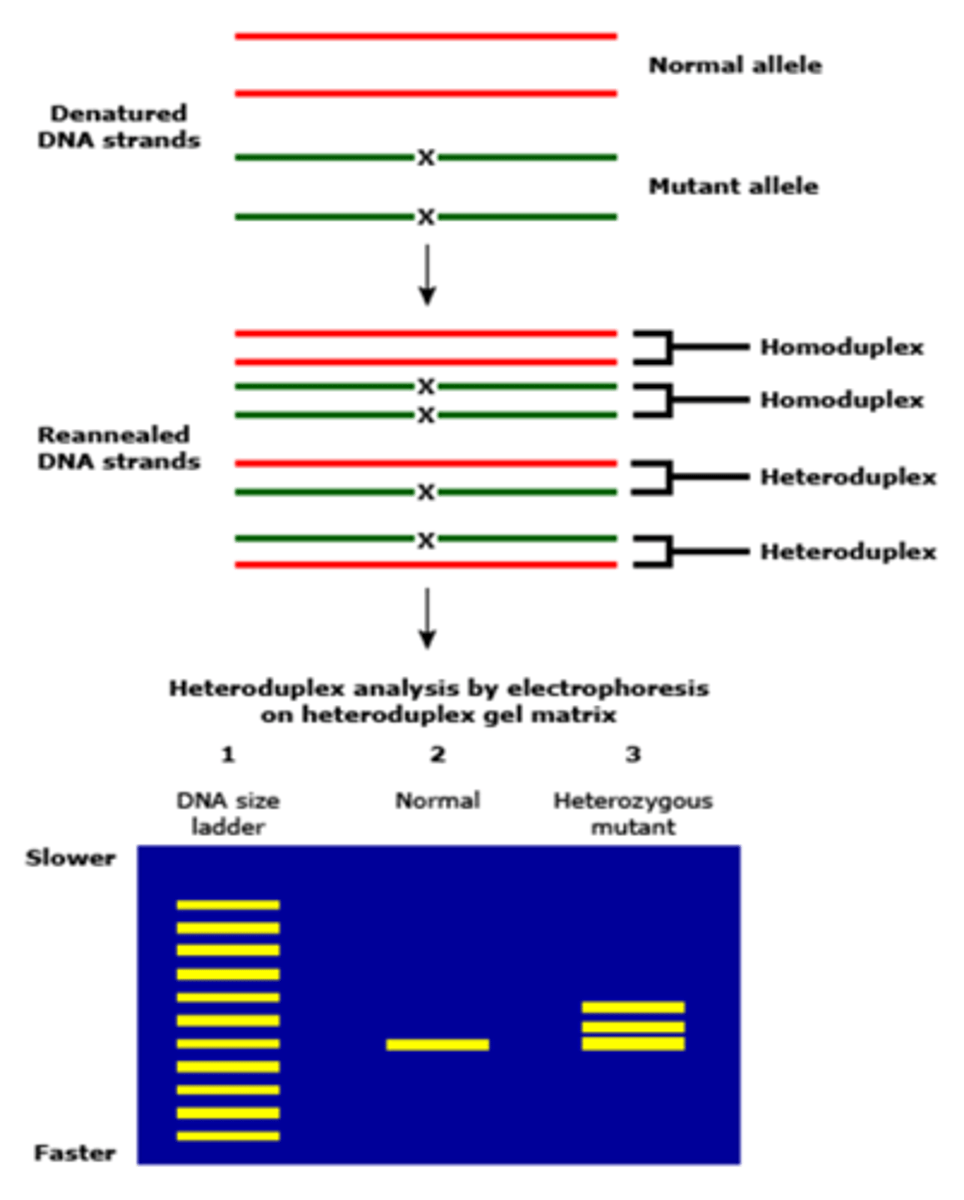
Heteroduplex Analysis
Solution hybridization and electrophoresis of test nucleic acid fragments mixed with reference nucleic acid fragments can reveal if there are mutations present. Heteroduplexes migrate differently than homoduplexes in polyacryl or agarose gel. Heteroduplex Analysis can also be performed by denaturing DHPLC products 150-400 bp long. When using DHPLC, the analysis is more sensitive than gel and has an increased screening capacity
How are heteroduplexes formed
Heteroduplexes are formed when single strands that are not completely hybridized to one another or when test PCR products amplified from genetically heterozygous species are denatured then renatured
Array Technology
single bp resolution by hybridization difference is achievable with High density oligonucleotide arrays. Large number of inquiries can be tested simultaneously. Bead array technology utilizes polystyrene beads in suspension act as a solid matrix and multiple loci can be tested from small samples simultaneously--requires flow cytometry instrument
