aggregate demand and supply
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
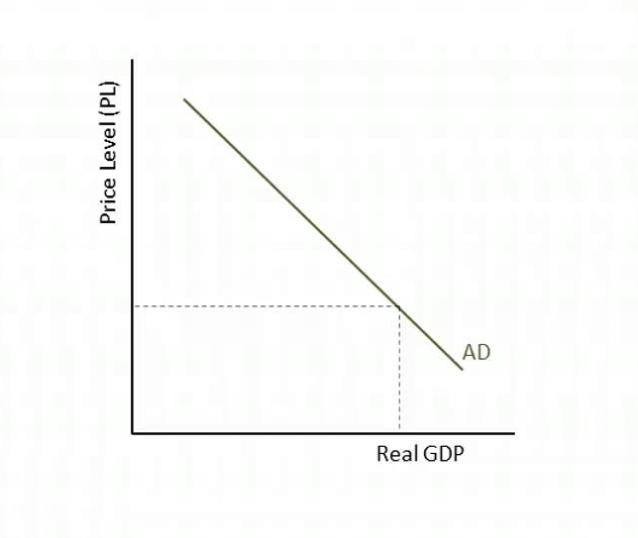
aggregate demand
sum of all demand within an economy
same as GDP
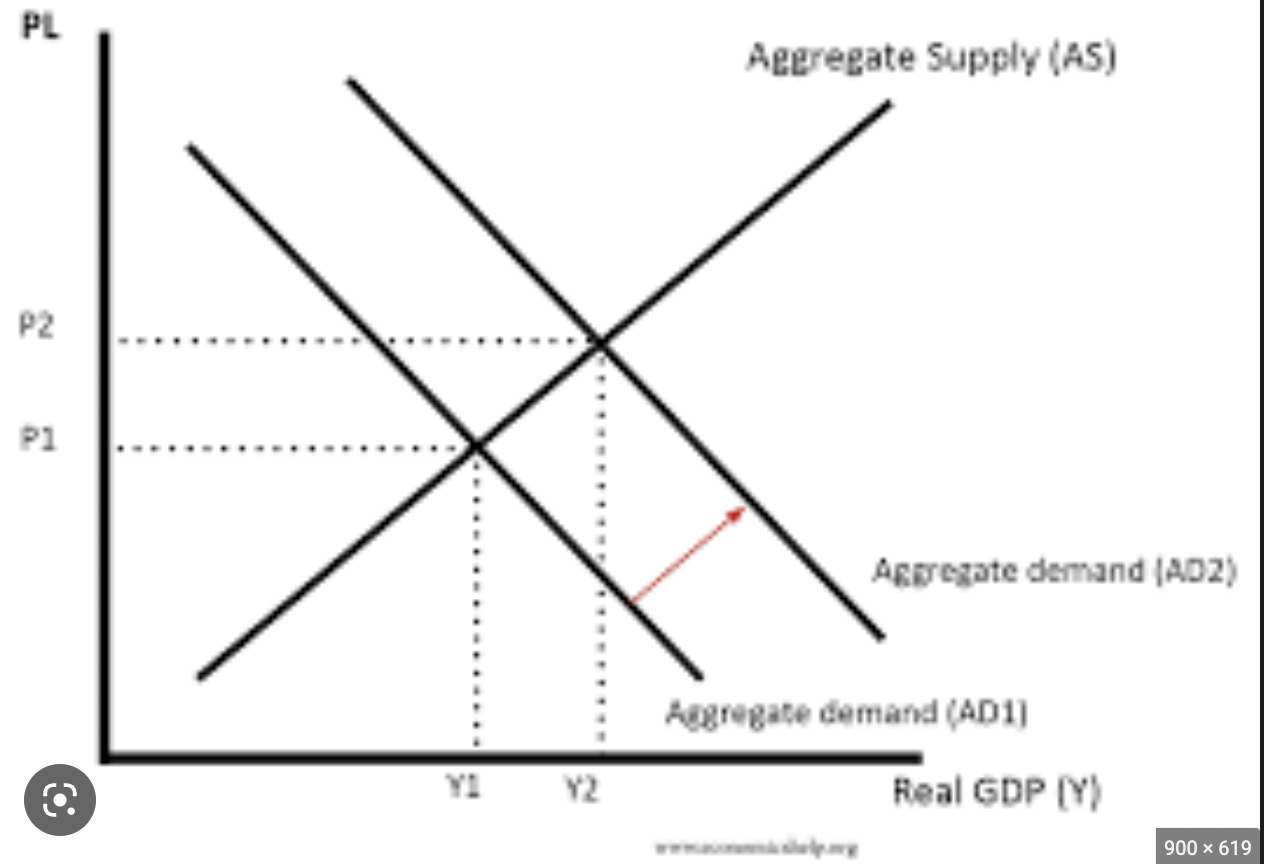
same as GDP
2
New cards
aggregate demand graph
3
New cards
components of aggregate demand
consumption, investments, government spending (except transfer payments), exports minus imports
4
New cards
consumption
all goods and services purchased by households
5
New cards
investments
all investments made by firms and households
6
New cards
government spending
all money spent by government (excluding transfer payments)
7
New cards
exports
goods produced in one country and sold to another
8
New cards
imports
goods produced by another country and then bought and brought
9
New cards
causes of change in consumption
changing incomes, changes in wealth, consumer expectation and confidence, household debt, interest rates
10
New cards
causes of change in investments
lower interest rates, rise in national incomes, business confidence, technology change
11
New cards
causes of change in government spending
spending on infrastructure, correcting market failure, war
12
New cards
causes of change in net exports
rise in foreign incomes could result in a rise in exports, strong currency could result in less exports, tariffs would reduce exports, high inflation would reduce exports
13
New cards
determinant of exchange rate in a country
supply and demand
