ASCI 442 Unit 2 Notes
1/158
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Thyroid, Parathyroid, Melanocortins, Pancreas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
TRH
thyrotropin releasing hormone
from the hypothalamus
7TM Gs or Gq
TSH
thyrotropin stimulating protein
from the anterior pituitary
7TM Gs
thyromegaly
enlarged thyroid, increased TSH, decreased T3 and T4
thyroid gland/hormone effects
cellular differentiation and development
metabolic pathways
synthesis and release of TSH
stored in secretory granules
carbohydrate added in golgi
release regulated by H
lesions in median eminence block release
stimulation of preoptic area causes release
estrogen stimulates release
SST and T3/T4 inhibit
TSH, LH, FSH, and hCG have same alpha subunit and distinct beta subunit
secondary responses of TSH
increase cellular uptake of iodine
synthesize thyroglobulin, iodotyrosine, iodothyrosines
proteolysis of thyroglobulin
thyroid gland
TSH receptors - estrogen stimulates synthesis of the receptor, T3 and T4 inhibit receptor synthesis
function unit → follicle → secretory cells
C cells - parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin
calcium homeostasis
Goiter
enlarged thyroid, case for iodized salt
T3 and T4 made from
2 tyrosine (from thyroglobulin)
3 or 4 iodine
thyroglobulin
allows for storage of hormones for up to 2 months
tyrosine coupling
Na+/I- symporter brings iodine into cell
Na+/K+ ATPase pump maintains Na+ gradient (out→in)
iodine must be at higher ocidative state for coupling, oxidized by thyroid peroxidase (PTO) H2O2 system, glucose regulation for NADPH production
endocytosis upon TSH → clipped off thyroglobulin → free T3/T4 secreted into the blood
excess iodine
iodoaldehydes with in the thyroid
Wolff-Chaikoff effect
impairs TPO leading to decreased T3 and T4 transient (1-2 d)
T3/T4 transport
serum levels: T4 70x > T3
half life: T4 - 7d; T3 - 1d
99% bound to proteins in circulation
thyroxine binding globulin
albumen (lower affinity)
diffuse through membranes
free hormone carrient into cell via carrier proteins (MCT8)
nuclear receptor → ligand modulated transcription factor
T3 receptor in liver and kidney
binding highly correlated with synthesis of GH (synergistic effects)
Thyroid hormone regulation of differentiation and growth
brain, cartilage, lungs, regulation of GH and PRL
metabolism: O2 consumption, mineral balance, CHO/lipid/protein metabolism
cardiovascular - heart rate and output
hepatic synthesis of vitamin A
increased intestinal glucose absorption
hypothyroidism
deficiency of synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones
cause
absence of thyroid gland
pathological destruction of thyroid gland
insufficient secretion of thyroid hormones - elevated TSH
compensatory goiter: weakness, dry/coarse skin, lethargy, edema, cold, infertility, constipation, weight gain, impaired memory
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
autoimmune attack of the thyroid gland
increased TSH
10x more common in women
Hyperthyroidism
toxic goiter (Grave’s disease): autoimmune attack of thyroid gland, enlarged eyes
increased basal metabolic rate, cardiac output, temp, food intake, GI activity, diarrhea → weight loss
T3 and T4 biosynthesis
iodine transport
oxidation → Tyr
coupling
storage (colloid 2 mo)
endocytosis (induced by TSH binging to 7TM Gs)
lysis
released into circulation
mechanism of action of T3 receptor
nuclear receptor
binds to TRE sequence of DNA
homo- or hetero-dimer
different forms of TR expressed through development
Thyroid hormone receptors
TRa1 - binds T3, DNA binding, heterodimer formation
TRa2 - does not bind T3, DNA binding, weak heterodimer formation
