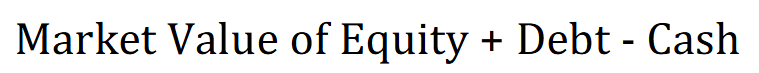Present Value Calculations
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PV Calculations, Finance 1 - Stockholm University
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Discount factor
A discount factor is a multiplier used to convert future cash flows into their present value. It reflects the time value of money, accounting for the risk and opportunity cost of capital.
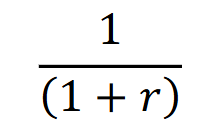
Interest Rate Factor
The interest rate factor is a multiplier that represents the effect of interest rates on the future value of cash flows, used to calculate the growth of an investment over time.
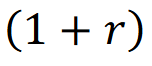
Present Value of single cash flow
The present value of a single cash flow is the current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flows, discounted at a specific interest rate. It reflects the time value of money, allowing for the assessment of investment opportunities.
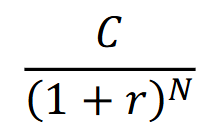
Present value of an annuity
The present value of an annuity is the current worth of a series of equal cash flows received at regular intervals in the future, discounted at a specific interest rate. It is used to evaluate the value of recurring payments over time.
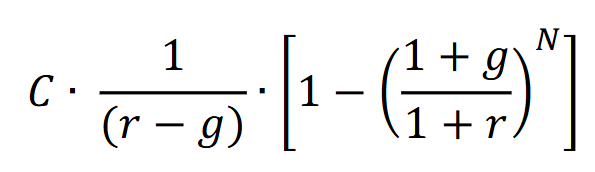
Present value of a growing annuity
The present value of a growing annuity is the current worth of a series of cash flows that grow at a constant rate, received at regular intervals in the future, discounted at a specific interest rate. It is useful for valuing payments that increase over time.
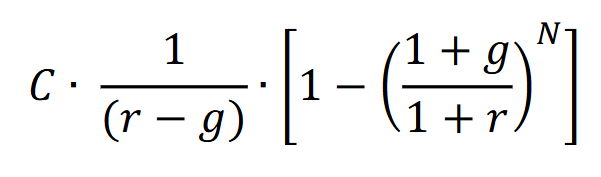
Present value of a growing perpetuity
The present value of a growing perpetuity is the current worth of an infinite series of cash flows that grow at a constant rate, received at regular intervals, discounted at a specific interest rate. It is used to determine the value of cash flows that continue indefinitely with growth.
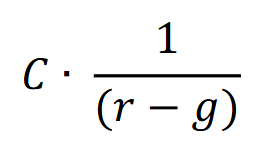
The Equivalent Annual Annuity
is a method used to compare the value of different investments or projects by converting their net present values into a uniform annual cash flow over a specified period. This allows for easier comparison of the financial viability of various options.
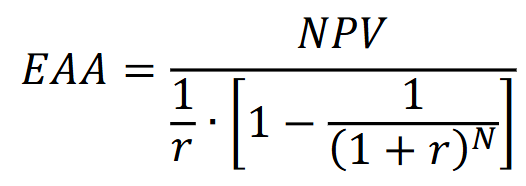
One-period dividend model
A valuation method that calculates the present value of a stock based on the expected dividend payment in one year, discounted back to the present using a required rate of return.
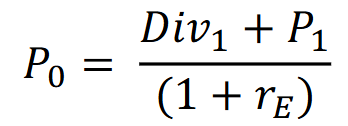
Constant dividend growth model
A method for valuing a stock by assuming that dividends will increase at a constant rate indefinitely. It calculates the present value of all future dividends based on this growth rate.
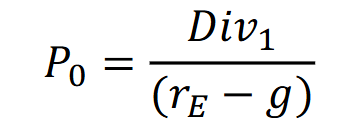
Dividend yield
is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays in dividends each year relative to its stock price, expressed as a percentage. It is an important measure for investors seeking income from their investments.
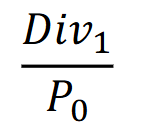
Capital gain rate
The rate of return on an investment resulting from the increase in its price, typically expressed as a percentage of the original purchase price. It represents the profit made when an asset is sold for more than its purchase price.
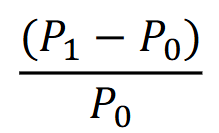
Free Cash Flow
The cash generated by a company after accounting for capital expenditures. It is a measure of a company's financial performance and is often used to assess its ability to generate additional cash for expansion, dividends, and debt reduction.
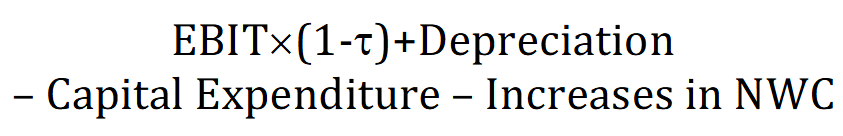
Firm’s Enterprise Value
The total value of a business, including its equity and debt, minus its cash and cash equivalents. It is used as a comprehensive measure of a company's overall value and is often considered in mergers and acquisitions.