Standard Tilting
base substitution in the immobilized probe is always in the 12th position from the 3' end used in array technology
Redundant tilting
same mutation placed at different places in the probe (can be found at the 5', middle, or 3' end) used in array technology
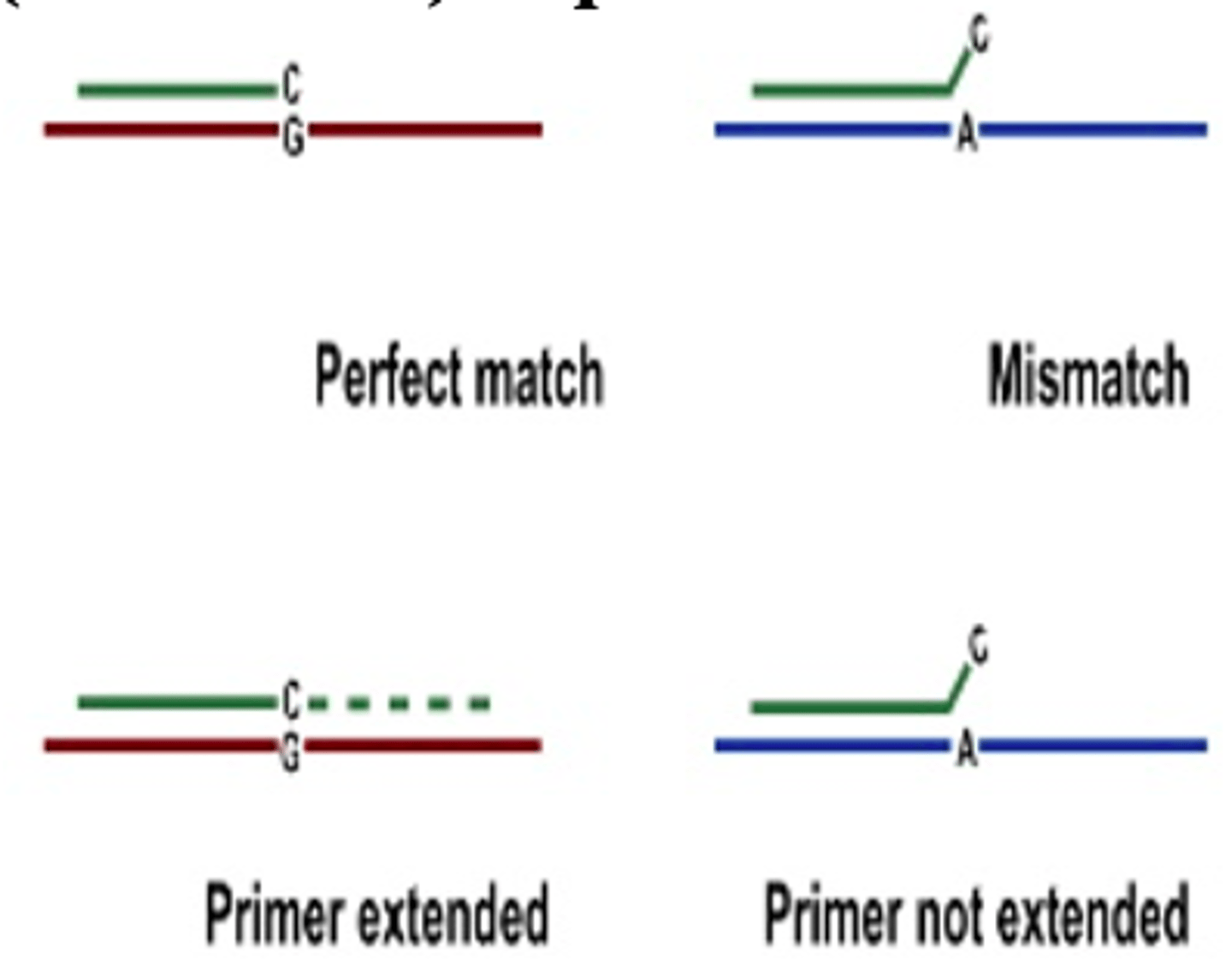
Sequence Specific Primer PCR
used to detect point mutations and other SNP. 3' end of the primer must exactly match template to be extended by Taq polymerase. Normal and mutant sequences are distinguished from one another by increasing the length or normal or mutant primer, resulting in differently sized products depending on template sequences. Routinely used for high resolution HLA typing and detection of commonly occurring mutations. High throughput application of bead array technology uses this.
