LIDS COMBINED
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
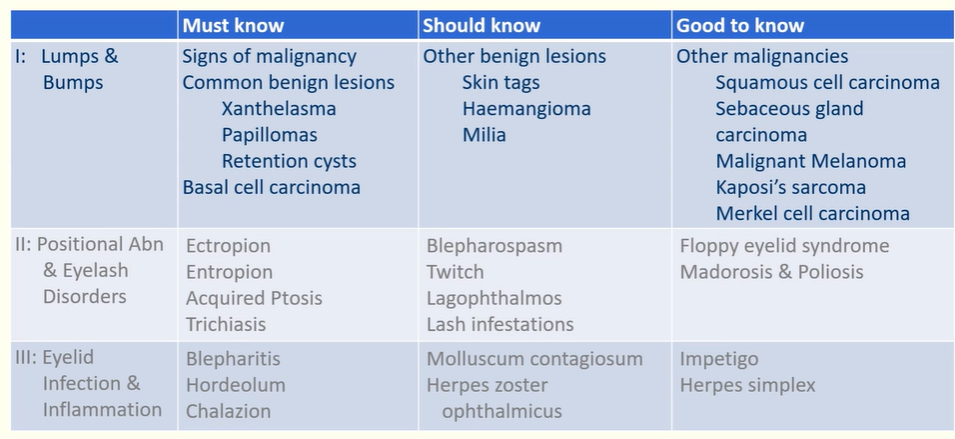
Name the 6 types of benign lesions
Xanthelasma
Papilloma
Skin tags
Haemangioma
Retention cysts
Milia
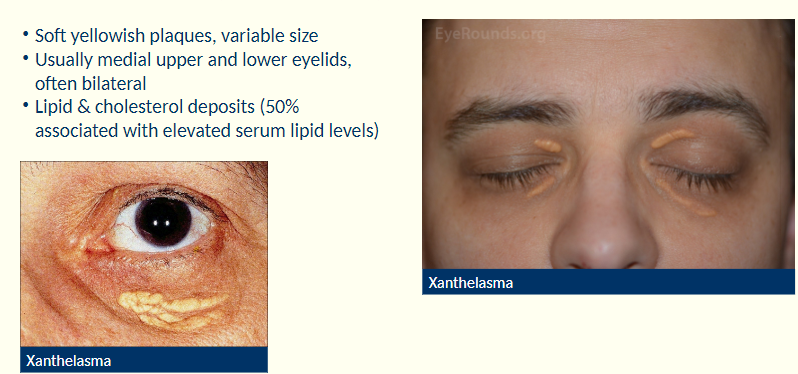
Describe the characteristics of xanthelasma
Soft yellowish plaques
variable size
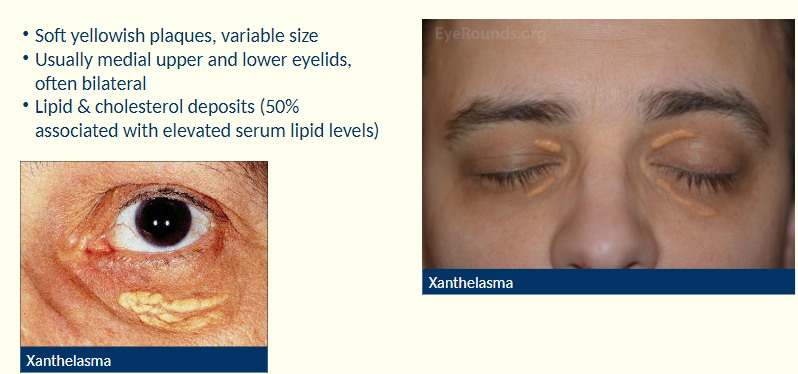
Where are xanthelasma usually found?
Usually on medial upper +lower eyelids, often bilateral
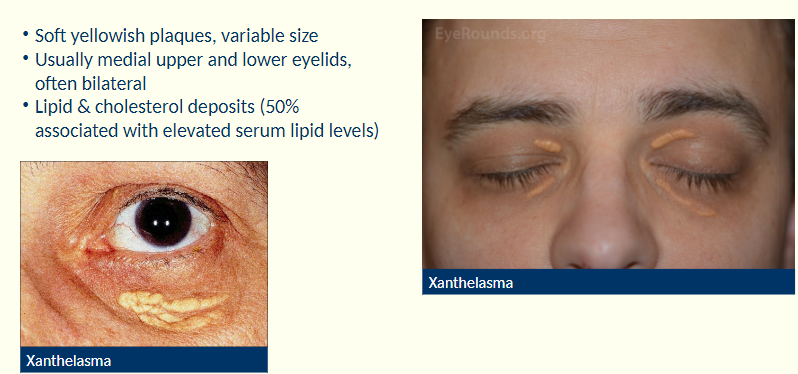
What are xanthelasma associated with?
Assoc’d w/ lipid and cholesterol deposits (50% related to elevated serum lipid levels).
