BIOL 1201 : Chapter 7
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
The ____________ is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings
plasma membrane
The plasma membrane is __________ permeable.
selectively
What are transport proteins often responsible for?
controlling passage across cellular membranes
review pictures
review pictures
What is the membrane in the fluid mosaic model?
a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
What are membranes held together by?
mainly weak hydrophobic interactions
Most of the _____ and some _____ can move sideways within the membrane
lipids ; proteins
What are the membrane proteins?
integral proteins and peripheral proteins
What are Peripheral proteins?
are bound to the surface of the membrane
What are Integral proteins?
penetrate the hydrophobic core
Integral proteins that span the membrane are called ______________.
transmembrane proteins
How does cell recognize each other?
by binding to molecules, often containing carbohydrates, on the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane
Membrane carbohydrates may be covalently bonded to what?
lipids (forming glycolipids) or, more commonly, to proteins (forming glycoproteins)
If a plasma membrane were compared to a sandwich, ____________ would be considered the filling.
Hydrophobic tails
Membrane structure results in what?
selective permeability
A _________ must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the ____________.
cell ; plasma membrane
Plasma membranes are _______ permeable, regulating the cells molecular traffic.
selectively
________ (nonpolar) molecules, such as ___________, can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and pass through the membrane rapidly.
Hydrophobic ;hydrocarbons
_________ molecules including ions and polar molecules do not cross the membrane easily.
Hydrophilic
Review pictures
Review pictures
What re Transport proteins ?
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane
What does carrier proteins do?
bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane
Which of the following molecules is most likely to passively diffuse across the plasma membrane?
carbon dioxide