allelic discrimination with fluorogenic probes
Real time PCR technique with differently labeled fluorescent probes. This technique uses a labeled 3' quencher probe and 5' probe with different fluorescence. Hybrid probe is digested with polymerase and the probe is released. The corresponding fluorescent signal will match and hybridize to test signal sequence <-this step will tell you if it was normal or mutated.
Enzymatic and Chemical Cleavage methods
Restriction Length Fragment Polymorphism can be used to detect sequence alterations caused by a mutation that changed structure of restriction enzyme target site or changes the size of a fragment generated by a restriction enzyme. Used for common mutations such as HFE and FLT3 kinase domain. PCR-RFLP can be multiplexed to detect more than 1 gene mutation simultaneously. (ex seperate gene mutations affecting same phenotype such as Factor V Leiden and prothrombin)
True or False: Procedures developed for a specific gene may not work as well for all genes
True
Single Low cost screening methods are ________________ but definitive direct target sequences are ___________
Good; preferred
Non-isotropic RNAse Cleavage Assay (NIRCA)
Heteroduplex analysis using duplex RNA. If a mutation is present, heteroduplexes form between normal and mutant transcripts which causes cleavage of the heteroduplexes by RNase I and T1. Remaining double stranded RNA is resolved on electrophoresis. The size of the fragments indicate placement of the mutation. Screens for Factor IX, TP53, Jak2 and BRCA mutations
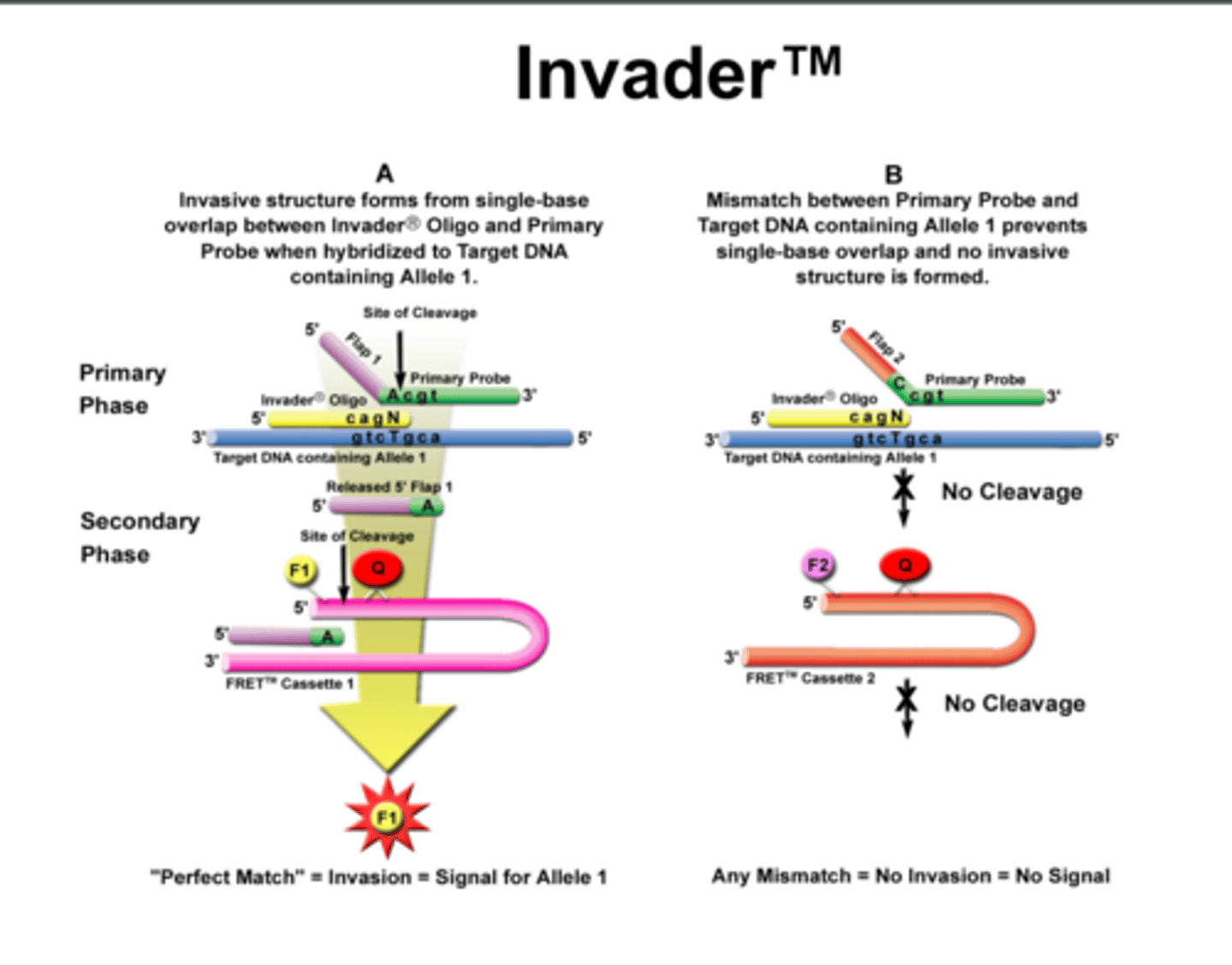
Cleavage Assay
Based on the characteristic enzymatic activity of a proprietary enzyme system (Cleavage). Uses 96 wells, plates, premixed reagents, DNA and controls. Cleavage recognizes the structure formed by a hybrid of normal/mutant probes to test sequence. During isothermal incubation, if the test sequence is complementary to probe, 2 enzymatic reactions occur resulting in fluorescence.
