Chapter 6: The Integumentary System
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 6, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Skin cancer
Cancer caused by exposure to the UV rays of the sun, most often on the head, neck, and hands of fair-skinned people and the elderly; one of the most common and easily treated cancers
Types of skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma (stratum basale)
Squamous cell carcinoma (stratum spinosum)
Malignant melanoma (melanocytes)
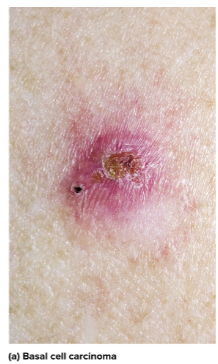
Basal cell carcinoma
The most common type of skin cancer in the stratum basale; forms a small shiny bump with central depression and is the least dangerous because it seldom metastasizes
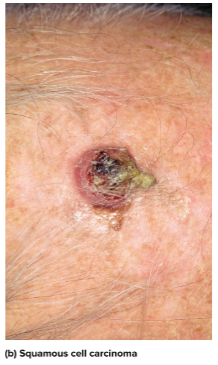
Squamous cell carcinoma
Arises from the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum on the scalp, ears, lower lip, or back of hand and can form a concave ulcer; early detection and removal can allow recovery but if untreated can spread to lymph nodes and become lethal
Malignant melanoma
Skin cancer that arises from melanocytes and is less than 5% of all skin cancer; can be removed if caught early but is fatal when metastasized—greatest risk is genetics in men, redheads, and severe sunburn victims in childhood
Burns
The leading cause of accidental death from extreme tempreatures, radiation, electricity, or acids; fluid loss, infection, or toxic eschar cause most deaths
Eschar
The burned, dead tissue that forms over a burn
Debridement
The removal of eschar
Burn classification
Made to the depth of tissue involvement; first, second and third degree
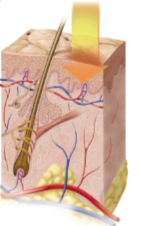
First-degree burn
Burns that only involve the epidermis that can cause redness, slight edema, and pain but heal within days
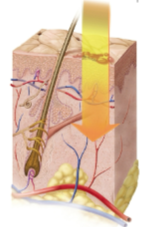
Second-degree burn (partial-thickness burn)
Burns that can involve part of the dermis and may appear red, tan, or white with blisters and pain; these take several months to heal and may leave scars
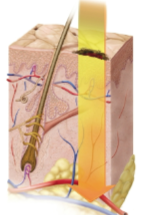
Third-degree burn (full-thickness burn)
Burns that involve all of the dermis and deeper tissue; they require skin grafts and need fluid replacement, infection control, and nutrition to recover
UV Rays
Rays from the sun that have the potential to cause cancer; sunscreens may provide protection but may provide a false sense of security and damage DNA through their chemicals
Skin graft
Taking skin and putting it on a burn (usually of the third degree)
Autograft
Skin grafts taking tissues from another location on the same person’s body
Split-skin graft
Taking the epidermis and part of the dermis from an undamaged area and grafting it elsewhere; is an autograft
Isograft
Using tissue from an identical twin in a skin graft
Homograft (allograft)
Using tissue from an unrelated person in a skin graft
Heterograft (xenograft)
Using tissue from another species in a skin graft
Other graft options
Using the amnion from afterbirth and artificial skin from silicone and collagen
Types of sweat glands
Apocrine and eccrine
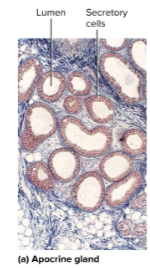
Apocrine glands
Type of sweat glands that are inactive until puberty and located in the axillary and groin region; the sweat produced is milky and contains fatty acids and pheromones
Bromhidrosis
The disagreeable body odor produced by bacterial action on sweat from apocrine glands
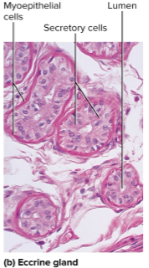
Eccrine glands
The most numerous skin glands; they are tubular and create a watery perspiration for thermoregulation
Myoepithelial cells
Cells found in both the apocrine and eccrine glands; they contact in response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system to squeeze perspiration out (as in stress sweating)
Sweat
A fluid made up of 99% water and a pH range of 4 to 6 to inhibit bacterial growth; begins as a protein free filtrate of blood plasma produced by deep secretory portion of gland
Sweat excretions
Sodium chloride (salt) and some drugs
Insensible prespiration
