ID Lecture 37: Pathophys & Therapeutics of Osteomyleitis, Septic Arthritis, and Diabetic Foot Ulcer | Quizlet
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU)
breakdown in the epidermis and dermis that is likely to be colonized by bacteria but NOT infected
Diabetic Foot Infection (DFI)
foot ulcer w/ inflammatory response due to invasion of pathogenic bacteria
Describe the pathophysiology of DFU
Diabetes (chronic high BG)
Vascular dx, neuropathy, and impaired neutrophil function
Impaired wound healing, ischemia, and dry/cracked skin
Diabetic foot ulcer
Charcot foot
repeat injury to the food that is not allowed to heal - no infection is present
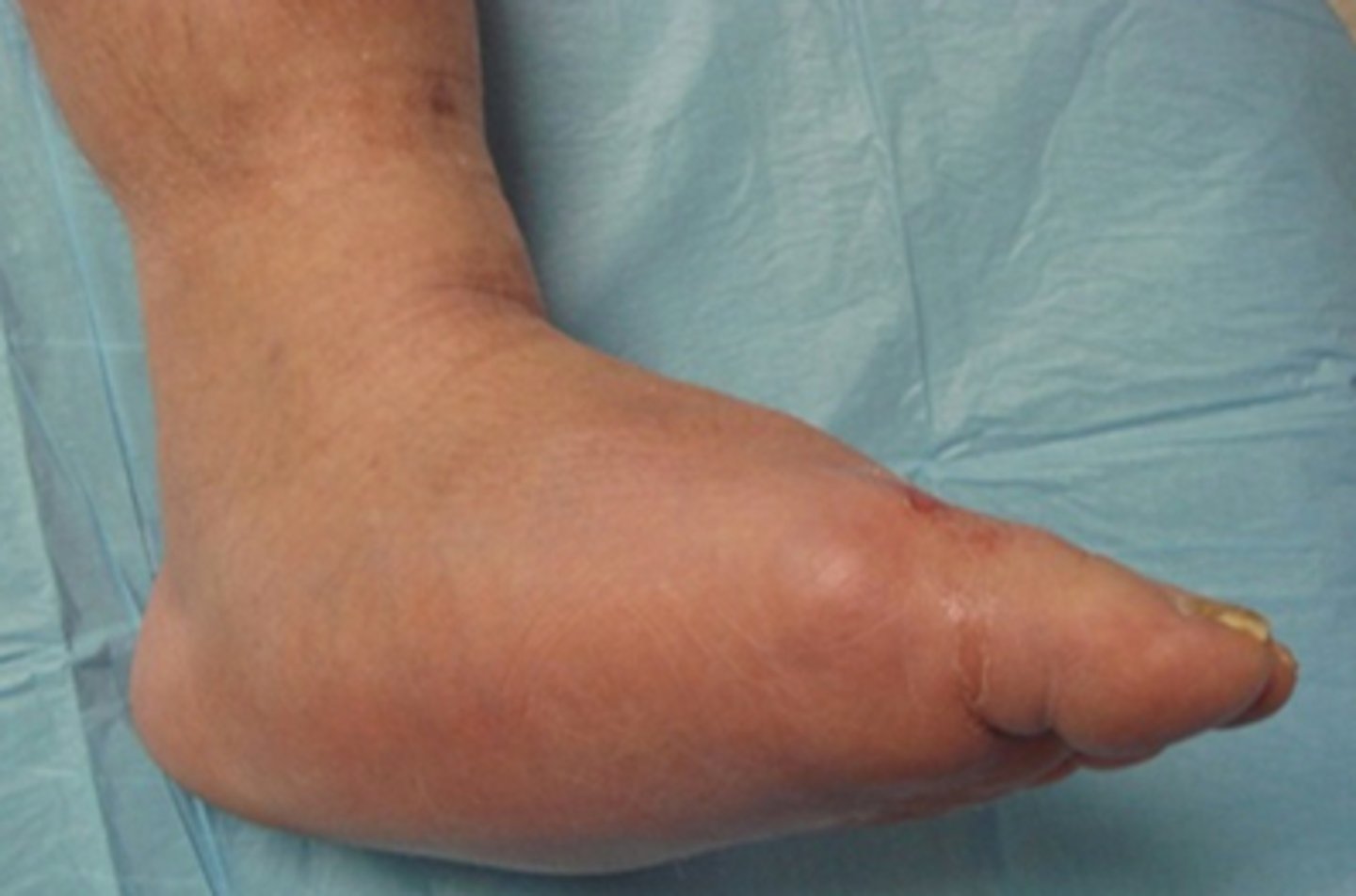
What are the s/sx of DFI?
Inflammation
Redness
Warmth
Swellling
Tenderness/pain
Purulent secretions
What is considered to be a mild DFI?
