Darby Clinical Oral Structure, Dental Anatomy, and Root Morphology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
CASE A
Permanent Dentition
A 29-year-old male presents for an initial dental hygiene appointment. The patient has no significant medical history. The patient brushes once a day. It has been 4 years since he has been to a dentist because he did not have dental insurance. He presents today with a chief concern about his front teeth breaking and would like a cleaning. He also notes that he thinks his teeth are getting yellower and is interested in whitening. During dietary counseling the clinician noted the patient drinks Mountain Dew all day.
questions 1 to 10
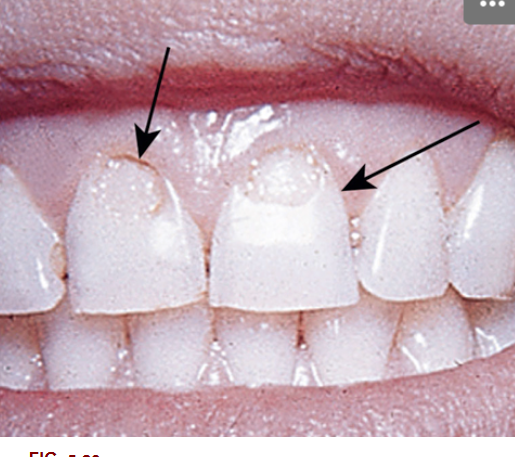
1. After reviewing Fig. 5.23, what term would you use to describe this wear?
a. Abfraction
b. Abrasion
c. Attrition
d. Erosion
d. Erosion
2. Using the Universal Numbering System what tooth numbers are wearing in Fig. 5.23?
a. 8, 9
b. 24, 25
c. 2.1, 1.1
d. 1.1, 3.1
a. 8, 9
3. What in the patient’s history could be contributing to his condition?
a. Not being to the dentist in 4 years
b. Drinking Mountain Dew
c. Not having dental insurance
d. Brushing his teeth
b. Drinking Mountain Dew
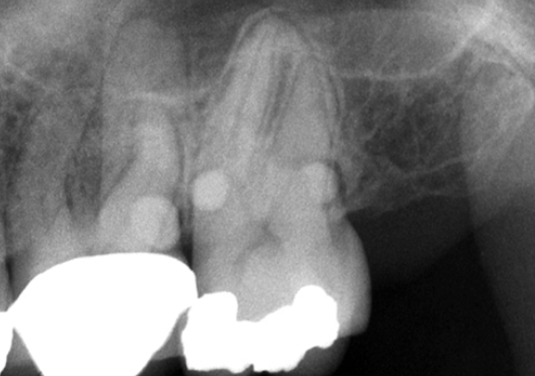
4. Using Fig. 5.24, what would you call the enamel projections seen on the maxillary molars?
a. Enamel pearl
b. Enamel projection
c. Hypercementosis
d. Dens in dente
a. Enamel pearl
5. What is the structure called on the hard palate that is firm and has irregular ridges branching off the palatine raphe?
