Medicinal Organic Chem part 2 (Sir Jan's Notes)
1/394
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
395 Terms
Cell Wall
Site of Action?
Bacitracin
Cephalosporin
Cycloserine
Penicillins
Vancomycin
Cell Membrane
Site of Action?
Amphotericin B
Nystatin
Polymyxins
Ribosomes
Site of Action?
chloramphenicol
50s subunit
Site of action?
Erythromycin
lincomycin
30s unit
Site of action?
aminoglycosides
tetracyclines
Nucleic acids
site of action?
actinomycin
griseofulvin
DNA and/or RNA
Site of action?
Mitomycin C
Rifampacin
Bacitracin
Mucopeptide synthesis
Cephalosporin
Cell wall cross-linking
Cycloserine
Synthesis of cell wall peptides
Penicillins
Cell wall cross-linking
Vancomycin
Mucopeptide synthesis
Amphotericin B
Membrane function
Nystatin
Membrane function
Polymyxins
Membrane integrity
Aminoglycosides
Protein synthesis and fidelity
R group:
1. Electron withdrawing groups
→ L nucleophilicity of carbonyl oxygen → T stability
2. Bulky groups provides resistance to B-lactamase
3. Polar groups make the structure more hydrophilic
Ertapenem
Benzoic acid contributes to high protein binding and prolongs the half-life of the drug
Teicoplanin
A glycopeptide from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus
• MOA: long alkyl chain anchors the antibiotic to the outer surface of the cell membrane
• Use: treatment of gram-positive infections
Ring 2
SAR: Aminoglycosides
Modifications of ________ (deoxystreptamine) functional groups are possible without
appreciable loss of activity in most of the aminoglycosides.
tetracycline
• Broadest spectrum of the antibiotics
• Have activity against gram positive & negative, spirochetes & atypical bacteria
• *Chlortetracycline- Streptomyces aureofaciens
• DOC: lime disease, ricketsiz
tetracycline
Binds to the 30s subunit of ribosomes which prevents aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the mRNA ribosome complex
Dalfopristin
interferes with the transfer of the peptide chain from one tRNA to the next
1,4 dihydro-4-oxo-3 pyridine carboxylic acid
Quinolone SAR
nucleus?
Enzyme inhibitor
•Products containing divalent and trivalent metal
Interactions of quinolones
Allylamines
MOA: inhibit squalene epoxidase
epipodophyllotoxins
• semisynthetic derivatives of podophyllotoxin, isolated from mayapple root
• MOA: inhibits Topoisomerase II
• Drugs: Etoposide, Teniposide
Beracizumab
inhibits human vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF), preventing
angiogenesis
Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action
• Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
• Inhibition of protein synthesis
• Inhibition of cell metabolism
• Inhibition of nucleic acid transcription and replication
• Interactions with plasma membrane
acylamido & Cis-stereochemistry
in penicillin
___ side chain & ____is essential
Cephalosporin C
Contains an unstable bicyclic system
• Beta-lactam & dihydrothiazine
• Nucleus: 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid (7-
ACA)
Cystein & Valein
cephalosporin C precursors?
Cefalexin
used for UTI in pregnant
Aminoglycosides
Bind to 30s ribosomal subunit to prevent the reading of the mRNA
Amikacin
semi synthetically derived from Kanamycin
• first prepared in Japan
macrolides
Binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit, inhibiting translocation.
Clarithromycin
• methylated erythromycin
• More stable in gastric acid and has improved oral absorption
• Use: treatment of ulcers causes by H. pylori
Roxithromycin
Semisynthetic macrolide derived from erythromycin (+N-oxime side chain)
Pritinamycin
source: Streptomyces pristinaespiralis
Sparfloxacin
Quinolone SAR
Lowest photosensitivity
Tuberculoid Leprosy (TT)
• Well demarcated, dry patch
• Minimal disfigurement
- No leonine facies
- No claw-shaped hands
- No pendulous ear lobes
• Good immune response (high resistance)
Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
Used in systemic fungal infections (before), topical (now) needs acidic pH to be absorbed
• s/e, interactions: hepatoxicity, antiandrogenic effects, enzyme inhibitor
• reduced production of testosterone, impotence, loss of libido, gynecomastia, dec. sperm count
Carbachol
More stable ester, resulting to long-acting effect • Used for glaucoma
alkyl
SAR: ACh
Addition of _______ group • less prone to susceptibility & more selective to muscarinic than nicotinic
benign neoplasm
does not invade surrounding tissues
G2 phase
• DNA synthesis ceases. RNA & other enzymes (e.g., topoisomerase I & II) are produced to prepare for cell duplication
Chloramphenicol
Protein synthesis
Erythromycin
Protein synthesis
Lincomycins
Protein synthesis
Tetracyclines
Protein synthesis
Actinomycin
DNA and mRNA synthesis
Griseofulvin
Cell division, microtubule assembly
Mitomycin C
DNA synthesis
Rifampin
mRNA synthesis
Bactericidal
Type of activity?
Bacitracin
Cephalosporin
Cycloserine
Penicillins
Vancomycin
polymycins
aminoglycosides
rifampicin
Fungicidal
Type of action?
Amphoterecin B
Nystatin
Bacteriostatic
Type of action?
Chloramphenicol
erythromycin
lincomycin
tetracyclines
Pancidal
Type of Action?
Actinomycin
Mitomycin C
Fungistatic
Type of action?
Griseofulvin
B lactam antibiotics
penicillin is a?
Alexander Fleming
Penicillin is discovered by?
Penicillium notatum
old name of penicillin
Penicillium chrysogenum
new name of penicillin
Florey & Chain
P. notatum and P. Chrysogenum are isolated by? by freezdrying/lyophilization
Penicillin
Contains an unstable bicyclic system (b-lactam & Thiazolidine ring
cysteine and Valine
Precursors of penicillin
half open book
shape of penicillin
acid stability
SAR of penicillin
Addition of electron withdrawing group
penicillin's resistant
SAR of penicillin
Addition of bulky groups
Increase spectrum activity
Addition of amino group
sulfur
in penicillin
___ is usual but not essential
Thiazolidine
in penicillin
5-membered saturated ring contains nitrogen. The geminal dimethyl group at C-2 position is a characteristic of the penicillin
Carboxylic group
1. Is usually ionized to form sodium of potassium salts.
2. Bind amino group of Lys at binding site
3. Is important for activity which is reduced it modified to alcohol or ester
B-lactam ring
in penicillin
___ strain is essential
Bicyclic system
confers further strain to B-lactam ring
increase strain --> increase activity → increase instability
Carbonyl oxygen:
Is electrophilic because the lone pair electrons on N is not provided for resonance.
Thus =0 is ready for nucleophilic attack
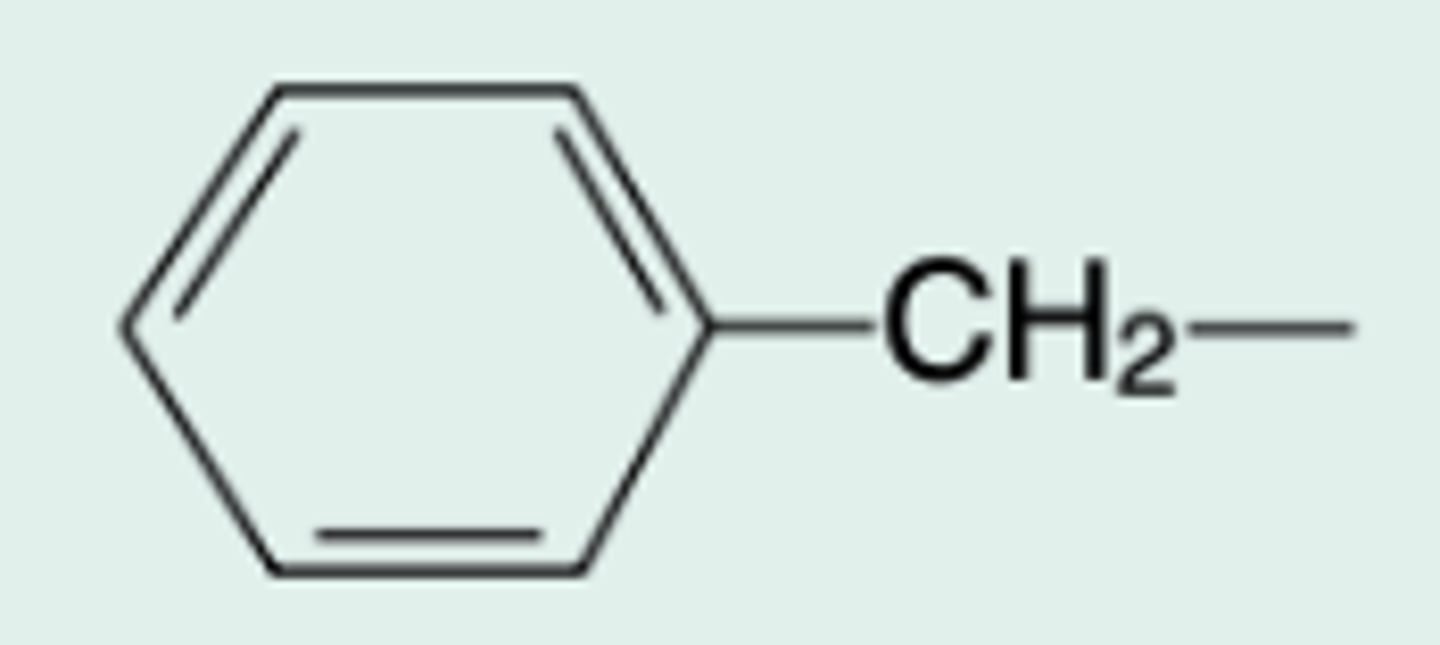
Pen G
Gen Name?
