human geo
1/297
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
298 Terms
geography
study of earths surface and processes that shape it
geography (another def)
studies how human activity effects or is influenced by earths surface
globalization
process by which businesses, trade, tech etc have made world more connected
spatial
related to space. ubderstand how we interact and use space around us
spatial perspective
use of space. when where why
spatial patterns
placement of objects. similar and different no relate?
time distance decay
things closer more related. further distance interaction/effect decreases
absolute distance
measure with unit of length
relative distance
compare social/economic/cultural similarities despite absolute distance
reference map
emphasizes geographic locations. displays boundaries, names, states, roads. FOCUS ON PLACES
topographic map
type of reference map that used isolines to show earths surface.
isolines
lines that links different places that share common value. often used for elevation.
thematic map
emphasizes spatial patterns. show distribution of attribute characteristics or relationships. FOCUS ON DATA
chloropleth maps
shows data aggregated for a specific geographic area, often using different colors to represent different values
cartograms
distorts geographic shape in order to show size of specific data point of variable
graduated circle maps
uses symbols (circles or dots) of different sizes to represent numerical values
dot density maps
uses dots to represent objects. dots can represent one of a number of objects.
prime meridian
0 degrees longitude (vertical)
equator
0 degrees latitude (horizontal)
Us census
government collecting demographic data every 10 years
GPS
satellite system orbiting earth. see satellite. GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM.
GIS
software app w data related to earths surface. GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM
remote sensing
scanning earth with satellite or plane. arial/satellite imaging.
space
areas occupied by humans but has no real value until humans make it
place
space modified by humans made important
time space compression
decreasing distance between places (travel time and cost)
interdependence
ties between regions/countries that create global economic system
spatial diffusion
spread of idea or characteristics from one place to another
hearth
point of origin
independent invention
similar innovation developed at same time in different places by people independent of each other.
expansion diffusion
idea or trait moves
relocation diffusion
people or person moves
expansion diffusion examples
hierarchical. reverse hierarchical. contagious. stimulus.
friction of distance
distance requires some amount of effort. measure of how absolute distance effects interaction between 2 places. (tech can help diminish)
heirchical/reverse hierarchical
ideas move through established structure (rich to poor vice versa)
contagious siffusion
spreads w no regard to heirarchy (ex viral)
stimulus diffusion
specific trait is rejected but underlying idea is accepted. makes new variants of item.
relocation diffusion
occurs when group move/migrate from one location to another and take culture with them
cultural barrier
some things not accepted in particular cultures
ecology
study of relationships between living things and environment
cultural ecology
study of interaction between societies
environmental determinism
environment shapes culture
environmental possibilism
possible for humans to overcome challenges in environments and shape their own culture
local
town, city
national
country
regional
multiple countries
global
world
glocal
global/local stimulus diffusion
formal region
have one or more common trait. have borders but rarely sharp and can overlap.
functional region
functions as unit. clearly defined borders. “real countries”
perceptual/vernacular region
feelings or attitudes by people who live there. sense of belonging or identificatiob
ecumenical
position of area on earths surface with permanent human settlements
developing countries
industrializing countries
developed countries
industrialized countries
mean center on population
balancing point in pop distribution.average location of higher population
arithmetic density
number of people/land area
physiological density
number of people/arable land area
agricultural density
number of farmers/arable land area
epidemiological transition
health services and living standards effect patterns of disease. Abdel Omran. 4 stages connected to DTM
Epidemiologic 1st stage
Pestilence and Famine
Epidemiologic 2nd stage
Receding Pandemics
Epidemiologic 3rd stage
Degenerative and Man made diseases
Epidemiologic 4th stage
Delayed degenerative diseases and emerging infections (hubristic)
IMR
infant mortality rate. # of infant deaths per 1000 people
IMR calc
number of infant deaths in a year/number of live births in same year*1000
RNI
rate of natural increase. if negative rate pop decreases. positive means increasing. does not include immigration
MEASURED IN PERCENT
RNI calc
CBR-CDR/10
Doubling time
#of years for pop to double. not include migration.
Doubling time calculation
70/ RNI percentage
Demographic equation
used to calculate total pop of country or place. based on cdr cbr and migration. year.
Demographic equation calc
total pop+-natural increase+-net migration
ZPG
zero population growth. RNI of 0.0
Crude Birth rate
CBR average # of births per 1000 people
crude birth rate calc
number of live births/total population *1000
Total fertility rate
TFR average # of children born to women within reproductive age
Replacement rate
minimum TFR needed for population to stay the same/not go down.