a. Palatine fovea
b. Rugae
c. Incisive papilla
d. Maxillary tuberosity
b. Rugae
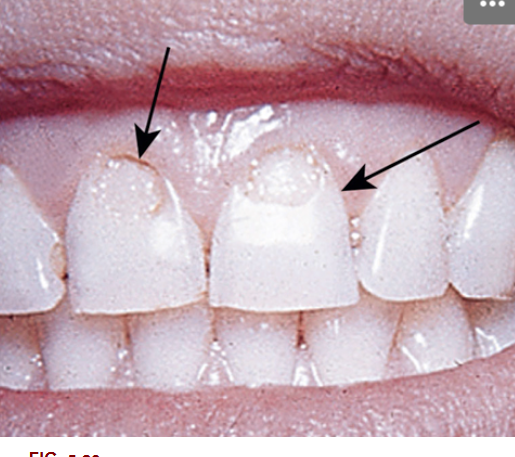
6. What tooth tissue is seen in Fig. 5.23 that is yellow in color?
a. Enamel
b. Dentin
c. Cementum
d. Pulp
b. Dentin
7. What is wear called on cusps of posterior teeth?
a. Wear facets
b. Grooves
c. Pits
d. Decalcification
a. Wear facets
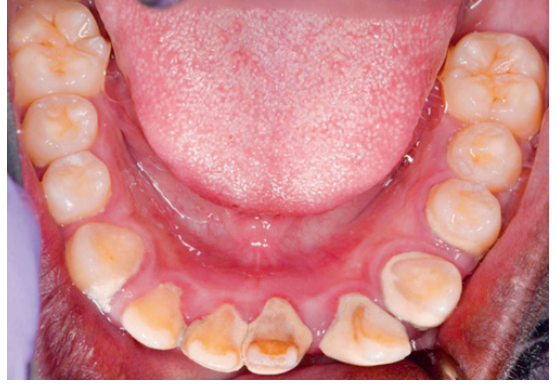
8. Looking at Fig. 5.25, what gingiva is edematous?
a. Gingival margin
b. Attached gingiva
c. Interdental papilla
d. a. and c.
d. a. and c.
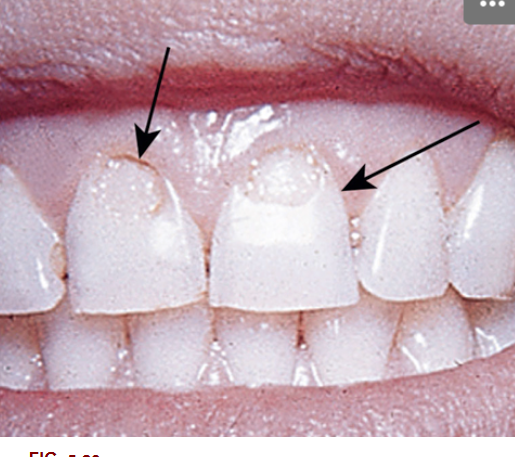
9. Looking at Fig. 5.23, which tooth/teeth looks suspicious on the mesial surface using the International Numbering System?
a. 1.2
b. 1.3
c. 2.3
d. b. and c.
a. 1.2
10. What would you call a tooth that is malpositionally rotated?
a. Torsiversion
b. Extrusion
c. Infraocclusion
d. Linguoversion
a. Torsiversion
CASE B
Mixed dentition
A 12-year-old female presents to your clinic for an initial hygiene appointment. Her medical history is significant for congenital syphilis.