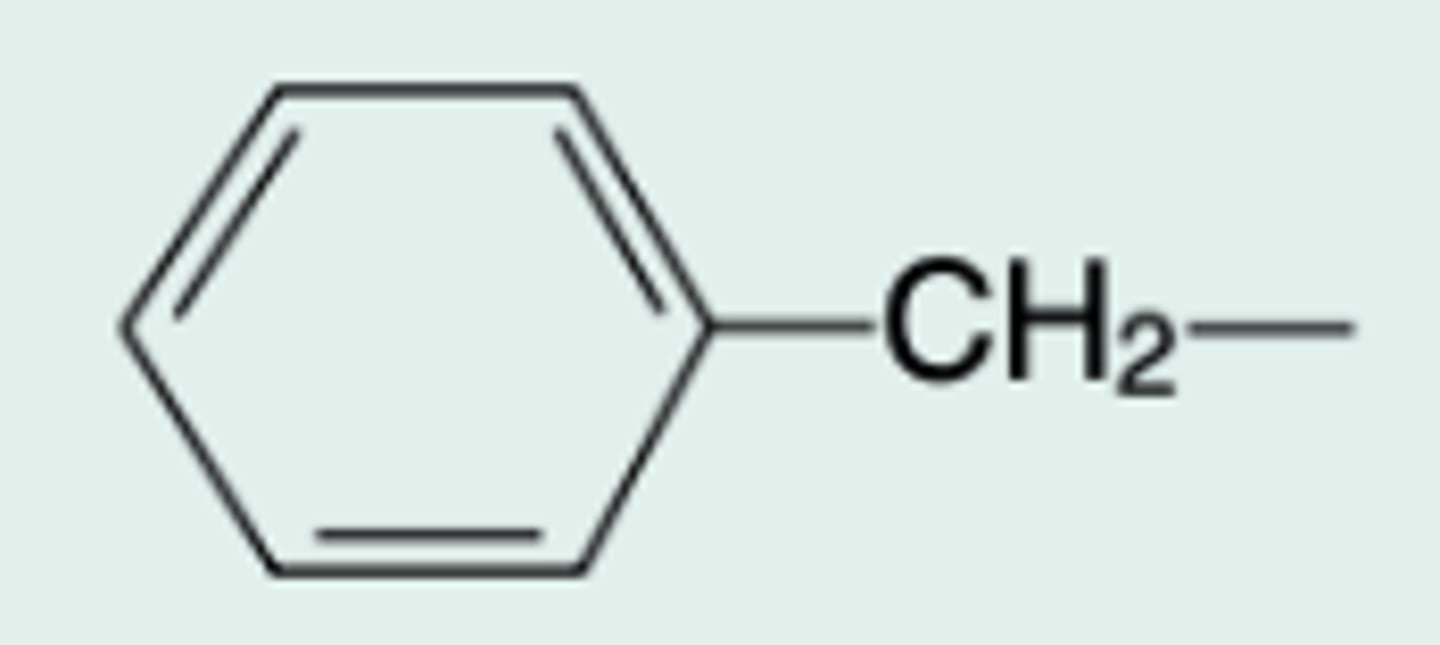
Pen G
Chem Name?
Pen V
Gen name?
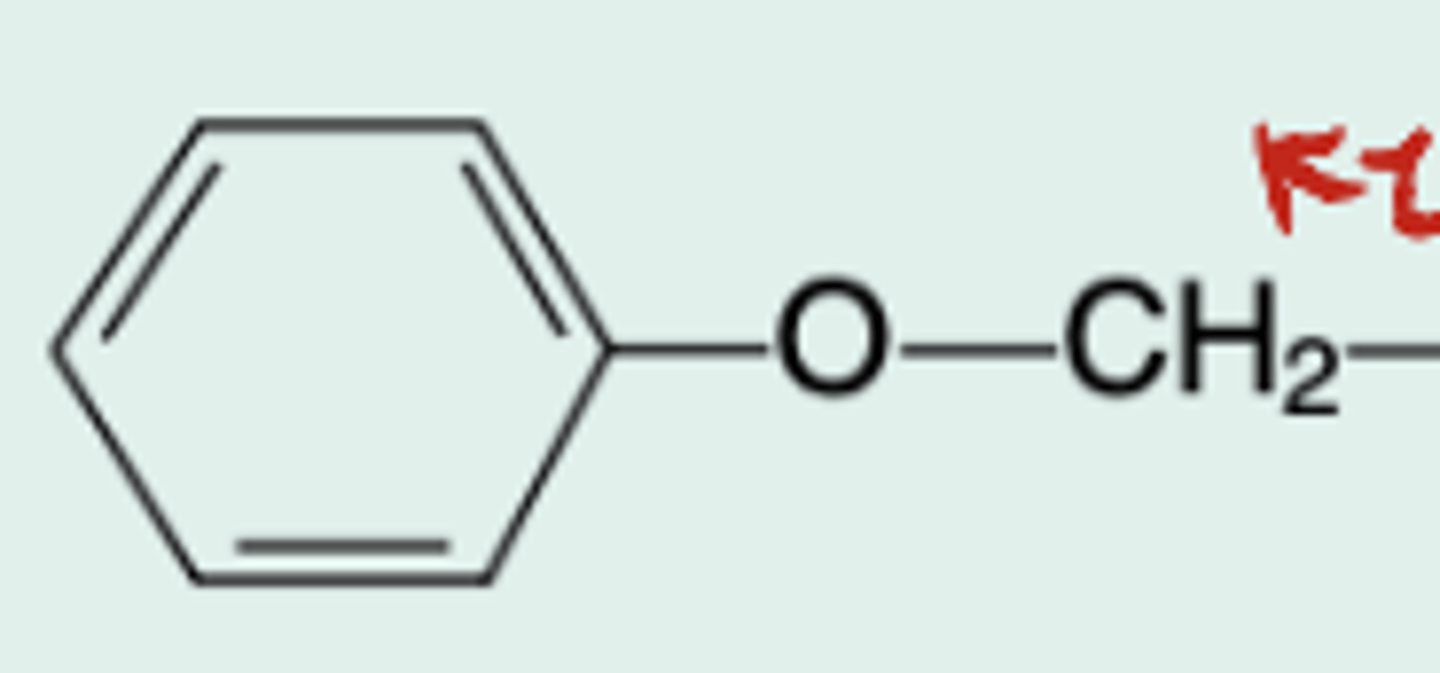
Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Chem name?
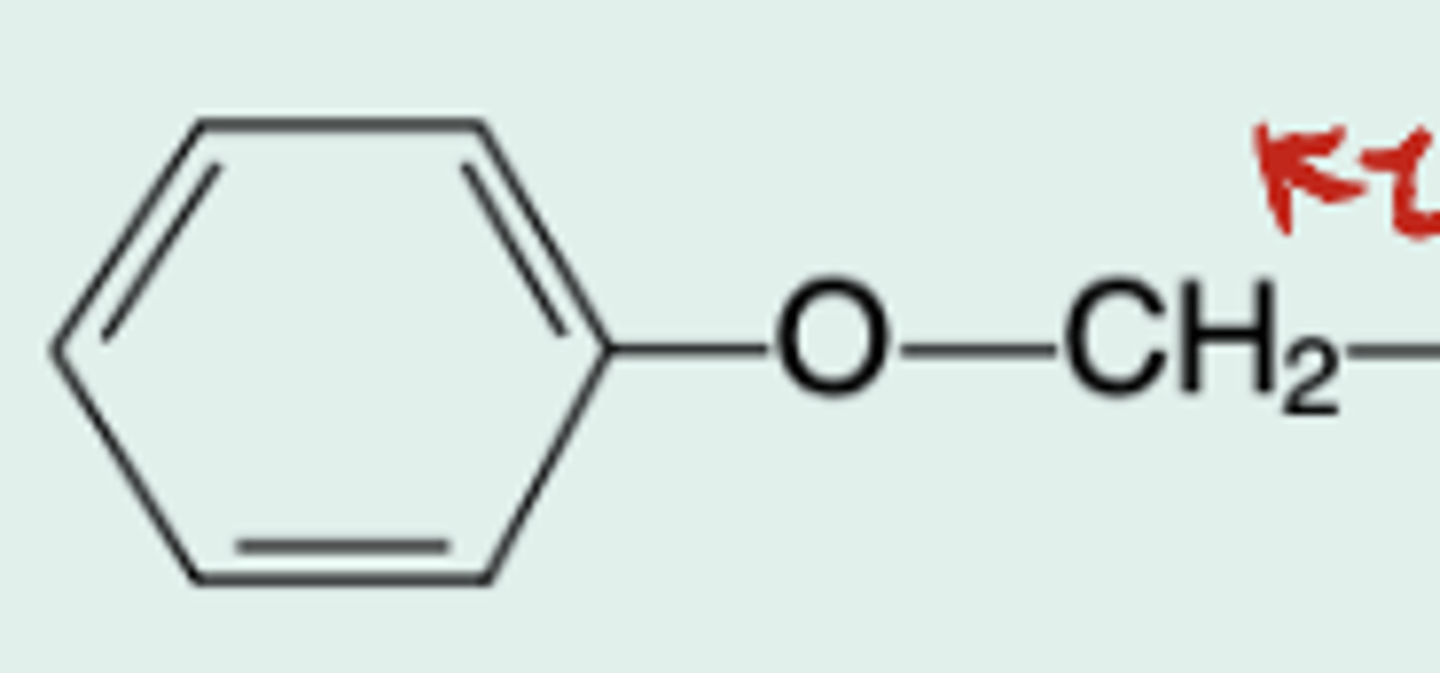
Methicillin
Gen Name?
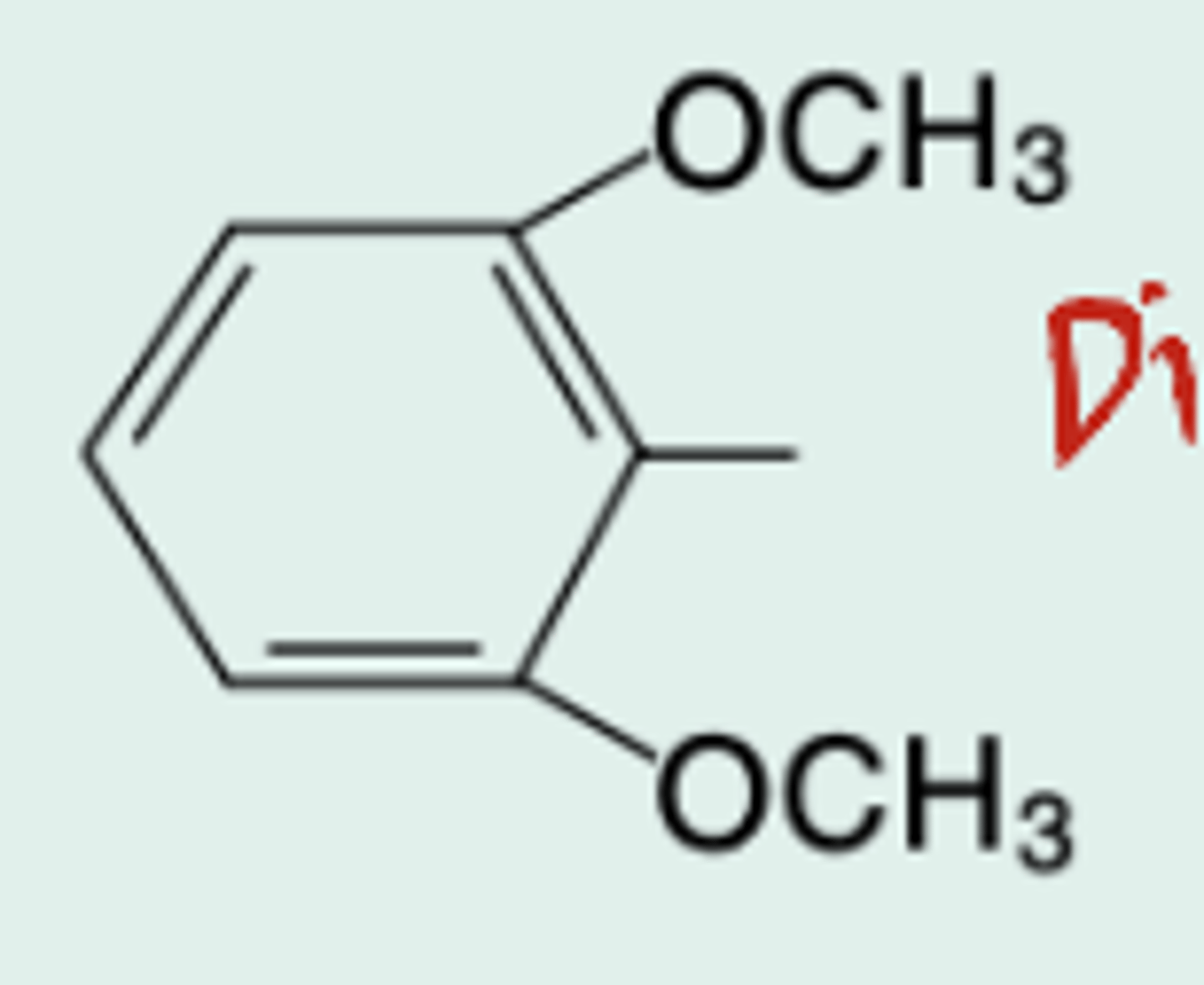
2,6-Dimethoxyphenyl-penicillin
Chemical name?