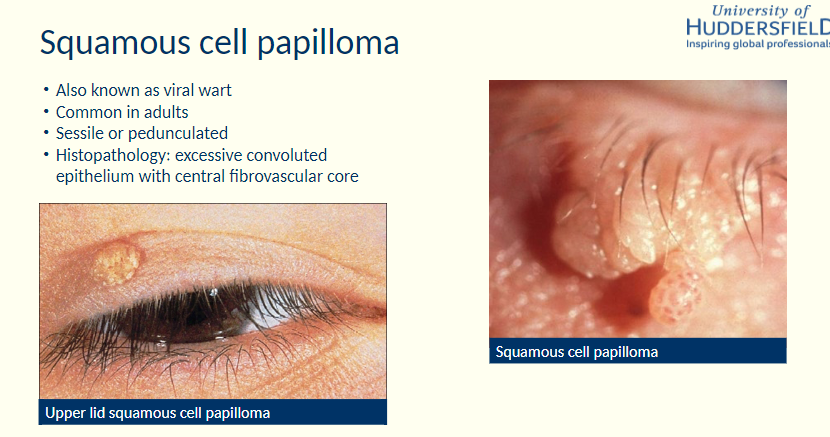
Describe squamous cell papilloma
-Histopathology?
Sessile or pedunculated
H: Excessive convoluted epithelium with central fibrovascular core
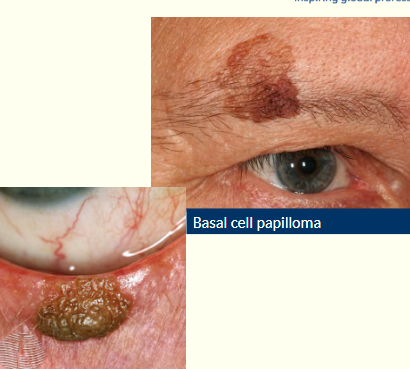
What is the appearance and cause of basal cell papilloma?
• Smooth, waxy/warty surface
• Slow growing, not painful or tender
• Flat or raised plaque
• Skin coloured/grey/brown
Describe dermatitis papulosa nigra
-What are they identical to?
Multiple small diameter black or
dark brown papules - face and
neck
ident to small seborrheic keratoses

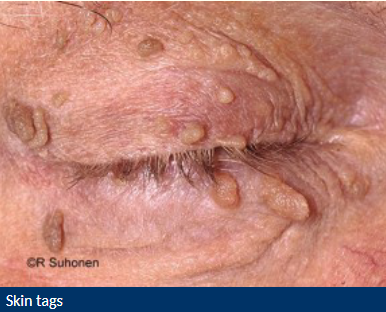
Describe characteristics of skin tags
Small, soft, skin coloured growth
Variable size, shape, colour and number
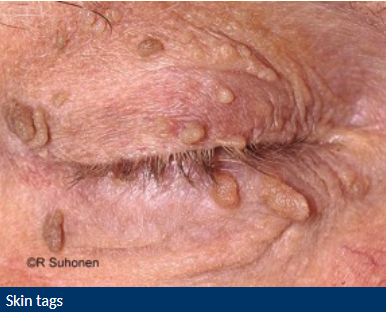
What are the cause of skin tags?
Clusters of collagen + blood vessels surrounded by skin
Describe a capillary haemangioma?
Evident in neonatal period
Grows in 1st year ,usually regresses by 5yo
May be cutaneous, orbital or mixed
Systemic associations
What does systemic associations mean in relation to a capillary haemangioma?
GP may need to investigate
Reassure parents it usually regresses with time
How can a capillary haemangioma affect the development of vision?
Can be present on top eyelid-causing ptosis or droopy lid
If lid low enough it can block visual axis
When does vascular malformation become present?
At birth
More prominent with time
What are retention cysts?
Small round non-tender cysts
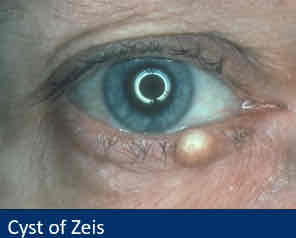
Describe cysts of Zeis ?
White cheesy (sebaceous) material
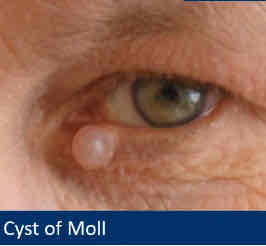
Describe cysts of moll
Clear fluid filled
How would you remove cyst of zeis/ moll?