gene vs protein nomenclature
gene names are completely CAPS and italicized w/o hyphens. Protein names are not completely caps and do not have italics.
KRAS gene vs K-Ras protein
TP53 gene vs protein TP53
Nucleotide Changes nomenclature
Position of nucleotide interval, type of change, changed nucleotide, > new nucleotide
This distinguishes nucleotide changes from amino acid changes in proteins
Nucleotide Changes: Deletion
position # nucleotide on Left_______Position # nucleotide on right and then del to indicate deletion occurred
#__#del
Nucleotide Changes: insertion
position # nucleotide on Left_______Position # nucleotide on right and then ins to indicate a insertion occurred
#__#ins
Nucleotide Changes: insertion
position # nucleotide on Left_______Position # nucleotide on right and then dup underline nucleotides that are duplicated
#__#dup______duplicated nucleotides_____
Nucleotide Changes: indel
Insertion with a concomitant deletion.3 ways to do this
#____#del___ins___
#____#delins______
#____#>_____________
How to notate nucleotides that underwent an inversion
INV # of nucleotides that have been inverted
How to notate gene mutations in recessive diseases
Gene mutations in recessive diseases (where both alleles are affected) are indicated with each mutation separated by +
How to notate loss of heterozygosity.
[0]. This indicates absence of entire reference coding sequence on the opposite chromosome.
Mutations in introns of genomic DNA are indicated by
position of mutation in genomic sequence of DNA or position from end of coding sequence + position in intron
Gene Variant in Proteins are indicated by
+1 at initial Amino Acid in protein sequence (Usually MET-M)
Stop Codons are designated by
X
Frame Shift mutation short hand
Amino Acid, Position, and "fs"
True or False Complex Changes and multiple concurrent mutations are reported as they occur. Some mutations, however, still can only be inferred.
