EXAM 1 of NUTR-23511 // Science of Human Nutrition @Kent State
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is the Leading Cause of Death in the US?
Heart Disease
What is Health and Longevity Affected by?
1). Diet
2). Lifestyle Behaviors
3). Genetic Traits
4). Environment
5). Access to health care

What are the 3 Major Nutrition Concepts?
1). Food Security -ACCESS AT ALL TIMES to sufficient supply of safe nutritious food
2). Food insecurity -INABILITY OR LIMITED ACCESS to safe nutritious foods whether available or not
3). Food Terrorism -FOOD AND WATER USED TO SPREAD ILLNESS
Who is at the Highest Risk for Food Insecurity and Why?
Female-headed households with young children living in inner-city areas b/c of low-socioeconomic status
What Percent of Households are food insecure?
12.6% of US households and 7.0% of Canadian households
What is needed for growth and health?
1). CALORIES - a unit of measure of the amount of energy supplied by food
2). NUTRIENTS - Chemical substances found in food that are used by the body for growth and health
3). PHYTOCHEMICALS and ANTI-OXIDANTS (aka: other substances in food)
What are the 6 Categories of Nutrients?
1). Carbohydrates
2). Proteins
3). Fats
4). Vitamins
5). Minerals
6). Water
What is an Essential Nutrient?
The body requires this nutrient but it needs to be ACQUIRED THROUGH DIET
What is a Non-Essential Nutrient?
The body requires this nutrient but DOES NOT NEED TO BE ACQUIRED THROUGH DIET
The Requirement of Nutrients Varies Based On?
1). Age
2). Gender
3). Growth status
4). Body size
5). Genetic Traits
In addition to certain conditions
1). Pregnancy
2). Breastfeeding
3). Illness
4). Drug use
5). Exposure to environmental contaminants
What is the difference between RDA (recommended dietary allowances) and DRI (dietary reference intake)
RDA= The amount of a nutrient per day that is considered necessary for maintenance of good health
DRI= Daily intake levels of a nutrient that is required to meet requirements of 98% of healthy individuals (the 4 nutrients at the bottom of nutrition label)
How Does Poor Nutrition Effect the Body?
1). Toxicities
2). Deficiencies
3). Faulty Diets
-heart disease (^ saturated fat)
-hypertension (^salt)
-cancer (low fruits and veggies
-osteoporosis (low calcium and vitamin D)
What is the most common nutritional disorder in the US?
OBESITY
-2 in 3 adults or children are overweight or obese
-2 in 5 children are considered obese
What does obesity increase the risk of?
1). Heart disease
2). Diabetes
3). Certain cancers
4). Hypertension
What are the 2 types of food?
1). Nutrient Dense Foods - High amounts of nutrients compared to their calorie value
2). Energy Dense Foods (empty calories) - Provide an excess of calories in relation to nutrients (JUNK FOOD)
Is there such a thing as "good" and "bad" foods?
No, just healthful vs. unhealthful foods or choose to choose more often vs. foods to choose less often
What are some things to take into consideration when trying to live a healthy lifestyle?
1). Quality of food
2). Quantity of food
3). Frequency of eating
4). Timing of meals
What do our bodies function best on?
BENIFICIAL: NOT BENIFICIAL
-Low in sugar -High in sugar
-moderate sodium -High in sodium
-Lean sources of protein -High animal/sat fat
-High complex carbs -Low grain intake
-High fiber -Low fiber
-High fruit and veggie intake -Low fruit and veggie intake
-Frequent small intake of food -Skipping meals and lg. meals

What Act was Passed in 1990?