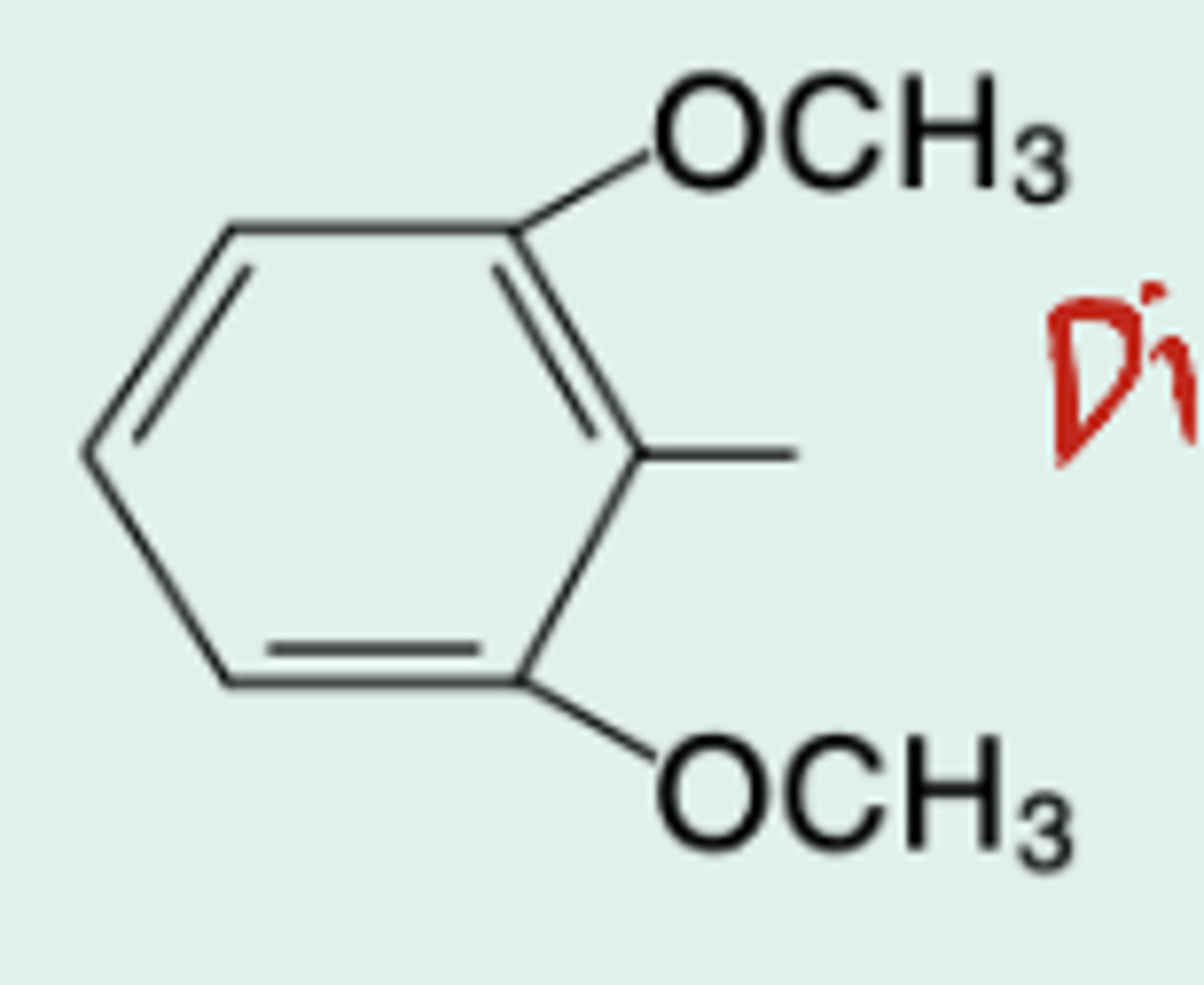
nafcillin
Gen Name?
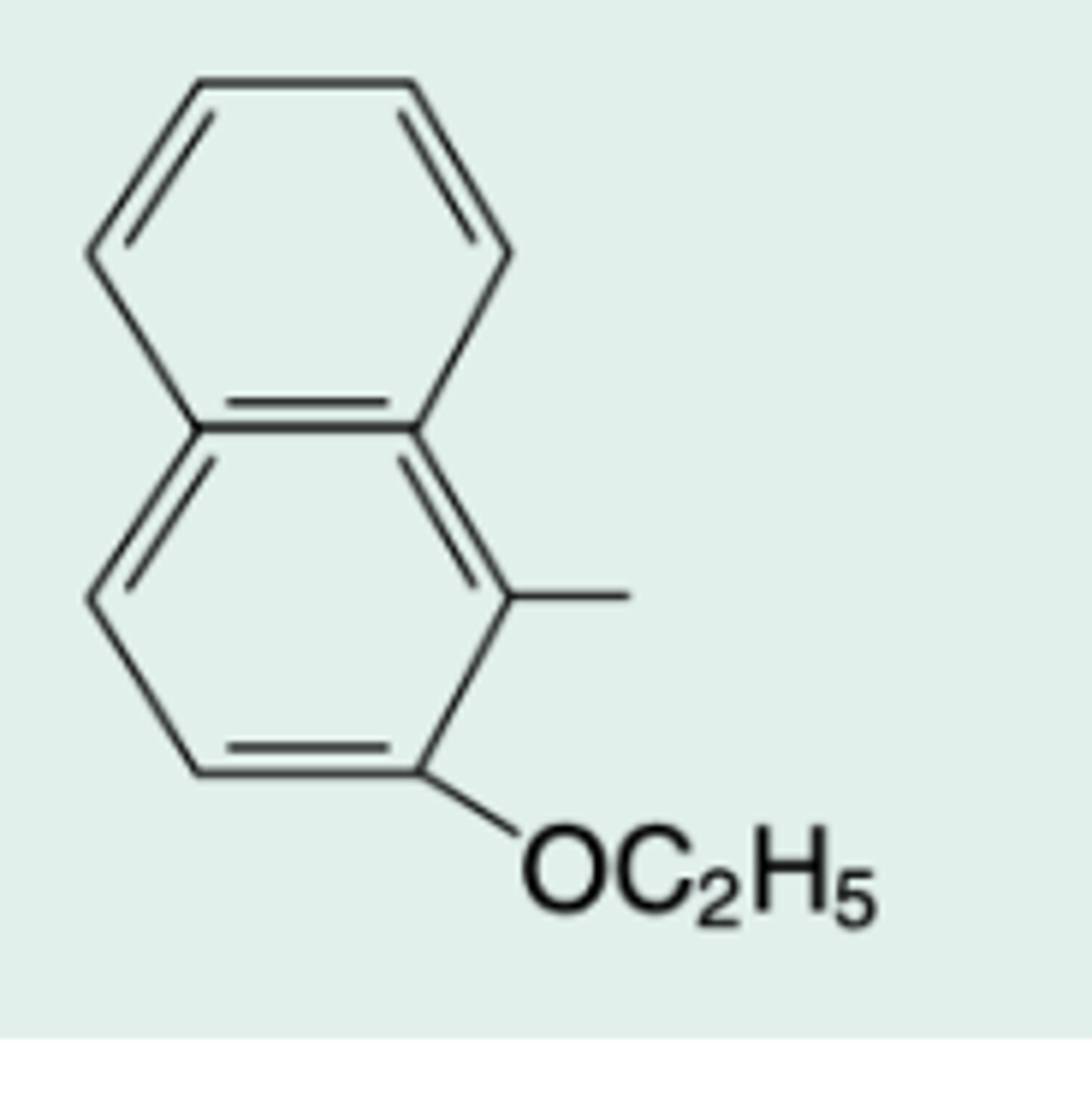
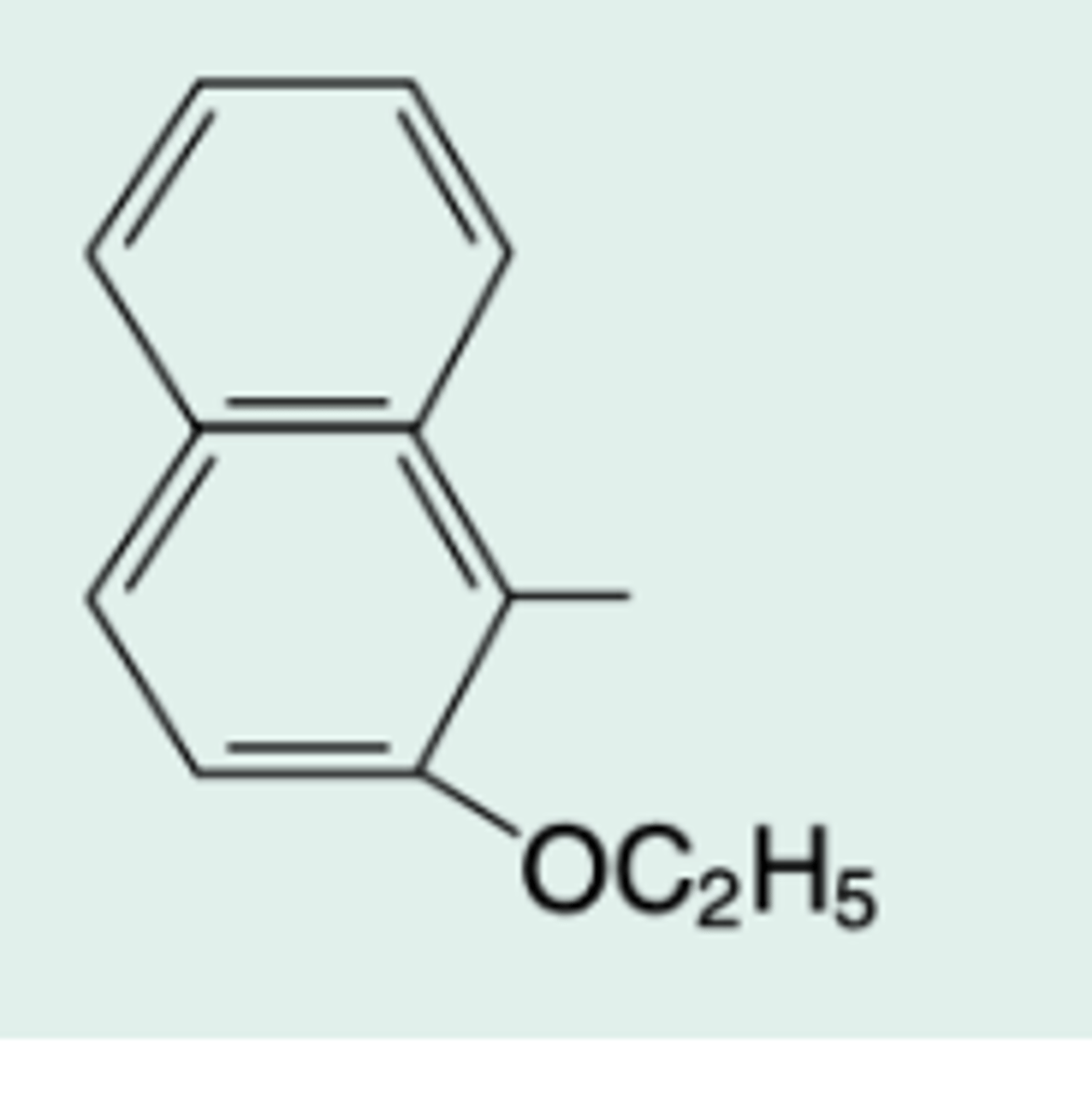
2-ethoxy-1-naphthyl-penicillin
Chem Name?