What is passive transport?
diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment
What is diffusion?
the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
Diffusion of a population of molecules may be ________.
directional
Where does substances diffuse down?
concentration gradient (high to low)
The _________ of a substance across a biological membrane is ______ because no energy is expended by the cell to make it happen.
diffusion ; passive transport
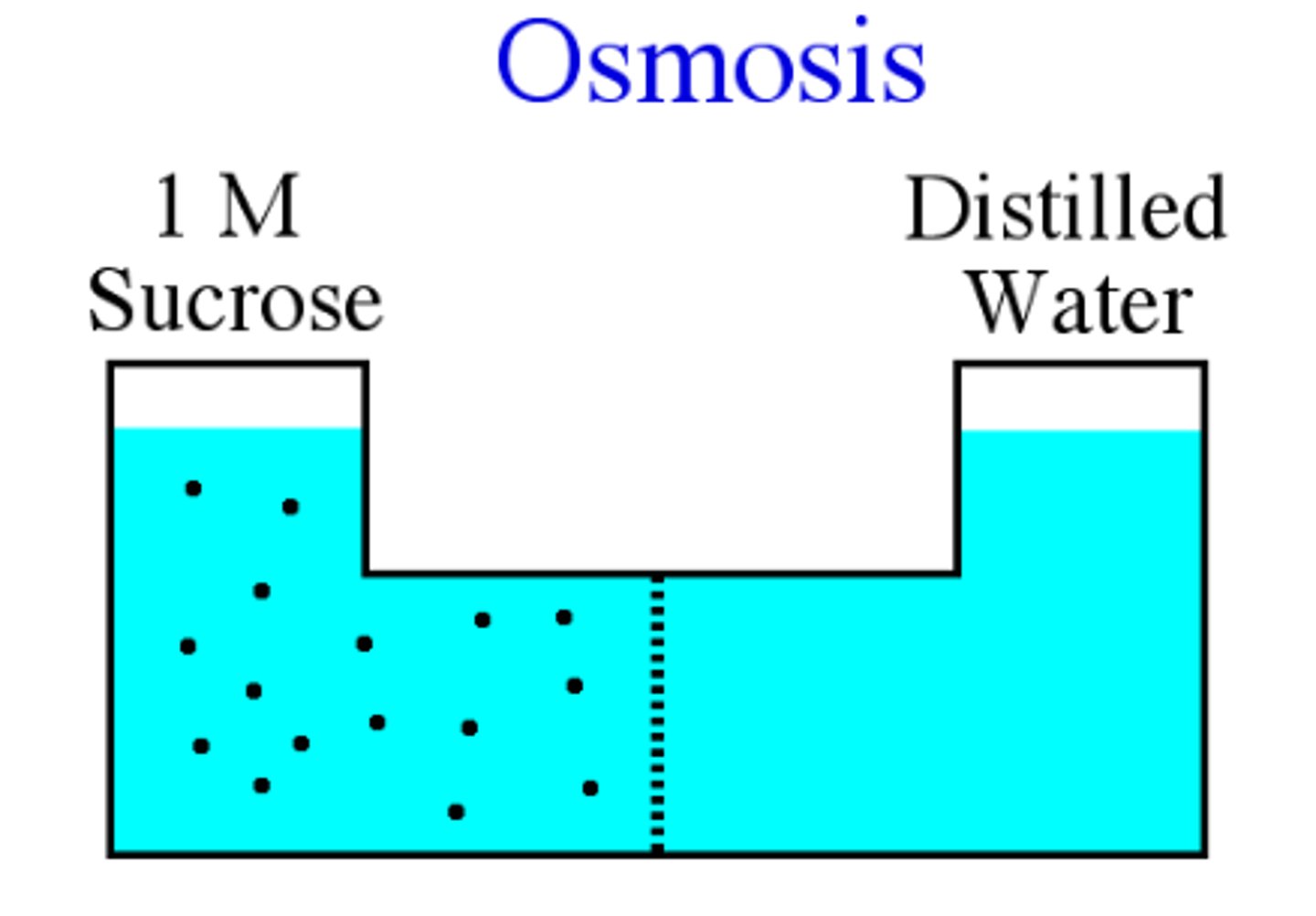
What is Osmosis?
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Water diffuses across a membrane from the region of _______ to the region of _______ until the solute concentration is equal on both sides
lower solute concentration ; higher solute concentration
What is hypotonic?
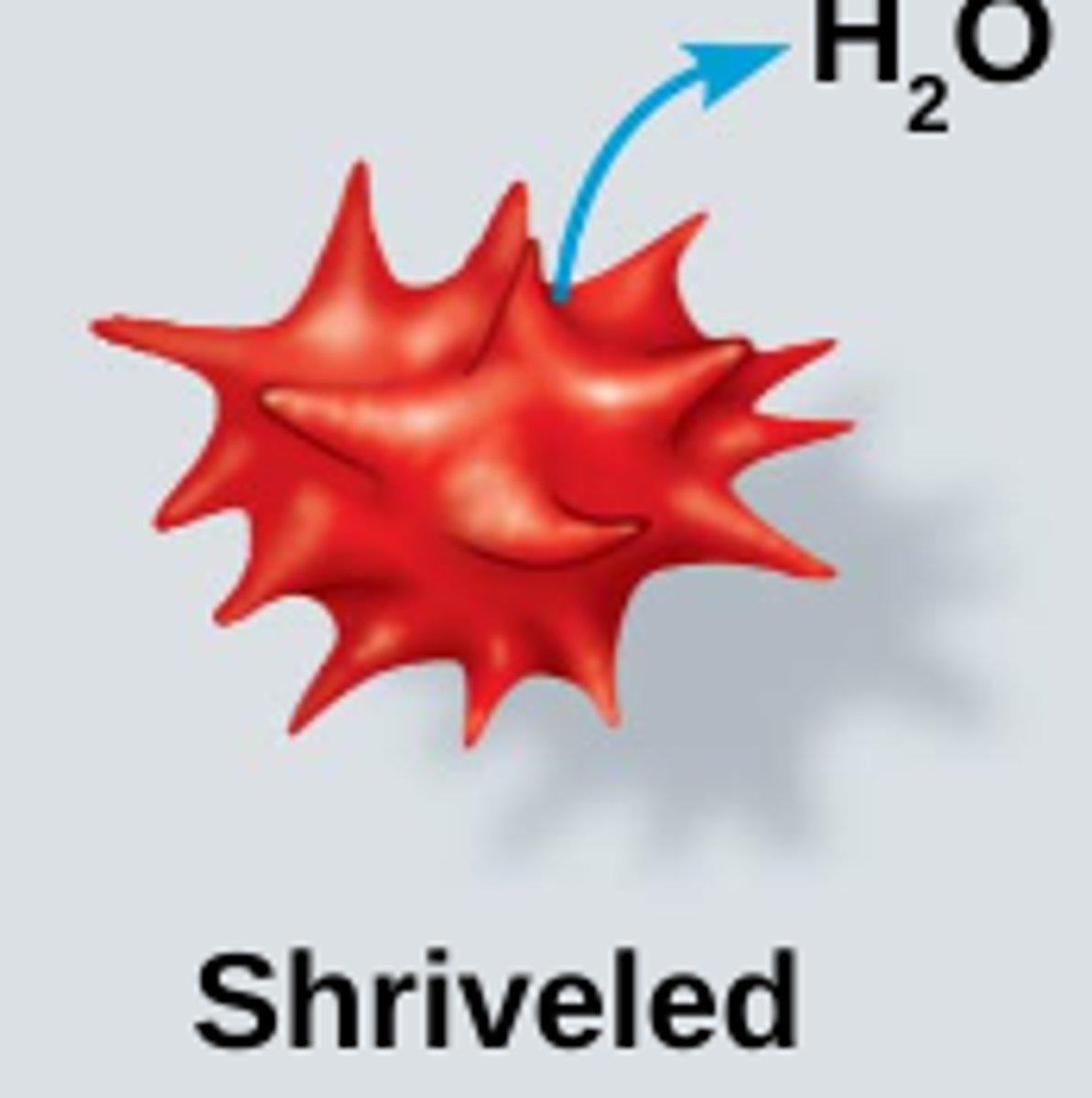
Lower concentration outside compared to inside
What is isotonic?
Equal concentration inside and outside
What is hypertonic?
Higher concentration outside compared to inside
Image of hypotonic?
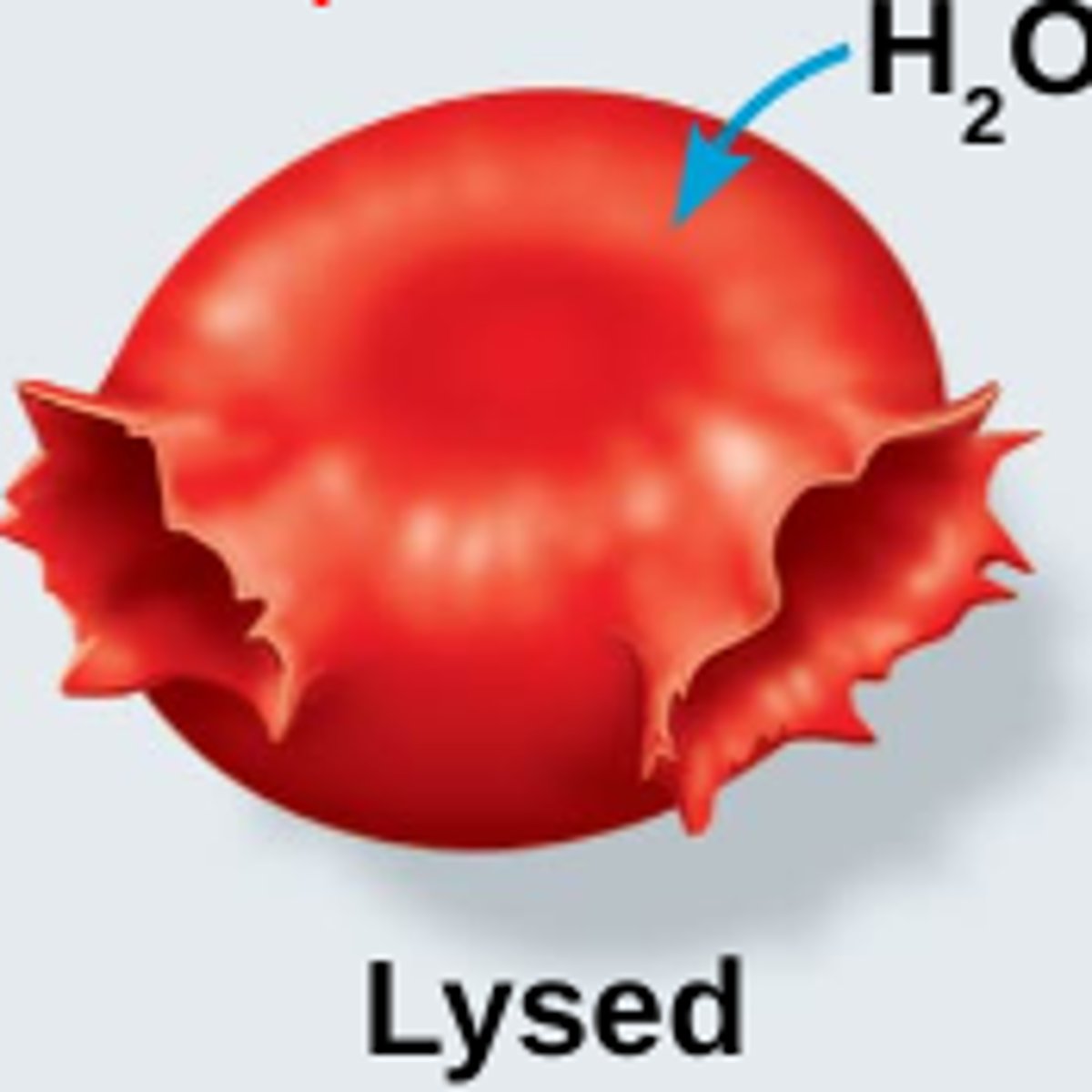
Image of isotonic?