Prespiration that does not produce visible wetness of skin; humans sweat up to 500 ml per day this way
Diaphoresis
Sweating with the wetness of the skin; humans lose 1 L of sweat per hour during exercise this way
Cutaneous transporation
The water loss from skin not due to sweating; diffuses between keratinocytes and evaporates from the skin
Sebum
The oily secretion of sebaceous glands to aid moisturization
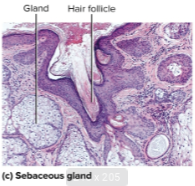
Sebaceous glands
Flask shaped glands that open into hair follicles that secrete sebum
Cerumen (earwax)
Yellow secretion combined with sebum and dead epithelial cells; it keeps the eardrum pliable, waterproof, and free from bacteria
Ceruminous glands
Coiled, simple tubular glands in the external ear canal; they are modified apocrine glands
Mammary glands
Glands that produce milk and develop only during pregnancy and lactation; they are heavily modified apocrine sweat glands
Mammary ridges (milk lines)
Two rows of mammary glands in mammals
Accessory organs of skin
The hair, nails, and cutaneous glands
Pliable soft keratin
Keratinized cells making up the stratum corneum of the skin
Compact hard keratin
Kertinized cells making up the hair and nails; tougher and more compact
Plius (pili)
A slender filament of keratinized cell growing from the skin called a hair follicle
Types of hair
Lanugo, vellus, and terminal
Lanugo hair
Fine hair that appears on the fetus in the last three months of development
Vellus hair
Fine and pale hair that replaces lanugo by the time of birth; two-thirds of hair in women, one-tenth hair in men, and all hair of children except eyebrows, eyelashes, and scalp hair
Terminal hair
Longer, coarser, and heavily pigmented hair; makes up eyebrows, eyelashes, scalp hair, and pubic, facial, and axillary hair after puberty
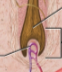
Hair bulb
The bottommost layer of the hair; swelling at the base where hair originates in the dermis
Hair root
Remainder of the hair in the follicle
Hair shaft
The portion of hair above the skin surface
Dermal papilla
Bud of vascular connective tissue encased by the bulb; the only source of nutrition for hair
Hair matrix
The region of mitosis above the papilla; hair’s growth center
Hair layers
Medulla, cortex, cuticle
Hair medulla
Core of hair, loosely arranged cells, and air spaces
Hair cortex
The center of the hair; contains elongated keratinized cells
Hair cuticle
The outer layer of the hair; multiple layers of thin and scaly cells that overlap
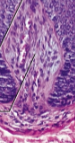
Hair follicle
Contains the hair root in a diagonal root; contains the epithelial root sheath as a source of stem cells and connective tissue root sheath which surrounds it
Hair receptors
Sensory nerve fibers around muscle; includes the arrector pili which attaches the follicle to the dermis
Hair texture
Related to the cross sectional shape of hair; straight is round, wavy is oval, curly is flat
Hair color
Determined by pigment granules in the cortex; brown has high eumelanin, while red has high pheomelanin (white has none)
Stages of hair
Anagen—the growth stage where stem cells multiply and continue making hair cells
Catagen—the degeneration stage where the hair keratinizes
Telogen—the resting stage when papilla reaches the bulge
Hair growth
About 1 mm per 3 days
Alopecia
Thinning of the hair or baldness
Pattern baldness
Having hair lost from select regions; most common in males due to baldness allele being sex-linked
Hirsutism
Excessive hairiness in areas not usually hairy
Functions of hair
Parasite detection with receptors
Vestigial warmth
Scalp hair to retain heat and protect against sunburn
Pubic hair to signify sexual maturity
Guard hairs to guard nostrils and ears
Eyelashes for nonverbal communication
Fingernails and toenails
Clear and hard derivatives of stratum corneum to improve grooming and food picking
Nail plate
The hard part of the nail
Free edge
Overhangs the fingertip on nails
Nail body
The visible, attached part of the nail
Nail root
Extends proximally under skin
Nail fold
Surrounding skin rising above nail
Nail groove
Separates nail fold from nail plate