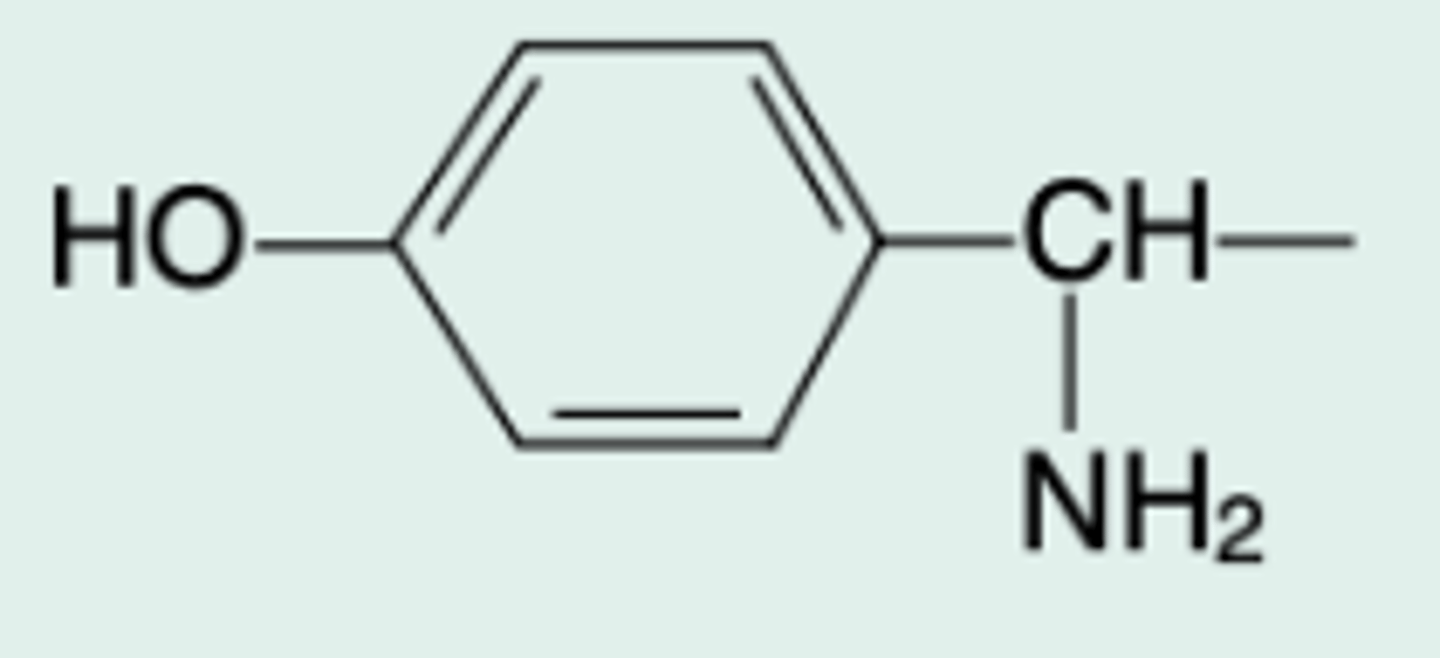
amoxicillin
Gen Name?
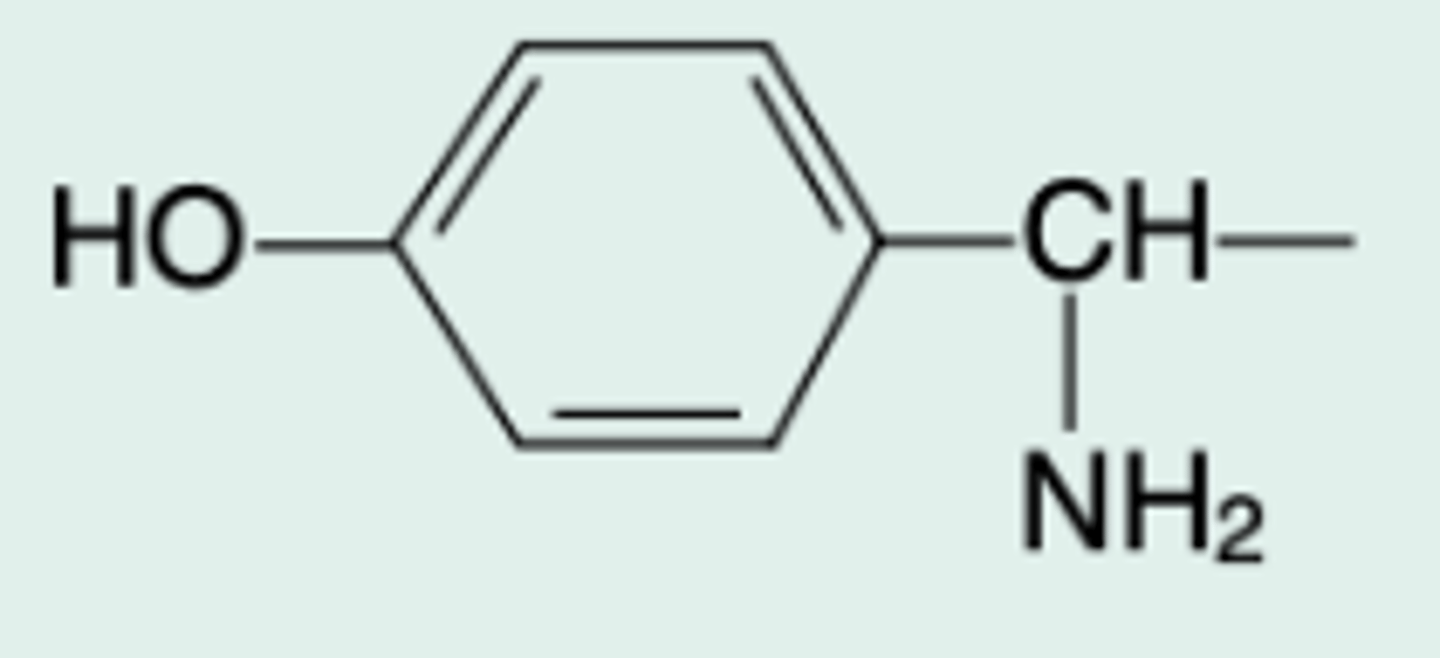
D-a-amino-p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin
Chem name?
