Coasts
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:45 AM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
What does littoral mean?
near shore
2
New cards
what are the 3 coast types
- cliffed
- sandy
- estuarine
- sandy
- estuarine
3
New cards
coastal dynamic equilibrium
the understanding that coasts are systems with both positive and negative feedback
4
New cards
what is the difference between a high and low energy coastline?
high energy coast lines have more erosion occurring resulting in erosional landscapes
but low energy coastlines have depositional landforms
but low energy coastlines have depositional landforms
5
New cards
what are the four ways of classifying coastlines
- by their formation process
- by their change in sea level
- their tidal range
- their wave type
- by their change in sea level
- their tidal range
- their wave type
6
New cards
what is the difference between primary and secondary coastlines
primary coastlines are formed by land based processes such as lava flows
but secondary are formed by marine processes such as erosion or deposition
but secondary are formed by marine processes such as erosion or deposition
7
New cards
what type of coastline is formed when the sea level drops
emergent
8
New cards
what type of coastline is formed when the sea level rises
submergent
9
New cards
waves…
can be constructive or destructive
\
depend on-
* wind strength
* water depth
* wave fetch (distance wave travels) hard or
\
depend on-
* wind strength
* water depth
* wave fetch (distance wave travels) hard or
10
New cards
what is weathering?
the insitu breakdown of rocks
11
New cards
what is erosion?
the wearing away of the land surface and removal of materials by river and seawater, ice or wind.
12
New cards
erosional landforms
* cliffs
→ wave cut notch and platforms
* headlands and bays
* CCASS (crack, cave, arch, stack, stump)
→ wave cut notch and platforms
* headlands and bays
* CCASS (crack, cave, arch, stack, stump)
13
New cards
what is transportation?
the movement of sediment due to waves
14
New cards
long shore drift
the movement of sand and small stones along the coast by waves travelling at an angle to the coast.
15
New cards
what is deposition?
the dropping of sediment when waves loose tehri energy
16
New cards
depositional landforms-
* beach
* spit
* spit
17
New cards
cuspate foreland
sand and shingle accumulated by long shore drift that extends outwards from the shoreline in a triangular shape.
18
New cards
tombolo
a spit or bar that connects to an island
19
New cards
sand dune succession
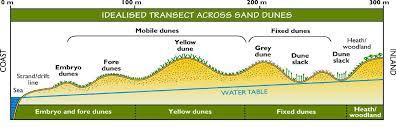
20
New cards
CASE STUDY - sand dunes
21
New cards
salt marsh (halosphere) succession
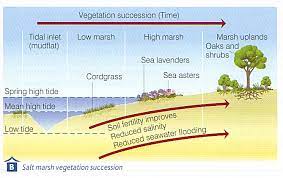
22
New cards
CASE STUDY- salt marsh
the blackwater estuary essex
23
New cards
what is the rough trend in rock type across the uk
above the tees-exe line is old sedimentary rock with some igneous patches.
Scotland is mostly metamorphic
and the south is sedimentary
exception being Cornwall (igneous)
Scotland is mostly metamorphic
and the south is sedimentary
exception being Cornwall (igneous)
24
New cards
what are the 4 types of erosion?
Abrasion, Attrition, Hydraulic action, Solution
25
New cards
what is beach morphology?
the shape of a beach and its characteristics as well as the processes leaving to that
26
New cards
what are the different coastal zones
* littoral zone (near shore, sunlight penetrates sediment so life can flourish, but is most rapidly changing)
* nearshore (near to sea)
* back shore (waves only reach during very high tides)
* off shore (out AT sea)
* nearshore (near to sea)
* back shore (waves only reach during very high tides)
* off shore (out AT sea)
27
New cards
Sub-aerial processes
weathering and mass movement (any process that does not involve the sea)
28
New cards
weathering
the insitu breakdown of rocks
29
New cards
name the types of mechanical weathering
- freeze thaw
- salt crystallisation
- salt crystallisation
30
New cards
what type of rock is more at risk of mechanical weathering?
porous and cracked rocks
31
New cards
name the types of chemical weathering
- carbonation (most important)
- hydrolysis
- oxidation
- hydrolysis
- oxidation
32
New cards
what is carbonation?
Rainwater abosorbs CO2 and becomes more acidic. allowing it to dissolve rocks such as limestone
33
New cards
what is hydrolysis?
water breaks down igneous and meta rocks to form clay
34
New cards
what is oxidation?
when oxygen reacts with compounds in the rock(eg iron) and increase the volume causing breakdown of the rock
35
New cards
name the types of biological weathering
- plant roots
- rock boring
- rock boring
36
New cards
what is rock boring?
when clams and molluscs bore into rock and may also secrete chemicals that dissolve rocks.