2.1
Crude death rate
CDR
average # of deaths per 1000 people
Crude death rate calc
number of deaths/ totol pop * 1000
Rapid/moderate growth pop pyramid
wide base. triangle shaped. wider base more rapid growth
slow growth pop pyramid
. birth rate just above death rate. pyramid shape but less wide than rapid growth.
stability or zero growth pop pyramid
birth and death rate similar, column shape
decline pop pyramid
narrow base top heavy. low or negative birth rate. pentagon cup shape
High child dependency
More kids
percent of population:
Youth dependency: 45+%
Elderly dependency: 15-%
Moderate child dependency
Slightly more kids
percent of population:
Youth dependency:29-45%
Elderly dependency:15-%
double dependency
Equal dependency
percent of population:
Youth dependency: 29-45%
Elderly dependency:15+%
high elderly dependency
More elderly
percent of population:
Youth dependency: 29-%
Elderly dependency:15+%
low overall dependency
more working pop
percent of population:
Youth dependency:29-%
Elderly dependency:15-%
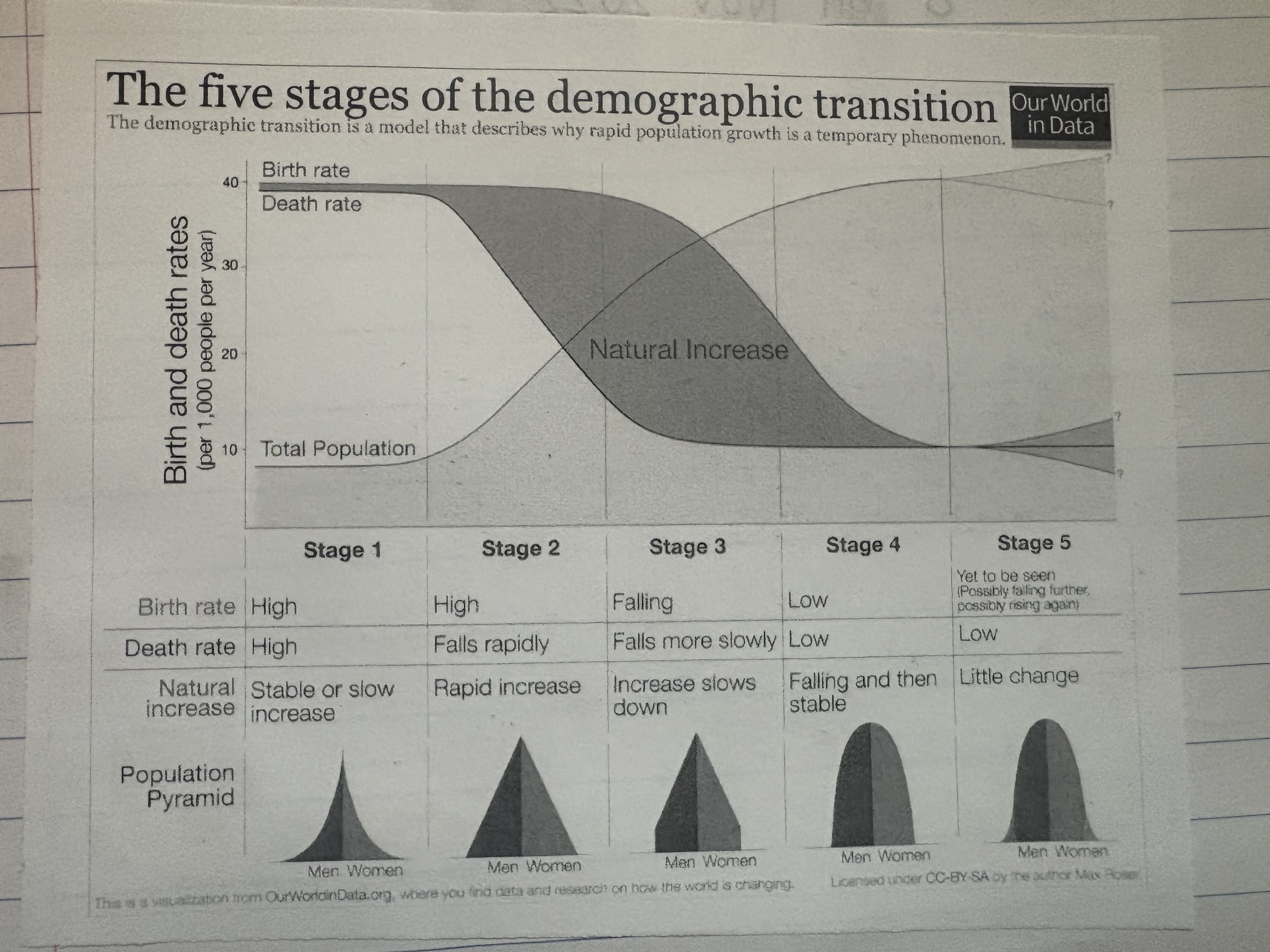
relationship between etm and dtm
just a reminder
Malthusian/Neo malthusians
believe population will eventually die. doomsters.