Cyclacillin
Gen Name
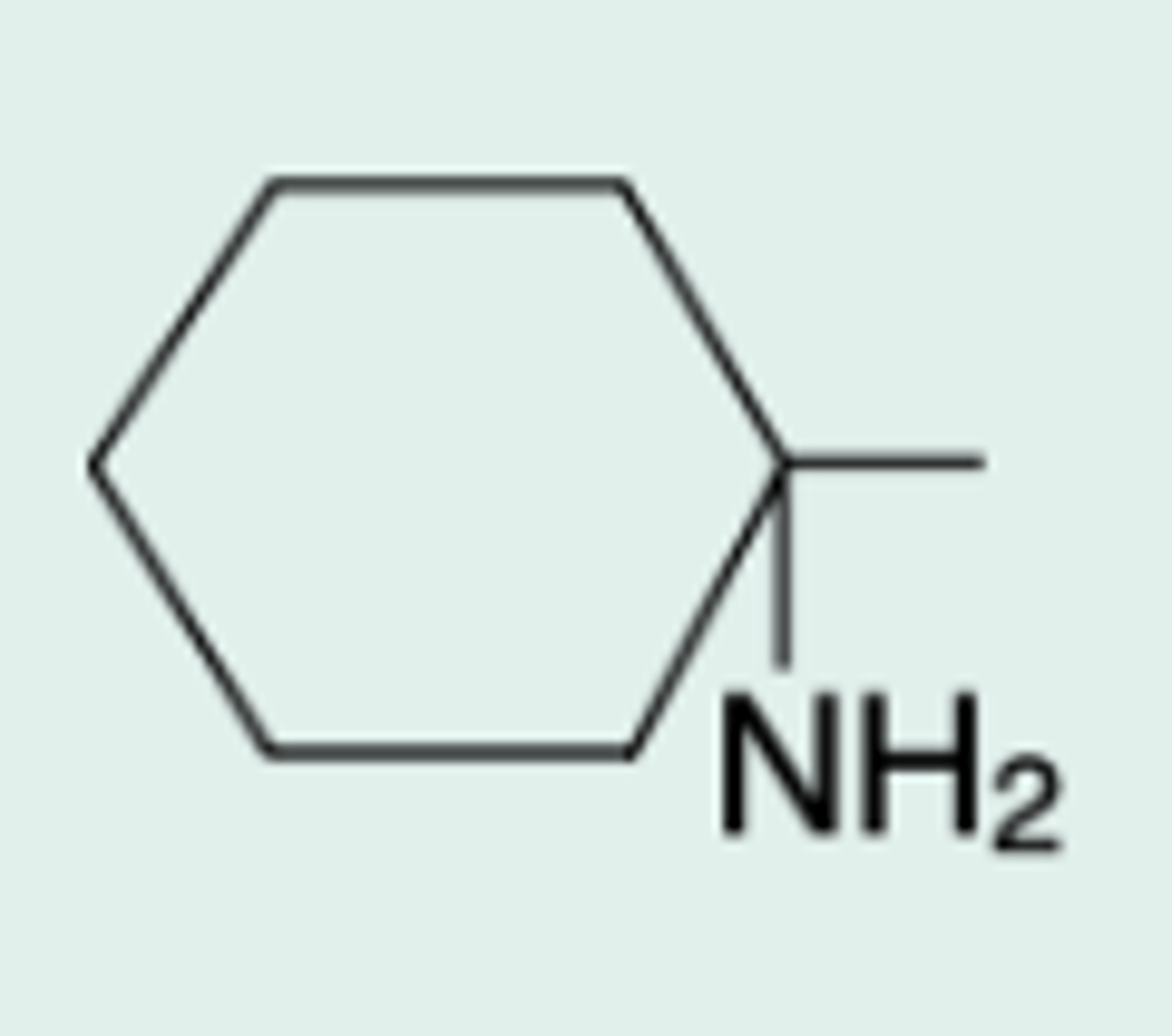
1-aminocyclohexyl-penicillin
Chem Name
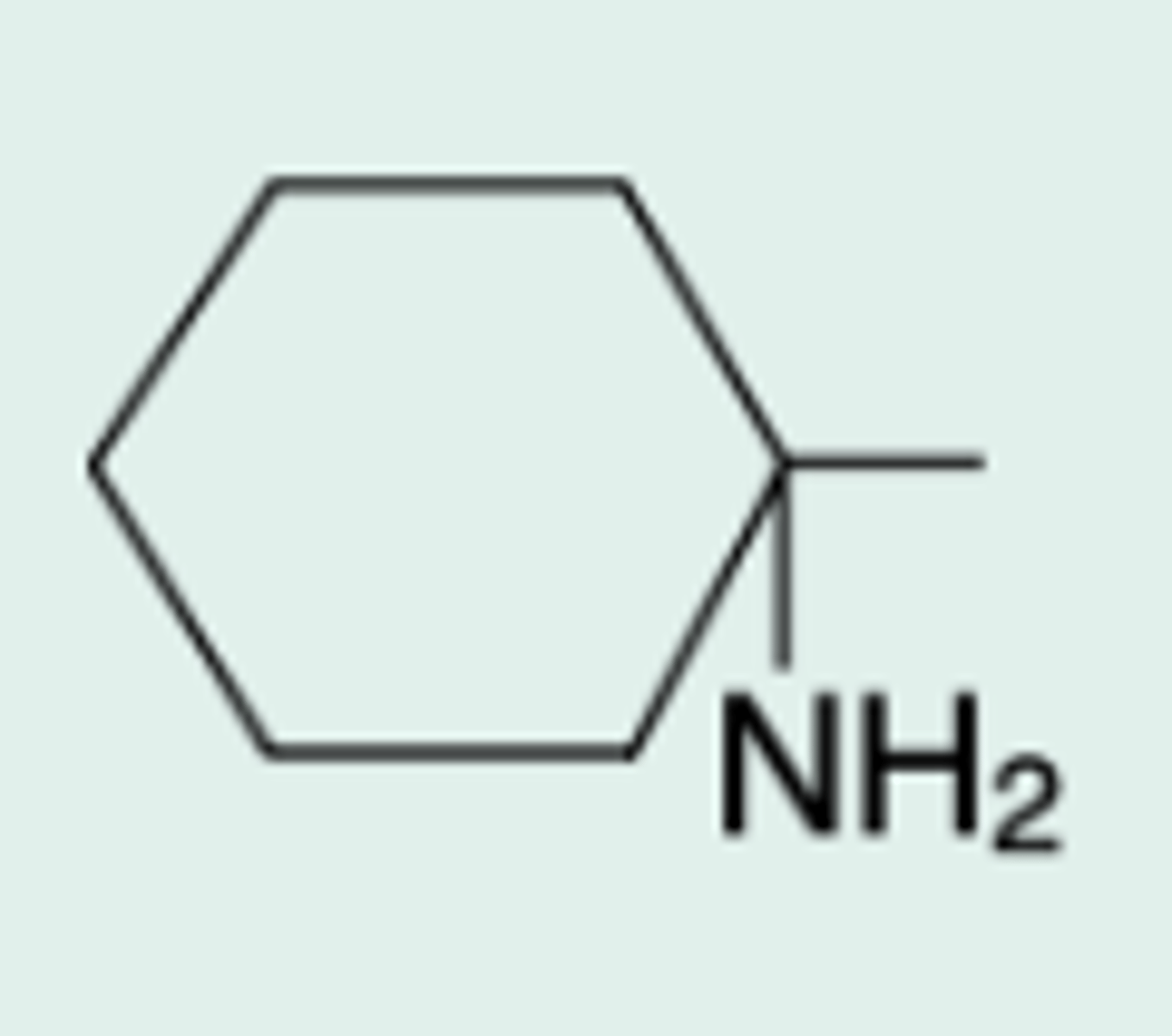
Carbenicillin
Gen Name?
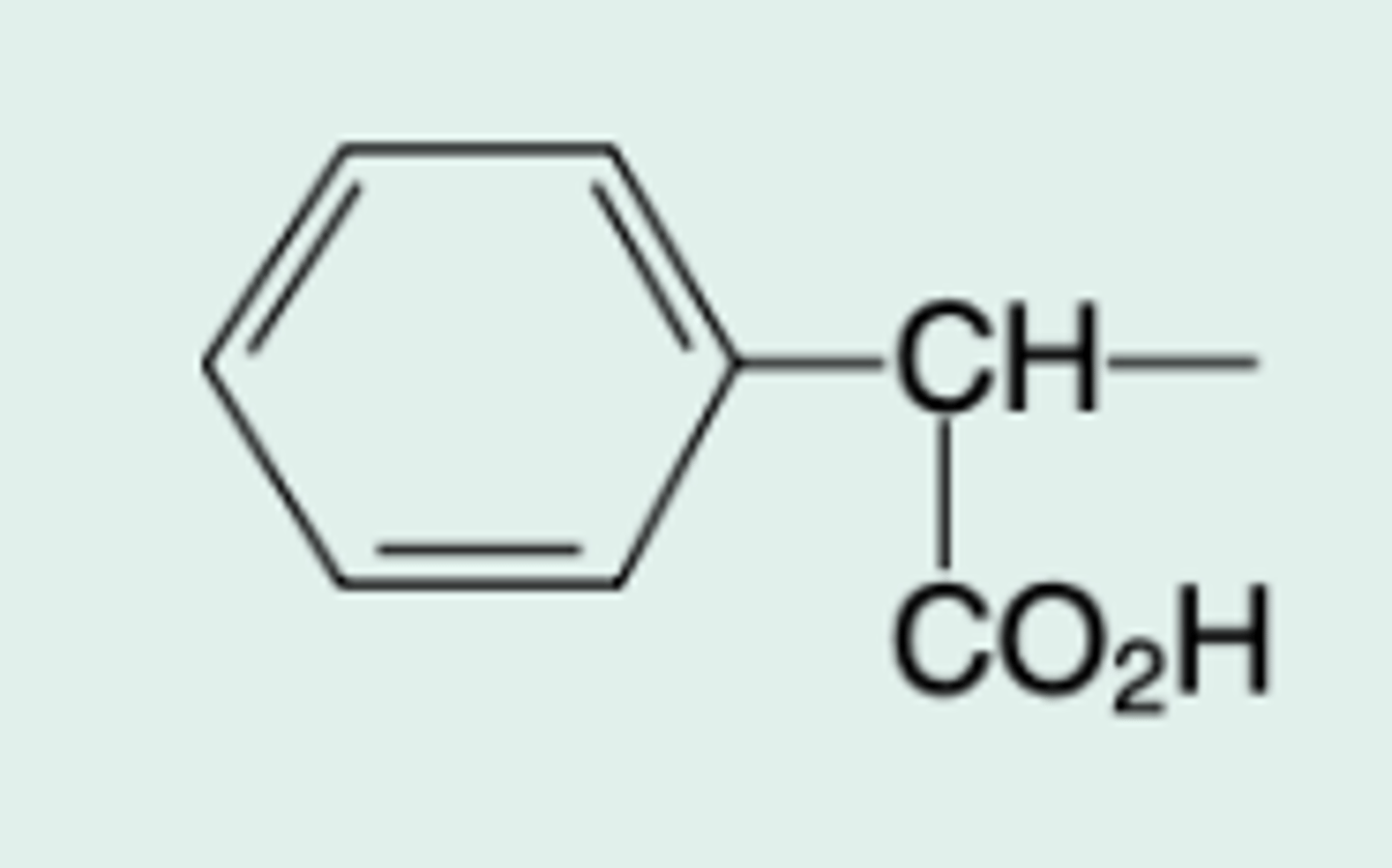
a-carboxybenzyl-penicillin
Chem Name?
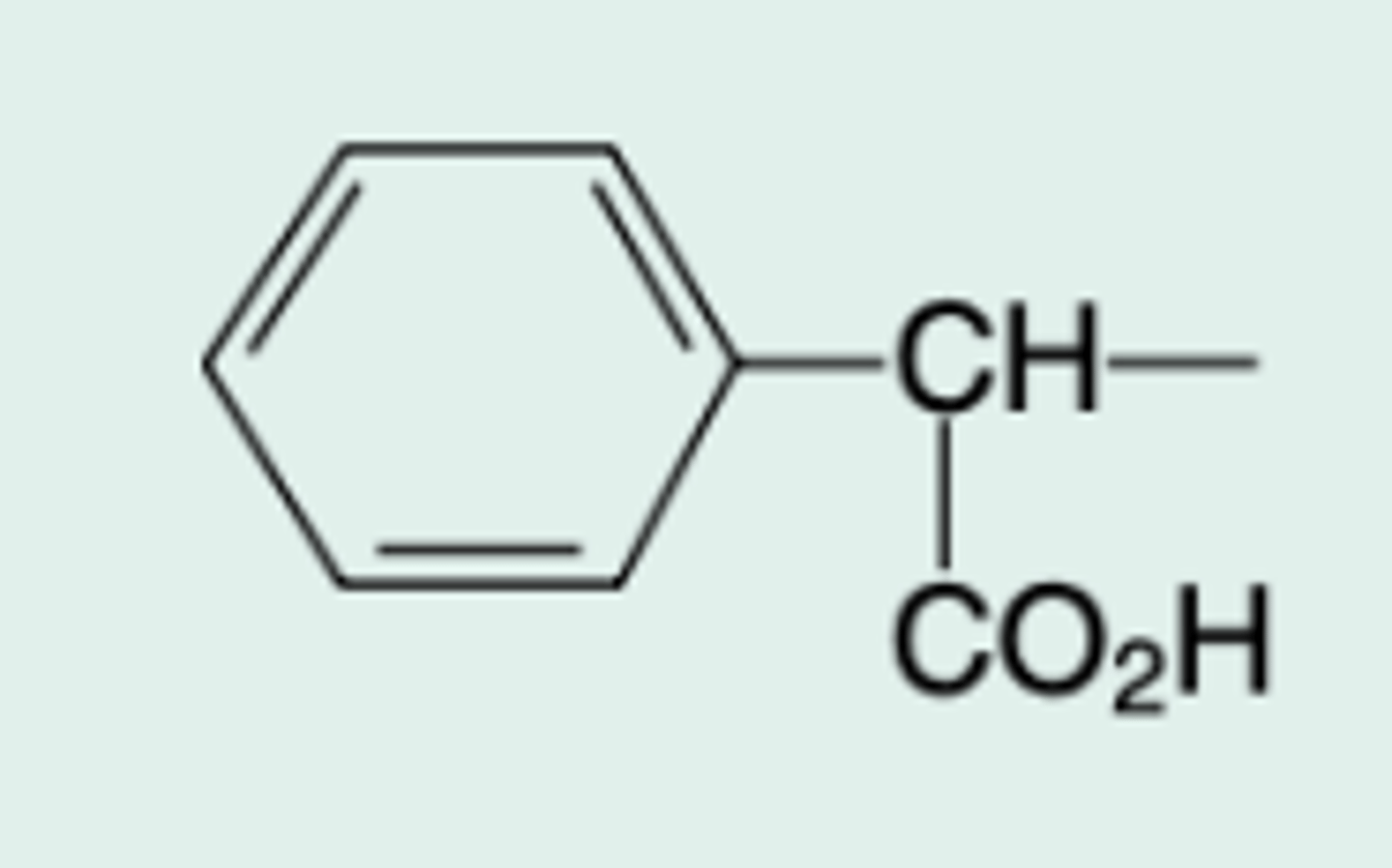
Ticarcillin
Gen Name?

