Chapter 4: Survey of Prokaryotic Cells
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are characteristics of the cells of living things?
Basic shape- spherical, cubical, cylindrical
Internal content- cytoplasm, surrounded by a membrane
DNA chromosome(s), ribosomes, metabolic capabilities
What are the two basic cell types?
eukaryotic and prokaryotic
What does eukaryotic mean?
true nucleus
What does prokaryotic mean?
before nucleus
What are the characteristics of Life?
Reproduction and heredity- genome composed of DNA packed in chromosomes; produce offspring asexually/sexually
Growth and development
Metabolism- chemical and physical life processes
Movement and/or irritability- respond to stimuli- self propulsion of many organisms, homestasis
Cell support, protection, and storage mechanisms like cells walls, vacuoles, granules, and inclusions
transport of nutrients and waste
The ability to grow
Nucleoid
found in prokaryotes like bacteria and archea
What is the plasma membrane made by?
phospholipid bilayer
What are the 2 major groups of appendages?
Motility- flagella and axial filaments
Attachment or channels- fimbriae and pili
Glycocalyx
surface coating
What are the flagellar arrangements?
Monotrichous, Lophotrichous, Amphitrichous, Peritrichous
Monotrichous
single flagellum at one end
Lophotrichous
small bunches emerging from the same site
Amphitrichous
flagella at both ends of cell
Peritrichous
flagella dispersed over surface of cell
Fimbriae
fine, proteinaceous, hairlike bristles emerging from the cell surface
What is the function of fimbriae?
adhesion to other cells and surfaces
Pili
rigid tubular structure made of pilin protein that is found only in gram negative cells
What is the function of pili?
join bacterial cells for partial DNA transfer called conjugation
What is biofilm?
community of microorganisms attached to a surface
cells stick together
What is the cell envelope?
external covering outside the cytoplasm that is composed of the cell wall and cell membrane that maintains cell intergrity
What are the 2 different groups of bacteria demonstrated by Gram stain?
Gram-positive and Gram negative bacteria
Gram Positive bacteria
thick cell wall composed primarily of peptidoglycan and cell membrane
Gram-Negative bacteria
outer cell membrane, thin peptidoglycan layer, and cell membrane
What does the cell wall determine?
determines cell shape to prevent lysis due to changing osmotic pressure
What is the primary component of cells walls?
peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan
unique macromolecule composed of a repeating framework of long glycan chains cross linked by short peptide fragments
What are the names of the alternating glycans in peptidoglycan?
NAG- N-acetyl glucosamine
NAM- N-acetyl muramic acid
Characteristics of Gram Positive Cell Wall
20-80 nm thick peptidoglycan
Includes: teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid
Some cells have a periplasmic space, between cell membrane and cell wall where bacteria fold proteins
What does teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid in Gram Positive Cell do?
function in cell wall maintenance and enlargement during cell division
move cations across cell envelope
stimulate a specific immune response
Characteristics of Gram Negative Cell Wall
Inner and outer membranes and periplasmic space between them contains a thin peptidoglycan layer
Outer membrane contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
8-11 nm
What are lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in Gram Negative Cells?
Lipid portion (endotoxin) may become toxic when released during infections and cause sepsis
May function as receptors and blocking immune response
contain porin proteins in upper layer- regulate molecules enetering and leaving cell
Number of layers in gram positive
One
Number of major layers in gram negative
Two
Chemical composition of gram positive
Peptidoglycan
Teichoic acid
Lipoteichoic acid
Mycolic acids and polysaccharides
Chemical composition of gram negative
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Lipoprotein
Peptidoglycan
Porin proteins
Overall thickness of gram positive
Thicker (20-80 nm)
Overall thickness of gram negative
Thinner (8-11 nm)
Does gram positive have an outer membrane?
No
Does gram negative have an outer membrane?
Yes
Periplasmic space in gram positive
Narrow
Periplasmic space in gram negative
Extensive
Permeability to molecules in gram positive
More penetrable
Permeability to molecules in gram negative
Less penetrable
Can some bacterial groups lack a typical cell wall structure?
Yes, some examples include mycobacterium and Nocardia
Gram-positive cell wall structure w/lipid mycolic acid (cord factor)
Pathogenicity and high degree of resistance to certain chemicals and dyes
Basis for acid-fast stain used for diagnosis of infections caused by these microorganisms
Characteristics of some prokaryotes that have no cell wall like Mycoplasma
cell wall is stabilized by sterols
Pleomorphic- can take on many different shapes
Fluid Mosaic Model
phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
polar lipid molecules have polar head(hydrophilic) and non-polar tails(hydrophobic)
Phospholipid bilayer functions
Providing site for energy reactions, nutrient processing, and synthesis
Passage of nutrients into the cell and discharge of wastes
Cell membrane is selectively permeable
Cell Cytoplasm
dense gelatinous solution of sugars, amino acids, and salts
is 70-80% water which serves as solvent for materials used in all cell function
What are the components of a nucleoid?
