Peripheral Vascular, lymphatic, and breasts
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are the main components of the peripheral vascular system?
The arterial, venous, and lymphatic systems.
What subjective data should be collected related to the peripheral vascular system?
Color, temperature, pulses, capillary refill, and edema.
What objective data should be collected during a peripheral vascular assessment?
Color, temperature, pulses, capillary refill, and edema.
What is the significance of identifying normal and abnormal findings in the peripheral vascular system?
It helps in the general survey, inspection, palpation, and auscultation of the systems.
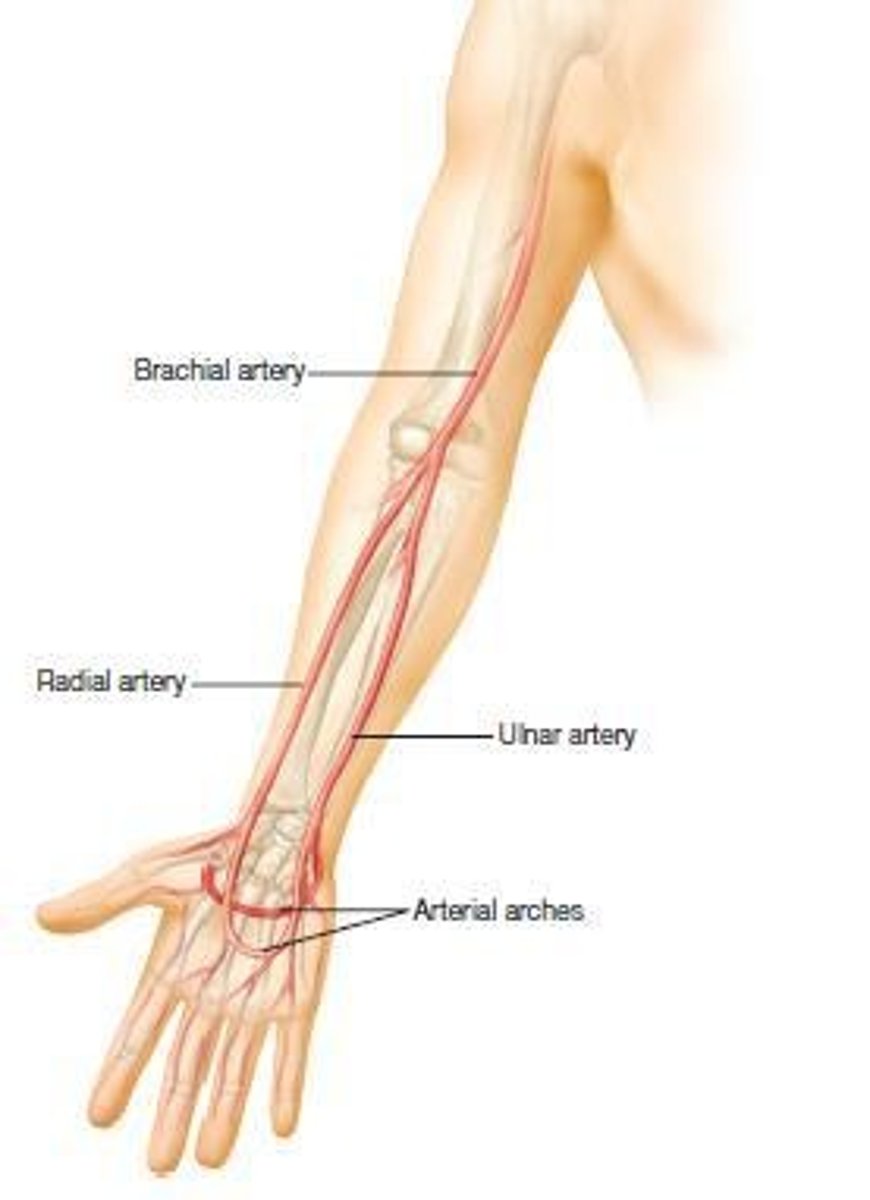
What are the locations of the major arterial pulses in the arms?
Brachial artery, radial artery, and ulnar artery.
