Stage 2 Chemistry, Unit 1.5- Monitoring the Environment-Atomic Spectroscopy
1/33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
How do elements emit light under a flame test?
Electrons absorb a specific energy wave length, causing them to jump shells from their ground state and become excited. When they come down from being excited, this specific energy is emitted, in the form of light.
Why does each element have a unique colour?
Each atom has special wavelengths needed to cause electrons to jump shells, and these unique colours are emitted at once to cause a unique colour.
What are the 4 types of subshells?
S,P,D,F
The period number is
the number of shells
The period blocks determine
what the valence subshell is
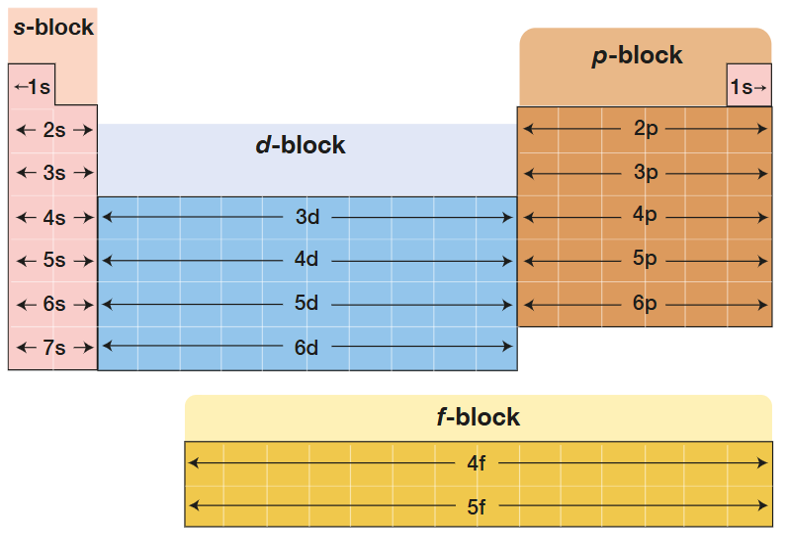
The group number indicates
the number of valence electrons,
What is the capacity of the S subshell?
2
What is the capacity of the P subshell?
6
What is the capacity of the D subshell?
10
What is the capacity of the F subshell?
14
How many subshells does shell 1 have?
1 subshell (S)
How many subshells does shell 2 have?
2 subshells (S,P)
How many subshells does shell 3 have?
3 subshells (S,P,D)
How many subshells does shell 4 have?
4 subshells (S,P,D,F)
How are electron subshells filled?
lower energy subshells are filled first, and higher subshells are filled in ortder of their increased energy
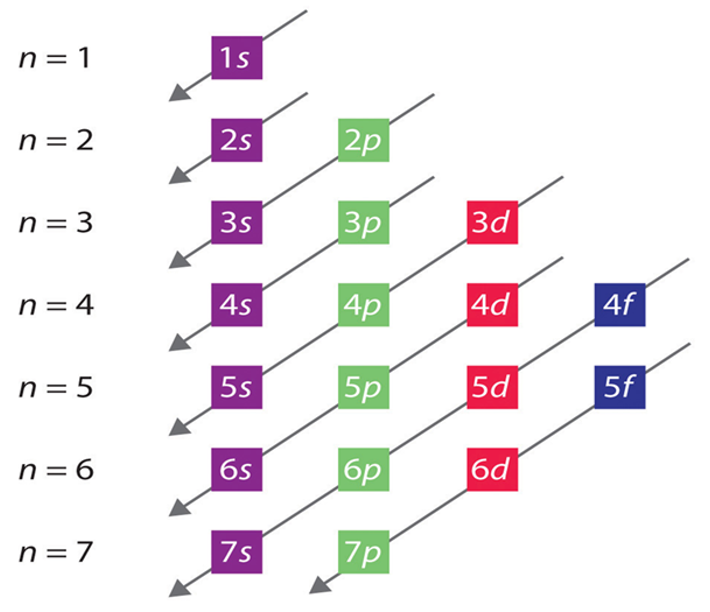
What two transition metals are exceptions with their subshells?
Cu and Cr (Copper and Chromium.) Both of their 4s shell only contains one electron.
For Transition metals
Subshell 3d is lower in energy than the 4s subshell. This means that 4s is lost first with ionic configuration.
The d-block transition metals prefer to lose electrons from the highest quantum number (n) first, ie, the 4s subshell before the 3d subshell.

Atom absorption spectrum
displays which colours have been absorbed by an atom.
Atom Emission spectra
displays what colours individual atoms emit when they release from their excited electron states.
AAS
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
ATomic Emission Spectroscopy allows for
The concentration of an element to be determined, according to the intensity of light emitted.
What are used in AAS?
A hollow Cathode lamp, a nebuliser (flame), a light slit, a monochromator, a detector.
Hollow cathode lamps
emit light that are specific for that element to become excited.
Hollow cathode lamps contain an inert (noble) gas
the anode and cathode within the lap are coated with the specific element.
