Science exam grade 9
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
As you go across a period what happens to reactivity
reactivity decreases because there are more [protons which means that there is a bigger attraction.
2
New cards
as you go across a period what happens to the elements
The size of the atom decreases because their are more protons.
3
New cards
For metals when you go down a group what happens
the size of the atom increases because their are more shells
4
New cards
is a compound a pure substance
Yes a compound is a pure substance
5
New cards
the attraction between a ion and a compound forms what
anions
6
New cards
What are covalent bonds?
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
7
New cards
What are ionic compounds
formed from metals and non metals
8
New cards
What are Isotopes.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have a different mass because electrons have no mass it has a different number of neutrons. Like a fat twin.
9
New cards
What are molecular compounds
compounds formed from two or more nonmetals
10
New cards
What are molecules?
atoms bonded together by covalent bonding.
11
New cards
What are the 7 diatomic elements?
H.O.F.Br.I.N.C.l
12
New cards
what do cations bond to
anions
13
New cards
what do molecular compounds form
compounds without metals
14
New cards
what does neutral mean
have an equal number of protons and protons.
15
New cards
What happens to the reactivity as you go down a group
the reactivity increases because the atom is bigger which means that there is less attraction between protons and valence electrons
16
New cards
what is a compound.
2 or more elements chemically combined
17
New cards
What is an alloy
a MIXTURE of 2 metals
18
New cards
what is an anion
A negatively charged ion
19
New cards
What is an cation?
A positively charged ion (metal)
20
New cards
What is an Ion
A charged atom
21
New cards
What is an Ionic compound
a metal and non metal this also completes both valence shells by giving not sharing
22
New cards
What is an molecular compound
2 non metals completes valence shell by sharing
23
New cards
What is the octete rule?
when a element fills there outer shell
24
New cards
When you have covalent bonds what order do you do it in.
the element that needs the most amount of electrons in the middle and add the ones that need the least at the end.
25
New cards
where are anions on the periodic table
right side
26
New cards
where are cations on the periodic table
left side
27
New cards
why are the diatomic elements special?
they can not be alone
28
New cards
why is an alloy good
takes the best qualities of both metals and combines them into one.
29
New cards
4 ways nitrogen is fixed
Lightning (turns 5% into nitrates), Nitrifying bacteria, Soil bacteria and Man-made
30
New cards
how are nutrients recycled
air, land,water, and living organisms
31
New cards
how do humans get their carbon and in what form
in the form of glucose and we get it by eating other organisms.
32
New cards
how is carbon found in the atmosphere
co2
33
New cards
How is CO2 put back into the atmosphere?
respiration, burning of fossil fuels, volcanoes, anything burning, weathering
34
New cards
what do decomposers do in the carbon cycle
return the co2 back into the atmosphere.
35
New cards
what do humans need carbon for
cell growth, cell repair, energy
36
New cards
what do producers turn co2 into
glucose
37
New cards
What does de-nitrifying bacteria do?
it unfixes bacteria and returns it to the atmposphere.
38
New cards
What is nitrogen used for
Cellular reproduction, DNA, and Proteins
39
New cards
what is the word equation for cellular respiration
glucose + oxygen --\> carbon dioxide + water + energy
40
New cards
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water + Energy--\> glucose + oxygen
41
New cards
why do nutrients have to be recycled
because if they did not there would be none left
42
New cards
Substances with electrons that move easily are called
Conductors
43
New cards
Substances with electrons that can not move easily are called
insulators
44
New cards
Objects with = number of protons and electrons have a…
neutral charge
45
New cards
Objects that gain electrons get
\- charge
46
New cards
Objects that lose electrons have a
\+ charge
47
New cards
What is Friction
rubbing 2 insulators together
48
New cards
What Happens to the electrons during friction
transfering of electrons between two neutral objects
49
New cards
What happens when a neutral object is touched with a charged object.
When a charged object touches a neutral object electrons move from the object with more electrons (from more to less). Objects end up having the same charges
50
New cards
how can an electroscope can be used to detect charge.
electroscope detects charges by contact or induction, leaves will spread or go closer together.
