Unit 2 Cognition
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms

selective attention
focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus

cocktail party effect
your ability to attend to only one voice within a sea of many as you chat with a party guest
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness

perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another

gestalt
an organized whole. gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes

figure-ground
the organization of the visual field into objects (the figures) that stand out from their surroundings (the ground)

grouping
the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups
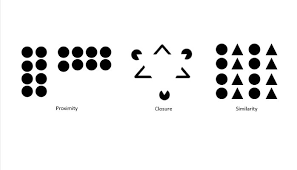
proximity
grouping nearby figures together
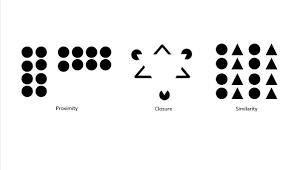
similarity
grouping objects according to how similar they are to each other
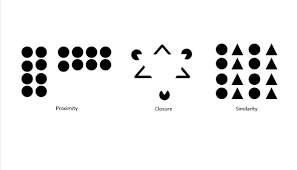
closure
filling in gaps to create a complete whole object
depth perception
the ability to see objects in three dimensions, although the images that strike the retina are two dimensional; allows us to judge distance

visual cliff
a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
binocular cue
depth cue, such as retinal disparity, that depends on the use of two eyes
convergence
acute nearby objects distance, enabled by the brain combining retinal images
retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth. by comparing retinal images from the two eyes, the brain computes distance— the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object
monocular cue
depth cue, such as interposition or linear perspective, available to either eye alone
relative clarity
because more light passes through objects that are farther away, we perceive these objects as hazy, blurry, or unclear. nearby objects, by contrast, appear sharper and more clear
relative size
if we assume two objects are similar in size, most people perceive the one that casts the smaller rental image as farther away
texture gradient
moving toward or away from an object changes our perception of its smoothness or texture. when a wall is viewed from a distance we will perceive it as smooth. viewing the same wall up close will reveal greater texture and detail
linear perspective
parallel lines appear to meet in the distance. the sharper the angle of convergence the greater the perceived distances.
interposition
if one object partially blocks our view of another, we perceived it as closer.
apparent movement
as we move, stable objects may also appear to move. if, while riding on a bus, you fix your gaze on some point— say, a house— the objects beyond the fixation point will appear to move without you. objects in front of the point will appear to move backwards
perceptual constancy
perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent color, brightness, shape, and size) even as illumination and retinal images change
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating
metacognition
cognition about our cognition; keeping track of and evaluating our mental processes
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
prototype
a mental image or best example of a category. matching new items to a prototype provides a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories (as when comparing feathered creatures to a prototypical bird, such as a crow)
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
accommodation
adopting our current schemas (understanding) to incorporate new information
creativity
the ability to produce new and valuable ideas
convergent thinking
narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions
functional fixedness
when our prior experiences inhibit our ability to find creative solutions
executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan, and implement goal-directed behavior
algorithm
a methodical, logical rule of procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem. contrast with the usually speedier - but also more air prone - use of heuristics
heuristic
a simple thinking strategy - a mental shortcut - that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more air prone than an algorithm
insight
a sudden realization of a problem solution; contrast with strategy based solutions
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or contradictory evidence
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
representative heuristic
judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represented, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
gambler’s fallacy
if people observe random events happening repeatedly they may unconsciously use the representativeness heuristic when judging the likelihood of future events
availability heuristic
judging the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct - to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements
sunk-cost fallacy
when we stuck to our original plan because we’ve invested our time even when switching to a new approach could save us time
belief perseverance
the persistence of one’s initial conceptions even after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information
alzheimer’s disease
a disease beginning with a difficulty to remember new information, progressing to an inability to do everyday takes. complex speech become simple sentence; family and friends become strangers; the brains memory centers become weak and wither away
recall
a measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test
recognition
a measure of memory in which the person identifies items preciously learned, as on a multiple-choice test
encoding
the process of getting information into the memory system— for example, by extracting meaning
storage
the process of retaining encoded information over time
retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage
parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
multi-store model
record to-be-remembered information as fleeting sensory memory
process information into short-term memory, where we encode it through rehearsal
information moves into long-term memory for later retrieval
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
short-term memory
briefly activated memory of a few items (such as digits of a phone number while calling) that is later stored or forgotten
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless archive of the memory system. includes knowledge, skills, and experinces
working memory
a newer understanding of short-term memory; conscious, active processing of both (1) incoming sensory information, and (2) information retrieved from long-term memory
maintenance rehearsal
prolonging memory storage through rehearsal over time
elaborative rehearsal
rehearsing information in ways that promote meaning
central executive
a memory component that coordinated the activities of the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad
phonological loop
a memory component that briefly holds auditory information
visuospatial sketchpad
a memory component that briefly holds information about objects’ appearance and location in space
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a nerve cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
explicit memory
retention of facts and experiences that we can consciously know and “declare” (also called declarative memory)
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection (also called non-declarative memory)
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and familiar or well-learned information, such a s sounds, smells, and word meanings
procedural memory
implicit memories for automatic skills
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
chunking
organizing items into families, manageable units; often occurs automatically
mnemonics
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
method of loci
adding vivid details to memories of a familiar place to create a clear mental image to remember specific information
hierarchies
something divided into concepts going from broad to narrow
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
massed practice
(cramming) producing speedy short-term learning. those who learn quickly forget quickly
distributed practice
distributing studying over a period of time to better learn it and cement it in memory
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information. also referred to as a retrieval practice effect or test-enhanced learning
shallow processing
encoding on a basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words
deep processing
encoding semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tends to told the best retention
structural encoding
encoding words letters
phonemic encoding
encoding words sounds
semantic encoding
encoding based on the meaning of information
semantic memory
explicit memory of facts and general knowledge; one of our two conscious memory stems (the other is episodic memory)
episodic memory
explicit memory of personally experienced events; one of our two conscious memory systems (the other is semantic memory)
infantile amnesia
the inability of adults to recollect early episodic memories