Tropical Storms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are tropical storms
Intense low-pressure systems
Types of tropical storms
Typhoons
Hurricanes
Cyclones
Characteristics
Heavy rainfall
High wind speed
High waves
Storm Surges
The Eye
Wind spiralling rapidly around a calm area
Diameter
2000km
Wind speeds
Aren’t constant across the diameter of the storm, they vary with the strongest being towards the eyewall
Distribution of Typhoons
South East of Asia
Distribution of cyclones
East of Africa & South of Asia
Distribution of Hurricane
West of Africa, South East + West of North America, North of South America
Formation of tropical storms; Ocean
Tropical storms gain large amounts of moisture from oceans for the formation of clouds and precipation
Formation of tropical storms; Surface temperatures
Over 27°
Formation of tropical storms; Low wind shear
High wind shear can disrupt the organization and intensity of tropical storms.
Formation of tropical storms; Atmospheric Instability
In tropical regions, warm, moist air near the surface rises, creating instability and promoting the development of storms.
Formation of tropical storms; Coriolis Effect
The rotation of the Earth causes the air to move around the centre of the eye in a circular motion
Degrees of latitude
Form over 5° and 20° north & south of the equator = ocean water warmest temperature and the coriolis effect is the strongest
At the equator (0°-5°)
The Coriolis effect isn’t strong enough
Storms loosing energy
When they reach land/areas of cooler water
High Winds Hazards
Over 119km/h = uprooted trees, damage to infrastructure & buildings, causing loss of life/injury
Intense Rainfall Hazards
flash floods - damage property/injuries from fast moving water
Storm surge
when large volumes of water are forced inwards by low pressure (sea surface rises) and strong winds associated with tropical storms
Storm surge hazards
several metres high = flooding, beach erosion, damaging sea defences & contaminating farmland & freshwater
Coastal & River flooding
Intense rainfall and storm surges = affects to large areas of low lying land - impacts on tourism/farmland
Landslides
Triggered when soil becomes saturated due to intense rainfall = unstable = damage to infrastructure and loss of life
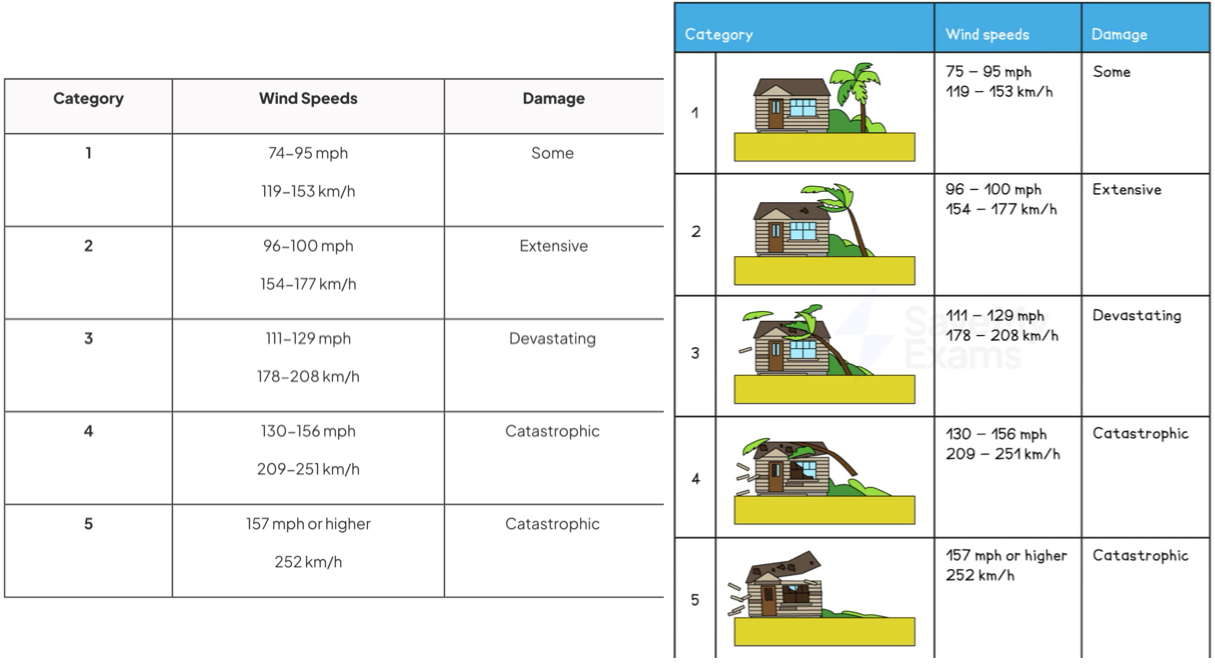
Measurement
Five point Saffir-Simpson scale based on wind speeds
Prediction
Satellites, Weather Balloons. Ocean Buoys
Data for prediction
Atmospheric Pressure, Wind Speed/Direction, Humidity, Sea Surface Temps, Ocean Currents
Use of data collected
Fed into computer models that stimulate atmospheric and ocean behaviour to predict the storm’s path & intensity
Why aren’t predictions accurate
Models although sophisticated still face uncertainties
Why is predicting the storm’s landfall difficult
Storm paths can be erratic = difficulty for precision & accuracy
What does NOAA do each year
releases long term predictions of storm activity for the upcoming season
What are NOAA predictions based on
Historical data, current/predicted climate conditions (ocean temps & atmospheric conditions