The Nutrition Labeling Act by Congress which prevents misleading messages and hazy health claims and tells us what exactly is in food
What Happened in 1993 in Regards to Nutrition/
The FDA published rules for nutrition labeling to be uniform
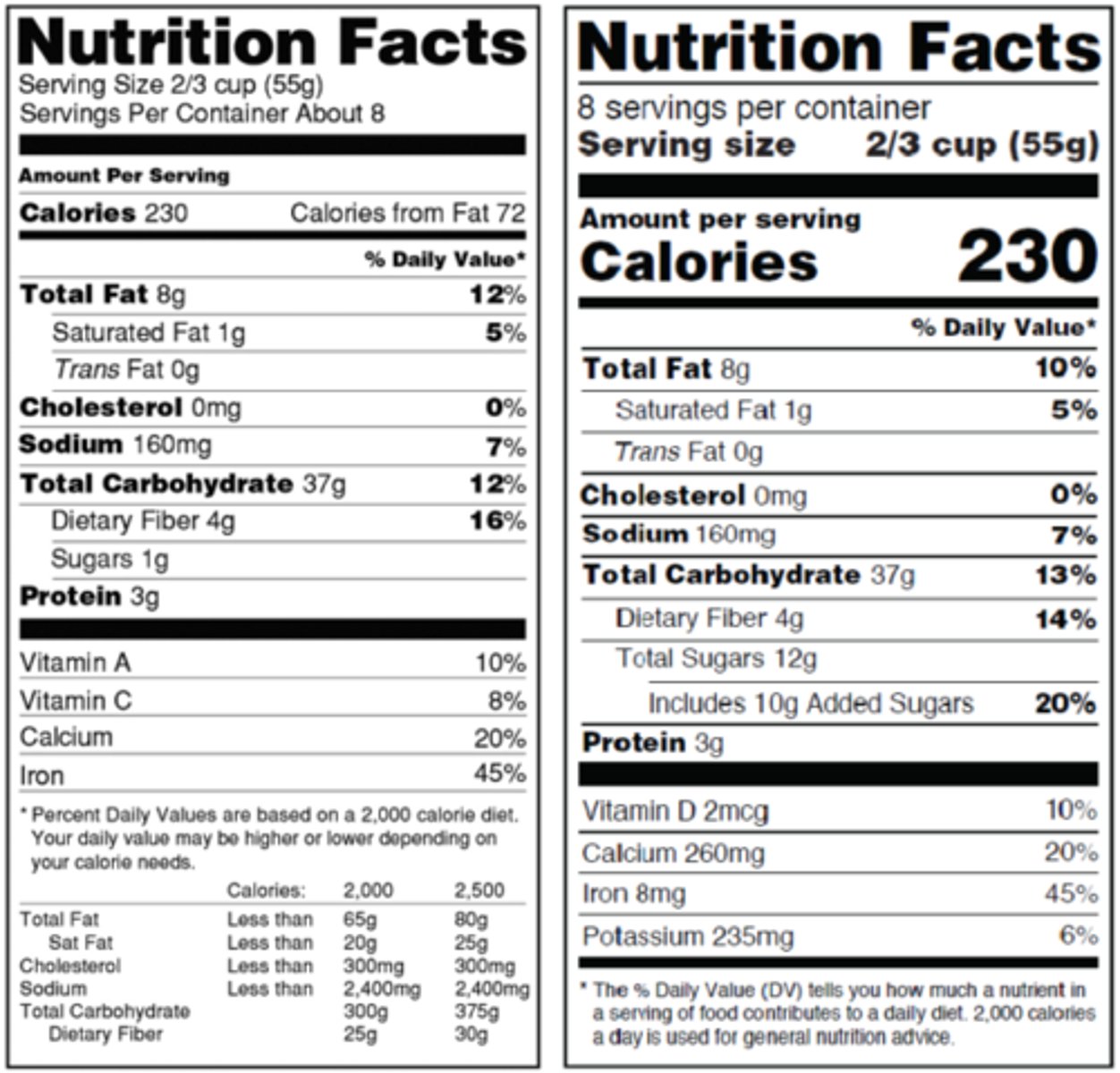
What are the Serving Sizes on Labels based off of?
DAILY VALUES of 2000 calorie diet and scientifically agreed-upon daily nutrient intake standards
What is Mandatory Labeling as of July 26, 2019?