Cosmetic excision
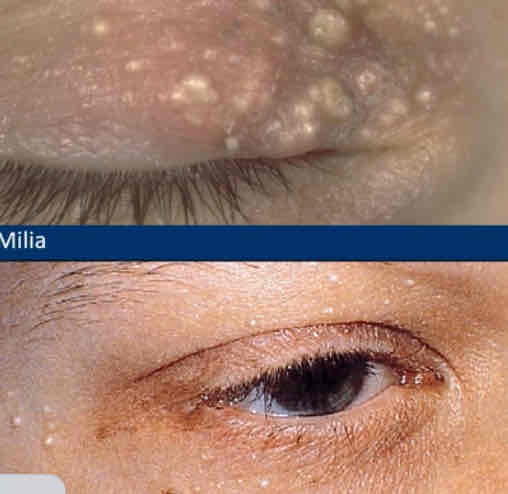
Describe milia
Tiny superficial white yellow dome shaped cysts
Usually multiple
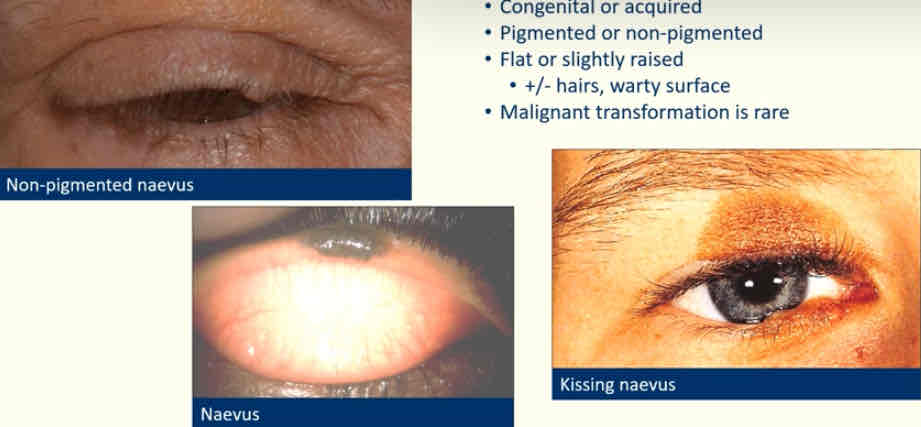
Describe naevi
Congenital or acquired
Pigmented or non pigmented
Flat or slightly raised - ± hairs, warty surface
Rare - turns malignant
Name premalignant lesions
Actinic keratosis
Keratoacanthoma
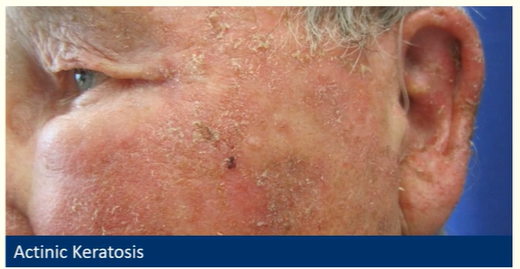
Describe actinic (solar) keratosis
Flat, Scaly lesions , rough skin
R/P/B/Skin coloured
Older age-history of sun exposure
May give rise to squamous cell carcinoma
Occasionally papillomatous/cutaneous horn
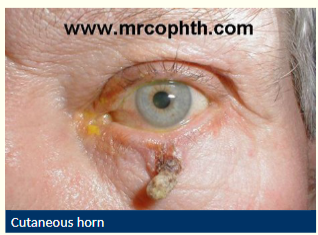
Describe a cutaneous horn
Keratin projection
Arise from benign, premalignant + malignant lesions
10% assoc’d w/ squamous cell carcinoma
Base= point of interest
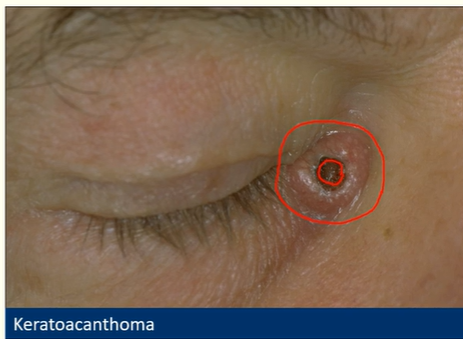
Describe keratoacanthoma
Rapidly enlarges (months)
Regresses or evolves into squamous cell carcinoma
Volcano shaped with keratin plug
Visually, often difficult to distinguish from BBC or SCC
Histopathology - arises from hair follicle skin cells
Name malignant lesions
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Malignant Melanoma
Kaposi’s sacroma
Merkel cell carcinoma
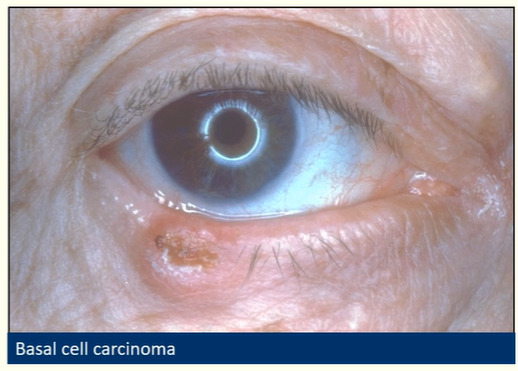
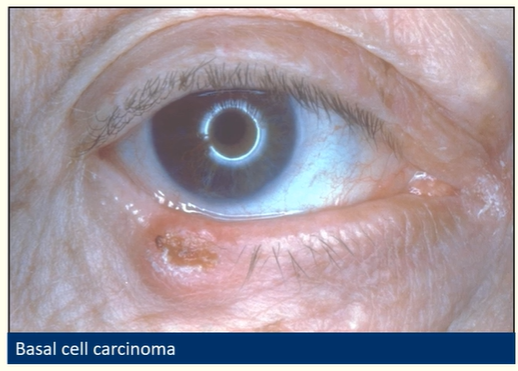
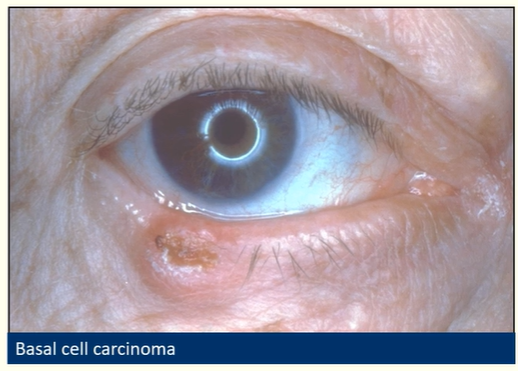
Describe basal cell carcinoma
Most common periocular malignancy
Slow growing, painless, often ulcerated
Do not metastasise but invade locally
Change in lid contour (shape/skin)/lash redirection

What does periocular mean ?