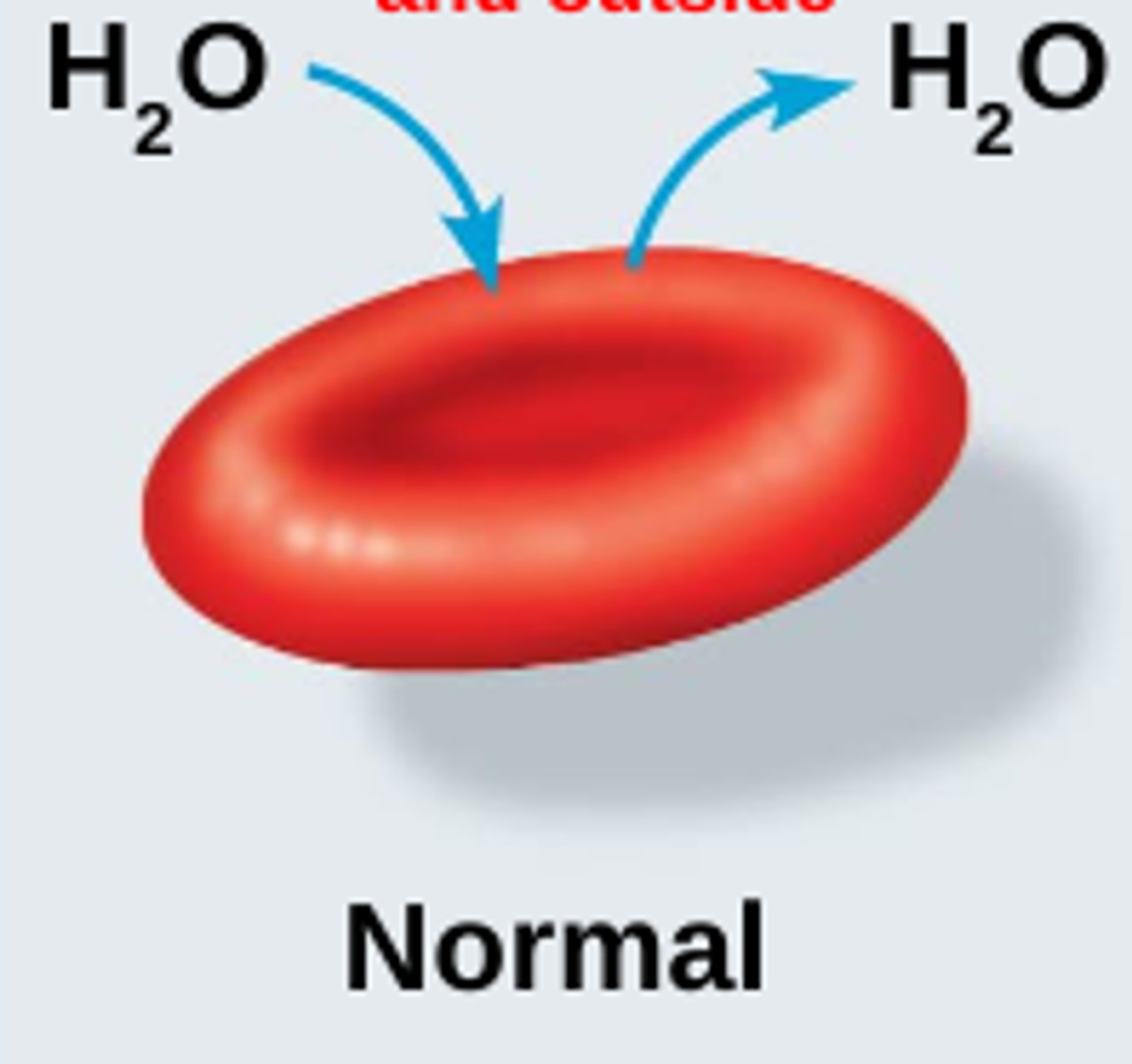
Image of hypertonic?