if there is a demand for the currency, it will get stronger
you have demand for a currency when you buy goods from that country, invest in a business in that country, put money in financial institutions of that country
if there is a demand for the currency, it will get stronger
you have demand for a currency when you buy goods from that country, invest in a business in that country, put money in financial institutions of that country
14
New cards
how do governments encourage consumption
increase incomes > lower taxes
affect interest rates > buy bonds increasing money supply
increase wealth > redistribute wealth through progressive taxes
decrease household debt > forgive student loans
affect interest rates > buy bonds increasing money supply
increase wealth > redistribute wealth through progressive taxes
decrease household debt > forgive student loans
15
New cards
aggregate supply
total amount of goods and services that all industries in the economy will produce at a given price
16
New cards
aggregate supply graph
17
New cards
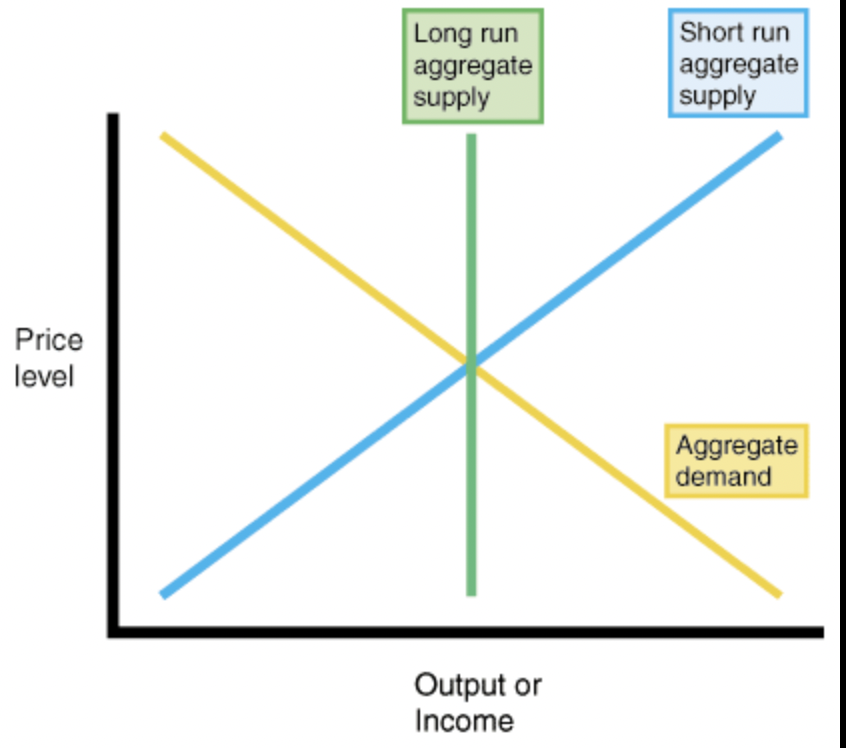
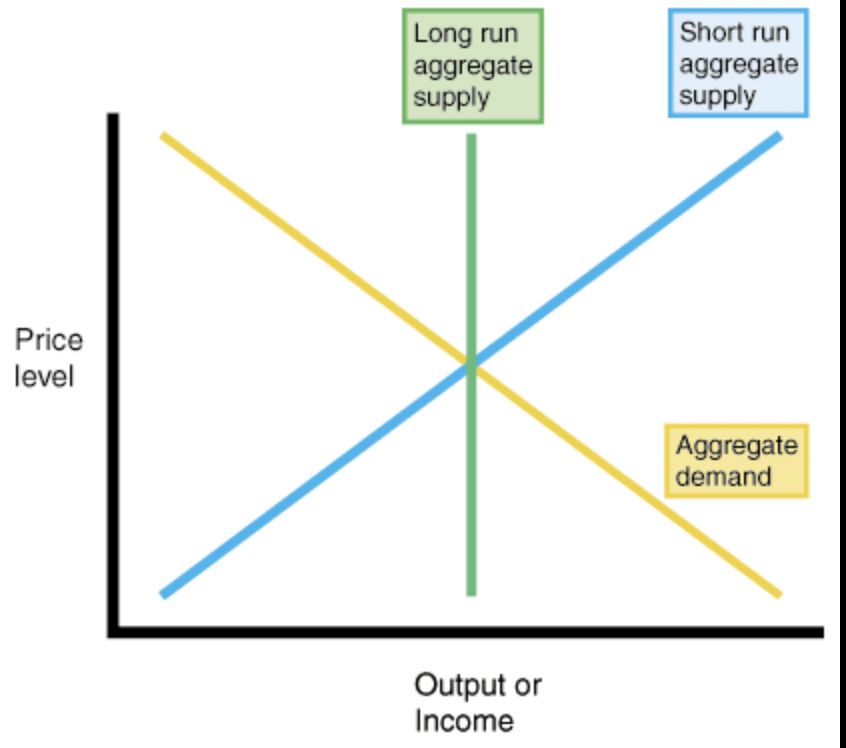
long run aggregate supply (new classical)
supply and output stays the same
demand can change and leads to price changes
employment and output don’t change
assumes that producers will always produce at a level in which all resources are employed
presumes wages and prices are flexible
government intervention will not help and the economy will self correct itself
demand can change and leads to price changes