Nail bed
Skin underlying the nail plate
Nail matrix
The mitotic growth zone of thickened stratum basale at the end of the nail
Hyponychium
The epidermis of the nail bed
Lunule
Opaque white crescent at the proximal end of the nail due to matrix thickness
Eponychium (cuticle)
The narrow zone of dead skin overhanging proximal end of nail
Dermatology
The scientific study and medical treatment of the integumentary system
Integumentary system
Contains the skin, accesory organs, hair, nails, and cutaneous glands
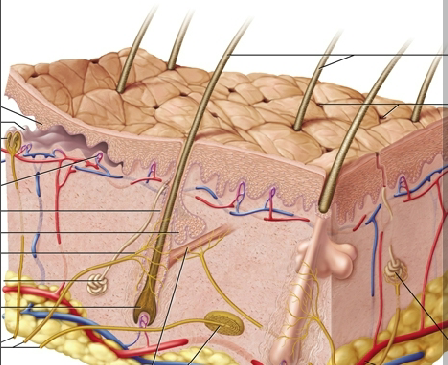
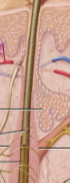
Skin
The body’s largest and heaviest organ; covers 1.5 to 2.0 m² and is about 15% of body weight—made of the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
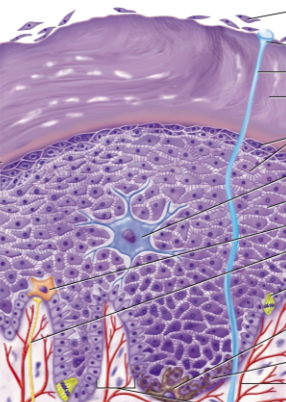
Epidermis
Outermost layer of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium on the skin; it is avascular with some nerve endings for touch
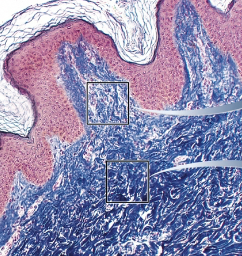
Dermis
The middle wavy layer of deeper connective tissue on the skin; made of the papillary and reticular layer and is 0.2 to 4 mm thick with hair follicles, blood vessels, glands, nerves, nails, roots, and muscles
Hypodermis
The bottommost layer of adipose tissue on the skin; contains more areolar and adipose tissue than the dermis and also contains blood vessels
Skin thickness
0.5 to 6 mm
Thick skin
Found on the palms of hands and soles of feet; only sweat glands and measures about 0.5 mm thick
Thin skin
Found on the rest of the body; contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands and measures about 0.1 mm thick
Functions of skin
Resistance to trauma and infection with keratin
Barrier functions for water retention and UV defense
Sensation of the outside world
Thermoregulation and sensation for vasoconstriction/dilation, perspiration
Facial expression
Vitamin D synthesis
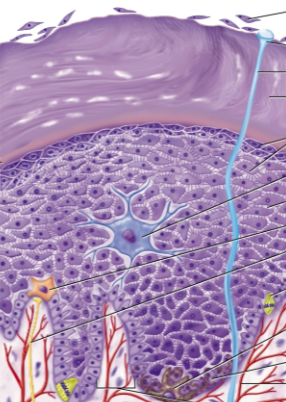
Epidermal cell types
Stem cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, tactile cells, dendritic cells

Stem cells
Undifferentiated cells in the epidermis that give rise to keratinocytes in the stratum basale (deepest layer)

Keratinocytes
The great majority of epidermal cells, synthesizes keratin
Melanocytes
Cells in the epidermis that synthesize the pigment melanin to shield DNA; located in the stratum basale but distribute melanin along keratinocytes
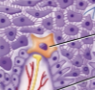
Tactile cells
Touch receptors associated with dermal nerve fibers in the basal layer; also called Merkel’s cells and are star-shaped
Dendritic cells
Macrophages from the bone marrow guarding against pathogens in the stratum spinosum/granulosum; also called Langerhans’s cells
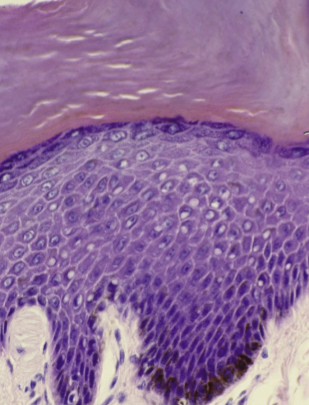
Strata
Layers of the epidermis
Stratum corneum (top)
Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale (bottom)
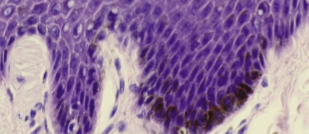
Stratum basale
The deepest epidermal layer; only contains a single layer of stem cells, keratinocytes, and a few melanocytes and tactile cells
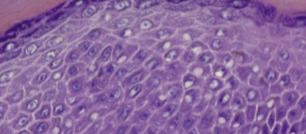
Stratum spinosum
Several layers of keratinocytes alongside some dendritic cells
Stratum granulosum
Three to five layers of flat keratinocytes

Stratum lucidum
Thin, pale layer only found in thick skin made up of keratinocytes with a clear protein
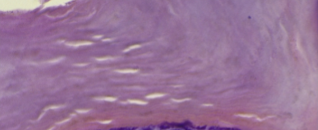
Stratum corneum
The surface layer of the skin, made up of several layers of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium to resist abrasion
Keratinocyte life
Protein is released to bundle keratin
Cells produce tough keratin protein under membranes
Lipids are released to waterproof cells on the membrane (retain water)
Organelles degenerate and die
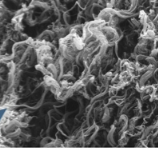
Papillary layer
The thin zone of areolar tissue in and near the dermal papilla with blood vessels; uppermost layer of dermis
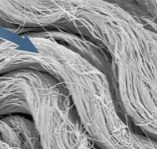
Reticular layer
The thick layer of dense irregular connective tissue that may have stretch marks due to stretched collagen; bottommost layer of dermis