Nebuliser
The Nebuliser draws the sample up as a liquid from a capillary tube (aspirates), and then evaporates the liquid into a high burning fuel for flame, atomising the compounds.
How is the Nebulizer used in AAS
The atomised sample within the flame absorbs the hollow cathode lamp’s ray and becomes excited, but then returns to a lower energy and emits it in all directions, reducing the beams intensity.
Monochromator
After the hollow cathode ray has passed through the flame and been reduced, it passes into the monochromator, a prism that separates the radiation into individual wavelengths
The Detector of AAS
the detector then measures the wavelength’s intensity, and the incident beam and the transmitted beam are compared
What is the incident beam?
the beam originally emitted from the Cathode lamp
What is the transmitted beam?
the beam after being reduced by the flame.
An AAS machine is calibrated by
a calibration curvew
what is a calibration curbe?
a series of measurements done by standard solutions, having known concentrations of the element. The light from the cathode lamp passes through the solutions.
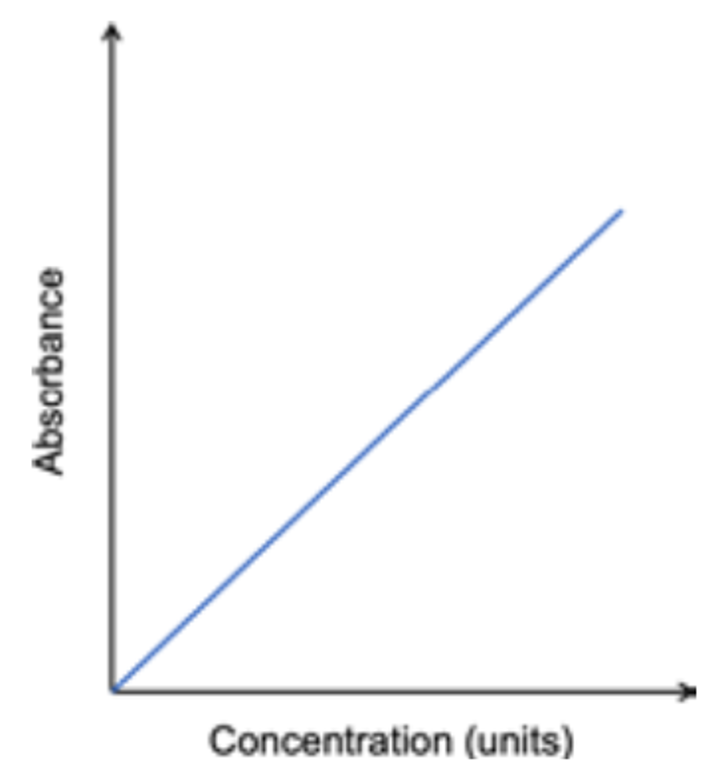
The degree of light absorbed by an element is
proportional to its concentration in the sample, creating a linear relation in the calibration curve.
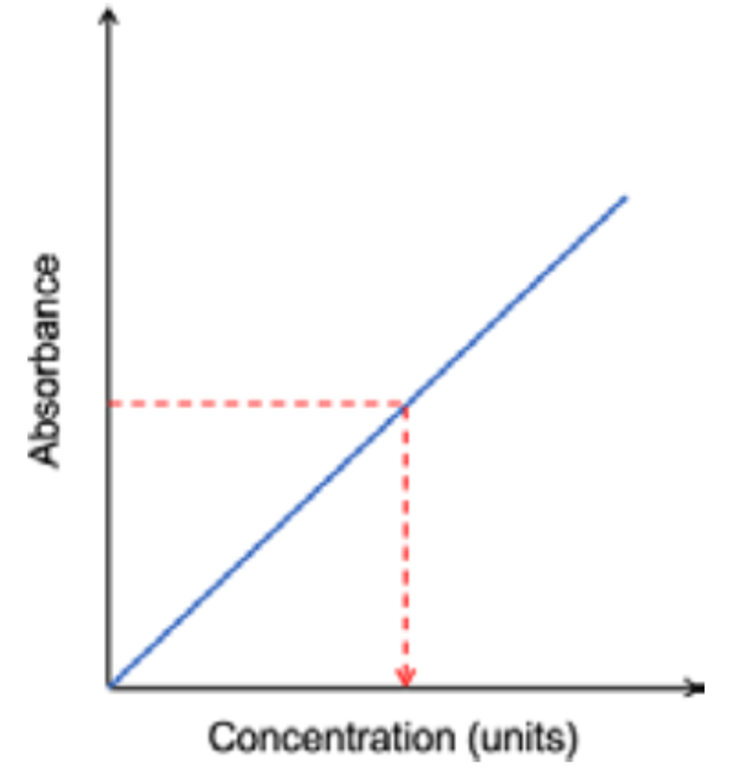
How is the calibration curve useful?
When the light passes through the sample, it can be plotted on the calibration curve due its absorbance. This can be drawn to the calibration curve’s concentration value, allowing for the concentration of the element to be found.
How can AAS be applied?
AAS is used to determine the concentration of metal ions within water wine, and soil, and determines the presence of toxic chemicals in e-liquids, as well as for toxicology.