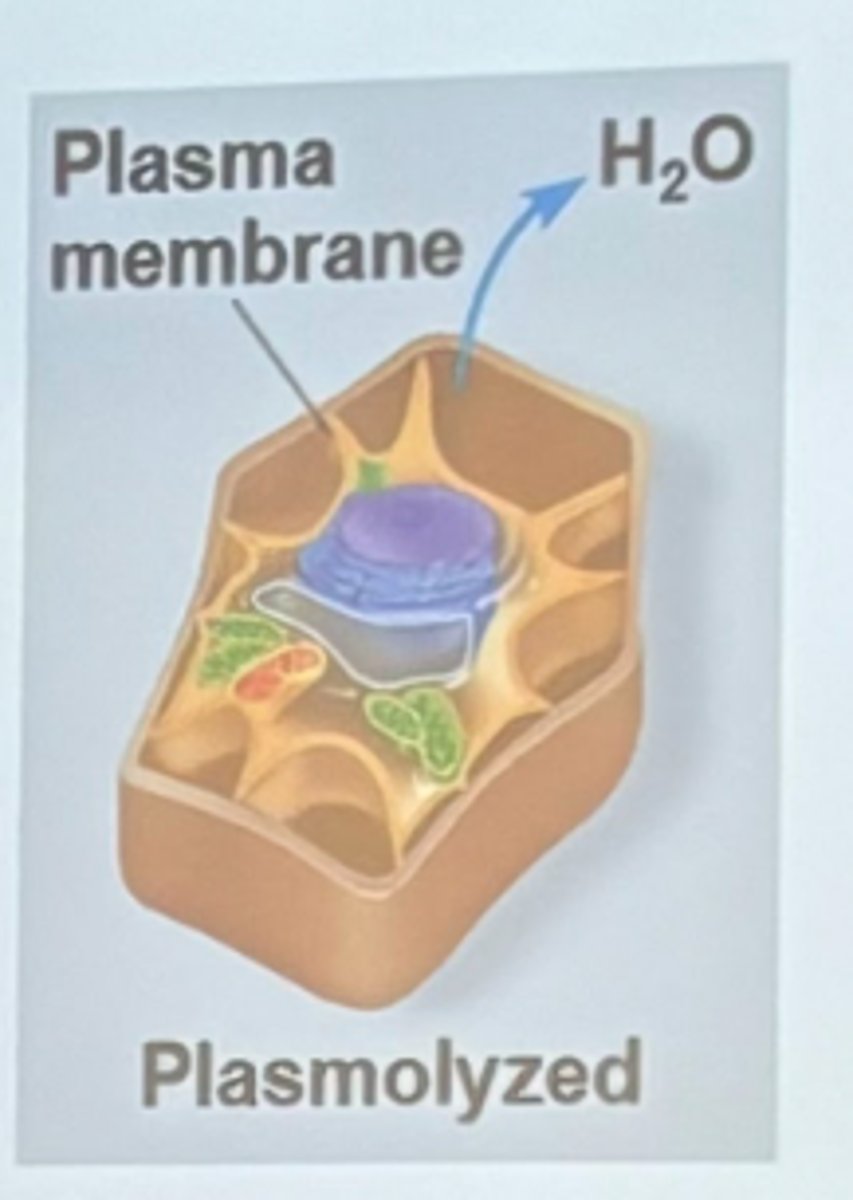
The internal solute concentration of a plant cell is about 0.8M. To demonstrate plasmolysis, it would be necessary to suspend the cell in what solution?