a-carboxy-3-thienhyl-penicillin
chem name
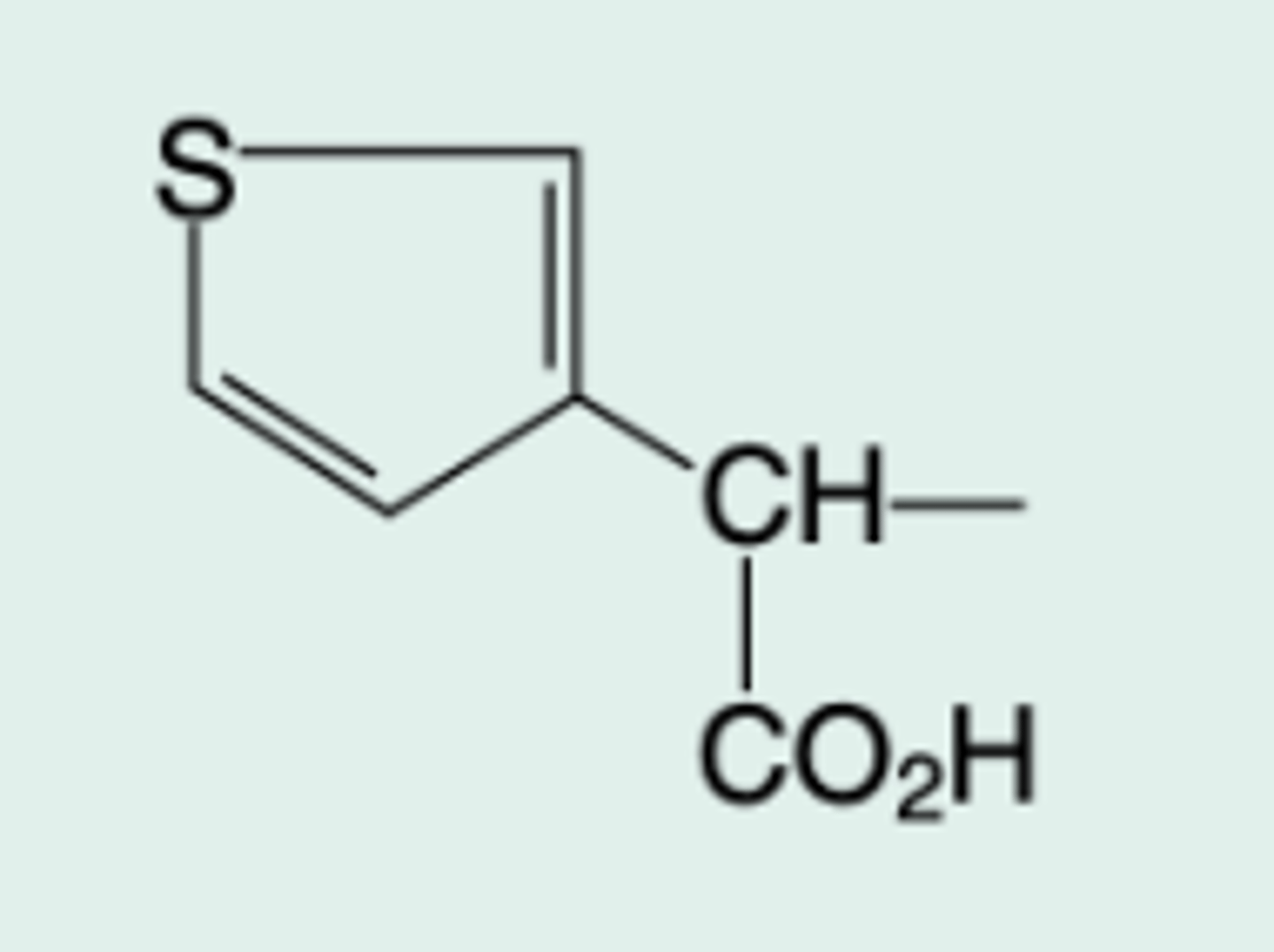
piperacillin
Gen Name
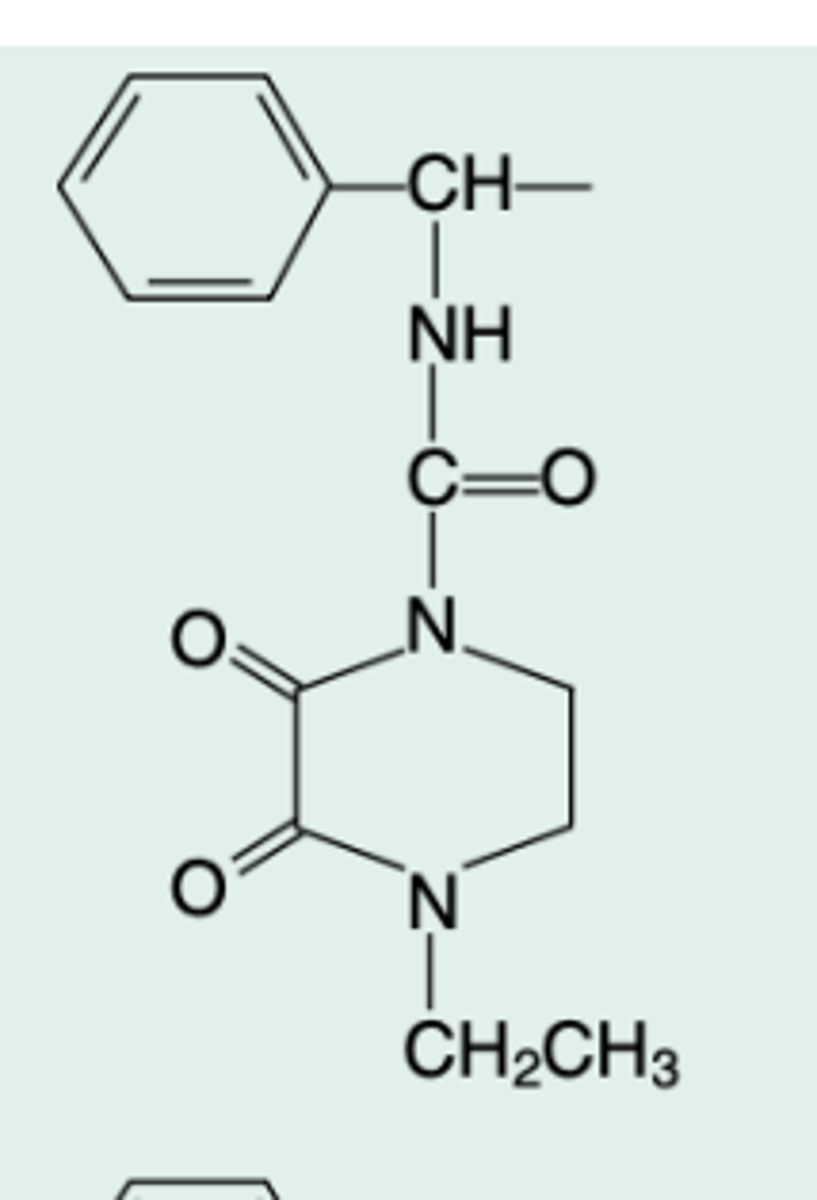
a-(4-Ethyl-2,3-dioxo-1-
piperazinylcarbonyl-
amino)benzylpenicillin
Chem Name?
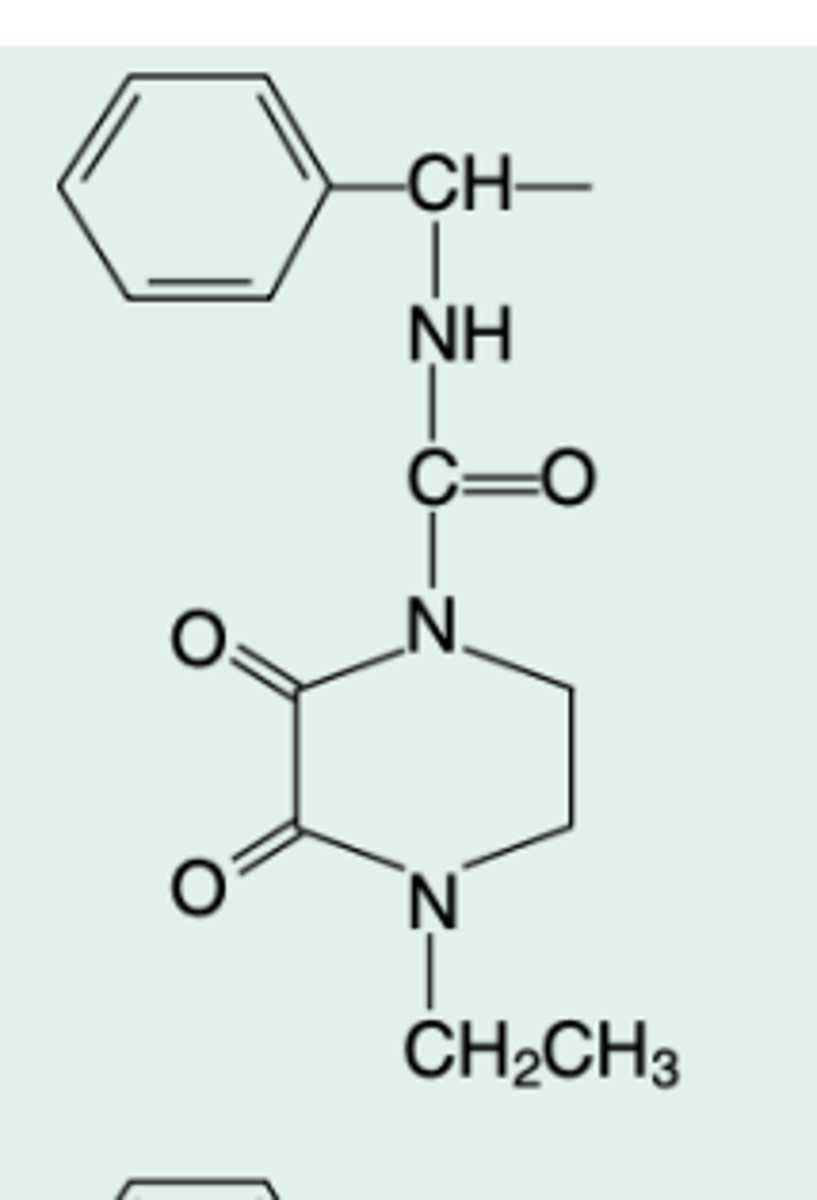
Mezlocillin
Gen Name?