Around the eye
Name the types of basal cell carcinoma
Nodular
Ulcerative
Sclerosing
How to manage basal cell carcinoma
Optometric management
Low risk skin cancer (don’t spread rapidly)
Urgent referral
Photographic documentation
How to manage basal cell carcinoma
Secondary care
Surgery-To remove lesion
Histology-Find out which cells are involved / type of cancer
Describe the characteristics of squamous cell carcinoma
May evoke inflammatory response
Symptomatic - patient concern about lesion, may irritate or itch, may bleed
Can look similar to BCC but more aggressive
More likely to metastasise than BCC
How to manage squamous cell carcinoma
Optometric management
Low risk skin cancer (don’t spread rapidly)
Urgent referral
Photographic documentation
How to manage basal cell carcinoma
Secondary care
Surgery
Histology
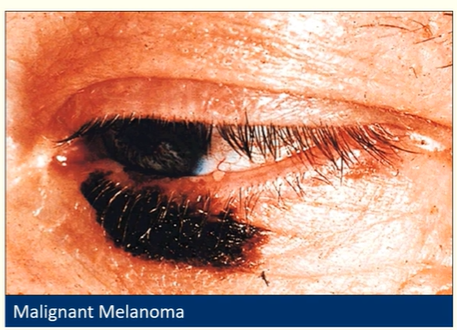
Describe the characteristics of malignant melanoma
V rare
Can appear out of nowhere or as a malignant transformation of a naevus
Signs inc itching, bleeding, pigmentary changes, increase in size
50% are non-pigmented
Describe sebaceous gland carcinoma
Originates from meibomian gland
Highly malignant/rare
Lump in eyelid -looks like a chalazion-when you invert eyelid =abnormal appearance -new BV’s,dark area
Urgent referral

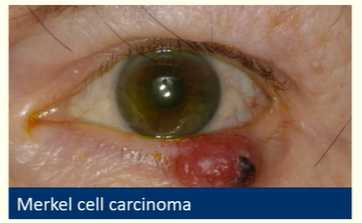
Describe Merkel cell carcinoma
V rare
Neuroendocrine tumour
Grow rapidly
Mortality rate =25-30%
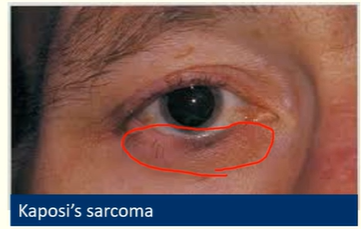
Describe Kaposi’s sarcoma
Purple/red-pink tumour
e.g on eyelid margin
Assoc’d w/ HIV/AIDS OR organ transplant in elderly or immunosuppressed
Risk factors for malignancy
Prior skin cancer
FH: skin cancer
Previous radiation exposure (excessive UV)
Fair skin
Older patients
Acute > chronic onset
Increasing in size
Bleeding/crusting
Key questions to ask
Suspicious lumps/bumps
How long has the lesion been present?
Has it enlarged since onset?
Has the lesion crusted or bled?
Has the colour changed?
Any history of skin cancer?