***NE
1). Total calories
2). Total calories from fat
3). Total Fat
4). Saturated fat
5). Trans fat
6). Total carbohydrates 7) Dietary fiber
8). Total sugar
9). Added sugar
10). Protein
11). Cholesterol
12). Sodium
13). Vitamin D
-prior was vitamin A
14). Potassium
-Prior was vitamin C
15). Calcium
16). Iron
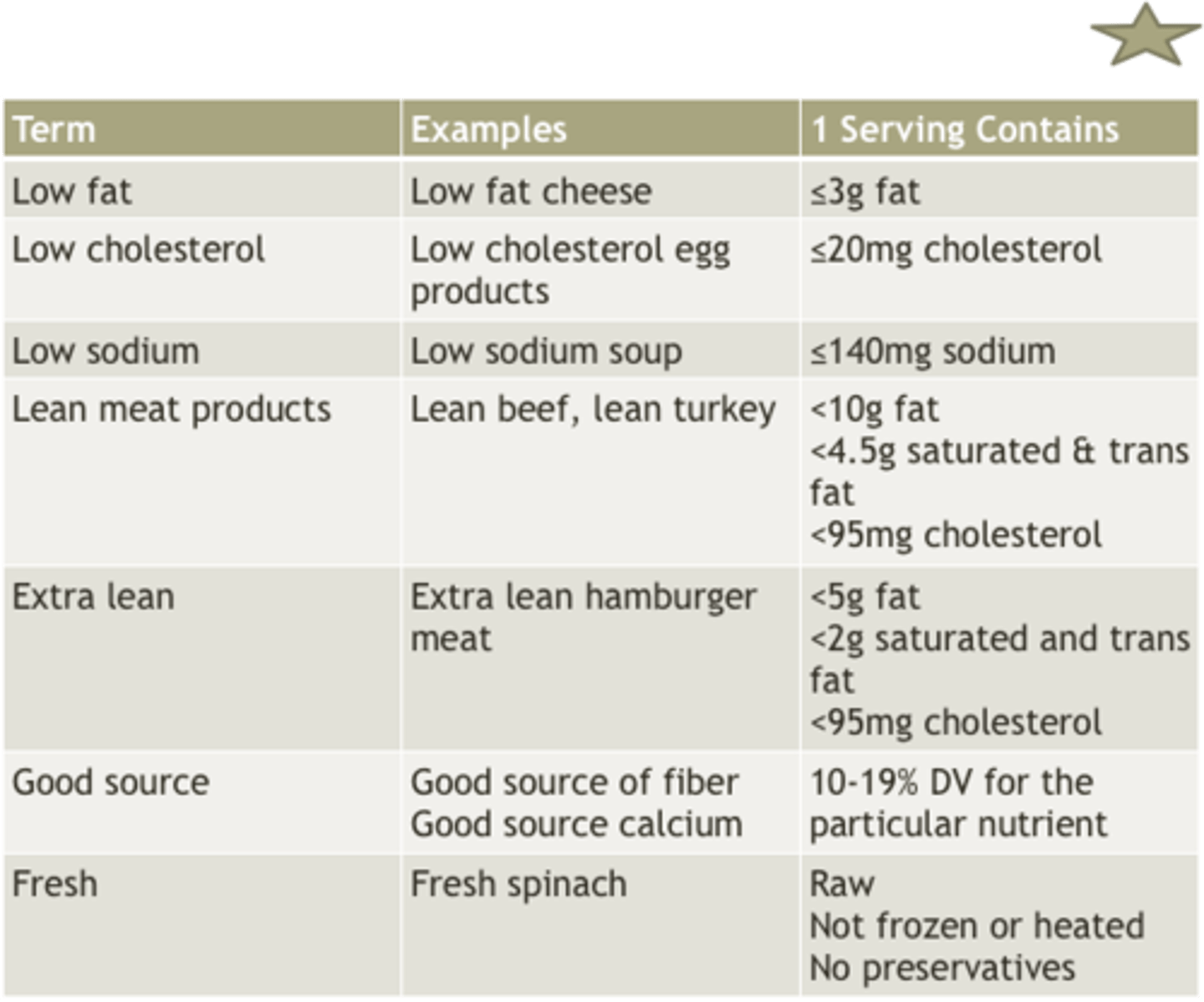
What are the Nutrient Content Claims and what do they mean?
^^^
What is a legitament health claim?
1). Approved by the FA
2). Benefits to disease prevention

What is the definition of enrichment?
Pertains only to refined grain products-Germ and bran removed during processing resulting in loss of vitamins and minerals so enrichments puts nutrients back in
What is the definition of fortification?
The addition of one or more vitamins and minerals to a food product
Why is a food enriched or fortified?
mainly to prevent deficiency
What is the Ingredient list rule #1?
Any food that contains more than ONE ingredient must have an ingredients list
Ingredients are listed in order of their contribution to weight of the food, from highest to lowest
What are the origins of food choices?
People are not born knowing what to eat, humans are born with mechanisms that help decide WHEN and HOW MUCH to eat
What is a list of the origins of food choices?
1). Food preferences
2). Culture
3). Genetic Influences/Heredity
4). Nutrition knowledge and beliefs
5). Practical considerations
what is the most common single nutrient deficiency?
IRON! Globally...
20% of men
35% of women
40% of children
are iron deficient, imparting intellectual performance and has lasting effects on functioning, like shortened attention span and reduced problem solving.