51
New cards
Define electrical discharge
When electrons move to or from a statically charged object all at once this is called electrical discharge
52
New cards
Describe the process of grounding and state its importance
Connecting an object to the ground. We do this to keep things neutral. It always involves conductors
53
New cards
Define current electricity
When electrons are made to flow through conductors (wires) in a controlled manner this is called current electricity.
54
New cards
Identify the positive and negative terminals of a battery
Identify the positive and negative terminals of a battery
55
New cards
What is the symbol for resistance
Ω
56
New cards
What can affect resistance
Diameter, Length, Temperature, Material
57
New cards
What is a series circuit
has only 1 way for the electrons to flow
58
New cards
Parallel circuit
more than 1 way for electrons to flow.
59
New cards
Which picture is seires
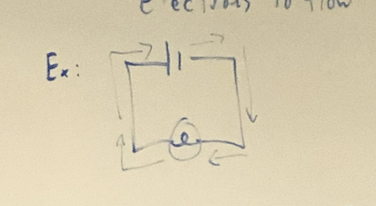
60
New cards
Which Picture is Paralel
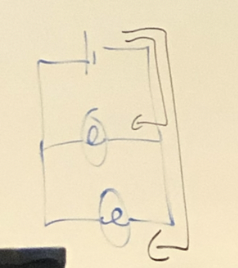
61
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle