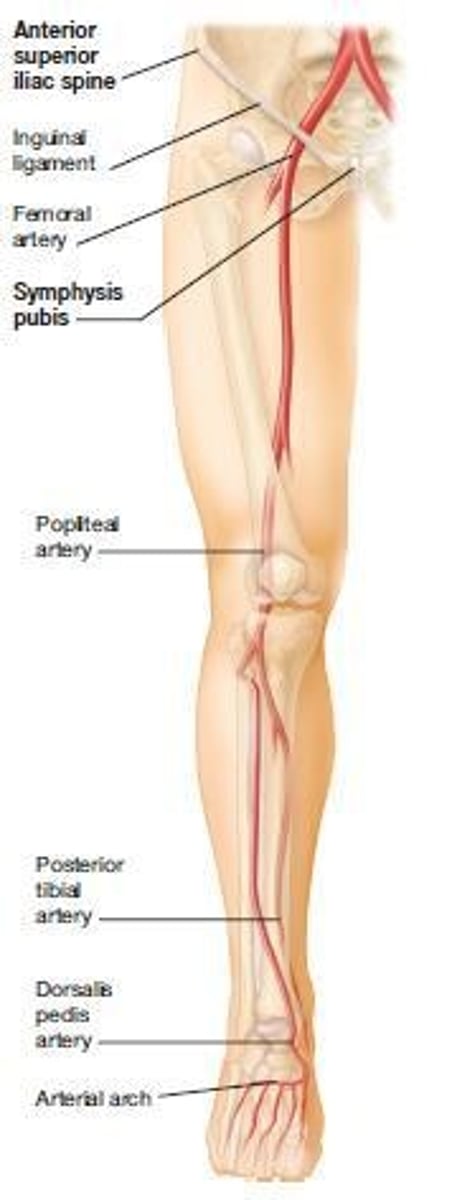
What are the locations of the major arterial pulses in the legs?
Femoral artery, popliteal artery, dorsalis pedis artery, and posterior tibial artery.
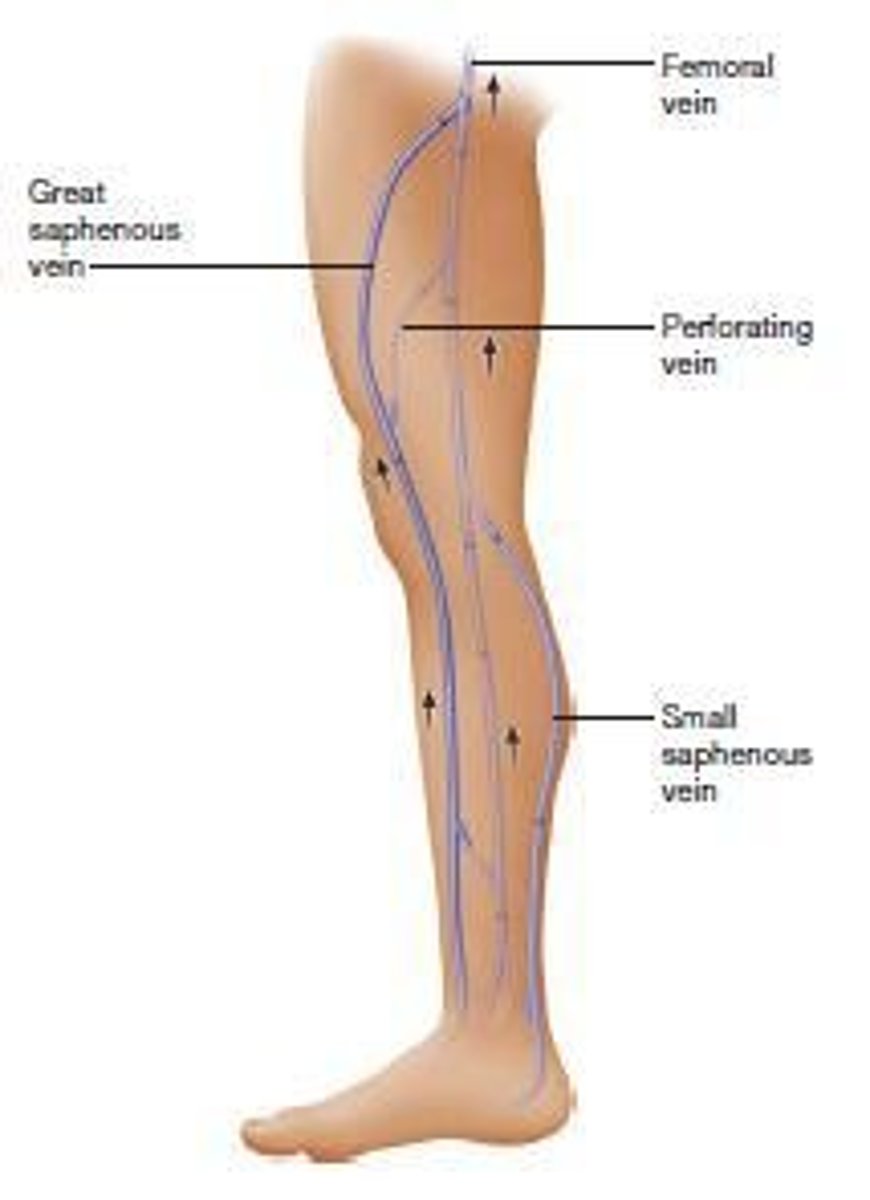
What are the two types of veins found in the legs?