Any history of significant UV exposure (e.g. lived in a hot climate, outdoor occupation, use of sunbeds)
Suspicious signs of malignancy
New
Increasing in size
Surface ulceration/induration
Neovascularisation - new blood vessels in and around the lesion, bleeding
Crusts
Lid margin changes - destruction of margin, loss of lashes
Recurrent infection/inflammation
More reassuring signs
-Benign
Long standing
Remain static in size
Smooth surface
Does not bleed with minor trauma
Doesn't form adherent crusts
Does not destroy eyelash follicles (may distort them)
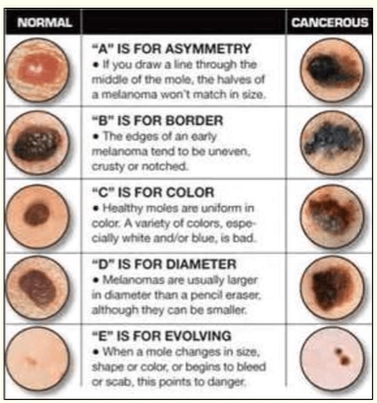
Things to look for with suspicious lumps and bumps
ABCDE
Asymmetry
Border
Colour
Diameter
Evolving
Optometric management of suspicious lumps and bumps
Majority of lumps and bumps are benign
Explain and reassure patient
Photographic documentation
If in doubt refer
Urgent referral (2 week pathway)
Secondary care for the management of suspicious lumps and bumps
Examination
Excision & biopsy
Summary
Be able to detect common eyelid positional abnormalities and eyelash disorders
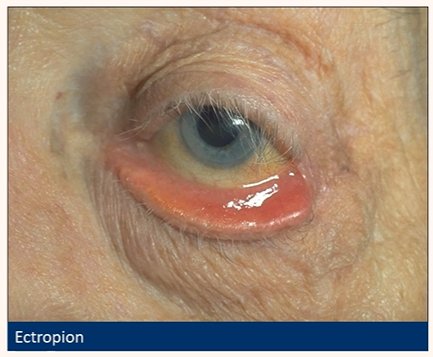
Ectropion
Outward rotation (eversion) of the eyelid margin (usually lower)
Occurs in ~4% of >50 yr olds
70% bilateral
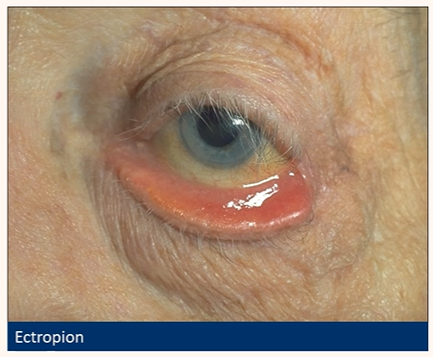
What are the main causes of an ectropion ?
Age-related (involutional)
Processes occur in BE but asymmetrically
CWMHPC
Horizontal lid laxity
Weakness of the orbicularis oculi and/or canthal tendons
Cicatricial: scarring +/- contracture of skin and underlying tissue- pulls eyelid tissue down (unilateral)
Paralytic (VII nerve palsy)
Mechanical/Inflammatory
Congenital
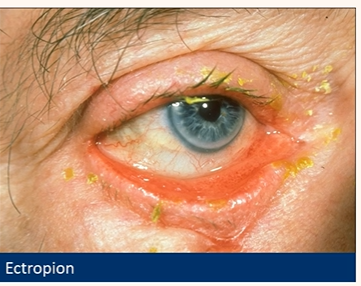
Be aware of their key signs
Ectropion
• Inferior lid margin not in contact with globe
• Lower punctum spontaneously visible (more exposed when looking at it using slit lamp)
• Exposed palpebral conjunctiva hyperaemia
(keratinisation)
• Exposure keratopathy (pictured)
• Mucous discharge
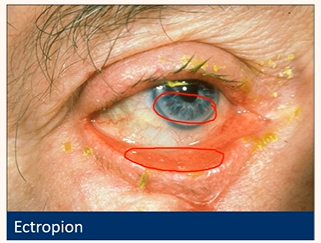
Be aware of their key symptoms
Ectropion
• Very variable
• Soreness
• Redness
• Watery eye (Epiphora)-bc lower lid puncta is no longer against the globe so tears build up in reservoir and spill over
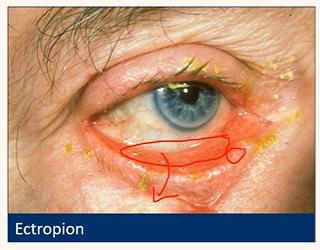
Risk factors
Ectropion
Older age
Lid scarring/pathology
Know how to manage patients with these conditions
Optometric management
Ectropion
Ocular lubricants (drops for daytime,
ointment at bedtime)Consider taping the lids closed at night
Advise lid rubbing may increase lid
laxityMonitor
Routine referral when necessary
(urgent if exposure keratopathy)
In the case of an ectropion, why can we ask the patient to consider taping the lids closed at night?
Reduces risk of exposure kerotopathy
Know how to manage patients with these conditions
Secondary Care
Ectropion
Address the cause
Surgery in the presence of
Exposure keratopathy
Chronic epiphora and irritation
Recurrent bacterial conjunctivitis
Poor cosmesis
Be able to detect common eyelid positional abnormalities and eyelash disorders
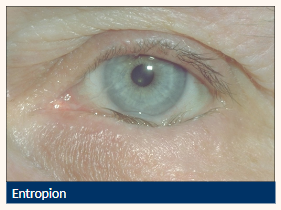
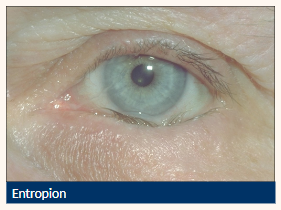
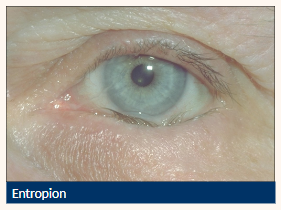
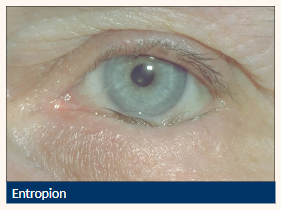
Entropion
Inward turning (inversion) of the tarsus and lid margin
Causes lashes to come into contact with the ocular surface
Affects ~2% of the elderly population
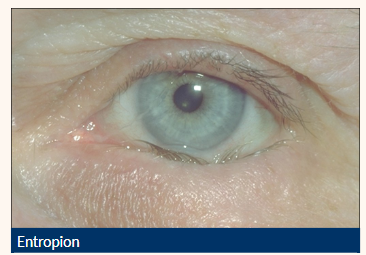
What are the main causes of an entropion ?