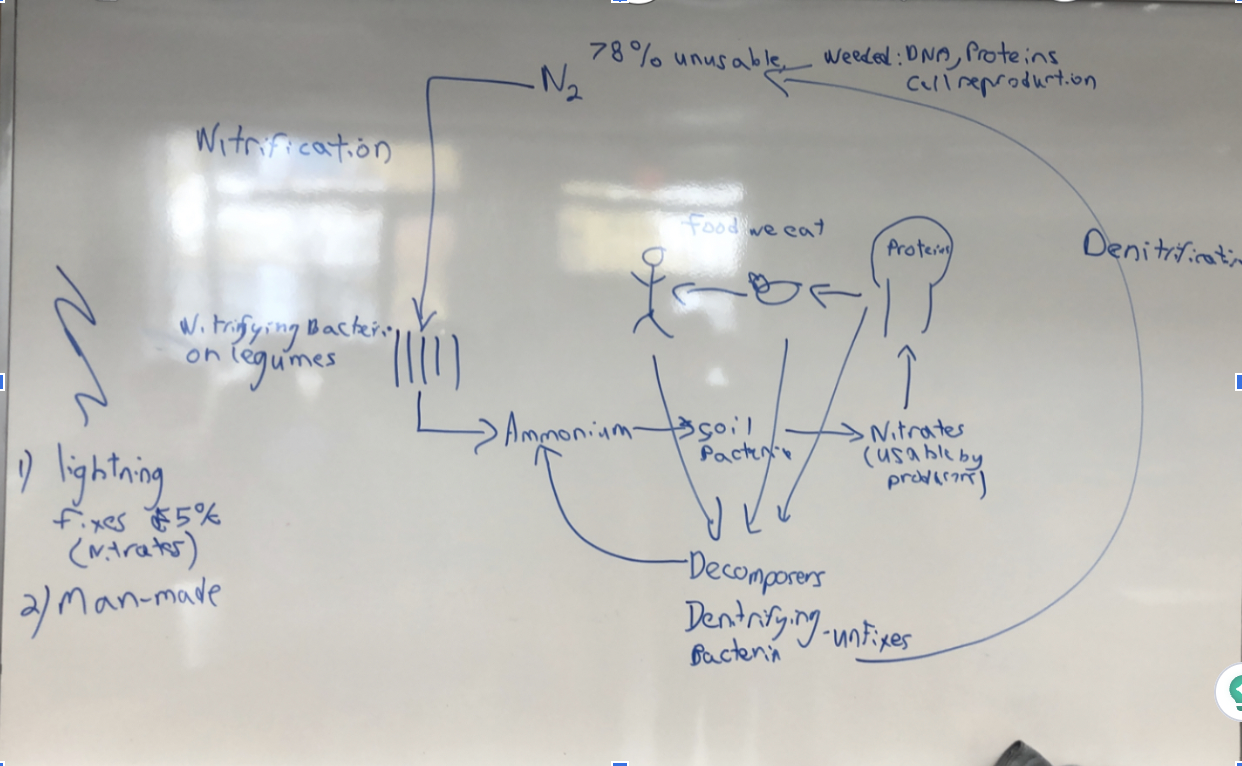
62
New cards
Carbon Cycle
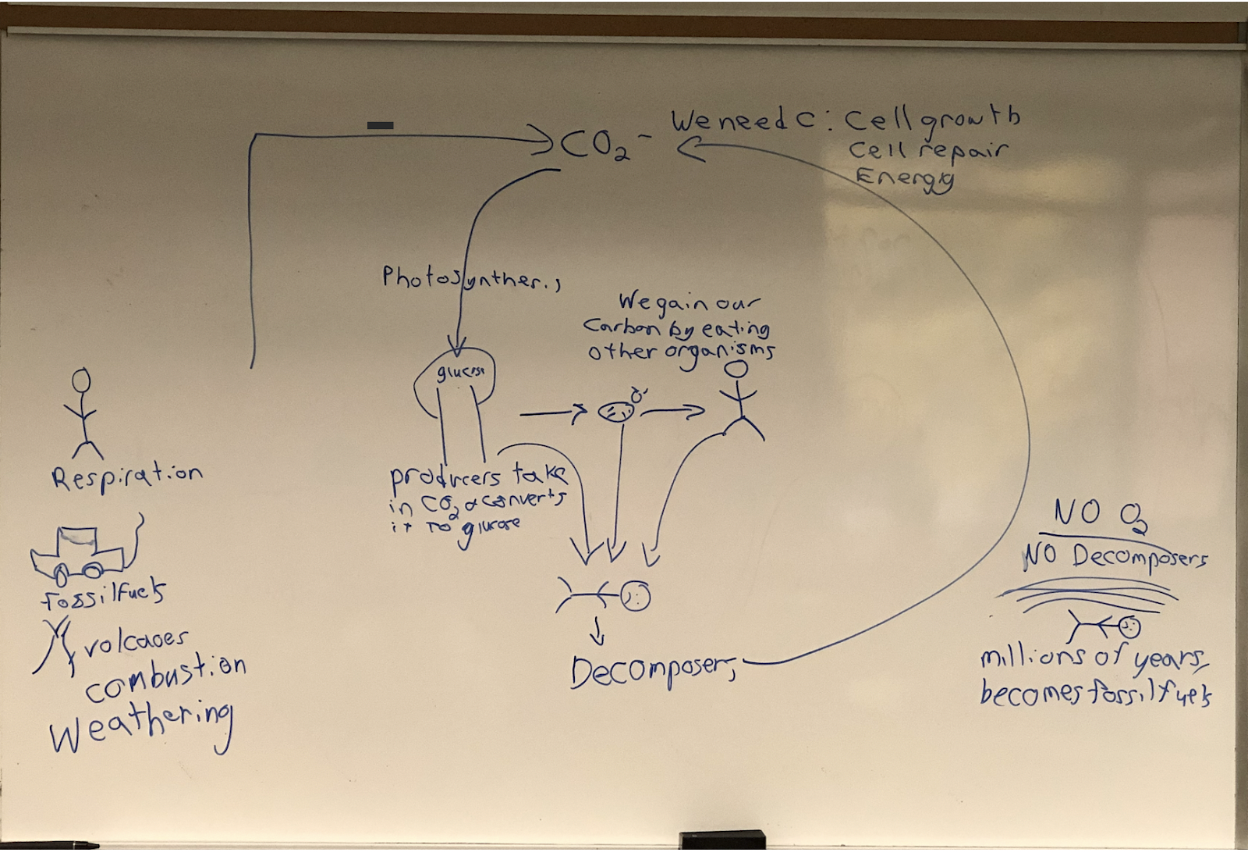
63
New cards
Food Web
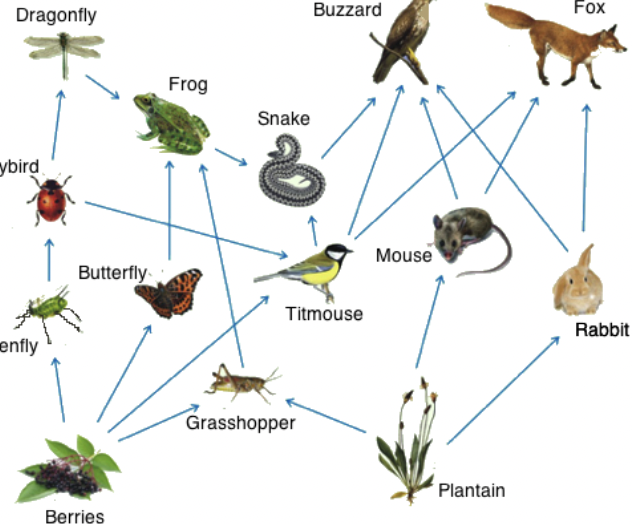
64
New cards
\+, - charged balloon with wall
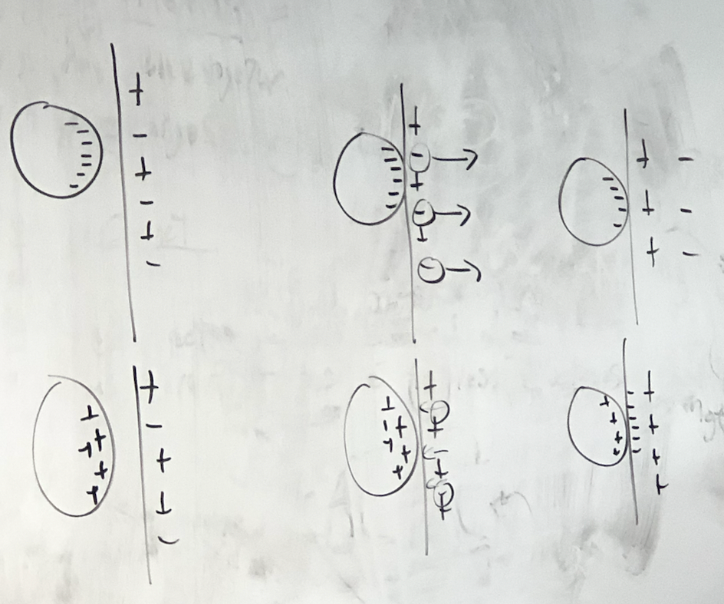
65
New cards
Negative rod and electroscope
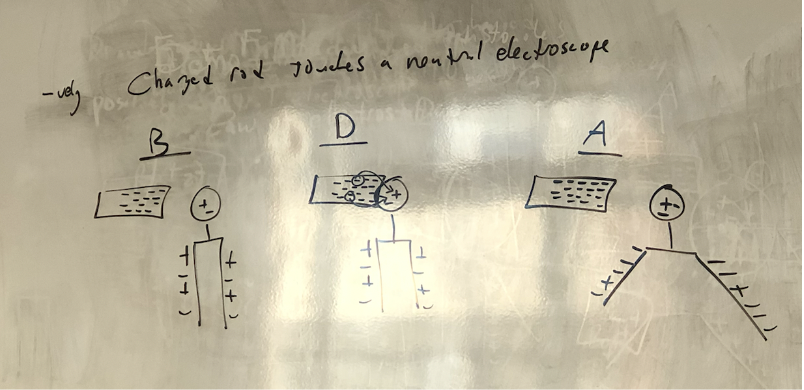
66
New cards
group 1 metals are called
alkali metals
67
New cards
group 2 metals are called
alkaline earth metals
68
New cards
group 3 metals are called
hallogens
69
New cards
group 4 metals are called
noble gasses