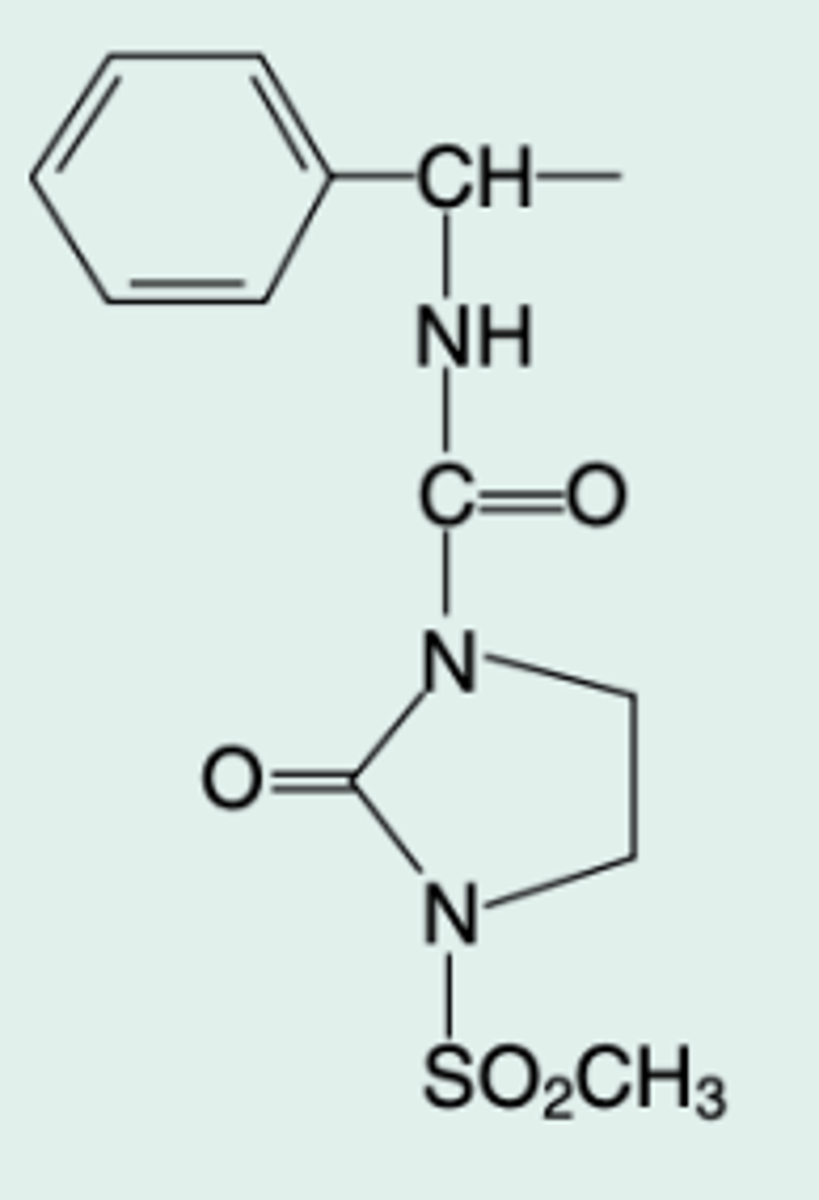
a-(1-Methanesulfonyl-2-
oxoimidazolidino-
carbonylamino)benzyl-
penicillin
Chem Name?
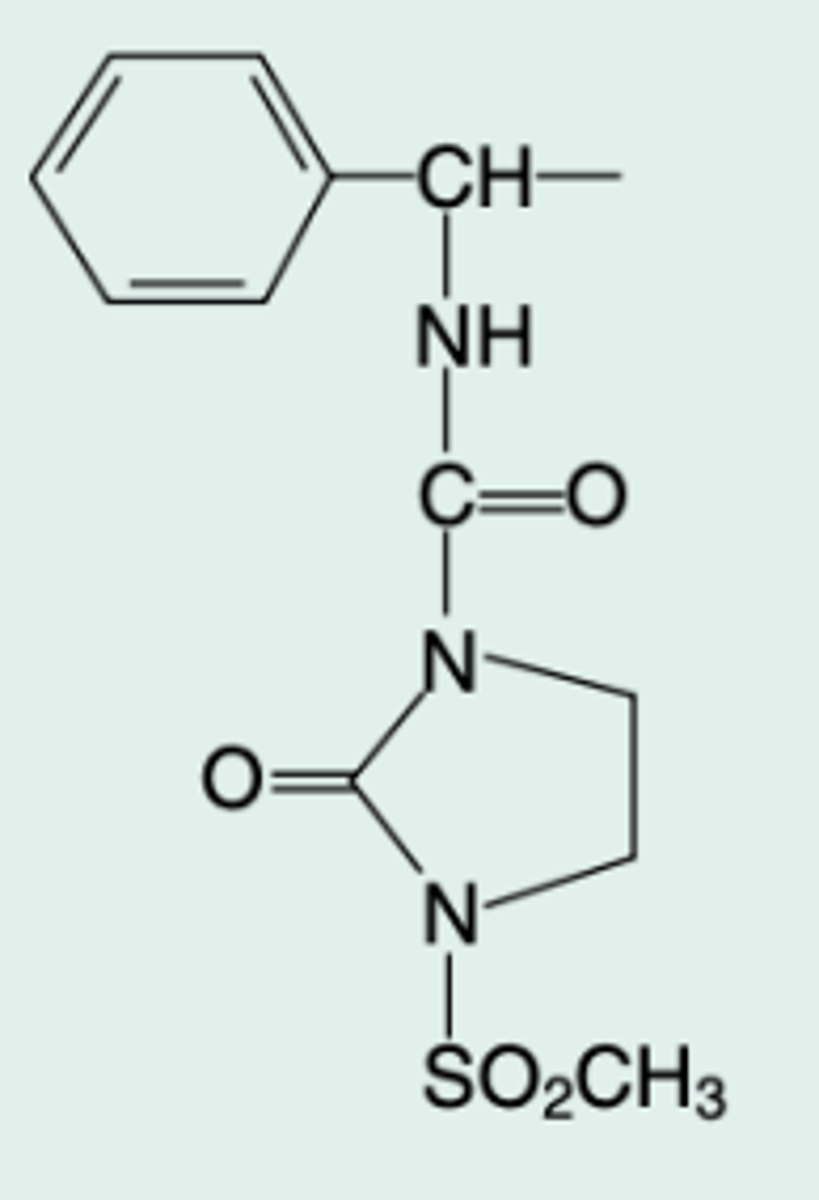
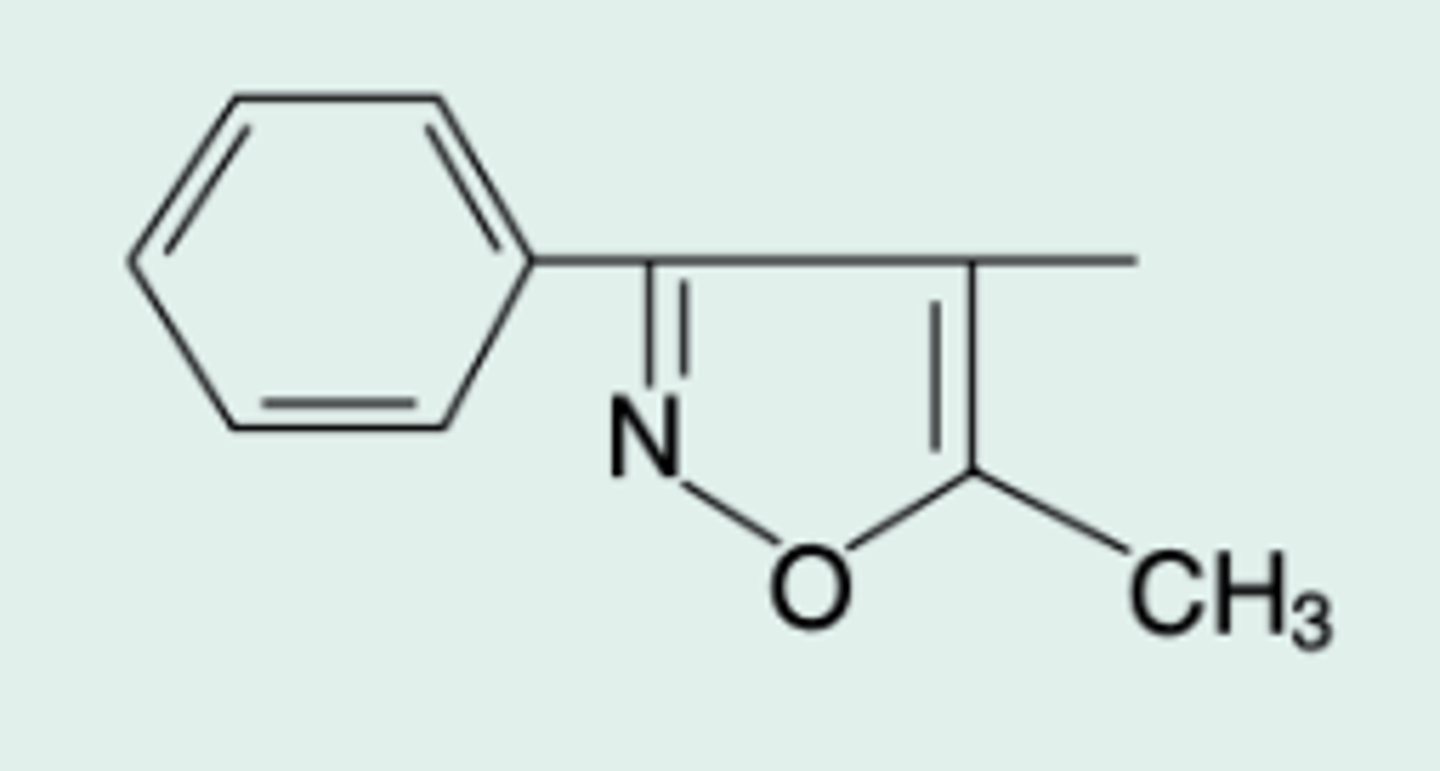
Oxacillin
Gen Name?