Small area is involved (<2 cm)
What is considered to be a moderate DFI?
Larger/deeper (>2cm)
+/- osteomyleitis
(no SIRS criteria)
What is considered to be a severe DFI?
Sepsis +/- Osteomyleitis
(SIRS criteria are met)
What are the common pathogens of a mild DFI with no other complicating factors?
Staph or streptococci
What are the common pathogens of a mild DFI with recent antibiotic use?
Staph, strep, and gram negative rods
What are the common pathogens of a mild DFI with a previous MRSA infection/colonization?
Staph, strep, gram negative rods, and MRSA
What are the common pathogens of a moderate/severe DFI with no other complicating factors?
Staph, Strep, and gram negative rods
What are the common pathogens of a moderate/severe DFI with a macerated ulcer or live in a warm climate?
Staph, Strep, gram negative rods, and PA
What are the common pathogens of a moderate/severe DFI with a ischemic limb, necrosis, or live in a dry climate?
Staph, Strep, gram negative rods, and anaerobes
What are the common pathogens of a moderate/severe DFI with risk factors for MRSA?
Staph, Strep, gram negative rods, and MRSA
True or false: Culture uninfected wounds.
False - something will grow and lead to false treatment
When should cultures be taken in infected wounds?
Deep tissue culture before starting antibiotics
What is arguably the most important thing besides antibiotics in DFIs?
Wound care
When should antibiotics be started in DFIs?
Systemic s/sx of infection
Culture positive
When would antibiotics not be started in DFIs?
no s/sx of systemic infection
What is the recommended treatment for mild DFIs with no complicating factors?
Cephalexin
Augmentin
What is the recommended treatment for mild DFIs with previous MRSA infection or colonization?
Bactrim
Doxycycline
Linezolid
Clindamycin (last line)
What is the recommended treatment for mild DFIs with recent antibiotic use?
Augmentin
What is the recommended treatment for moderate to severe DFIs with no other complicating factors?
IV
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam
- Ceftriaxone
PO
- Augmentin
What is the recommended treatment for moderate to severe DFIs with a warm macerate ulcer or warm climate?
IV
- Zosyn
- Cefepime
PO
- Levofloxacin
- Augmentin + Ciprofloxacin
What is the recommended treatment for moderate to severe DFIs with an ischemic limb, necrosis, or gas?
IV
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam
- Ceftriaxone + Metronidazole
- Carbapenems
PO
- Augmentin
What is the recommended treatment for moderate to severe DFIs with MRSA risk factors?
Add to any regimen:
IV
- Vancomycin
- Linezolid
- Daptomycin
PO
- Doxycycline
- Bactrim
- Linezolid
What antibiotics are options for treatment of osteomyelitis?
highly bioavailable PO antibiotics
What are some non-pharmacological treatments of DFUs?
Wound care
Off-loading
Vascular eval
Glycemic control
Smoking cessation
How long should the duration of antibiotics be for mild DFI without osteomyelitis?
1-2 weeks
How long should the duration of antibiotics be for moderate/severe DFI without osteomyelitis?
2-4 weeks
True or false: Antibiotics need to be continued until the wound is healed.
False
How long should antibiotics be taken in DFI with osteomyelitis where there is no residual infection?
2-5 days
How long should antibiotics be taken in DFI with osteomyelitis where there is residual soft tissue infection but no bone?
1-2 weeks
How long should antibiotics be taken in DFI with osteomyelitis where there is residual but viable bone?
3 weeks
How long should antibiotics be taken in DFI with osteomyelitis where there is no surgery or residual non-viable bone?
6 weeks
What antibiotics are highly bioavailable orally?
Clindamycin
Bactrim
Doxycycline
Quinolones
Septic arthritis
inflammation of the joint caused by infection
What are the risk factors for septic arthritis?
Age
Previous joint injury
IV drug use
Alcoholism
IA injections
Cutaneous ulcers
Diabetes
What are the most common pathogens seen with septic arthritis?
S. aureus
Streptotocci
How does septic arthritis typically present?