What is a vitamin A toxicity from animal sources?
It can cause severe malformation in the fetus..
-Bendectin, Thalidomide: it is used for morning sickness and linked to severe birth defects in the fetus
-Retina-in Anti-wrinkle creams
What is chronic inflammation related to?
1). Diabetes
2). Heart disease
3). Arthritis
4). Etc.
What are the 5 stages to changing behavior?
Stage 1). Pre-contemplation
Stage 2). Contemplation
Stage 3). Preparation
Stage 4). Action
Stage 5). Maintenance
What is the definition of appetite?
a desire, rather than a need, to eat
What is the definition of hunger?
the natural physical drive to eat, prompted by the body's need for food
What is the definition of satiety?
the state of being satisfactorily full and unable to take on more
What are some characteristics of healthy dietary patterns?
There are a variety of different "healthy" diets, but...
1). Adequacy (wide variety of foods that together provide sufficient levels of calories and essential nutrients)
2). Variety (is most important b/c the nutrient content of food differs)
3). Balance (Provides the perfect amount of calories, nutrients, and other components in food within the right proportion)
4). Health maintenance
How balanced is the American diet?
CARBS
-Recommended=45-65%
-US=52%
-Added sugars
-Recommended=25%
-US=28%
PROTEINS
-Recommended=10%-35%
-US=15%
FATS
-Recommended=20-35%
-US=33%
What is an aspect of maintaining health?
Nutrients and phytochemical interacting with each other to impact health overtime
What is the Typical Diet in the United States?
1). Low intake of nutrients
-Potassium, Vitamin D, Calcium,
and fiber
2). Daily, only 14% of adults consume:
-3 or more servings of vegetables
-2 or more servings of fruit
3). Daily, about 10% of adults consume:
-at least 1 serving of dark green or
colorful veggies
What are the Dietary Guidelines for Americans/
1). THEY ARE SCIENCE-BASED RECOMMENDATIONS - they promote health and reduce risk for major chronic diseases through diet and physical activity
2). UPDATED EVERY 5 YEARS-Current is the 2015 guidelines
They aim to reduce the risk of
-obesity
-heart disease
-diabetes
-nutrient inadequacies
and have physical activity that suggests
-at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity per week
What is the DASH diet?
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension
but it also played a role in:
-reducing the risk of cancer
-reducing the risk of osteoporosis
-reducing the risk of heart disease
What does the DASH diet emphasize and Limit?
Emphasizes
-fruits and veggies
-low-fat dairy
-whole grains
-lean meats such as fish/chicken
-nuts and seeds
Limits
-Sodium
-Trans fat
-Saturated fats
What is anabolism?
Building up
What is catabolism?
breaking down
What are the most common elements?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
How much of our body weight is replaced by new tissue?
5%
How often is the cell lining in the intestinal tract replaced?
every 1 to 3 days
What are the 2 major processes?
Digestion and absorption
What are the 2 types of digestion?
Chemical (enzymes and hormones) and mechanical
What is Digestion?
Where ingested food is converted into substances that can be absorbed
What is absorption?
Taking digested food and ABSORBING It into the body
What is the difference between micro and macro nutrients?
Micronutrients give no source of fuel or energy, while macronutrients do
What are the two micronutrients?
vitmanins and minerals
What are the 3 macronutrients?
1). Carbohydrates (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen)
2). Proteins (Carbon Hydrogen, NITROGEN)
3). Fats (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen)
What is an amine in a protein?
any organic compound that contains a basic nitrogen atom
What is a triglyceride?
a lipid made of one glycerol and three fatty acids
What do amylase, sucrase, lactase, and maltase all do?
Break down carbohydrates
What does hydrochloric Acid (HCI) do?
It is produced in the stomach, and is very strong and acidic so helps to break down polysaccharides by breaking their bonds so we can absorb the molecules.
what is pepsin?
it is produced in the stomach and begins digestion of proteins in the stomach
What is lipase?
Produced in the salivary gland and pancreas breaking down fats
What is bile?
a bitter greenish-brown alkaline fluid that aids digestion, think of it like dawn dish soap :)
Where is bile produced?
in the liver
where is bile stored?
in the gallbladder
What secretes bile?
The intestine
what two enzymes do the salivary glands secrete?
1). Amylase (active)
2). Lipase (inactive)
what three enzymes does the pancreas secrete?
1). Amylase
2). Lipase
3). Trypsin
What three enzymes does the small intestine secrete?