questions 11 to 15
11. After the clinical exam notching of the maxillary incisors is seen, what are these incisors called?
a. Hutchinson’s incisors
b. Mulberry incisors
c. Peg incisors
d. Macrodontia incisors
a. Hutchinson’s incisors
12. What other anatomy anomalies can be caused due to congential syphilis?
a. Microdontia
b. Fusion
c. Mulberry molars
d. Dens in dente
c. Mulberry molars
13. Using the Universal Number System, which teeth are showing notching of the incisors?
a. O and P
b. 24 and 25
c. E and F
d. 8 and 9
d. 8 and 9
14. What surface of the incisors is affected by the notching (Hutchinson’s incisors)?
a. Marginal ridge
b. Facial ridge
c. Lingual ridge
d. Incisal ridge
d. Incisal ridge
15. A small fold of soft tissue located on each side of the frenulum linguae in the floor of the mouth is called:
a. Sublingual folds
b. Labial folds
c. Vermillion folds
d. Foliate folds
a. Sublingual folds
16. Which trait would distinguish a premolar from a canine?
a. Set trait
b. Type trait
c. Class trait
d. Arch trait
c. Class trait
17. Another term for cervical line would be?
a. Gingival crest
b. Line angle
c. Cemento-dentinal junction
d. Cemento-enamel junction
d. Cemento-enamel junction
18. In which quadrant is tooth #4.3 located?
a. Maxillary right
b. Maxillary left
c. Mandibular right
d. Mandibular left
c. Mandibular right
19. What is formed by the junction of the distal and occlusal surfaces of a posterior tooth?
a. An incisal edge
b. A point angle
c. A cusp tip
d. A line angle
d. A line angle
20. For mandibular incisors, on which surface is a root depression usually more distinct?
a. Facial
b. Lingual
c. Mesial
d. Distal
d. Distal
21. Which tooth has the longest root in the oral cavity?
a. Maxillary canine
b. Mandibular canine
c. Maxillary first premolar
d. Mandibular first premolar
a. Maxillary canine
22. Which premolar develops from five lobes?
a. Maxillary first premolar
b. Maxillary second premolar
c. Mandibular first premolar
d. Mandibular second premolar
d. Mandibular second premolar
23. Which premolar usually has a deep, mesial depression on the crown and the root?
a. Maxillary first premolar
b. Maxillary second premolar
c. Mandibular first premolar
d. Mandibular second premolar
a. Maxillary first premolar
24. Which term is used to describe an extra rounded projection on a tooth usually found on the cingulae of anterior teeth or occlusal surface of posterior teeth?
