HELMINTH
1/187
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Also known as flat worms
Are hemaphroditic
No body cavities
Uses flame cells for excretion.
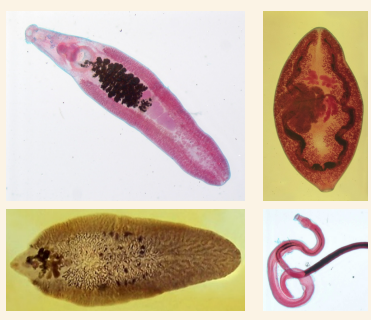
Classes under the Phylum Platyhelminthes
Tubellaria (Planarians)
Trematoda (Flukes)
Cestoda (Tapeworms)
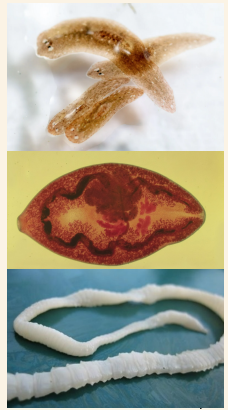
Class Tubellaria
Also known as planarians, they are non-parasitic helminths, resides in fresh water

Class Trematoda
Also known as Flukes, they are parasitic, monozoic or have unsegmented body.
Long & Narrow bodies (e.g. Schistosoma)
Thickly fleshed (e.g. stomach flukes)
Leaf-like (e.g. fasciola)
They have NO alimentary tract and rely on their tegument (outer covering that absorbs nutrients) uses pincoytosis and diffusion.
Class Cestoda
Are known as tapeworms are parasitic, and polyzoic or have segmented body.
Subclass Monogenea, Subclass Digenea
The classification of Class Trematoda based on LC (Flukes) are:
Subclass Monogenea
Subclass of Class Trematoda that uses ONE HOST for reproduction
Mostly parasitize fishes, amphibians and reptiles.
LC is DIRECT no Intermediate Host
Subclass Digenea
Subcalss of Class Trematoda that needs MORE THAN ONE host for reproduction.
An Endoparasite of Dom & Wild Animals.
Exhibits Sexual reproduction in FH (In vertebrates)
Exhibits Asexual rep in IH (In mollusks)
more commonly seen in veterinary medicine
Are Hermaphroditic endoparasites.
Have indirect LC, involving sexual and asexual generations involving diff hosts.
LC of Subclass Digenea
Egg —> Miracidium —> Sporocyst —>
Redia —> Cercaria —>Metacercaria —>Marita —> Adult (EMSRCMMA)
Marita
young fluke
Microcercous, Cercariaecum, Trichocercous
Classification of Flukes based on their tail
Microcercous
(Paragonimus spp.) Has small stumpy tail
Cercariaecum
No tail
Trichocercous
Spiny tail
Monostome, Aphistome, Distome, Holostome, Echinosrtome, Schistomes
Classification of Flukes based on anatomical structure:
Monostome
E.g Cyclocoelum spp.
WITH Oral sucker
NO Ventral sucker
Amphistome
E.g. Zygocotyle spp.
With Oral Sucker
Acetabulum found at the posterior end.
Distome
E.g. is Alloglossidium spp.
WITH oral and ventral sucker located away from posterior end.
Holostome
e.g Cyathocotyle spp.
Type of distome that has the body split into distinct anterior and posterior portions.
Echinostome
Echinostoma spp.
WITH Spines surrounding oral sucker / head collars are present.
Schistosome
E.g Schistosoma spp.
Has strong oral sucker and acetabulum near the anterior end.
Lymnaea truncatula, Lymnaea viridis
IH of Fasciola hepatica
Ruminants
FH of F. hepatica
17 weeks
Life cycle of F. hepatica usually last until ____
3 hrs
Miracidium of F. hepatica must find a snail host within how many hrs?
Aquatic environment
Sporocyst of F. hepatica needs what type of env. to become a Redia?
6 weeks
F. hepatica miracidium usually takes how many weeks to become a Metacercaria?
600
One miracidium of F. hepatica can produce how many metacercaria?
Liver parenchyma
Predilection site of f. hepatica metacercaria / young flukes are found here and they will stay for about 6-8 weeks.
Bile ducts (occasionally gall bladder)
When F. hepatica becomes an adult, it will then go to which body organ?
10-12 weeks
Prepatent period of F. hepatica
Liver rot
Fasciola may cause this to sheeps, alpaca and llamas. It may become a subclinical infection in cattle.
Acute fascioliasis
Occurs when >2000 fasciola metacercaria are ingested in short period.
CS: Distended and painful abdomen, anemia, sudden death after 2-6 weeks of infection.
Can be accompanied by infection w/ Clostridium novyi w/ css Black diseas. Proliferate on the lesions young fluke create on the liver parenchyma.
Subacute fascioliasis
Occurs when 500-1500 fasciola metacercaria are ingested over a longer period. CS: Hemorrhage in the liver, anemia, death 7-10 wks post infection.
