chp 9 - products, branding & packaging decisions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
core customer value
the basic problem solving benefits that consumers are seeking
product complexity
actual product
brand-name
quality level
packaging
features/design
associated services
financing
product warranty
product support
associated services
The non-physical attributes of the product, including product warranties, financing, product support and after-sale services
types of products
specialty
shopping
convenience
unsought
consumer products
Products & Services used by people for their personal use
speciality products
products or services toward which customers show a strong preference and for which they will expend considerable effort to search for the best suppliers
ex → canadian goose
shopping products
Products or services—such as apparel, fragrances, and appliances—for which consumers will spend time comparing alternatives.
ex → perfumes
convenience products
Products or services for which the consumer is not willing to spend any effort to evaluate prior to purchase.
ex → bread & soup
unsought products/services
Products/services consumers do not search out or do not know about.
ex → coffins, insurance
product mix
The complete set of all products offered by a firm
product lines
Groups of associated items, such as those that consumers use together or think of as part of a group of similar products.
product category
An assortment of items that the customer sees as reasonable substitutes for another
brands
The names, terms, designs, symbols, or any other features that identify one seller’s good or service as distinct from those of other sellers.
product mix breadth
The number of product lines, or variety, offered by the firm
product line depth
The number of products within a product line.
changing breadth
INCREASE | DECREASE |
add new product lines to capture new or evolving markets
| Bc delete product lines 4 changing market/firm need |
changing depth
INCREASE | DECREASE |
add products w/in a line for changing consumer pref/ comp to boost sales | delete product categories to realign resources / Not taken lightly decision |
branding
Company lives or dies based on brand awareness
Consumers can't buy products that they don't know exist
Even if the overall brand name is familiar it won't help sales of individual products unless consumers know what products are available under that that name
what makes a brand
brand name → facilitate purchasing
URL → establish loyalty
logos and symbols → protect from competition
characters → reduce marketing costs
slogans → are assets
jingles → impact market value
value of branding
brands facilitating purchasing
brands establish loyalty
brands protect from competition
brands reduce marketing costs
brands are assets
brands impact market value
brands facilitate purchasing
Brands are often easily recognized by consumers and bc they signify a certain quality level and contain familiar attributes, brands help consumers make quick decisions
Ex → Pepsi is familiar and easy to purchase
brands establish loyalty
ex → band-aid always perform the same way
brands protect from competition & price competition
strong brands are somewhat protected fr competition & price completion
Ex → Lacoste, Golf shirts, perceived as higher quality and can command a premium price
brands reduce marketing costs
Firms well-known brands can spend relatively less on marketing costs than firms w little known brands
Ex → Lululemon, Stylized "A" logo, very recognizable
brands are assets
Must be legally protected through trademarks, and copyrights & constitute unique ownership
Ex → Rolex & Canada Goose, watch market for counterfeits that dilute brand
brands impact market value
Having well-known brands can have direct impact on the company's bottom line
Ex. RadioShack -> Seeking a Walkman
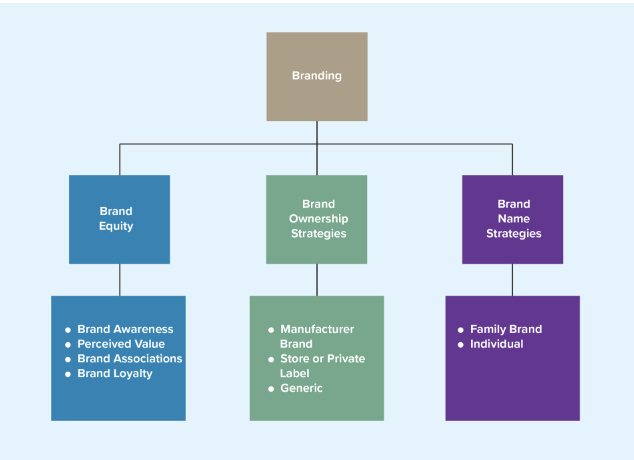
brand overview
brand equity
brand awareness
perceived value
brand associations
brand personality
brand loyalty
manufacturer brands
Brands owned and managed by the manufacturer.
private label brands
Brands developed and marketed by a retailer and available only from that retailer.
generic
A product sold without a brand name, typically in commodities markets.
brand ownership strategies
manufacturer
private label/store brand
generic
types of brand names
individual brands
family brands
family brands
Firm can use its corporate name to brand similar product lines and products
Ex. Kellogs → Kellogg Corn Flakes, Kellogg Froot Loops, Kellogg Rice Krispies
individual brands
The use of individual brand names for each of a firm’s products.
how to choose a brand name
The brand name should be descriptive & suggestive of benefits and qualities associated w the product
The brand name should be easy to pronounce, recognize, and remember
Ex. Tide, Crest, Kodak
The company should be able to register the brand name as a trademark and legally protect it
For companies looking to global markets, the brand name should be easy to translate into other languages
brand extension
The use of the same brand name for new products being introduced to the same or new markets.
advantages of using same name for product
Bc brand name is already well-established, less money on developing consumer brand awareness
Brand is known for high quality, will carry to new product
When brand extensions are used for complementary products, synergy exists b/w two products that can increase overall sales
brand dilution
Occurs when a brand extension adversely affects consumer perceptions about the attributes the core brand is believed to hold.
cobranding
practice of marketing two or more brands together, on the same package or promo
brand licensing
A contractual arrangement between firms, whereby one firm allows another to use its brand name, logo, symbols, or characters in exchange for a negotiated fee
branding awareness
Measures how many consumers in a market are familiar with the brand and what it stands for; created through repeated exposures of the various brand elements (brand name, logo, symbol, character, packaging, or slogan) in the firm’s communications to consumers.
perceived value
The relationship between a product or service’s benefits and its cost
brand associations
the mental links that consumers make between a brand and its key product attributes; can involve a logo, slogan, or famous personality
brand personality
refers to a set of human characteristics associated with a brand, which has symbolic or self-expressive meanings for consumers
brand loyalty
occurs when a consumer buys the same brand’s product or service repeatedly over time rather than buying from multiple suppliers within the same category
purpose of packaging
serves to protect products
can aid in sustainability
help suppliers save costs
labelling
Labels on products and packages provide information the consumer needs for his or her purchase decision and consumption of the product