TRB1 - binds T3, DNA binding, heterodimer formation
TRB2 - binds T3, DNA binding, heterodimer formation
NO T3 = co-repressor (CoR) inhibits transcription
T3 binding = activation of transcription
Grave’s disease
fatigue, restlessness, tachycardia, weight loss despite eating, GI issues, increased temp
TSH low, thyroid enlarged
autoimmune - antibodies stimulate TSH receptor
hyperthyroidism
treat with antagonist for TSH receptor or T3 receptor
Calcium importance
muscle contraction, neurotransmission, cell signaling, skeletal support, coagulation enzyme and hormone regulation, exocytosis (secretion of hormones), mitosis
Ca and P
two most abundant elements
Ca transport
Ca typically bound
sequestered in mitochondria and ER
movement across membranes via channels and ATPase pumps
Calcium binding proteins
Troponin C - striated muscle
Parvalbumin - muscle
S-100 protein - nervous system, melanocytes
Vitamin D-dependent CaBP - cartilage, bone, teeth
Vitamin K-dependent CaBP - osteoblasts
Calmodulin - ubiquitous binding protein in all animals and plants
Ca regulated by
parathyroid - releases PTH in low Ca levels
kidney - regulates excretion of Ca and vitamin D
bone - bone mineralization, major source of Ca
PTH axis
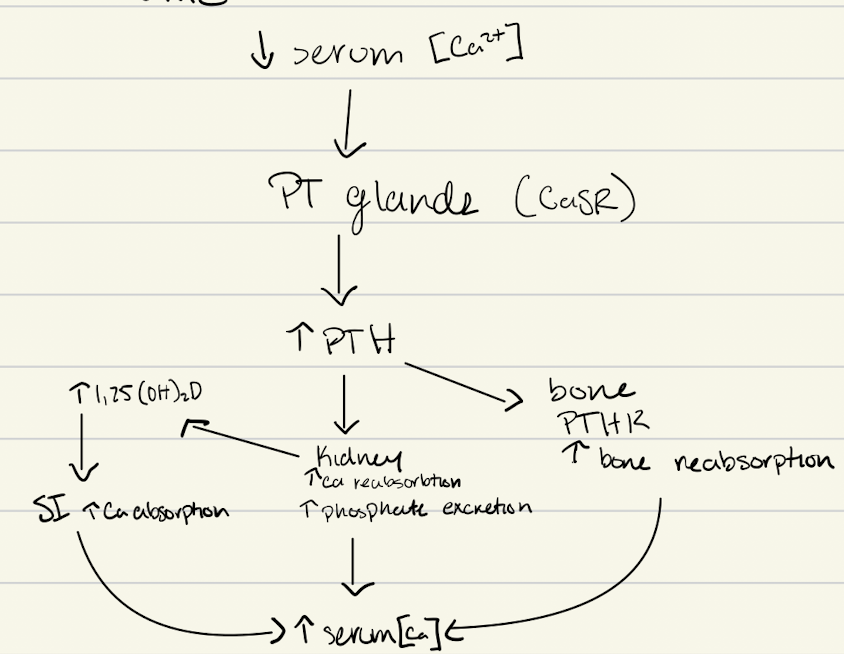
parathyroid Ca receptor (CaSR)
7TMGPCR (Gi)
activation of PLC system through binding of Ca to CaSR to inhibit transcription of gene for PTH
low/no Ca → inhibition removed and PTH genes transcribes
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
produced and secreted by parathyroid gland
synthesized in pre-pro form → 84 aa
regulated by changes in [Ca]
decreased Ca → increased PTH synthesis/secretion
secretion - fusion of secretory granule and exocytosis
parathyroid hormone related protein (PTHrP)
similar structure to PTH
works in similar manner, back up, in multiple tissues, 7TMGPCR
PTH mechanism to increase Ca
increased PTH → osteoblasts → produce RANKL → activate osteoclasts → breakdown bone
calcitonin
thyroid C-cells produce
inhibit action of osteoclasts and pre osteoblasts→osteoclasts
small effect compared to PTH
RANKL binding
estradiol and OPG (binding protein) - bind RANK L
estradiol protects bone by making OPG
PTH-R
7TMGPCR (Gs & Gq)
cause production of RANKL by osteoblasts, make pre osteoclasts from precursor cell
PTH action
direct in bone and kidney
bone - osteoblasts → RANKL → maturation of osteoclasts
kidney - formation of avtive vitamin D, increase Ca reabsorption, increased PO4 excretion
indirect: SI via vitamin D → increases Ca absorption
Bone cells
osteoblasts - build up bone
osteoclasts - break down bone
PTH on kidneys
cAMP
Ca reabsorption in distal tubules
increased PO4 excretion - proximal tubule, don’t want PO4 to increase with Ca
increased activity of a1-hydroxylase to form active vitamin D (1,25(OH)2D3)
Calcitonin
Gs
secreted by thyroid C-cells/parafollicular cells
protein with extreme PTM
regulation of secretion
slight increase in Ca → increase in calcitonin secretion
gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin and glucagon stimulate release (anticipatory)
SST inhibits calcitonin
calcitonin in bone
inhibits resorption of Ca by osteoclasts
may not affect bone formation but protects bone mass
calcitonin in renal cortex
renal tubules have receptors
increase urinary excretion of Ca, PO4, Na, K
actions of vitamin D
increased Ca reabsorbtion in gut
bone formation and resorption
Ca reabsorption in kidney
intestine: increase permeability of SI to Ca
bone: mobilization of Ca
kidney: increased reabsorption of P and possibly Ca
muscle: increased muscle tone and contraction through Ca flux
DBP - binding protein
cholecalciferol → hydroxylated in liver and kidney → calcitriol (active)