1). Sucrase
2). Lactase
3). Maltase
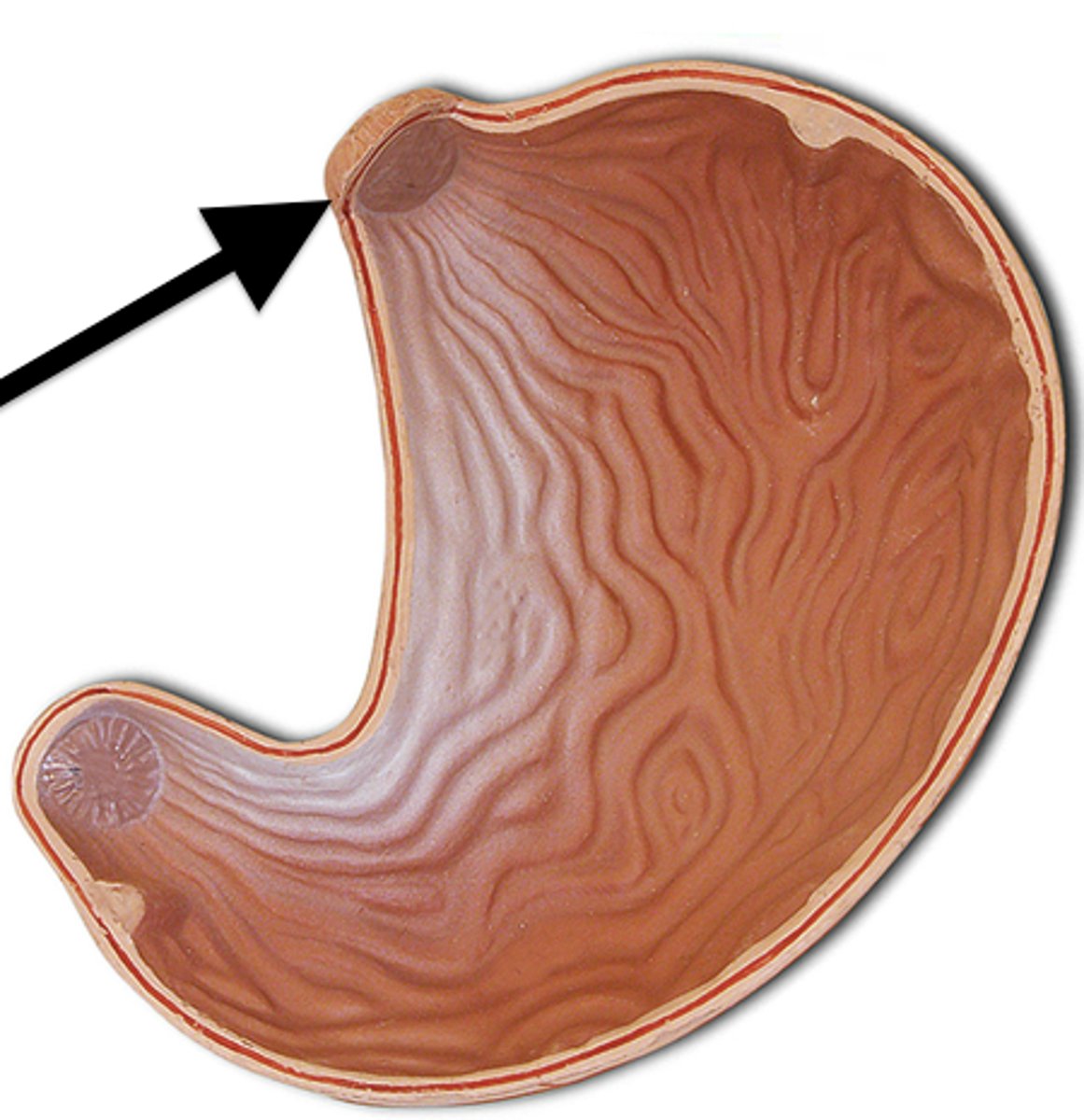
What and where is the gastroesophageal Sphincter?