Deep veins and superficial veins.
What are the names of the major superficial veins in the legs?
Great saphenous vein and small saphenous vein.
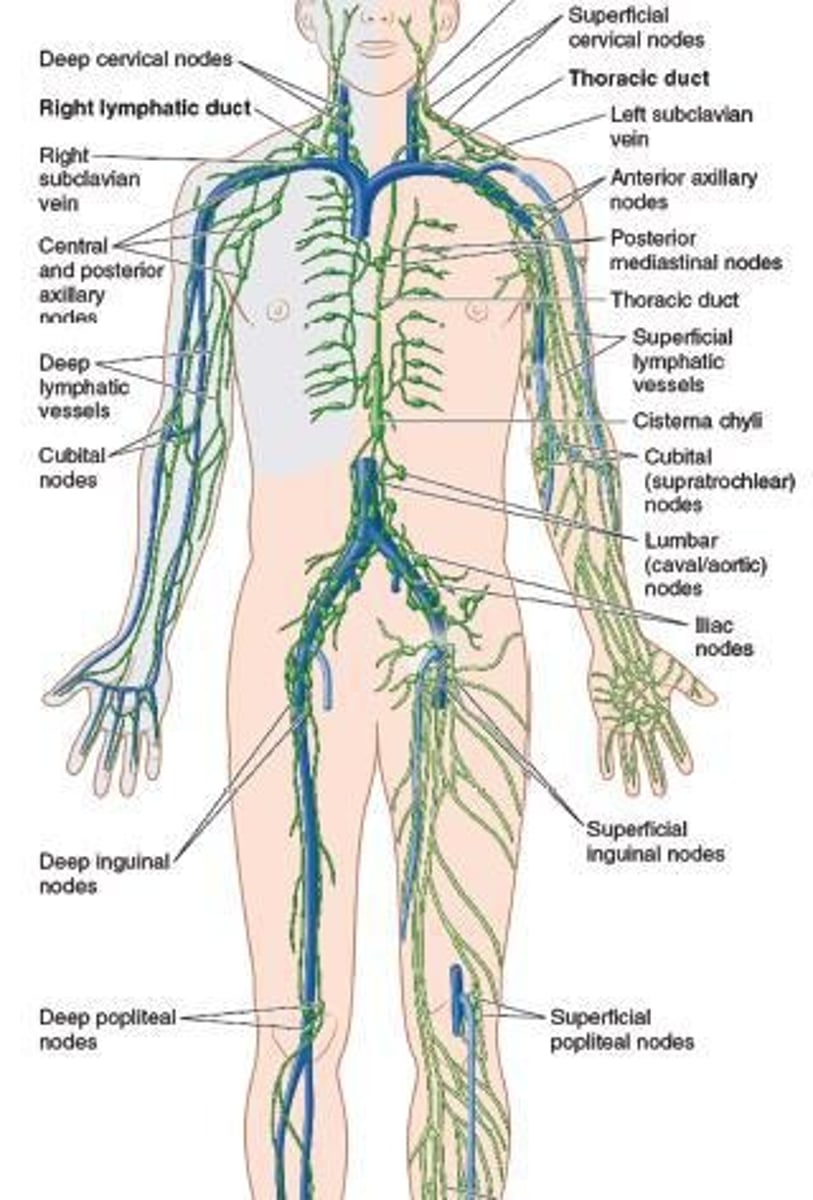
What are the primary functions of the lymphatic system?