Age-related (involutional)
Degenerative changes result in horizontal lid laxity
Cicatricial
Scar tissue pulls the lid inwards
Burns, surgery, rheumatoid arthritis
Muscle Spasm
Congenital (rare)
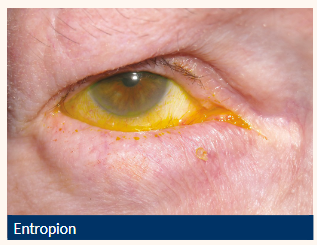
Risk factors of an entropion?
Increasing age
Severe cicatrising disease
Ocular irritation or previous surgery
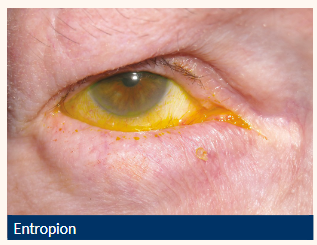
Be aware their key signs and symptoms
Entropion
Inward directed lower lid (can be intermittent)
Lashes contact globe
Vertical corneal +/- conjunctival staining
Lid laxity
Localised conjunctival hyperaemia
Risk of corneal scarring

Be aware their key symptoms
Entropion
Foreign body sensation
Watering
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Optometric management
Entropion
Taping eyelid (temporary)-protect cornea from scratches
Ocular lubricants
Referral - speed depends on extent of
corneal involvement
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Sequelae
Entropion
Ocular irritation
Recurrent bacterial conjunctivitis
Ulceration and microbial keratitis
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Secondary care
Entropion
Surgery
Botulinum toxin if unfit for surgery
What is ptosis
Drooping / abnormally low position of the upper lid
Assoc’d w/ the reduction in the palpebral fissure height (lid to lid)
Normal lid measurements
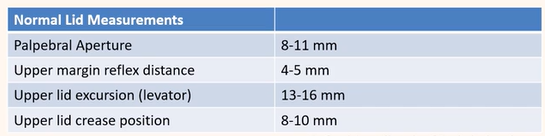
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Age-related (Aponeurotic or involutional)
Muscle is stretched out or disinsertion of the levator palpebrae superioris
Inc’s w/ age (post surgery, trauma + CL use)
Uni/bilateral
High upper crease
Compensatory brow lift
Low relative position in downgaze
Refer routinely if functional-consider surgery
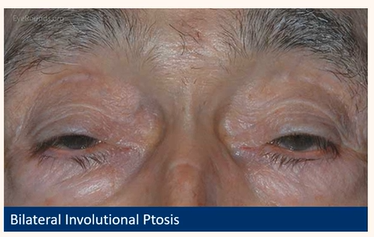
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Myogenic
Weak muscle
Muscular dystrophy
bilat ptosis in pic
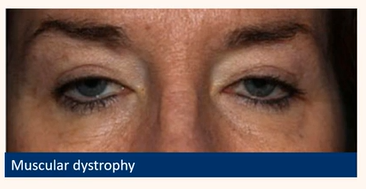
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Neurogenic
Problem with the nerve controlling the lid
Third Nerve Palsy
Horner’s syndrome
Marcus gun jaw-winking
Myasthenia gravis
(variable Coogan’s sign)
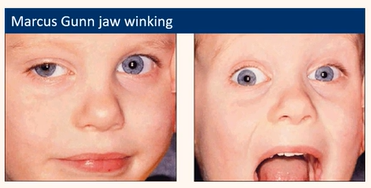
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Mechanical
Physical pushing or weighing the lid down
Blepharochalasis
Eyelid tumours
Oedema
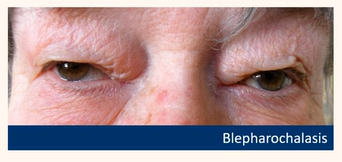
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Traumatic
Result of injury
e.g could be result of severed nerve -complete ptosis
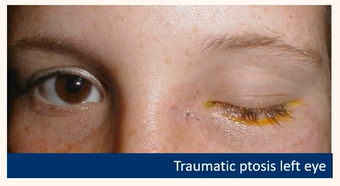
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Acquired ptosis
Pseudotosis
Normal lid, another anatomical anomaly
Microphthalmia
Hypertropia
e.g smaller (red) cornea to other eye ,bc eye=smaller ,eyelid comes down lower bc of size of globe
OR
hypertropia ,if one eye higher than other,can look like ptosis
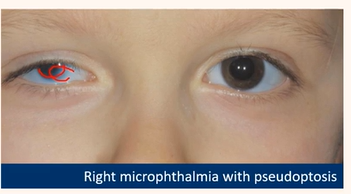
Be aware their key signs
Acquired ptosis
Brow elevation (frontalis overaction)
Chin up head posture
Reduction in the palpebral fissure (narrow)
Signs relating to the underlying
cause
Be aware their key symptoms
Acquired ptosis
Cosmesis e.g droopy lid
Tired eyes
Neck pain
What should you do first when assessing ptosis ?