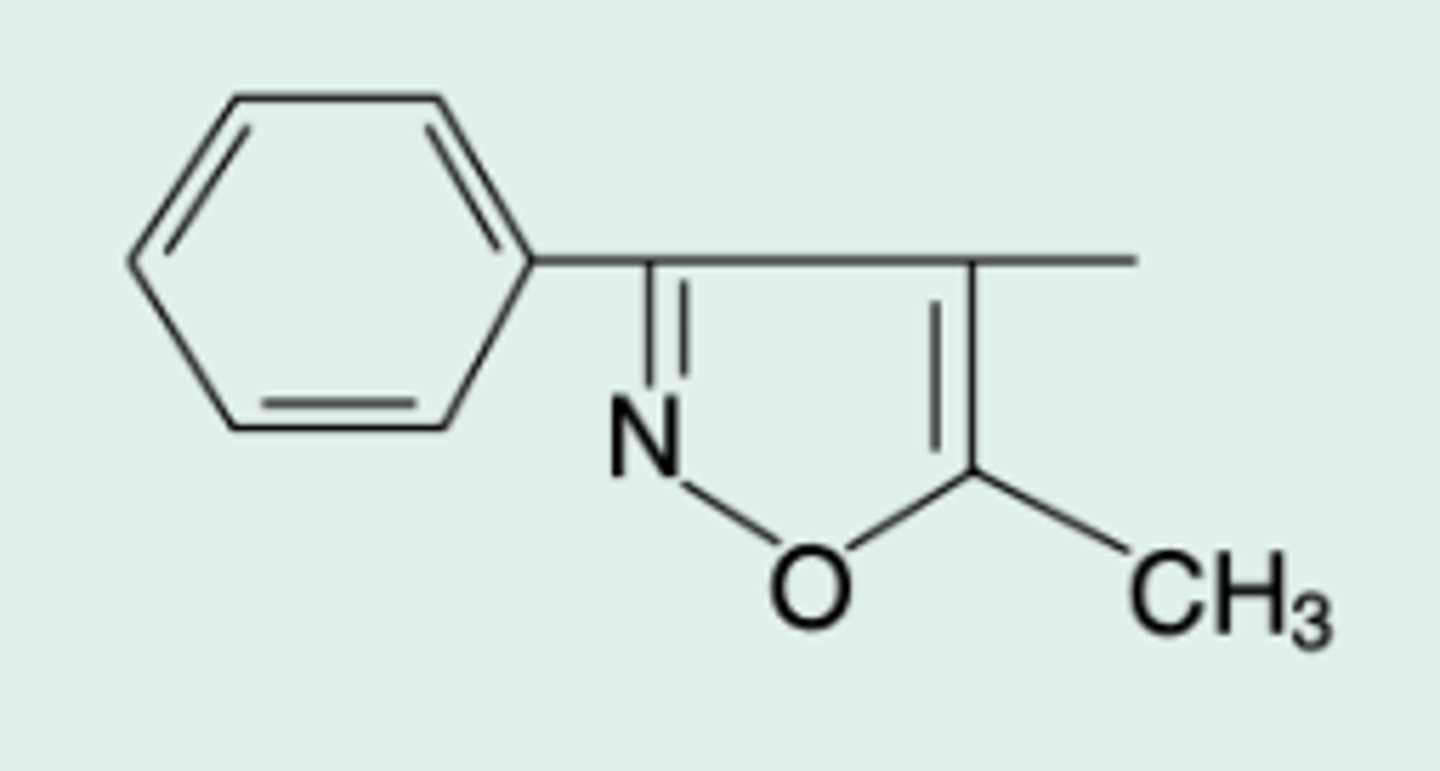
5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazoly|penicillin
Chem Name?
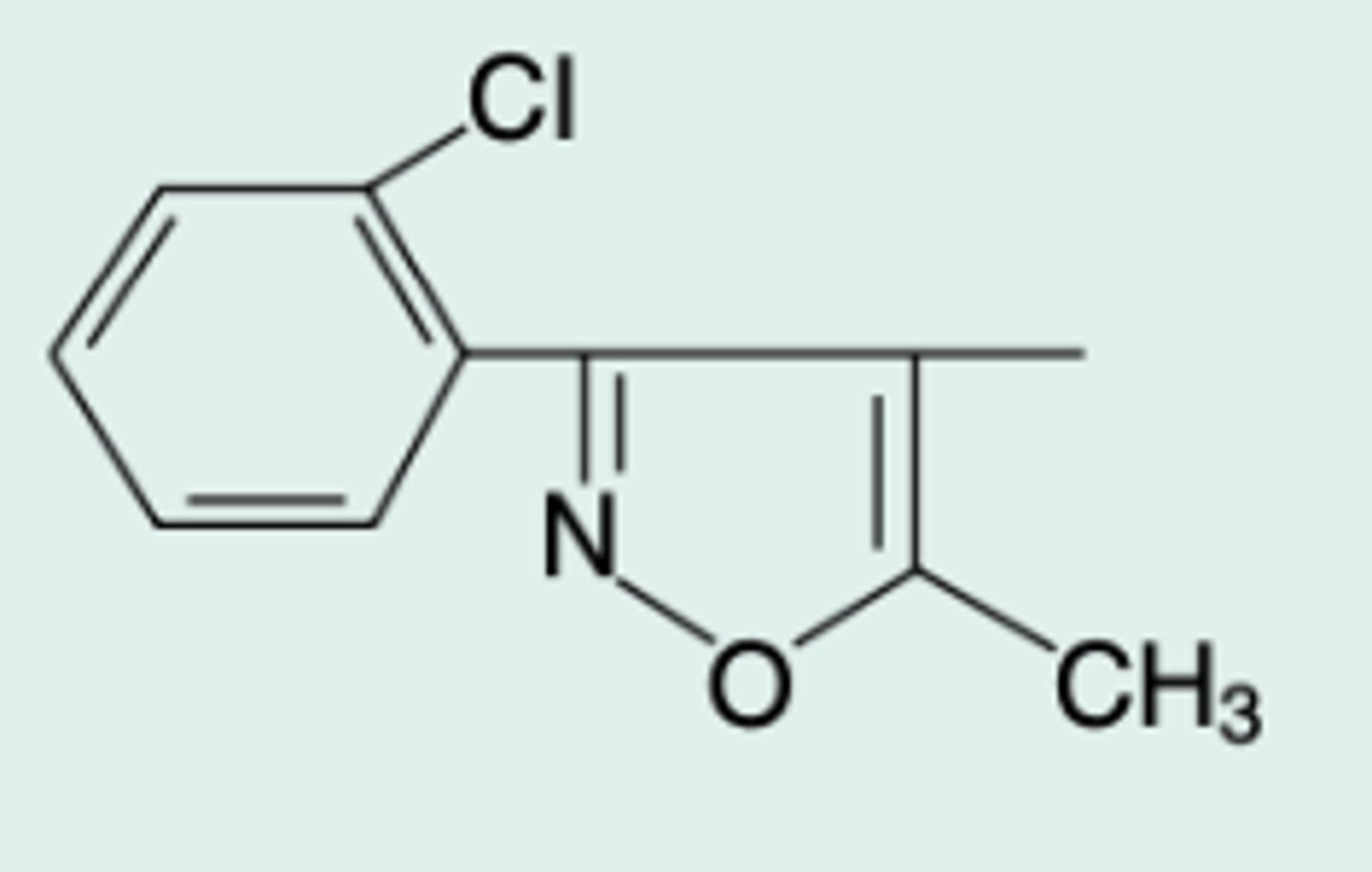
cloxacillin
Gen Name?
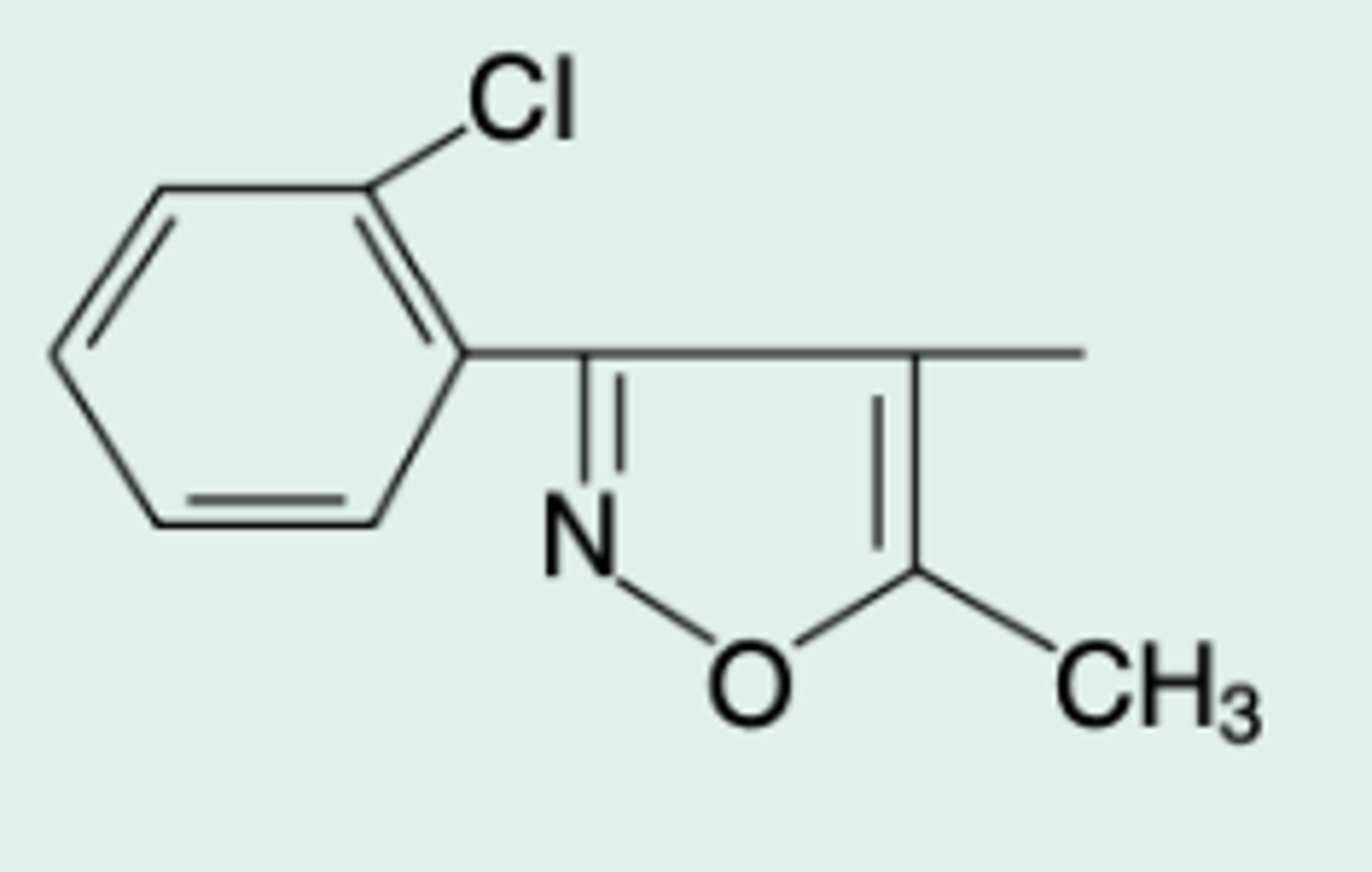
5-Methyl-3-(2-
chlorophenyl)-4-isoxazoly|penicillin
Chem Name?