Vascular functions and immune functions.
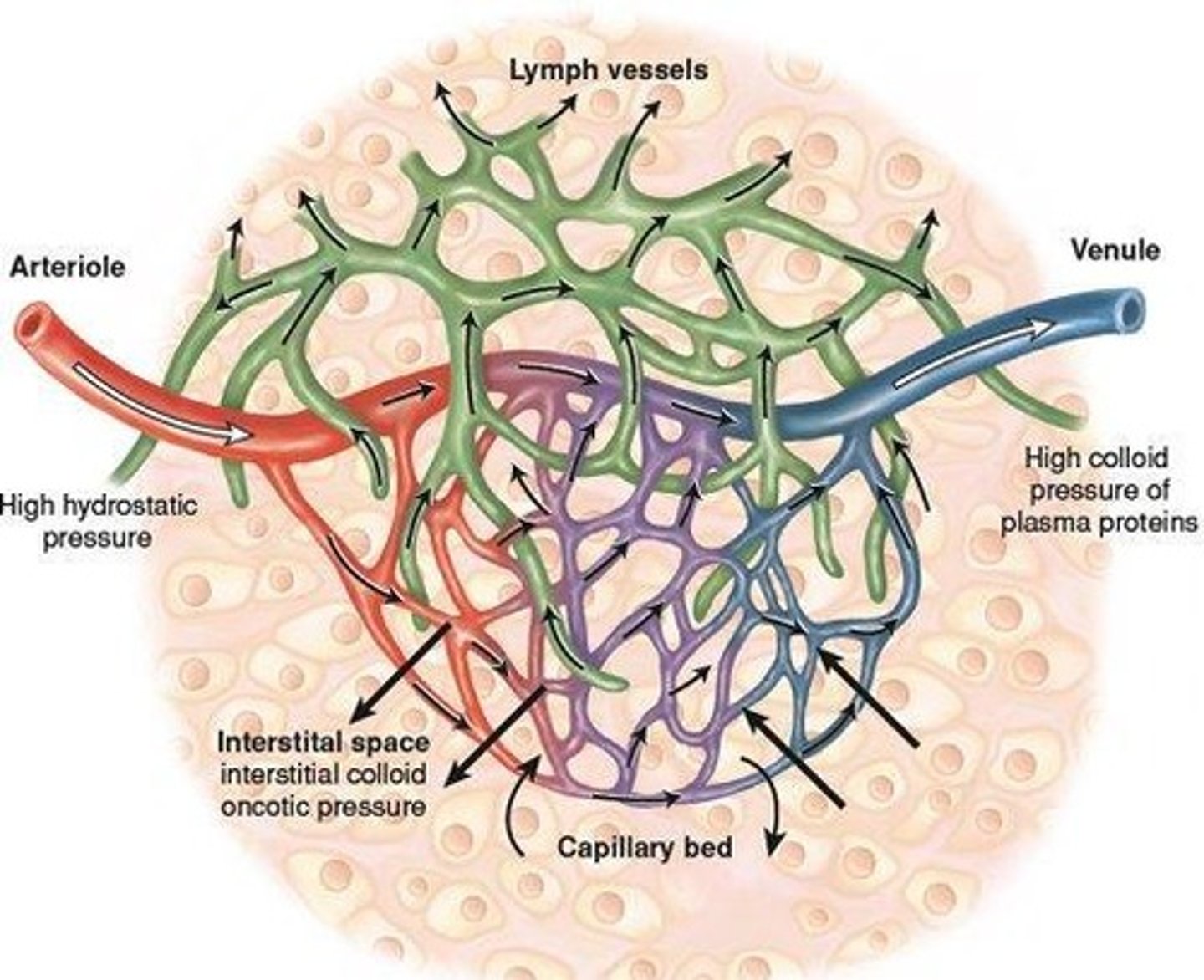
What is the significance of hydrostatic pressure in the capillary bed?