True
RNA Nucleotides that have undergone mutations are uppercase or lowercase
Lowercase
DNA Nucleotides that have undergone mutations are uppercase or lowercase
Uppercase
Shorthand mutation nomenclature: coding (complementary or copy DNA)
c
Shorthand mutation nomenclature: genomic DNA
g
Shorthand mutation nomenclature: mitochrondrial DNA
m
Shorthand mutation nomenclature: RNA
R
Shorthand mutation nomenclature:protein sequences
p
Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) Picture
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Picture
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Picture
Gas Chromatography (GC) Picture
MALDI_TOF Picture
ESI Spectrophotometry Picture
single strand conformation polymorphism Picture
Melt Curve Analysis
Heteroduplex analysis Picture
Sequence Specific Primer amplification
Multiplex allele specific PCR Diagram
PCR-RFLP Diagram
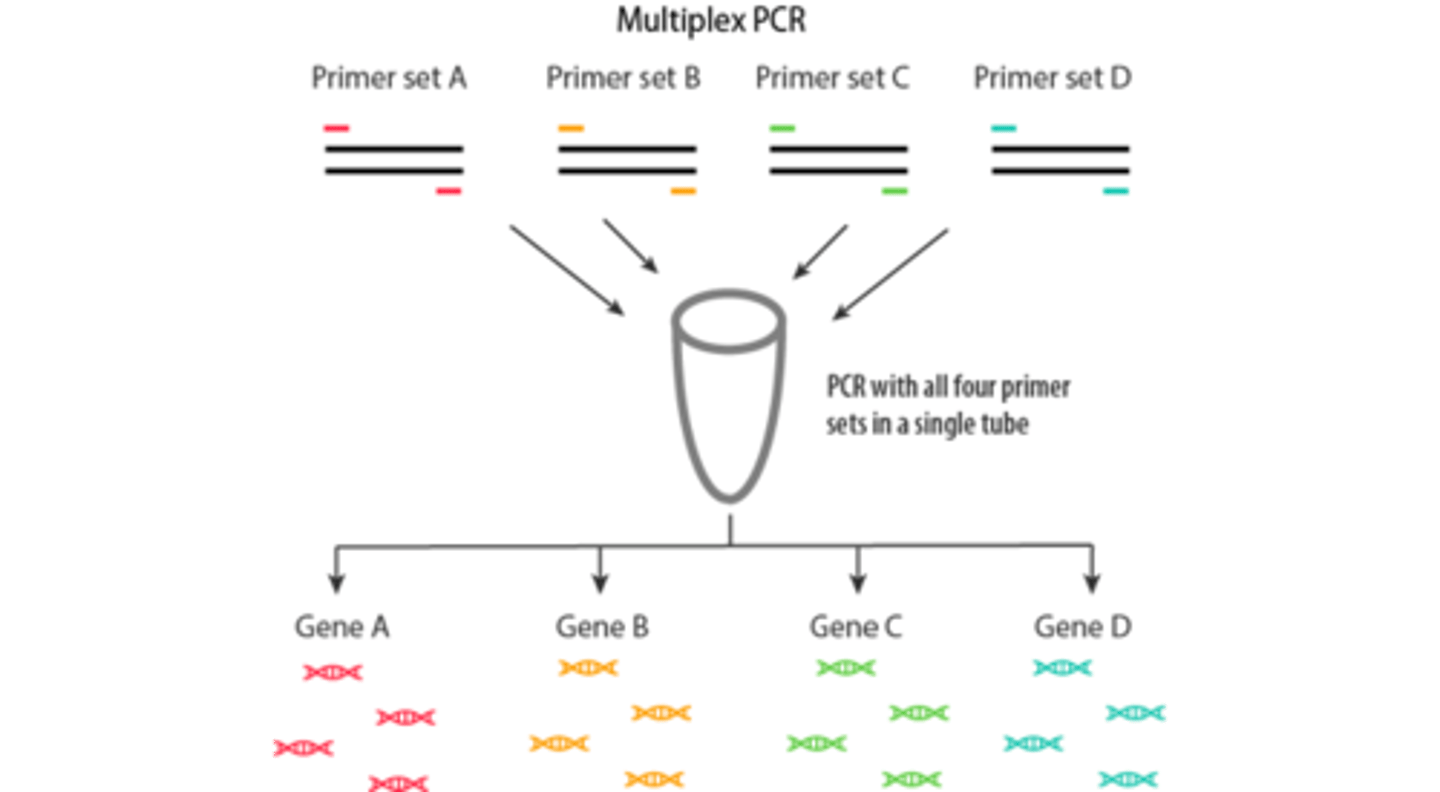
Multiplex PCR (not allele specific)
Cleavage assay