RUle out any serious (underlying) causes e.g
Third Nerve palsy (eye positioned down and out, dilated pupil)
Malignancy (sudden onset, exophthalmos)
Myasthenia Gravis (variable with fatigue, Coogan’s sign)
Potential for amblyopia in childre
How to assess pt’s with ptosis ?
History - onset, progression, variability/fatigue
Check ocular motility & pupils (neurological cause)
Consider old photos
Exclude pseudoptosis (e.g. microphthalmia, hypertropia in eye with ptosis OR lid retraction, prominent eye, hypotropia in fellow eye
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Ptosis
Treat underlying cause e.g. myasthenia gravis
Surgery proportional to levator function
Lubricants with myogenic ptosis as risk of corneal exposure
Spectacles with ptosis props; scleral contact lenses
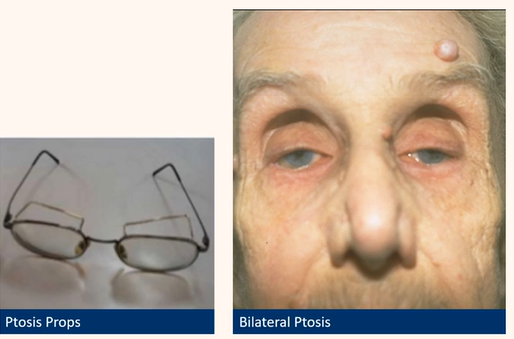
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Congenital ptosis
Dysgenesis of the levator
Usually idiopathic
Present from birth-check photos
Can indicate other pathology
Ptosis reversal in downgaze
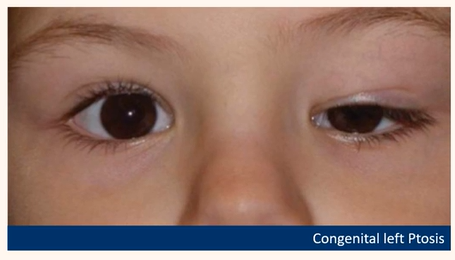
Why is there a risk of amblyopia/astigmatism with congenital ptosis ?
if lid goes over pupil vision can’t develop properly
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Lid retraction
Suspected when eyelid margin is above or level with the superior limbus
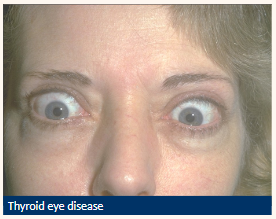
Possible causes of lid retraction?
Neurogenic
Mechanical
Congenital
TED – thyroid eye disease
auto immune condition where the eyes appear to bulge
Neurogenic
e.g. Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking
Mechanical
e.g. surgical overcorrection of a ptosis
Congenital
e.g. Duane’s syndrome
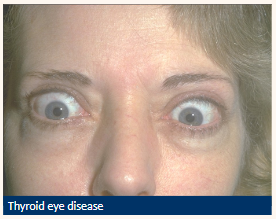
Due to lid retraction there is a risk of …
Exposure keratitis
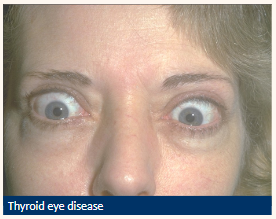
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Lagophthalmos
Inadequate eyelid closure leads to
• Tear film disturbance
• Corneal desiccation
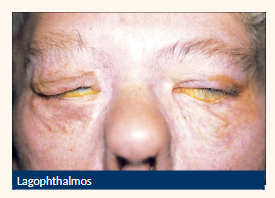
Be aware their key symptoms
Lagophthalmos
Grittiness
Burning
Increased lacrimation
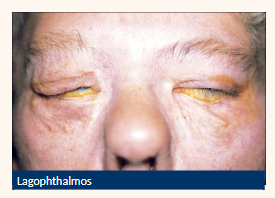
Be aware their key signs/associated with
Lagophthalmos
CN VII (facial nerve) palsy
Proptosis e.g. TED
Night time (while sleeping) incomplete eyelid closure
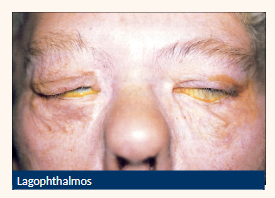
Know how to manage patients with these
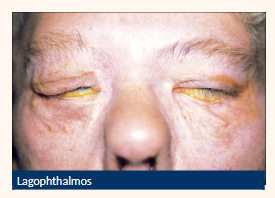
conditions
Lagophthalmos
Ocular lubricants
Eyelid taping (esp. nocturnal)
Surgery - depending on cause
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome
Generalised laxity of eyelid tissues
Unilateral / bilateral
Lids spontaneous evert during sleep
Be aware their key signs
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome
SPK
easy distraction of lid from globe
easy upper lid eversion, lower lid ectropion
ptosis
chronic papillary conjunctivitis
whitish mucous discharge
Be aware their key symptoms
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome
Non-specific ocular irritation
Redness
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome
Lubricants
Eye shield for sleep
Wedge excision
Canthal tendon repair
Floppy eyelid syndrome is associated with…
Sleep apnoea (life threatening)
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Facial Nerve Palsy
Partial or complete paralysis of the facial nerve (VII cranial nerve)
Facial nerve
Bell’s palsy
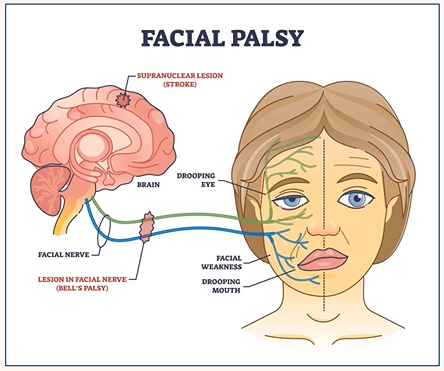
Which functions does the facial nerve control?