It plays a role in fluid exchange.
What is the purpose of the ankle-brachial index?
To assess peripheral arterial disease (PAD) by comparing blood pressure in the ankle with that in the arm.
What should be the patient's position when measuring the ankle-brachial index?
Supine.
What are the 7 P's to assess for complete arterial occlusion?
Pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis, poikilothermia, and edema.
What are some modifiable risk factors for peripheral vascular disease?
Smoking, diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity.
What are some non-modifiable risk factors for peripheral vascular disease?
Genetics, advancing age, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia.
What changes occur in the arteries as individuals age?
Arteries become more rigid, increasing the risk of claudication and peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
What is the role of subjective and objective data in peripheral vascular assessments?
To analyze findings and plan interventions.
Why is it important to individualize peripheral vascular assessments?
To consider the patient's condition, age, gender, and culture.
What should be documented and communicated after a peripheral vascular assessment?
Data using appropriate medical terminology.
What is the purpose of collecting past medical history in peripheral vascular assessments?
To identify risk factors such as cardiovascular disease, lymphedema, and trauma.
What lifestyle factors should be assessed in patients regarding peripheral vascular health?
Tobacco use, exercise habits, and duration of sitting or standing.
What is the formula for calculating the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)?
Divide both ankle pressures by the highest brachial pressure.
What is the normal range for the Ankle-Brachial Index?
1.0 - 1.4
What ABI range indicates borderline results?
0.91 - 0.99
What ABI value is considered abnormal?
Less than 0.90
What ABI value indicates noncompressible arteries?