employment and output don’t change
assumes that producers will always produce at a level in which all resources are employed
presumes wages and prices are flexible
government intervention will not help and the economy will self correct itself
18
New cards
short run aggregate supply (new classical)
only new classical economists believe in this
period in time when the factors of production do not change
wage rate is fixed
to meet an increase in demand, suppliers will have to offer incentives, such as overtime pay
costs go up as supply goes up
period in time when the factors of production do not change
wage rate is fixed
to meet an increase in demand, suppliers will have to offer incentives, such as overtime pay
costs go up as supply goes up
19
New cards
shifts in short run aggregate supply
WRISST
changes in wage rates
changes in cost of raw materials
supply shock
subsidies and taxes
changes in wage rates
changes in cost of raw materials
supply shock
subsidies and taxes
20
New cards
changes in wage rates
shift in short run aggregate supply
if wages go up, the SRAS will shift left
if wages go down, the SRAS will shift right
if wages go up, the SRAS will shift left
if wages go down, the SRAS will shift right
21
New cards
changes in cost of raw materials
shift in short run aggregate supply
if the cost of raw materials go up, SRAS will shift left
if the cost of raw materials go down, SRAS will shift right
if the cost of raw materials go up, SRAS will shift left
if the cost of raw materials go down, SRAS will shift right