Chromosome and plasmids
Chromosome
single, circular, double stranded DNA molecule that contains all the genetic information required by a cell (housekeeping genes)
Plasmids
free small circular, double stranded DNA
Not essential to bacterial growth and metabolism
used in genetic engineering- readily manipulated and transferred from cell to cell
Ribosomes
made of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% and is the site of protein synthesis that consists of 2 subunits
Translates RNA —> protein
What are the 2 subunits?
Large and small
What is the Svedburg unit of ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
Large- 50S
Small- 30S
Ribosome(total)- 70S
Inclusions and granules (internal structure)
intracellular storage bodies
vary in size, number, and content
bacterial cell can use them when environmental sources get depleted
can be made by proteins, carbs, lipids, etc
Cytoskleton
internal network of protein polymers that is closely associated with the cell wall
gives the cell its shape
What are endospores?
inert, resting, cells produced by some G+ genera like Clostridium, Bacillus, and Sporosarcina
What are the 2-phase life cycle of endospores?
Vegetative cell and endospore
Vegetative cell
metabolically active and growing
Endospore
when exposed to adverse environmental conditions; capable of high resistance and very long term survival
Sporulation of endospore
formation of endospores and is the hardiest of all life forms
withstands extremes in heat, drying, freezing, radiation, and chemicals
not a means of reproduction
Germination of endospores