melanocortin origins
cleaved from POMC
prohormone convertase
PC 3/1, PC2
melanocortins
ACTH, alpha MSH, beta MSH, gamma MSH
protein hormones
melanotrophs, intermediate pituitary in color changing species and brain in mammals
PC1/3
endopeptidase found in anterior pituitary corticotrophs
in golgi of cells and packaged in pro-hormone form into endocytotic vesicles with prohormone
POMC cleaved into ACTH, beta LPH and other peptides - also found in different parts of hypothalamic nuclei that produce alpha MSH
PC2
endopeptidase found in brain and pancreatic islet cells
in the brain, ACTH is further cleaved to alpha MSH and CLIP, and beta LPH is digested into gamma LPH and beta endorphin
carboxypeptidase E (CPE)
cleaves carboxyl end of protein
melanocortin receptors
5 receptors, 7TMGPCR (Gs) (some Gi some Gq)
MC1R, MC2R, MC3R, MC4R, MC5R
always need ACTH but a,b,y, MSH are interchangeable for most part because MC2 only binds ACTH
MC1R
a=B=ACTH>y
agouti - antagonist
pigmentation, anti inflammatory
MC2R
binds ACTH only
Agouti - antagonist
glucocorticoid production, stress-induced lipolyis
MC3R
a=B=ACTH=y
AgRP - antagonist
energy homeostasis, anti inflammatory, pro-inflammatory cytokine release
MC4R
a=B=ACTH>y
AgRP, agouti - antagonist
body weight regulation, pain processing, grooming, sexual behavior, penile erections
MC5R
a=B=ACTH>y
agouti - antagonist
natriuresis, sebum secretion, preputial lipogenesis
functions of genes in POMC prepro-polypeptide
mutations in POMC gene affect coat color and cause obesity
a-MSH binds to MC1R to act on skin and MC4R to regulate obesity
agouti overexpression antagonizes aMSH in skin → yellow coat
AgRP overexpression antagonizes aMSH in H → obese phenotype
aMSH regulates skin pigmentation - chameleons via reflection of light off light/dark background on retina (dark increases aMSH release from IP)
aMSH affects melanocytes to alter skin color/pigmentation
receptor downregulation
signal attenuation: B arestin → receptor engulfed in vesicle → ribosome phosphatase removes ligand → receptor to lysosome or back to plasma membrane (determined by protein on c-terminal)
MC2R actions
in adrenal gland, binds ACTH and stimulates zones of cortex
zona fasciculata - glucocorticoids
zona glomerulosa - mineralocorticoids
also in adipocytes and mediates lipolytic effects of ACTH
MC4R actions
regulation of feed intake/appetite → suppresses appetite
KO mice results in obesity with human adolescents that have the mutation, they also have obesity in adolescence
hyperinsulinemia, diabetes (adult onset)
MC5R actions
closely homologous with MC4R, but mainly in peripheral tissues
KO mice - wetter in swin trial → less hair lipid production, water repulsion, thermal regulation
may be involved in release of pheromones
regulates aldosterone secretion
regulation of POMC
food restriction and weight loss - decreased POMC
increased feed intake - increased POMC
insulin and leptin - increased POMC
increased ACTH, a-MSH, B-MSH, y-MSH - decreased POMC
discovery of insulin
1921 - Banting and McLeod Nobel Prize
experiment in dogs - removing pancreas
purified insulin from bovine pancreas and transplanted into 14 yo boy'
insulin
protein hormone, synthesized as preproinsulin, varies across species
necessary for glucose homeostasis
stimulates glucose uptake by cells, stimulates glucose → glycogen in liver
pancreas
exocrine function aids in digestion (digestive enzymes)
endocrine function in islets of langerhans
alpha cells, beta cells, delta cells, F cells
alpha cells (A cell)
20% of pancreatic cells
alcohol insoluble (large red) granules
located at periphery of islet
secrete glucagon
beta cell (B cell)
75% of pancreatic cells - most numerous cell type