22
New cards
supply shock: covid, flood, war
shift in short run aggregate supply
if supply shocks occur, SRAS will shift left
if supply shocks dont occur, SRAS will stay the same
if supply shocks occur, SRAS will shift left
if supply shocks dont occur, SRAS will stay the same
23
New cards
subsidies and taxes
shift in short run aggregate supply
if subsidies are given, SRAS will shift right
if taxes are imposed, SRAS will shift left
if subsidies are given, SRAS will shift right
if taxes are imposed, SRAS will shift left
24
New cards
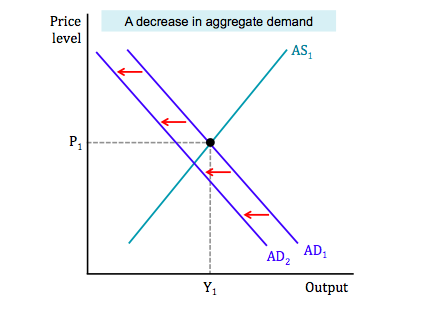
decrease in AD (new classical)
demand shifts left which causes prices to deflate workers will (eventually) accept lower wages
there is no unemployment (unless its voluntary)
costs go down (prices and wages)
SRAS shifts to the right
because wages and costs are lower, so are prices
economy will always self correct
wages have gone down but real wages are the same because costs always go down
there is no unemployment (unless its voluntary)
costs go down (prices and wages)
SRAS shifts to the right
because wages and costs are lower, so are prices
economy will always self correct
wages have gone down but real wages are the same because costs always go down
25
New cards
new classical opinion on government intervention
unemployment benefits, minimum wages, price controls, and trade unions are harmful to the economy because they set boundaries upon wages, prices, and costs and don’t allow the economy to self correct