37
New cards
name all 5 types of mass movement
- rock falls
- rock topples
- transitional landslides
- rotational landslides (slumping)
- mudflows
- rock topples
- transitional landslides
- rotational landslides (slumping)
- mudflows
38
New cards
what is formed as a result of rockfalls?
scree talus slopes (a slope of material that has fallen vertically from a cliff)
39
New cards
what can be the cause of rock topples?
joints in the rock and their location
40
New cards
if bedding plane is parallel to the surface, what mass movement may occur?
sliding
41
New cards
what conditions increase the risk of slumping?
- saturated conditions
- permeable rock layer on top of impermeable rock layer
- permeable rock layer on top of impermeable rock layer
42
New cards
what can be formed as a result of slumping?
- rotational scars
- Terrance cliff profile (areas of grass lowing down like steps as a result f repeated slumping)
- Terrance cliff profile (areas of grass lowing down like steps as a result f repeated slumping)
43
New cards
how are mudflows different to sliding?
slides stay intact whereas mudflow material becomes mixed up
44
New cards
what are the two types of sea level change?
isostatic change and eustatic change
45
New cards
what is isostatic sea level change
change in sea level due to the rise and fall of land
46
New cards
what is eustatic sea level change
change in sea level due to water volume change
47
New cards
what can cause isostatic change?
ice caps-
- are heavy and cause land to sink
- but when they melt land moves back up gradually (isostatic rebound)
- are heavy and cause land to sink
- but when they melt land moves back up gradually (isostatic rebound)
48
New cards
what causes eustatic change?
- thermal expansion
- ice caps melting
- ice caps melting
49
New cards
what is the difference between marine regression and transgression?
marine regression is when an emergent coastline if formed due to sea level fall. but marine transgression produces a submergent coastline due to sea level rise
50
New cards
name the landforms created due to marine regression
- raised beach
- fossil cliff
- fossil cliff
51
New cards
name the landforms created due to marine transgression
- ria (flooded riVer valley)
- fjord (flooded glacier/ u shaped valley)
- Dalmatian coast
- fjord (flooded glacier/ u shaped valley)
- Dalmatian coast
52
New cards
case study for sea level change is....
kiribati
53
New cards
flooding case study
bangladesh
54
New cards
flooding case study
UK in 1953 and then again in 2012 ‘the north sea flood’
55
New cards
sediment cells
A length of coastline within which the movement of sand and shingle is largely self-contained (dynamic equilibrium)
56
New cards
coastal management
protecting coastlines from threats such as erosion or transportation
57
New cards
coastal defences types
hard or soft engineering
58
New cards
coastal defence **soft** engineering examples
* beach replenishment (adding sediment to a beach)
* cliff regrading (reducing angle of cliff to stabilize it)
→ and drainage (removed water to prevent slumping)
* dune stabilisation (planting marram grass)
* marsh creation (managed retreat - allowing lowlying areas to be flooded)
* planting mangroves
* cliff regrading (reducing angle of cliff to stabilize it)
→ and drainage (removed water to prevent slumping)
* dune stabilisation (planting marram grass)
* marsh creation (managed retreat - allowing lowlying areas to be flooded)
* planting mangroves
59
New cards
CASE STUDY- flooding management using mangroves
Bangladesh and sri lanka
60
New cards
CASE STUDY - flooding in the uk
uk storm surges
cyclone xavier
cyclone xavier
61
New cards
coastal defence **hard** engineering examples-
* groynes
* sea walls
* rip rap
* revetments (wooden or concrete sloping structured that reduce wave power)
* offshore breakwaters (boulders placed offshore under water)
* sea walls
* rip rap
* revetments (wooden or concrete sloping structured that reduce wave power)
* offshore breakwaters (boulders placed offshore under water)
62
New cards
sustainable coastal management
managing coastline to maintain for today without causing damage in the future
63
New cards
holistic strategies
strategies used to please as many stakeholders as possible
64
New cards
cost- benefit analysis
comparing the total costs to the total expected rewards of undertaking a project
65
New cards
environmental impact assessment
the assessment of the environmental consequences of a project
66
New cards
ICZM strategies / SMP (shoreline management plans)
plans and management schemes on shorelines- balancing SEE impacts eg, jobs, biodiversity and erosion
\
but are not gov run so are not technically compulsory
\
but are not gov run so are not technically compulsory
67
New cards
SMPs can be used holistically by
* involving all stake holders
* making plan long term
* work alongside natural processes
* opportunity for plans to be changed if needed
* consider culture/ heritage of area and ecological value
* making plan long term
* work alongside natural processes
* opportunity for plans to be changed if needed
* consider culture/ heritage of area and ecological value
68
New cards
SMP 4 policies and CASE STUDIES
1. hold the line Eg brighton sea wall
2. no active intervention (do nothing) Eg durdel door
3. advance the line eg salt marshes in kent
4. strategic realignment (retreat the line) Eg Abbots Hall farm
69
New cards
CASE STUDIES for SMPs
* holderness coast (impacts of SMPs)
* happisburg (no active intervention)
* sussex kent and dorset sediment cells
* happisburg (no active intervention)
* sussex kent and dorset sediment cells