Relaxes to allow bolus to enter stomach and then closes to prevent contents from re-entering esophagus
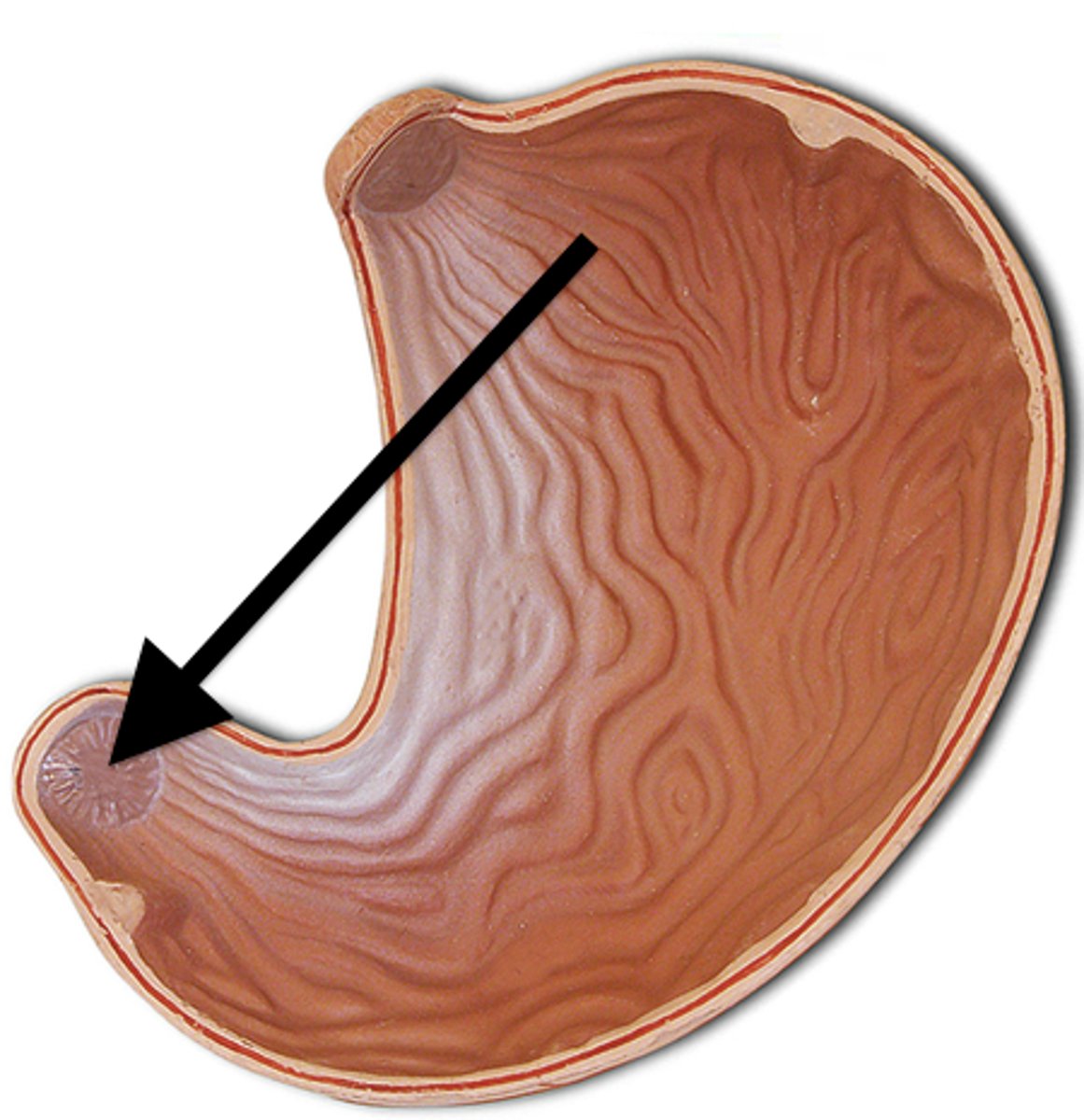
What and where is the pyloric sphincter?
It allows 1 teaspoon of chyme to be released into the small intestine at a time to allow for the slow process of digestion to occur
What are the 7 functions of HCI?
1). Extremely acidic
2). Sterilizes foreign materials
3). Activates pepsin
4). Activates salivary lipase
5). Breaks down proteins
6). Breaks down carbs
7). Breaks down fats
What are the 3 parts of the small intestine?
1. Duodenum
2. Jejunum
3. Ileum
What makes HCI less acid in intestine?
Bicarbonate
What are the 2 main things absorbed in the Large intestine?
Water and sodium
What process does cancer cause?
oxidation, therefore you need ANTIoxidants
what are the 4 identified nutrients that were poor in the US diet in 2010?
Fiber, Vitamin D, potassium, and Calcium
What is the wave like action that occurs in the Small intestine?
Mechanical action of segmentation done by the smooth muscle