Chronic fascioliasis
Occurs when 200-500 fasciola metacercaria are ingested over a longer period.
CS: Unthriftiness, anemia, pipe stem liver, hepatic fibrosis, submandibular edema, reduced milk prod. - Most common form in the country
Fecalysis (Sedimentation technique), ELISA Tests
Diagnosis for Fascioliasis
Triclabendazole, clorsulon, albendazole, netobimin
TOC for fascioliasis
Fasciola gigantica
Is larger than F. hepatica and is more common in the PH with 3% in Cattle, 35% in Carabaos s (than F. hepatica 1% in Cattle, 7% in Carabaos)
Lymnaea auricularia rubiginosa, Lymnaea viridis/ philipenensis
Fasciola gigantica IH
Fasciola jacksoni
Spp of Fasciola that occurs in the Bile ducts of elephants
Fasciola nianze
Spp of Fasciola that occurs in the Hippopotamus in Africa
Fascioloides magna
Is under the Genus Fascioloides, lacks anterior Projecting Cone
Share similar LC with Fasciola may reach 17 months before completion
Requires colder habitat
Except PPP is 30 weeks
Low Pathogenicity And RARELY Css Death In Cattle.
Problems Usually Are Confined To Liver Condemnation
GOATS & SHEEP Severely Affected; However, Deaths Have Been Reported Due To The Migration Of These Flukes To Other Organs.
Histologically, Infected Liver May Show Black, Tortuous Tracts Due To The Migration Of The Flukes.
Css. BLACK PORPHYRIN PIGMENTS show up on liver
Liver, Bile ducts
Main predilection site of Fascioloides magna
Giant Liver Fluke, Large American liver fluke, Deer fluke
Fascioloides magna is also known as _________
white-tailed deer, elk, caribou
Reservoir hosts of Fascioloides magna in the North american countries
red deer, fallow deer
Reservoir hosts of Fascioloides magna in the European countries
Fossaria, Lymnaea, Stagnicola
Intermediate host of Fascioloides magna
Oxyclozanide
TOC for Fascioloides magna effective for white-tailed deer.
Triclabendazole
TOC for Fascioloides magna effective for red deer
Rafoxanide
TOC for Fascioloides magna effective in cattle.
Albendazole
TOC for Fascioloides magna effective for sheep
Fasciolopsis buski
Still under genus Fascioloides whose reservoir host are pigs and final hosts are man and dogs
Mainly seen in small intestine of man.
They infect final hosts through ingestion of Metacercariae that encyst on aquatic plants. PPP: 9-13 weeks
Planorbis, Segmentina, Hippeutis
IH of Fasciolopsis buski
Family Paramphistomatidae
Also known as Rumen flukes
Conical (pear-shaped), thicker and fleshier than their relatives.
Paramphistomes / Amphistomes
Are mainly parasites of the Ruminant Forestomach
Giganticotyle
Part of the Family Paramphistomatidae found on the liver and duodenum instead.
Paramphistomum
Also known as Rumen Flukes
Parasitize the rumen. - Resemble maggots.
WELL-DEVELOPED ventral sucker is located at the posterior extremity.
PPP: 7-10 WEEKS
DOC: Oxyclozanide
4 weeks
How long does it take for Miracidium of Parahistome need to become a cercaria?
Paramphistomum cervi
Spp of Paramphistomum/ Rumen fluke that parasitize the rumen of cattle, sheep, goat and deer.
IH: Planorbis & Bulinus snails
Gigantocotyle explanatum
Spp of Paramphistomum/ Rumen fluke found in liver, bile ducts, gallbladder & duodenum of cattle and buffalo.
IH: Galba snails
Paramphistomum daubnei
Spp of Paramphistomum/ Rumen fluke found in Rumen of Cattle and goat.
IH: Omphiscola snails
Cotylophoron cotylophorum
Spp of Paramphistomum/ Rumen fluke found in Rumen and reticulum of sheep, goat & cattle.
IH: Bulinus snails
Family Gastrodiscidae
Parasitize the Large intestines of larger animals (horses, cattle, and pig)
Also known as Intestinal fluke
Have SHORT CONICAL ANTERIOR end and a large posterior discoid body.
LC is COMPLETE
Reported to cause colic, lethargy, and diarrhea in severe/ heavily infected cases.
are mostly nonpathogenic
Gastrodiscus aegyptiacus
Found in the intestines of horses, donkeys, & pigs.
IH: Bulinus and Cleopatra snails.
Gastrodiscus secundus
Found in the large intestine of elephants and horses;
IH: Planorbis snails
Gastrodiscus hominis
Found in the cecum and colon of humans and pigs.
IH: Helicorbis snails.
Homalogaster paloniae
Found in the large intestine of cattle and buffalo.
IH: Hippeutis and Polypylis snails.