Sensory, motor + parasympathetic
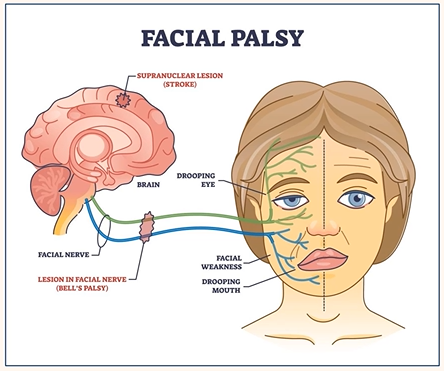
What is Bell’s palsy?
Idiopathic lower motor neurone facial nerve dysfunction
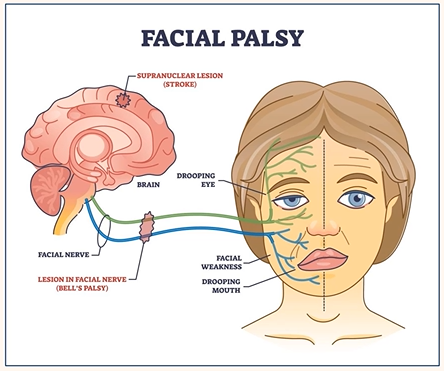
Aetiology of facial nerve palsy
Idiopathic
Latent virus infection (HSV, herpes zoster)
Others (infection, trauma, tumour)
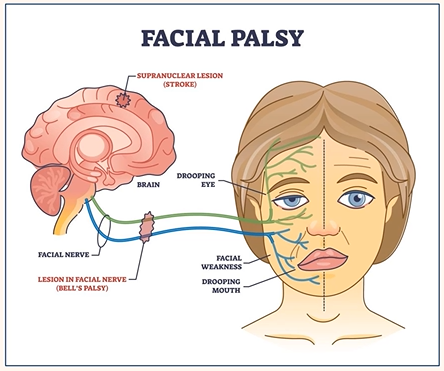
Risk factors of facial nerve palsy
Pregnancy
Diabetes
HIV
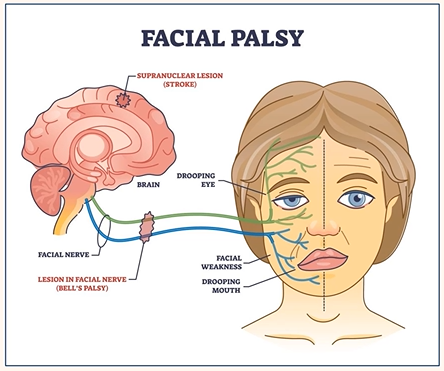
Be aware their key signs
Facial Nerve Palsy
Sudden onset
Unilateral
Weakness or inability to move one side of the face
Eyebrow droop/inability to raise
Incomplete blink → corneal drying
Lagophthalmos
Ectropion
Epiphora and tear pooling (loss of lacrimal pump mechanism)
Be aware their key symptoms
Facial Nerve Palsy
Possible changes in taste and salivation
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Facial Nerve Palsy
e.g New case with loss of corneal sensation
First aid measures and same day referral
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Facial Nerve Palsy
e.g Recovering and established cases (no referral necessary)
Tape lids at night
Sunglasses for photophobia
Ocular lubricants
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Facial Nerve Palsy
Secondary care
Steroids
Tarsorrhaphy
Be able to detect common eyelid positional
abnormalities and eyelash disorders
Blepharospasm
Involuntary tonic, spasmodic, bilateral eyelid closure
More common in older indiv’s (60+)
What are the causes of Blepharospasm?
Idiopathic, Parkinson’s disease, psychogenic drugs e.g. psychotropics
Know how to manage patients with these
conditions
Blepharospasm
botulinum toxin injections into orbicularis oculi