1.0 M
The "cell" in the beaker in the figure below is made up of a semipermeable membrane that allows water to pass but not salt. The solution in the "cell" is
________ compared to the solution in the beaker.
hypertonic
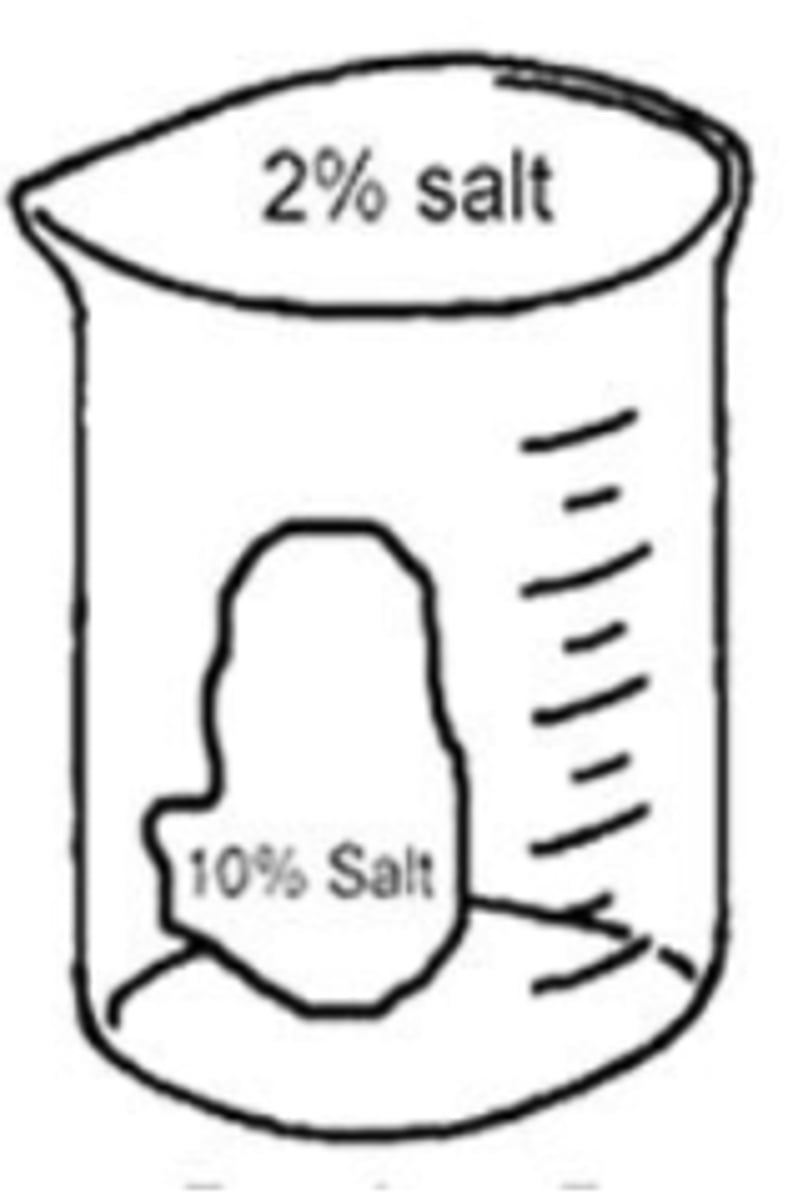
In which direction will there be net movement of water?
to the left
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
- Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- Ion channels facilitate the transport of ions
- Some ion channels, called gated channels, open or close in response to a stimulus
What are gated channels?
they open or close in response to a stimulus
______ facilitate the transport of ions.
Ion channels
What uses energy to move solutes against their gradients?
Active transport
______ diffusion is still passive because the solute moves down its concentration gradient, and the transport requires no energy.
Facilitated
Where does active transport requires energy from?
ATP hydrolysis, to move substances against their concentration gradient
In passive transport, what does the concentration go from?
high to low
In active transport, what does the concentration go from?
low to high
The cytoplasm of a certain cell, such as a neuron, already has a high concentration of K+ ions. How can K+ ions continue to enter the cell?
active transport
Bulk transport across the plasma membrane occurs by what?
exocytosis and endocytosis
Small molecules and water enter or leave the cell through the ________ or via _______.
lipid bilayer ; transport proteins
Large molecules, such as ______ and ______, cross the membrane in bulk via vesicles.
polysaccharides ; proteins
Bulk transport requires ______.
energy
What is Phagocytosis?
Cell eating
What is Pinocytosis?
bring in small solutes by bulk (cell drinking)
What is Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis?
cells will have receptors in membrane and bind specifically with them to form a vesicle