don’t believe in government intervention
don’t believe in government intervention
26
New cards
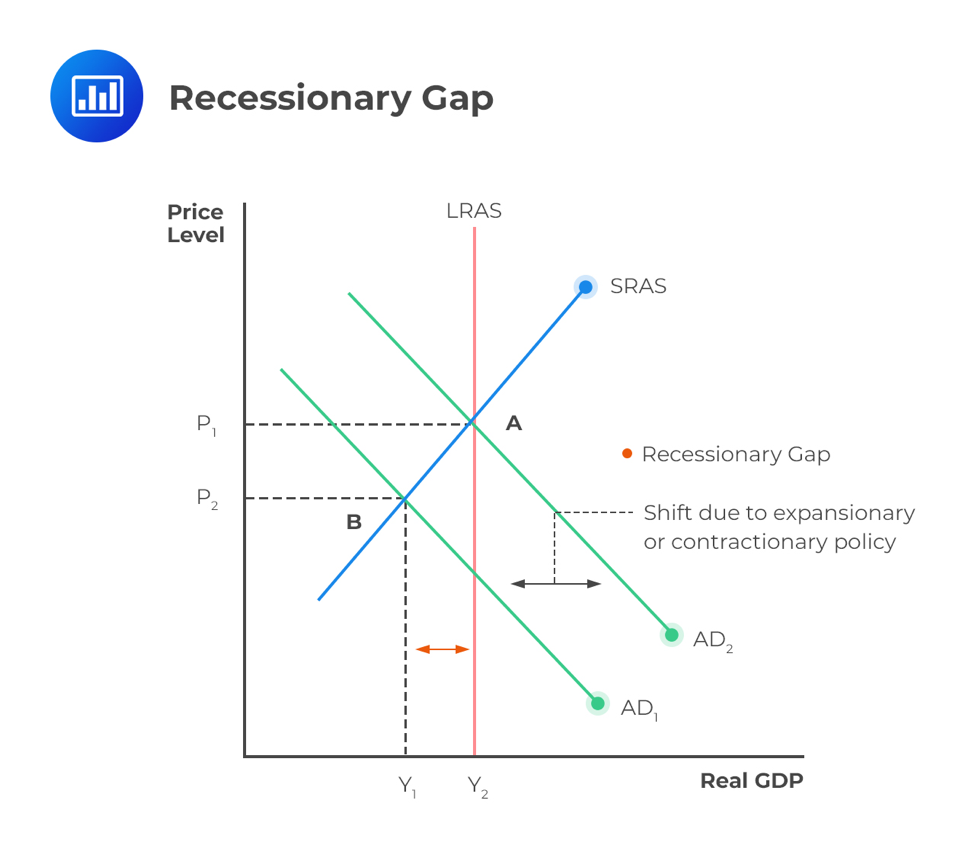
increase in AD (new classical)
demand shifts to the right causing price inflation
firms compete to higher workers to keep up with demand, pushing wages and costs up
firms lay off workers and output declines (SRAS shifts left)
only the price level increases (inflation) with an AD increase
SRAS shifts to the left because wages and costs go up
if the government increases spending to help the economy/shift SRAS to the right, it will only be inflationary and not help with growth
firms compete to higher workers to keep up with demand, pushing wages and costs up
firms lay off workers and output declines (SRAS shifts left)
only the price level increases (inflation) with an AD increase
SRAS shifts to the left because wages and costs go up
if the government increases spending to help the economy/shift SRAS to the right, it will only be inflationary and not help with growth
27
New cards
Keynesian theory
believes that wages and prices will not easily go down
people won’t take pay cuts
at a certain point increasing AD will not cause growth but AS increases growth in an economy
people won’t take pay cuts
at a certain point increasing AD will not cause growth but AS increases growth in an economy
28
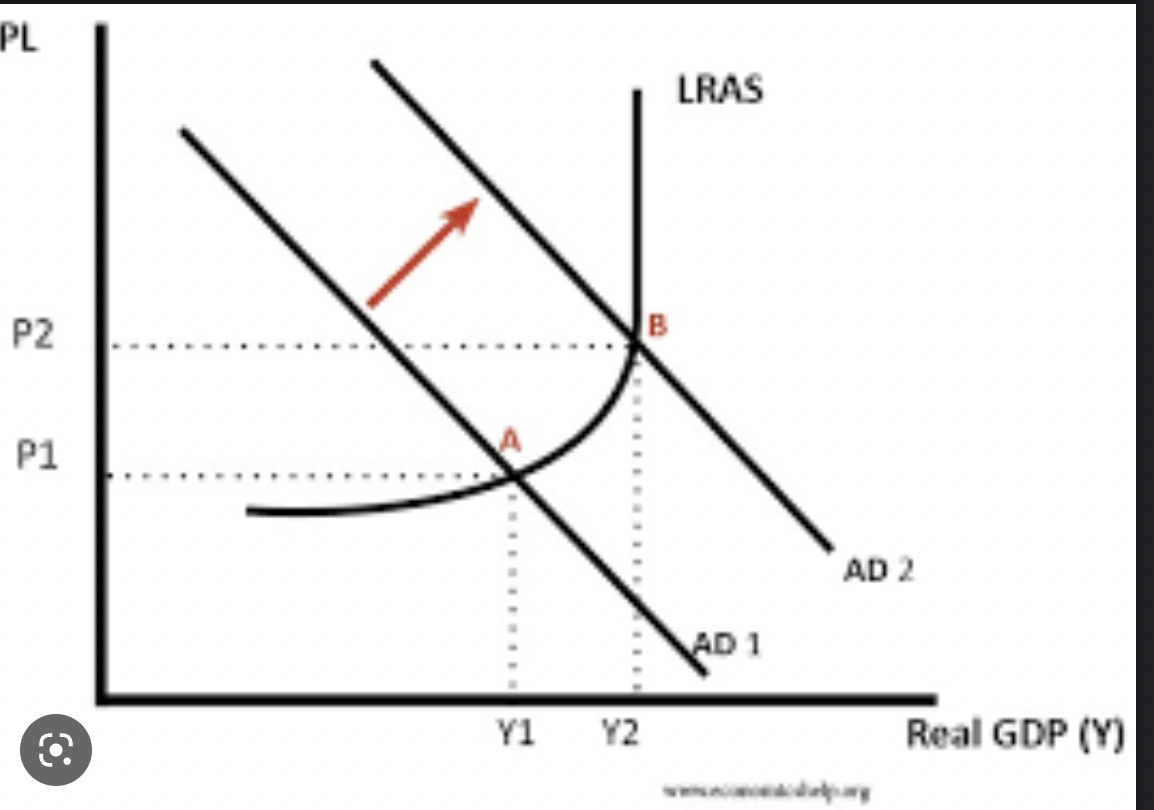
New cards
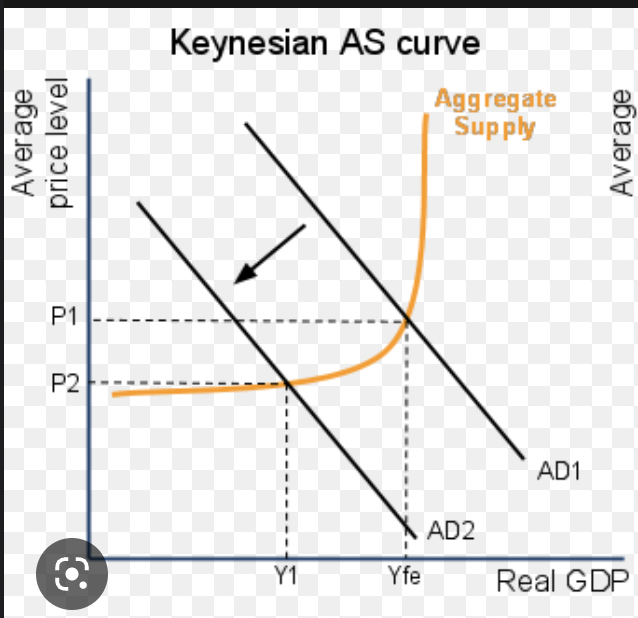
keynes graph
1. resources are under utilized
2. everyone that wants a job has a job