Greater than 1.40
What are common symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
Muscle atrophy, pallor, and erythema.
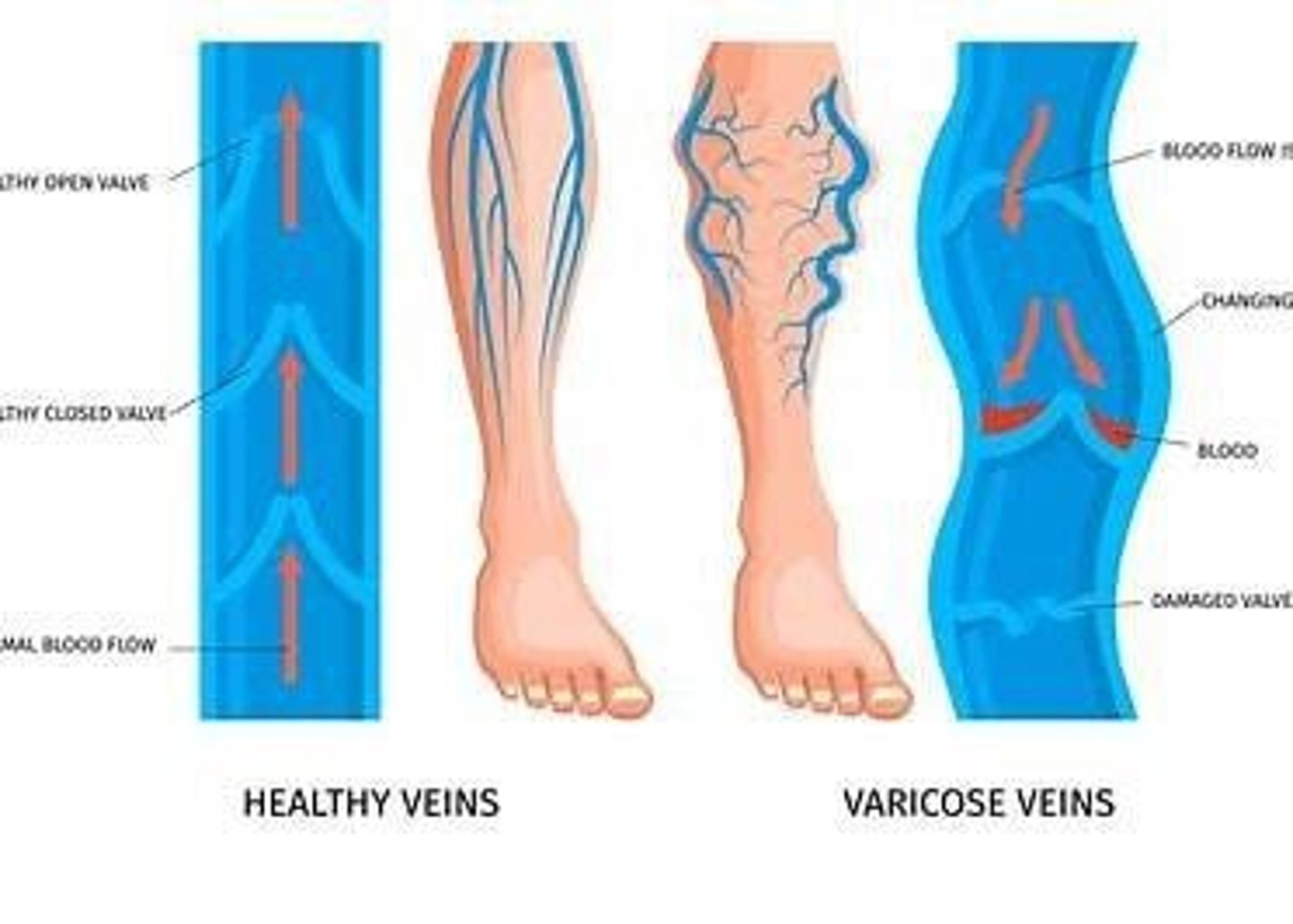
What should be assessed during the inspection of the arms?
Size, symmetry, color, varicose veins, and capillary refill.
What does a DVT assessment include?
Palpation of the legs, checking for edema, and assessing pulses.
What is the significance of the Allen test?
It assesses the patency of the radial and ulnar arteries.
What are the characteristics of arterial ulcers?
Located at the end of toes, deep with noticeable margins, and little drainage.
What are the characteristics of venous ulcers?
Located on the medial parts of the lower legs, swollen with drainage, and shallow.
What is Raynaud's phenomenon?
A vasospastic disorder causing numbness, tingling, and color changes in response to cold or stress.
What lifestyle changes can help manage Raynaud's phenomenon?
Quit smoking, avoid cold, and practice stress management.
What is the role of Montgomery glands?
They provide lubrication during lactation.
Where do most breast cancers occur?
In the upper outer quadrant of the breast.
What is the significance of the BRCA gene?
It is associated with a 50% increase in breast cancer risk.
What are common benign causes of breast lumps?
Cysts, fibroadenomas, and mastitis.
What is mastalgia?
Severe breast pain often caused by trauma or infection.
What factors increase the risk of breast cancer?
Birth control, menopausal hormones, obesity, age, and alcohol consumption.
What is the recommended mammogram schedule for women at normal risk starting at age 45?
Every year.
What should be assessed during breast inspection?
Color, symmetry, texture of the skin, and any signs of retraction or dimpling.
What is the ideal time to perform a breast exam?
The 4th to 7th day after the menstrual cycle.
What does peau d'orange indicate?
Edema from lymphatic fluid, often associated with advanced cancer.
