Cell Structure: Foundations in Biology: Biology OCR A Level
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Outline how a student could prepare a temporary mount of tissue for a light microscope.
1. Obtain thin section of tissue e.g. using ultratome or by maceration.
2. Place plant tissue in a drop of water.
3. Stain tissue on a slide to make structures visible.
4. Add coverslip using mounted needle at 45° to avoid trapping air bubbles.
Describe how light microscopes work.
1. Lenses focus rays of light and magnify the view of a thin slice of specimen.
2. Different structures absorb different amounts and wavelengths of light.
3. Reflected light is transmitted to the observer via the objective lens and eyepiece.
Describe how a transmission electron microscope (TEM) works.
1. Pass a high energy beam of electrons through a thin slice of specimen.
2. More dense structures appear darker since they absorb more electrons.
3. Focus image onto fluorescent screen or photographic plate using magnetic lenses.
Describe how a scanning electron microscope (SEM) works.
1. Focus a beam of electrons onto a specimen’s surface using electromagnetic lenses.
2. Reflected electrons hit a collecting device and are amplified to produce an image on a photographic plate.
Describe how a laser scanning confocal microscope works.
1. Focus a laser beam onto a small area on a sample’s surface using objective lenses.
2. Fluorophores in the sample emit photons.
3. Photomultiplier tube amplifies the signal onto a detector. An image is produced pixel by pixel in the correct order.
How should the field of view in microscopy be recorded?
Draw a diagram with a sharp pencil. Do not use sketchy lines or shading.
Include a scale bar. Annotate visible structures.
State an equation to calculate the actual size of a structure from microscopy.
actual size = image size / magnification
Define magnification and resolution.
Magnification: factor by which the image is larger than the actual specimen.
Resolution: smallest separation distance at which 2 separate structures can be distinguished from one another.
Why do samples need to be stained for light microscopes?
Coloured dye binds to the structures.
Facilitates absorption of wavelengths of light to produce image. Differential staining: contrast between heavily & lightly stained areas distinguishes structures.
State the magnification and resolution of a compound optical microscope.
magnification: x 2000
resolution: 200 nm
State the magnification and resolution of a TEM.
magnification: x 500 000
resolution: 0.5 nm
State the magnification and resolution of an SEM.
magnification: x 500 000
resolution: 3 - 10 nm
Explain how to use an eyepiece graticule and stage micrometer to measure the size of a structure.
1. Place micrometer on stage to calibrate eyepiece graticule.
2. Line up scales on graticule and micrometer. Count how many graticule divisions are in 100μm on the micrometer.
3. Length of 1 eyepiece division = 100μm / number of divisions.
4. Use calibrated values to calculate actual length of structures.
Describe the structure of the nucleus.
● Surrounded by a nuclear envelope, a semipermeable double membrane.
● Nuclear pores allow substances to enter/exit.
● Dense nucleolus made of RNA & proteins assembles ribosomes.
Describe the function of the nucleus.
● Contains DNA coiled around chromatin into chromosomes.
● Controls cellular processes: gene expression determines specialisation & site of mRNA transcription, mitosis, semiconservative replication.
Describe the structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
● Cisternae: network of tubules & flattened sacs extends from cell membrane & connects to nuclear envelope:
● Rough ER: many ribosomes attached for protein synthesis & transport.
● Smooth ER: lipid synthesis.
Describe the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus.
Planar stack of membrane-bound, flattened sacs, cis face aligns with rER. Molecules are processed in cisternae. Vesicles bud off trans face via exocytosis
● Modifies & packages proteins for export.
● Synthesises glycoproteins.
Describe the structure and function of ribosomes.
Formed of protein & rRNA.
Have large subunit which joins amino acids & small subunit with mRNA binding site.
Describe the relationship between the organelles involved in the production and secretion of proteins.
The ribosomes that synthesise proteins are attached to the rER. The Golgi apparatus, which modifies proteins for secretion, aligns with the rER.
Describe the structure of a mitochondrion.
● Surrounded by double membrane.
● Folded inner membrane forms cristae: site of electron transport chain.
● Fluid matrix: contains mitochondrial DNA, respiratory enzymes, lipids, proteins.
Describe the structure of a chloroplast.
● Vesicular plastid with double membrane.
● Thylakoids: flattened discs stack to form
grana; contain photosystems with chlorophyll.
● Intergranal lamellae: tubes attach thylakoids in adjacent grana.
● Stroma: fluid-filled matrix.
State the function of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
● Mitochondria: site of aerobic respiration to produce ATP.
● Chloroplasts: site of photosynthesis
to convert solar energy to chemical energy.
Describe the structure and function of a lysosome.