return to vegetative growth
Characteristics of endospores
dehydrated, metabolically inactive w/thick coat
Longevity verges on immortality, 250 million years
resistant to ordinary cleaning methods and boiling; only way to destroy is to pressurize them at 120oC for 20-30 mins
What are the 3 basic shapes?
Coccus, bacillus, spirillum
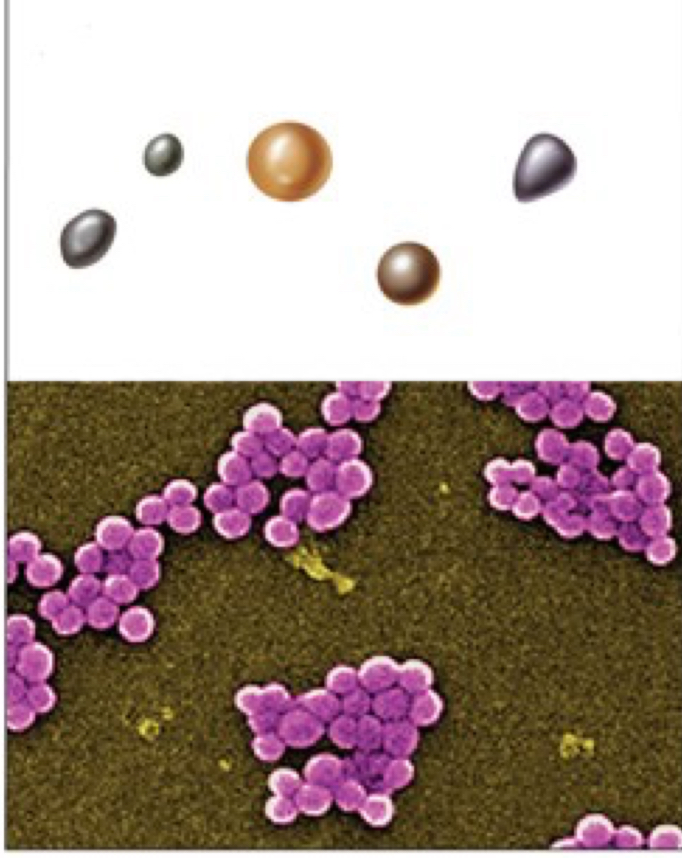
Coccus
spherical shape
Bacillus
rod shaped
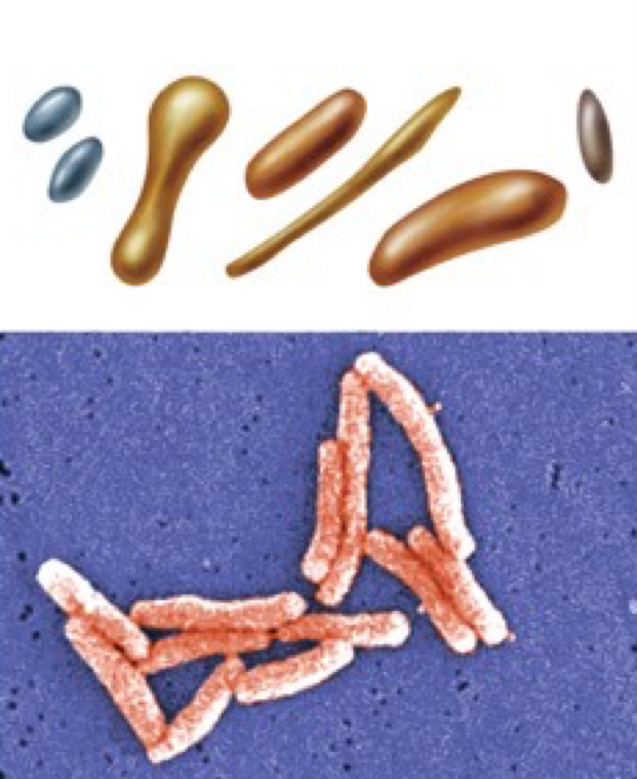
Coccobacillus
very short and plump that looks like a football
vibrio
gently curved rod
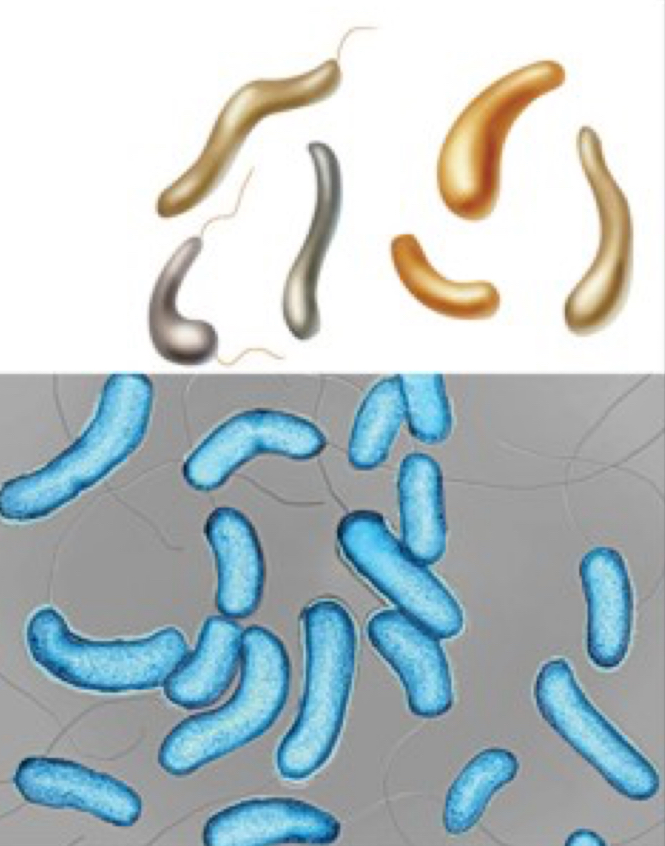
Spirillum
helical, comma, twisted rod, corkscrew shaped
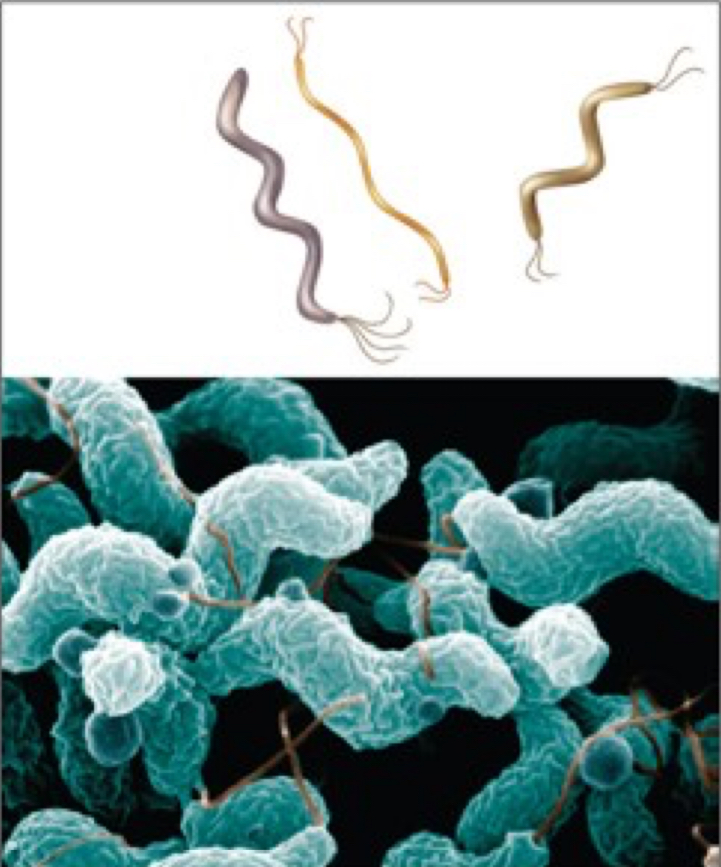
Spirochete
spring like shape
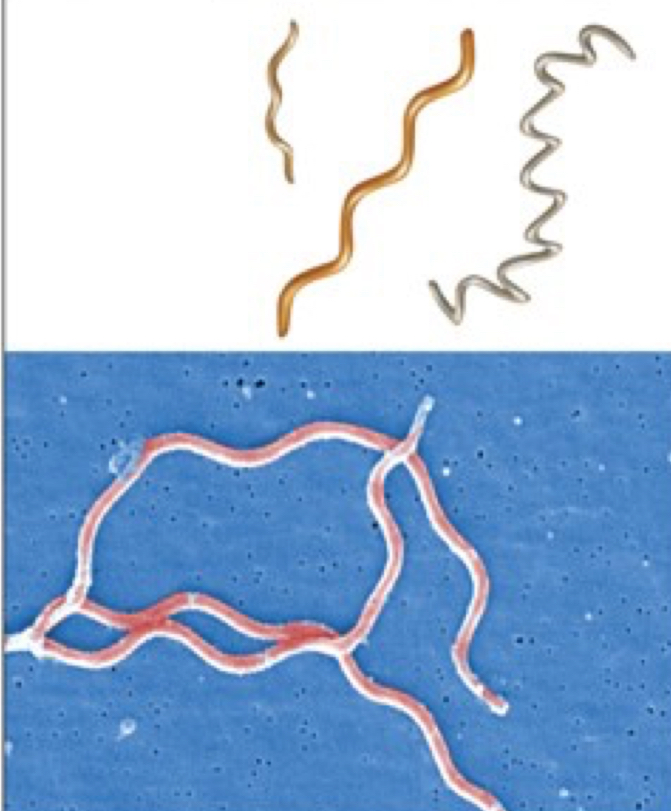
Pleomorphism
variation in cell shape and size within a single species and some species are noted for their pleomorphism
Cocci bacterial arrangement
singles
Diplococci- in pairs
Tetrads- groups of fours
Irregular clusters
chains
Cubical packets (sarcina)
Bacilli bacterial arrangement
Diplobacilli
Chains
Palisades
What measurment is bacteria measured in?
micrometers
Photosynthetic bacteria
use photosynthesis, can synthesize required nutrients from inorganic compounds
What are examples of photosynthetic bacteria?
cyanobacteria(blue-green algae), green and purple sulfur bacteria, and gliding, fruiting bacteria
Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green algae)
gram negative cell walls
extensive thylakoids(where they do photosynthesis) with photosynthetic chlorophyll pigments and gas inclusions