alcohol soluble (brownish) granules
secrete insulin
delta cells (D cell)
pancreatic cell type fewest in number
cytoplasm stains blue
secrete SST
F cells
secrete pancreatic polypeptide (PP)
proinsulin → insulin
cleaved by prohormone converting enzymes
biosynthesis of insulin
synthesized in B cell
preproinsulin synthesized in rER
pre sequence cleaved and disulfide bridges added → pro-insulin
proinsulin converting enzymes synthesized in ribosomes
proinsulin and converting enzymes enclosed in vesicles → cis Golgi → trans Golgi
clathrin coated vesicles pinch off and are rich in proinsulin
acidification (pH 6.5→5.5) of the vesicle induces activation of proinsulin converting enzymes
proteolysis of proinsulin and C-peptide
vesicles lose clathrin coat and mature into secretory granules rich in insulin
stored in cytoplasm until stimulated to undergo exocytosis by actions of glucose
biosynthesis of insulin (condensed)
B cells (rER) → prepro in vesicle with converting enzymes → cis/trans Golgi → proinsulin in clathrin coated vesicles → pH 6.5 to 5.5 → converting enzymes cleave proinsulin and vesicle loses clathrin coating → secretory granules stored in cytoplasm
control of insulin secretion
anabolic hormone, energy storage
stimulated for release by elevated blood levels of glucose, fatty acids, or amino acids
anticipatory signals - GI tract motility and stimulation by parasympathetic nerves
activation of insulin by acetyl choline
presence of carbohydrate in intestine causes release of gastric inhibitory peptide which is an insulin secretagogue
regulation of insulin secretion
intracellular regulators of insulin secretion are induced by metabolic products in B-cells
calcium, cyclic nucleotides and products of phospholipids
metabolism of glc, FA, and some AA within the B-cell results in closure of ATP-sensitive K+ channels
leads to depolarization of the cell and a consequent influx of Ca++ through voltage-sensitive channels
calcium then induces the secretion of insulin
insulin receptor
receptor tyrosine kinase
2 glycoprotein subunits (heterodimer, 2 alpha + 2 beta)
insulin binds to alpha and signals through beta
cascade of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation (Ser & Thr)
2nd: IRS1 (docking protein) (phosphorylated by receptor)
events following insulin receptor binding
insulin internalized and degraded
receptors not degraded - recycled to membrane
actions on cells: increase rate of glucose uptake
seconds: binds receptor Tyr-Kinase activity
minutes: hexose transport, altered enzyme activity, gene regulation, receptor internalization and down regulation
hours: induction of DNA, RNA, protein, and lipid synthesis, cell growth, downregulate insulin receptor… long acting growth promoting through IGF-1 receptor
mechanism of insulin action
anabolic hormone: converts building blocks to “storage forms”
glycogen, proteins, triglycerides
affects metabolism by altering substrate flow
insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose within cells (recruitment of GLUT 4 transporters → increased rate of uptake)
elevated levels of glucose-6-phosphate allosterically activates glycogen synthesis
blocks and reverse effects of other hormones
activates phosphatases (de-phosphorylate)
reverses phosphorylation of proteins by cAMP-induced protein kinases
other regulators of insulin
hormones and neurotransmitters causing increase in insulin
gastrin, secretin, CCK, GIP
catecholamines inhibit secretion of insulin
ketoacidosis
severe deficiency of insulin
conversion of FFA to ketones for energy (liver) rather than using glc for energy
lowers blood pH
glucagon
29aa, linear peptide
produced by a-cells