Family Gastrothylacidae
Also knowns as Pouched Amphistomes
Characterized by their EXTREMELY LARGE VENTRAL POUCH that covers the ventral surface of the fluke.
Mainly parasitize ruminants with the generas.
IH: FRESHWATER SNAILS
FH: CATTLE and BUFFALO
Gastrothylax cuminifer
Spp of Pouched Amphistomes occurs in the rumen and reticulum of ruminants.
Fischoederius elongatus
Spp of Gastrothylacidae/ pouched amphistomes occurs in the rumen, and duodenum of ruminants and rarely humans.
Carmyerius spatosius
Spp of Gastrothylacidae/ pouched amphistomes in the RUMEN of ruminants
Family Echinostomatidae
Characterized as Flukes with Head collars
Are more elongated than their other relatives and their oral suckers are surrounded by HEAD COLLARS.
The number of spines on their head collars can be used to differentiate spp.
Have TWO IH:
a.) Primary IH: Snails
b.) Secondary IH: Fish or Frogs
Eggs —> Miracidium —> Snail host
PPP: 1-2 WEEKS
Kidneys of tadpoles
Cecaria of Echinostomatidae emerge from snail host and may infect or encyst on ______
Light infection
_______________ of these echinostomatidae flukes generally cause no significant effect on hosts
Heavy infection
_______________ of these echinostomatidae flukes leads to inflammation, enteritis, anemia, colic, diarrhea, and emaciation.
DOC: ORFA Oxyclosamide, Rafoxamide, Fenbendazole, Albendazole
Echinostoma, Echinoparyphium, Hypoderaeum
Spp of Echinostomatidae that mainly parasitize birds
Echinoschasmus, Isthmiophora, Euparyphium
Spp of Echinostomatidae mainly parasitize fish-eating mammals.
Echinostoma revolutum
# of Head collars: 37 spines, some grouped as “corner spines”
Spp of Flukes with head collars that occurs in CECA, CLOACA and RECTUM Waterfowls, Pigeons occasionally humans.
2nd IH: Tadpoles
Echinostoma paraulum
#of Head collars: 37 Spines w/ “double row” pattern.
Occurs in the Small intestines of Ducks, Pigeons and Humans:
Secondary IH: Fish
Echinoparyphium recurvatum
#of Head collars: 45 spines with corner spines.
Occurs in the Small intestines of Avian spp & humans
IH: Snails, fish, shellfish and tadpoles
Echinostoma ilocanum
No Head collars
Occurs in the small intestine of man, dog, cat and rat.
Infection in man is usually through ingestion of raw infected snails.
Gyraulus convexiusculus
1st IH snail of Echinostoma ilocanum
Pila luzonica
2nd IH snail of Echinostoma ilocanum
Hypoderaeum conoideum
Head collars: 50 small spines
Occurs in the Small intestines of Avian spp.
IH: Snails, fish, shellfish and tadpoles
Euparyphium melis
Head collars: 27 spines
Occurs in the Small intestines of Carnivorous mammals such as Cat, fox, mink, badger, otter and hedgehogs.
2nd IH: Tadpoles
Echinochasmus perfoliatus
Head collar: 24 spines in a “single row.”
Occurs in the Small intestines of Dog, cat, fox, and pig.
Family Philophthalmidae
Also known as Eye flukes
ONLY have a SINGLE spp under this family that is of veterinary importance.
Philophthalmus gralli
Known as “ORIENTAL AVIAN EYE FLUKE”
parasite of the conjunctival sac of chickens, ostriches, and wild birds.
PATHOGENIC EFFECTS Causes Conjunctivitis, keratitis, watery discharge, and mild edema.
TX: Repeated use of Levamisole
contact with water
What triggers the hatching of embryonated eggs of Philopthalmus gralli?
Melanoides tuberculate
Philopthalmus gralli miracidium will become a single redia after penetrating what spp snail host?
Snail’s heart
Predilection site of P. gralli redia, that they will penetrate to release new rediae
Sporocyst stage
What stage does the Philopthalmus skips?
95 days
New redia of philopthalmus will migrate into the digestive glands and after ____ days will produce cercariae
Herbage, Crop
Where do Philophthalmus spp. encyst? When ingested?
Esophagus, Nasal passages, lacrimal gland
Encysted metacercaria of philopthalmus will migrate within an hour to which parts of the avian spp?
Characterized by their ABSENCE OF ORAL SUCKERS.
Parasites of Aquatic Birds in the; body cavity, air sacs or nasal cavities.
They are slightly flattened, lack an oral sucker and usually a ventral sucker
Typhlocoelum, Hyptiasmus
Two important genera of Family Cyclocoelidae
Redia
Which stage in the LC does the Cyclocoelidae fluke enters the host?
sporocyst
Familly cycloelidae lacks this stage in LC?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Cercariae of Family Cyclocoelidae will NOT LEAVE THE SNAIL HOST. They will encyst while w/in the host.