produces ½ of the O2 that we breath
Green and Purple Sulfur Bacteria
photosynthetic
contain photosynthetic pigment bacteriochlorophyll
Do not give off oxygen as a product of photosynthesis
Bacteriochlorophyll
used in an-oxygenic photosynthesis and produces sulfur compounds instead
obligate intracellular parasites
grow and reproduce inside a cells of a host
What are examples of obligate intracellular parasites?
Rickettsias and Chlamydias
Rickettsias
Very tiny, gram-negative bacteria
most are pathogens
cannot survive or multiply outside of a host cell
Rickettsia rickettisii- Rocky mountain spotted fever
Chlamydias
tiny and not transmitted by arthropods (ticks, fleas)
Chlamydia trachomatis
severe eye infection and one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases
Chlamydia pneumoniae
lung infections
Is archaea related more to Eukarya or Bacteria?
more closely related to Eukarya
Archaea
contain unique genetic sequences in their rRNA and have unique membrane lipids and cells walls
only organism with ether bonds
most are ancient and unchanged
Type of ribosomes in archaea
70S but structure is similar to 80S
Cell membrane lipids in bacteria
Fatty acids with ester linkages
Cell membrane lipids in archaea
Long-chain, branched hydrocarbons with ether linkages
Habitats of archaea
live in the most extreme habitats in nature, extremophiles
What are archaea adapted to?
heat, salt, acidic pH, pressure, and atmosphere
What is included in archaea?
methane producers, hyperthermophiles (hot loving), extreme halophiles (salt loving), and sulfur reducers