CHEM320-lecture12-Simple Bonding Theory
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
VSEPR
considers mostly electrostatics in determining the geometry of the molecule
valence bond theory
considers quantum mechanics and hybridization of atomic orbitals
molecular orbital theory
upon bond formation, new orbitals that are linear combinations of the atomic orbitals are formed
Valence shell electron pair repulsion
aka VSEPR
theoretical tool to approximate the structures of molecules or ions
MINIMIZES the electrostatic repulsion between the regions of high electron density around a central atom
more
lone pairs take up ___ room than bonding pairs which can lead to bond angle compression relative to idealized version
Same can be said for multiple bonds compared to single bonds, as well as for larger atom compared to smaller ones.
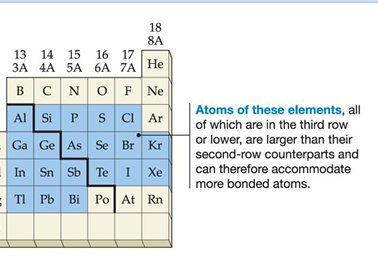
shell expansion
elements that on occasion break the octet rule, usually stays on the right end of the periodic table, starting at the 3rd row.
Xn
bond charge cloud
Em
lone pair charge cloud
A
central atom in VSEPR notation
AX2
linear
180
AX3
trigonal planar
120
AX2E1
bent
120
AX4
tetrahedral
109.5
AX3E1
trigonal pyramidal
109.5
AX2E2
bent
109.5
AX5
trigonal bipyramidal
90 angle up and down
120 angle in same plane as central atom
AX4E1
seesaw
90 angle up and down
120 angle in same plane as central atom
AX3E2
T-shaped
90 angle up and down
120 angle in same plane as central atom
AX2E3
linear
90 angle up and down
120 angle in same plane as central atom BUT more like 180 between bonded atoms
AX6
octahedral
90 bond angle
AX5E
square pyramidal
90 bond angle
AX4E2
square planar
AX3E3
T-shped
AX2E4
linear
increases, decreases
atomic size ___ down a group and ___ across a period
electronegtaivity
measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself
decreases down a group and increases across a period
polar
a ___ bond/molecule has a net dipole moment
molecules will be ___ if the bonds are __ and the molecule is NOT symmetric, aka the dipole moments do not cancel each other out
greater
the __ the difference in electronegativity between atoms, the more polar the bond