Sac surrounded by single membrane embedded H+ pump maintains acidic conditions contains digestive hydrolase enzymes.
Glycoprotein coat protects cell interior:
● digests contents of phagosome
● exocytosis of digestive enzymes
Describe the structure and function of a plant cell wall.
● Made of cellulose microfibrils for mechanical support.
● Plasmodesmata form part of apoplast pathway to allow molecules to pass between cells.
● Middle lamella separates adjacent cell walls.
What are bacterial and fungal cell walls made of?
bacteria: peptidoglycan (murein)
fungi: chitin
Describe the structure and function of centrioles.
● Spherical group of 9 microtubules arranged in triples.
● Located in centrosomes.
● Migrate to opposite poles of cell during prophase & spindle fibres form between them.
Describe the structure and function of the cell-surface plasma membrane.
‘Fluid mosaic’ phospholipid bilayer with extrinsic & intrinsic proteins embedded.
● Isolates cytoplasm from extracellular environment.
● Selectively permeable to regulate transport of substances.
● Involved in cell signalling / cell recognition.
Explain the role of cholesterol, glycoproteins & glycolipids in the cell- surface membrane.
● Cholesterol: steroid molecule connects phospholipids & reduces fluidity.
● Glycoproteins: cell signalling, cell recognition (antigens) & binding cells together.
● Glycolipids: cell signalling & cell recognition.
Describe the structure and function of flagella.
● Hollow helical tube made of the protein flagellin.
● Rotates to propel (usually unicellular)
organism.
Describe the structure and function of cilia.
● Hairlike protrusions on eukaryotic cells.
● Move back and forth rhythmically to sweep foreign substances e.g. dust or pathogens away / to enable the cell to move.
Why is the cytoskeleton important?
● Provides mechanical strength.
● Aids transport within cells.
● Enables cell movement.
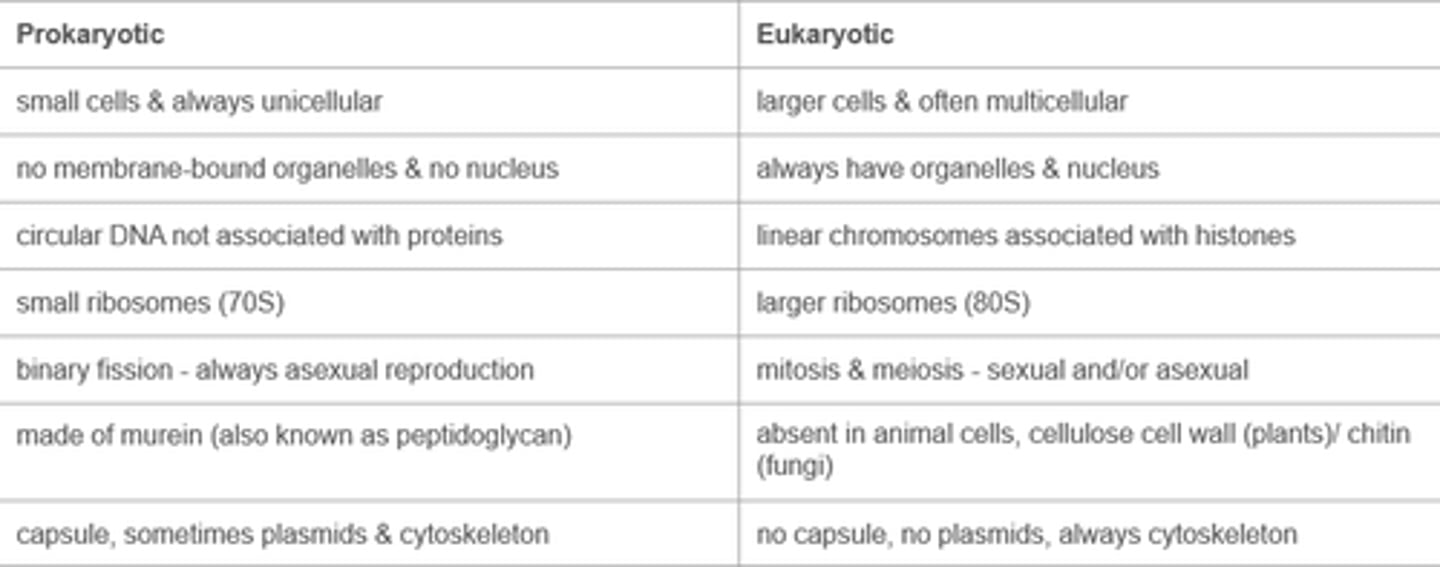
Compare eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Both have:
● cell membrane
● cytoplasm
● ribosomes
Contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.