3. increase in demand is purely inflationary
29
New cards
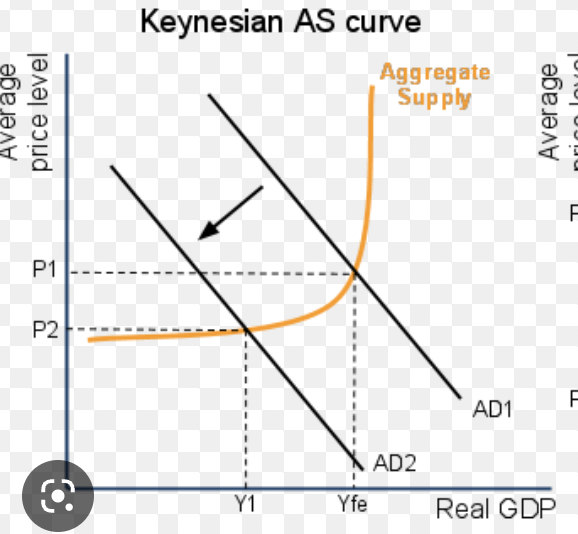
decrease in AD (keynesian)
shift to the left
firms must lay off workers since wages are sticky
output falls, unemployment increases
deflation will be slight, or non existent (prices slip a bit)
happens because people refuse to take a pay cut
the economy will slip into a recession
requires government intervention to fix itself
firms must lay off workers since wages are sticky
output falls, unemployment increases
deflation will be slight, or non existent (prices slip a bit)
happens because people refuse to take a pay cut
the economy will slip into a recession
requires government intervention to fix itself
30
New cards
keynesian opinion on government intervention
unemployment benefits, minimum wages, and government spending are helpful in a recession because it stops other people from being unemployed and keeps the economy stable and prevents outputs from falling
government intervention is required
government intervention is required
31
New cards
increase in ad (keynesian)
employment and output will increase
prices will remain stable
eventually at full capacity, prices will begin to inflate
finally, an increase in demand will be “purely inflationary”
purely inflationary- prices keep going up
prices will remain stable
eventually at full capacity, prices will begin to inflate
finally, an increase in demand will be “purely inflationary”
purely inflationary- prices keep going up