Cornucopians
believe humans will overcome problems and population won’t die out. Anti malthusians.
Thomas Malthus
1766-1834
human population will exceed available resources and terrible outcomes will happen
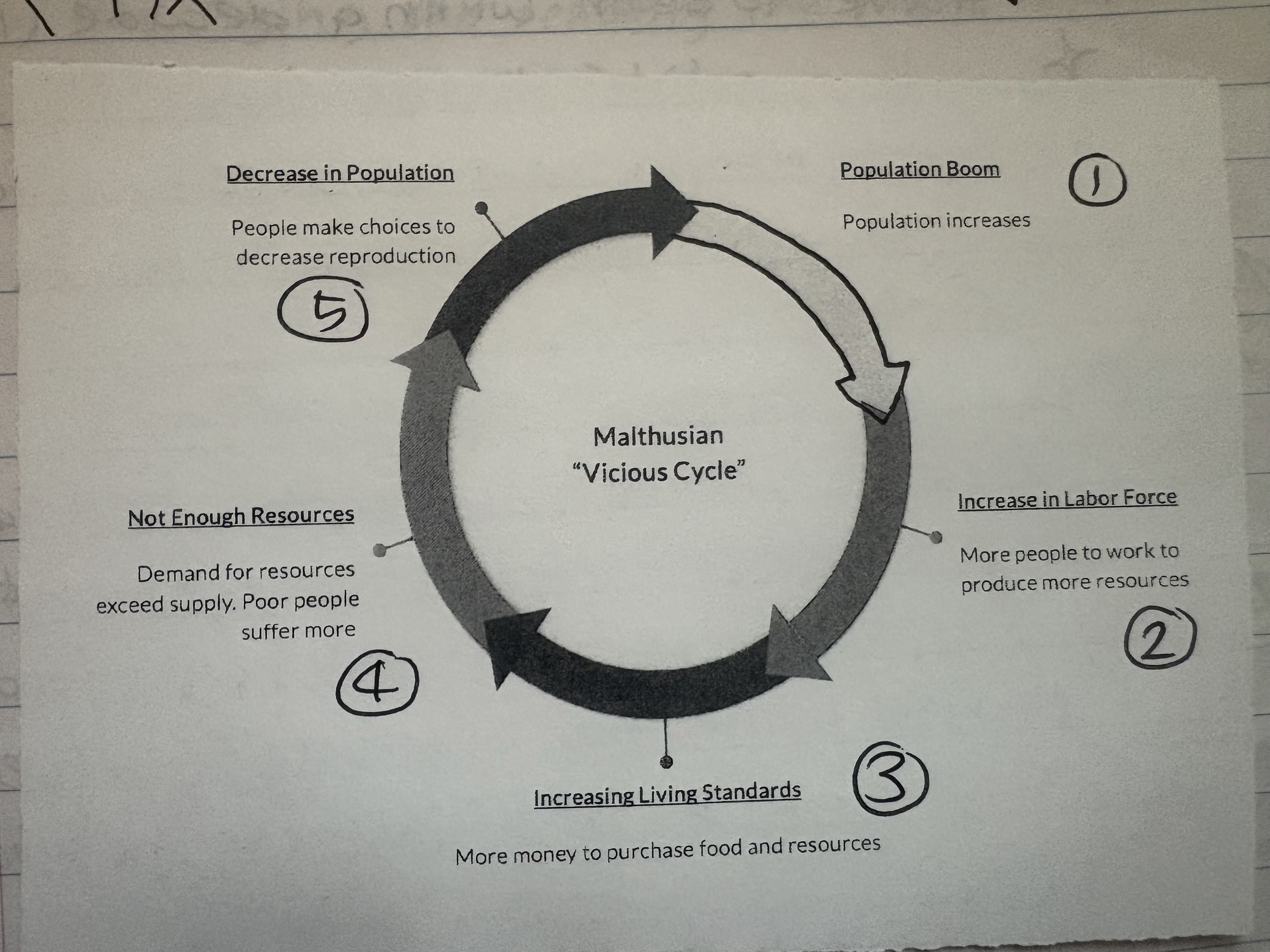
Malthusian cycle
reminder for ya
population bomb
society ticking closer and closer to scarcity and problems
Marxism
semi communism. believed that starvation and warfare was result of unequal distribution not population.
Boserup effect
Particularly intensification theory. can prevent food shortages with new farming methods
Antinatal
reduce population using policies
Pronatal
boost population using policies
Net migration
in migration-out migration
NM
Net migration ratio
NM/total pop *1000
NMR
Ravensteins laws of migration
1834-1913
served as basis for other migration theories
11 laws