a. Enamel pearl
b. Mammelon
c. Tubercle
d. Exostosis
c. Tubercle
25. What class of teeth is present in the permanent dentition that is NOT present in the primary dentition?
a. Incisors
b. Canines
c. Premolars
d. Molars
c. Premolars
26. Which tooth tissue is the most calcified?
a. Pulp
b. Cementum
c. Dentin
d. Enamel
d. Enamel
27. Which permanent tooth erupts into the space previously held by the primary second molar?
a. First molar
b. Second molar
c. First premolar
d. Second premolar
d. Second premolar
28. How many pulp horns does tooth #13 have?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b. 2
29. Which anterior tooth may have a bifurcated root?
a. Maxillary canine
b. Mandibular canine
c. Maxillary central incisor
d. Maxillary lateral incisor
b. Mandibular canine
30. Which tooth has a mesial marginal ridge groove?
a. Maxillary first premolar
b. Maxillary second premolar
c. Mandibular first premolar
d. Mandibular second premolar
a. Maxillary first premolar
31. Which molar usually has the roots closest together?
a. First premolar
b. First molar
c. Second molar
d. Third molar
d. Third molar
32. Name the roots of the maxillary first molar.
a. Mesial and distal
b. Facial and lingual
c. Mesiobuccal, distobuccal, and buccal
d. Mesiobuccal, distobuccal, and lingual
d. Mesiobuccal, distobuccal, and lingual
33. Where is a cervical enamel projection normally found?
a. Near any furcation
b. Near the incisal edge
c. Near the apex
d. Near the occlusal surface
a. Near any furcation
34. Which term is used to describe the amount of vertical overlap of maxillary teeth?
a. Crossbite
b. Overjet
c. Overbite
d. Supraversion
c. Overbite
35. Which is usually the first permanent tooth to erupt in the oral cavity?
a. Mandibular central incisors
b. Maxillary central incisors
c. Maxillary first molars
d. Mandibular first molars
d. Mandibular first molars
36. What statement is TRUE of teeth that are dilacerated?
a. The root and/or crown may be unusually bent
b. The root is unusually short
c. The marginal ridges are very prominent
d. There is a deep crevice in the cingulum
a. The root and/or crown may be unusually bent
37. The anterior teeth in Fig. 5.29 exhibits:
a. Perikymata
b. Fluorosis
c. Attrition
d. Mamelons
d. Mamelons
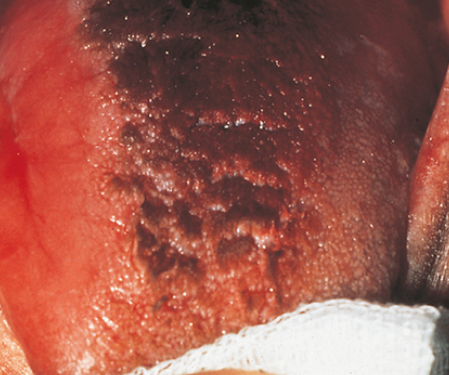
38. What type of papillae is involved with the condition seen in Fig. 5.26?