elevate blood glucose levels
catabolic - antagonizes insulin - stimulates liver glycogenolysis
aided by epinephrine (EP)
EP and glucagon act by increasing cAMP (7TMGs)
Cortisol plays a complementary role (stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver)
GLP-1 and GLP-2
act like glucagon
GLP-1
decreased glucagon
increased insulin
increased somatostatin
decreased gastric emptying
increased sensation of satiety
decreased appetite
GLP-2 (less known)
increased blood flow
increased mucosal growth
decreased apoptosis
increased nutrient transport
decreased gastric motility
decreased intestinal permeability
regulation of blood glucose
insulin (B-cells in response to low insulin) decrease blood glucose
glucagon (a-cells in response to low blood glucose) increase blood glucose
after a meal blood glucose rise above normal (80-90ng/100ml)
release insulin → bind receptors (increase glc transporters) → glc remove from blood and stored in muscle as glycogen → inhibits gluconeogenesis in liver
if blood glucose falls below 80ng/100ml
a cell’s release glucagon → degradation of glycogen and release of glucose into the blood
glucagon on liver
inactivates glycogen synthetase and activates phosphorylase a, which leads to an activation of glycogenolysis
increases activity of glucose-6-phosphate
enhances synthesis of glucose from pyruvate and lactate as well as amino acids, especially arginine and alanine → activates gluconeogenesis
glucagon on muscle
no response
glucagon on adipose
in large doses can stimulate lipolysis, under normal circumstances there is no effect
glucagon on pancreas
stimulates insulin secretion, particularly after intestinal absorption of amino acids
glucagon on brain
no response
insulin on liver
sufficient
no effect on glucose uptake
stimulates biosynthesis of hexokinase IV and activates glycogen synthetase
promotes glycolysis and formation of ATP
deficient
uptake of FFA and conversion to ketones
insulin on muscle
sufficient
stimulation of glucose uptake
stimulates biosynthesis of hexokinase II and pyruvate kinase
stimulates glycolysis and formation of ATP
increases muscle glycogen levels and creatine phosphate
deficient
impaired blood glucose
insulin on adipose
sufficient
stimulation of glucose uptake
enhances glycolysis which makes available glycerol phosphate which enhances triglyceride synthesis
inhibits lipase activity
deficient
decreases triglyceride synthesis due to a lack of glycerol phosphate
stimulation of lipolysis and release of FFA into the bloodstream
insulin on the brain
no direct actions of insulin
brain is dependent of blood glucose
osteoporosis
lack of estrogenm
metastatic bone disease
primary cancer that has metastasized to bone
Symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency
secondary hyperparathyroidism
osteopenia (bone loss)
fatigue, muscle and bone pain, muscle cramps and weakness, mood changes
symptoms of POMC deficiency
early onset obesity → insatiable hunger
red hair, pale skin
hypoglycemia
adrenal insufficiency
treatment for POMC deficiency
Setmalenotide - MC4R, MC3R, and MC1R agonist, SQ injection
Glucocorticoid substitution - oral, not ACTH because it is a protein which would be more likely to elicit an immune reaction, since glucocorticoids are steroids they can diffuse through membranes
symptoms of GLP-1 medication
activates receptors on vagus nerves which slow peristaltic waves in the stomach → delayed gastric emptying
stimulates insulin secretion and decreases glucagon secretion
medications for Type II Diabetes
regulate blood glucose levels, lifestyle and weight management
metformin
GLP-1 agonis
orexigenic center
feeding and eating
AgRP, NPY
anorexigenic center
satiety
a-MSH, CART