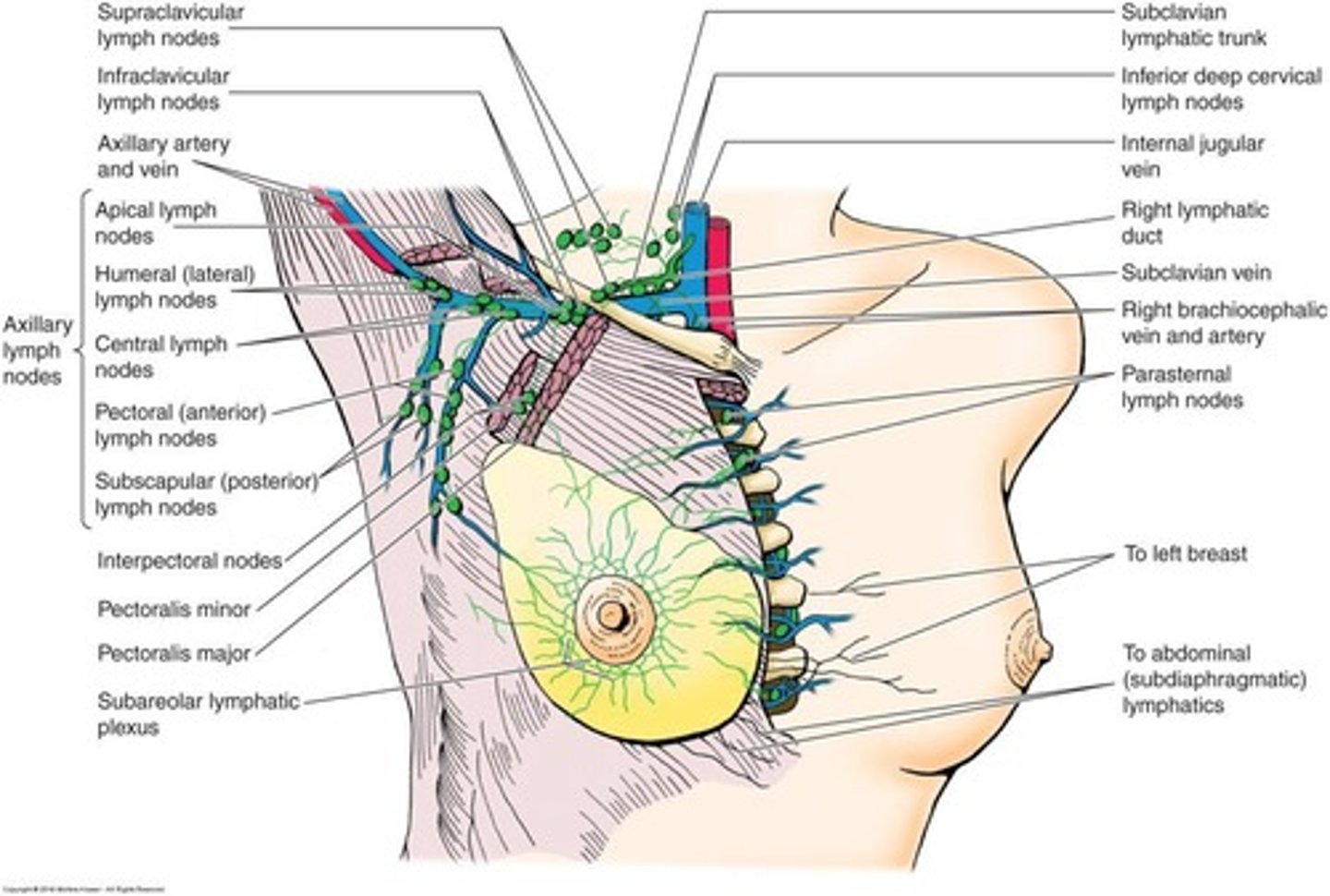
What is the importance of palpation during breast examination?
To detect nodules or lesions that may indicate cancer.
What is a bimanual palpation technique used for?
To assess patients with large pendulous breasts.
What should be done if a patient has a history of breast cancer?
New lumps are 2-4 times more likely to be cancerous.
What should be included in a health assessment of the breasts?
Subjective data on symptoms like pain, rash, lumps, and nipple discharge.
What is the significance of nipple changes during breast examination?
Eversion to inversion may indicate cancer.