a. Fungiform
b. Circumvallate
c. Foliate
d. Filiform
d. Filiform
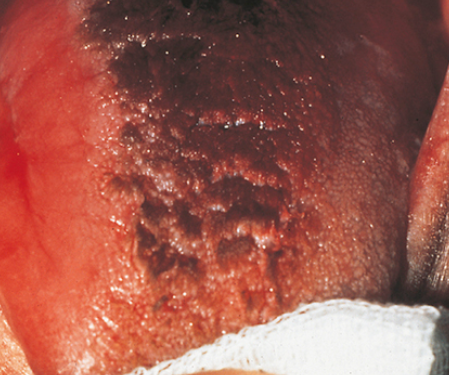
39. Which of the following is the correct assessment of the following patient’s tongue? (Fig. 5.26)
a. Hairy
b. Fissured
c. Coated
d. Ulcerated
a. Hairy
40. When there is a space between the maxillary central incisors, what is the space called?
a. Open bite
b. Fremitus
c. Centric relation
d. Diastema
d. Diastema
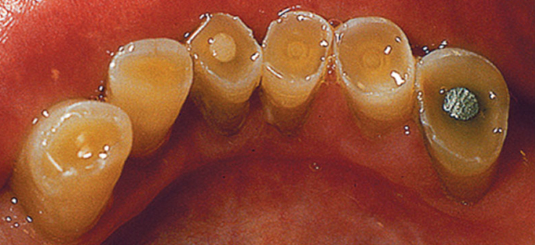
41. What is seen on the incisal edge of the picture (Fig. 5.27)?
a. Recession
b. Abrasion
c. Attrition
d. Abfraction
c. Attrition
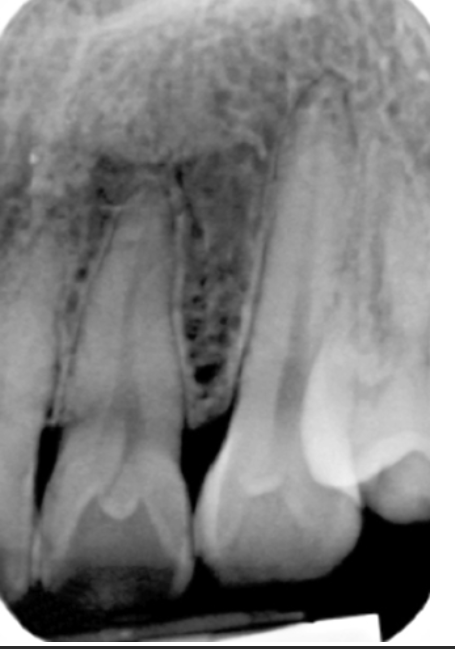
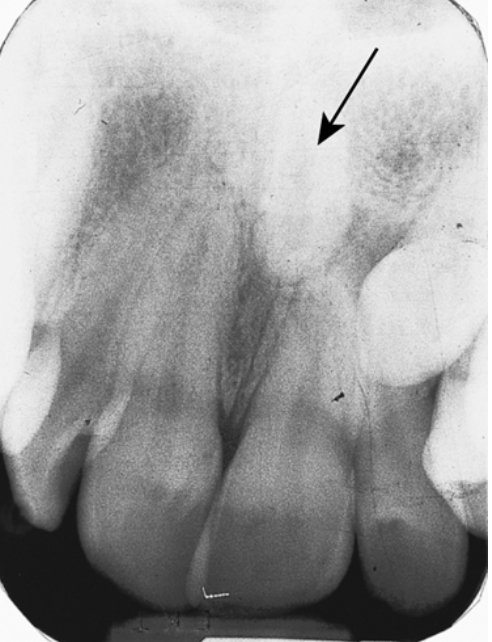
42. What is seen in the radiograph (Fig. 5.28) on tooth #7?
a. Peg lateral
b. Dens in dente
c. Supernumerary tooth
d. Bifurcated root
b. Dens in dente
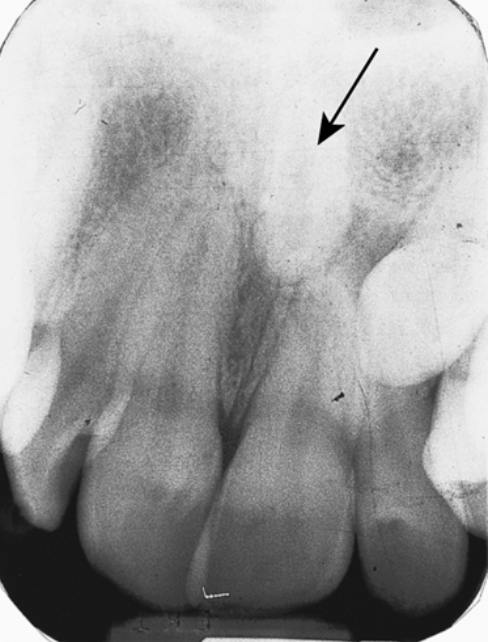
43. What is the term for the extra tooth in Fig. 5.29 pointed out by the arrow?
a. Mesiodens
b. Macrodontia
c. Microdontia
d. Anodontia
a. Mesiodens
44. What is another name for the corner of the mouth?
a. Philtrum
b. Buccal mucosa
c. Commissure
d. Frenum
c. Commissure
45. What tonsillar tissue hangs from the soft palate and closes the nasopharynx when swallowing?
a. Palatine tonsils
b. Uvula
c. Pterygomandibular raphe
d. Pharyngeal tonsils
b. Uvula
46. The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar meets up with the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. What type of occlusion relationship is this?
a. Class I
b. Class II Division I
c. Class II Division II
d. Class III
a. Class I
47. What papilla on the tongue function in taste of bitter?
a. Fungiform
b. Filiform
c. Foliate
d. Circumvallate
d. Circumvallate
48. What structure on the buccal mucosa carries saliva from the parotid gland?
a. Parotid papilla
b. Stenson’s duct
c. Wharton’s duct
d. a. and b.
d. a. and b.
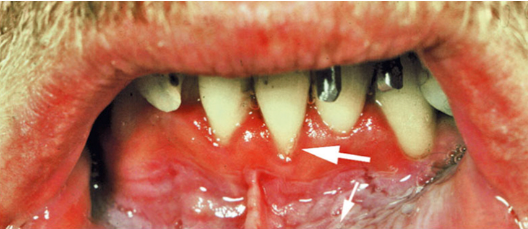
49. What is a possible cause of the recession seen in Fig. 5.30?
a. Labial frenum attachment
b. Chewing tobacco
c. Toothbrushing
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
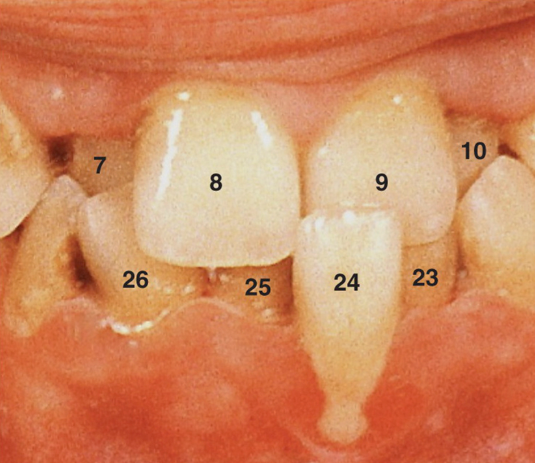
50. What terminology would you use to describe the location of tooth #24 seen in Fig. 5.31?
a. Torsiversion
b. Infraocclusion
c. Labioversion
d. Linguoversion
c. Labioversion