Monoarticular
Knee (most common)
Severe pain that limits mobility
Warmth and redness
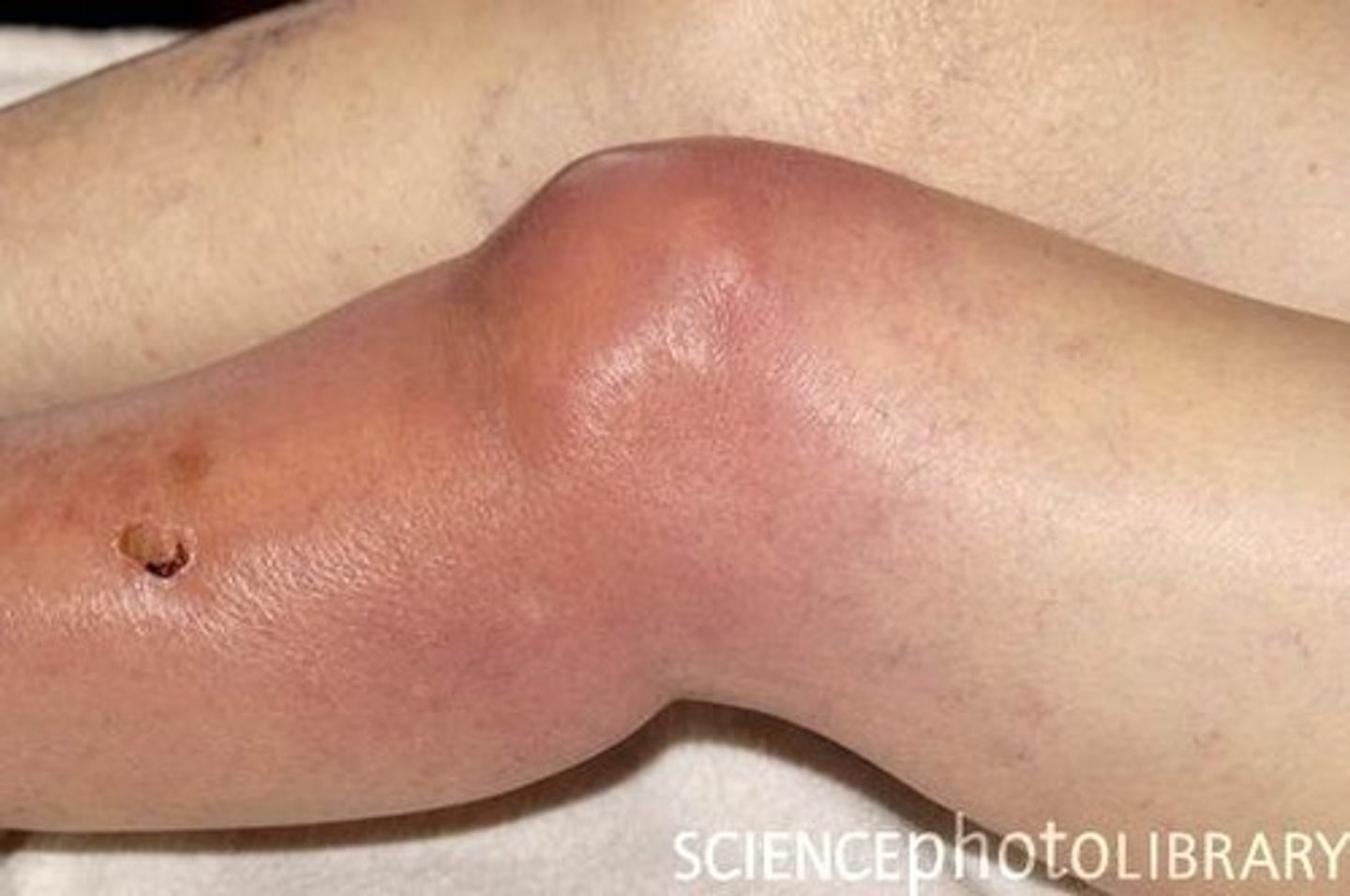
What is used to diagnose septic arthritis?
Athrocentesis with WBC >50,000
What is important to look for besides WBC in septic arthritis? Why?
Presence of crystals - because gout presents like septic arthritis
What antibiotics are recommended for septic arthritis?
Vancomycin IV +/- Ceftriaxone if there are risk factors for Gram negative or gonorrheal infection
When should antibiotics be started in septic arthritis?
After aspiration of synovial fluid
OR
Septic
What are the most common bacterial causes of prosthetic joint infections?
S. aureus
Gram negative rods
Coagulase negative staph
Corynebacterium
Propionibacterium
Bacillus spp
*CREATE BIOFILMS*
What is the s/sx of prosthetic joint infections?
Similar to septic arthritis
Joint loosening
Painful prosthesis
Draining sinus tract
When should antibiotics be started in prosthetic joint infections?
After intra-op cultures are obtained
Systemic infection
What treatment is recommended for prosthetic joint infections if debridement and retention of prosthesis occured?
2-6 weeks of IV and PO Rifampin
What treatment is recommended for prosthetic joint infections had a resection arthroplasty w/ or w/o planned staged reimplantation?
6 weeks IV or PO
What is the treatment recommendation of a 1 stage exchange in a prosthesic joint infection?
2-6 weeks IV therapy
PLUS Rifampin
Followed by Rifampin PLUS therapy for 6 months