cell biology final
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
its chemistry
what about a ligand determines its solubility
hydrophilic ligands
neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, amino acids, neuropeptides are all examples of what kinds of ligands
true
true or false: acetylcholine receptors can be ligand gated ion channels
ligand binds receptor at outside surface of cell --> binding sets off chain of intracellular signaling events --> cellular/metabolic effect
cell signaling via cell surface receptors (basic pathway)
excitatory synapse
type of synapse that causes depolarization
inhibitory synapse
type of synapse that causes hyperpolarization
false, neurotransmitters can bind to several different receptors
true or false: a specific neurotransmitter can only bind to one specific receptor
indirect
G-protein-coupled receptors are an example of what kind of transmission
direct transmission
if a ligand binds to a receptor (that is also an ion channel) and this induces opening of the ion channel, this is an example of what kind of transmission
indirect transmission
if a ligand binds to a receptor which causes intracellular effects that eventually open an ion channel, this is an example of what kind of transmission
transmembrane protein associated with a G protein
indirect receptor could be described as
false
true or false: neurotransmitters are the only ligands that use G-protein-receptor signaling
hormones
chemical messengers released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands
slow
hormone's effects are quick or slow
steroid and thyroid hormones
what kind of hormones penetrate plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors
non-steroid hormones
what kind of hormones bind to membrane receptors
on plasma membrane
where does hormone receptor binding occur
G protein
what does hormone receptor binding activate (indirect transmission)
cAMP is produced
what happens after the G protein is activated (general pathway)
metabolic reaction
what is the target cell's function (indirect transmission)
activated enzymes
what catalyze metabolic reactions
7 times
how many times does G protein coupled receptor pass through membrane
ICF
GEF is located in the ECF or ICF
alpha subunit
which subunit of G protein activates adenylyl cyclase enzyme
GTP
alpha subunit of G protein is activated because it has what molecule attached
adenylyl cyclase
what enzyme synthesizes cAMP
ATP
hydrolysis of what molecule leads to cAMP synthesis
GTP
G protein is activated when it has what molecule attached
GAPase activating protein (GAP)
what protein catalyzes GTP hydrolysis and returns G protein to resting state
glycogen phosphorylase
what enzyme catalyzes breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate
epinephrine
amino acid derivative produced by adrenal medulla
kinases
when these type of enzymes are used, the signal can be amplified
glucose can enter bloodstream and be taken up by cells that need energy
what is the net effect for cell of epinephrine using G protein
fast
speed of effect of G-protein coupled receptor
false
true or false: if ligand levels are low, cell signaling will be low using indirect transmission
very large
even just binding a couple ligands to a receptor, using indirect transmission, effect can be
cAMP
during 2nd messenger system, what is the main enzyme that brings the signal from outside to inside
ECF
where are 1st messengers located
ICF
where are 2nd messengers located
false
true or false: cAMP is the only 2nd messenger
contraction, secretion, metabolism
examples of cellular response to 2nd messengers include
changes its conformation
how does phosphorylating a protein activate a protein
Ser, Tyr, Thr
most common phosphorylation targets (amino acids)
monomer
what form of the receptor tyrosine kinase is inactive
dimer
what form of the receptor tyrosine kinase is active
ECF
location of ligand binding domain
ICF
location of tyrosine kinase domain
once
how many times does receptor tyrosine kinase pass through membrane
true
true or false: growth factors often bind to receptor tyrosine kinases
growth/differentiation and immune cell proliferation
growth factors have what function in adults
no
can animal cells grow without growth factor
kinases autophosphorylate each other
what occurs after receptor tyrosine kinases are dimerized
phosphorylated tyrosine residues
downstream factors recognize what part of tyrosine receptors
phospho-tyrosine binding sites (SH2 domains)
proteins that bind receptor Tyr kinases have what binding sites
false
true or false: once a ligand binds to a tyrosine kinase, each downstream effect is the same
receptor tyrosine kinases
what are MAPK, PI3, PLC all activated by
Ras-GEF
what protein exchanges GDP for GTP to activate Ras
Raf
when Ras is active, what protein does it activate
GTP
Ras is active when it has what molecule attached
GDP
Ras is inactive when it has what molecule attached
Grb2
in Ras pathway, what protein has the SH2 domain (binds directly to receptor tyrosine kinase)
MEK (map kinase kinase) --> ERK (MAP kinase) --> cellular response
once Raf is activated, it causes downstream activation of what molecules
phosphorylates transcriptional activators
how can ERK influence transcription
suppresses apoptosis and promotes cell survival
main function of PI3 kinase pathway
regulates cell cycle
main function of phospholipase C pathway
true
true or false: many signaling pathways usually work in parallel in the cell
non-receptor tyrosine kinases are not receptors themselves (attached to receptors)
how are non-receptor tyrosine kinases different than receptor tyrosine kinases
non-receptor tyrosine kinases
cytokines and growth hormone use what kind of cell receptors
extracellular matrix
during integrin signaling, what is the ligand
posttranslational
what type of modification is ubiquitination
groups (like phosphate) are added to it
how is a protein targeted for ubiquitination
proteasome
when a molecule is targeted for ubiquitination, what is the protein that actually degrades it
ligand and receptor both membrane bound
during contact-dependent signaling, what parts are membrane bound
false
true or false: contact-dependent signaling requires ATP hydrolysis
false
true or false: a ligand-receptor pathway can only be inhibited at one location
feedback loops
how is the activity of pathways regulated
positive feedback
what type of feedback
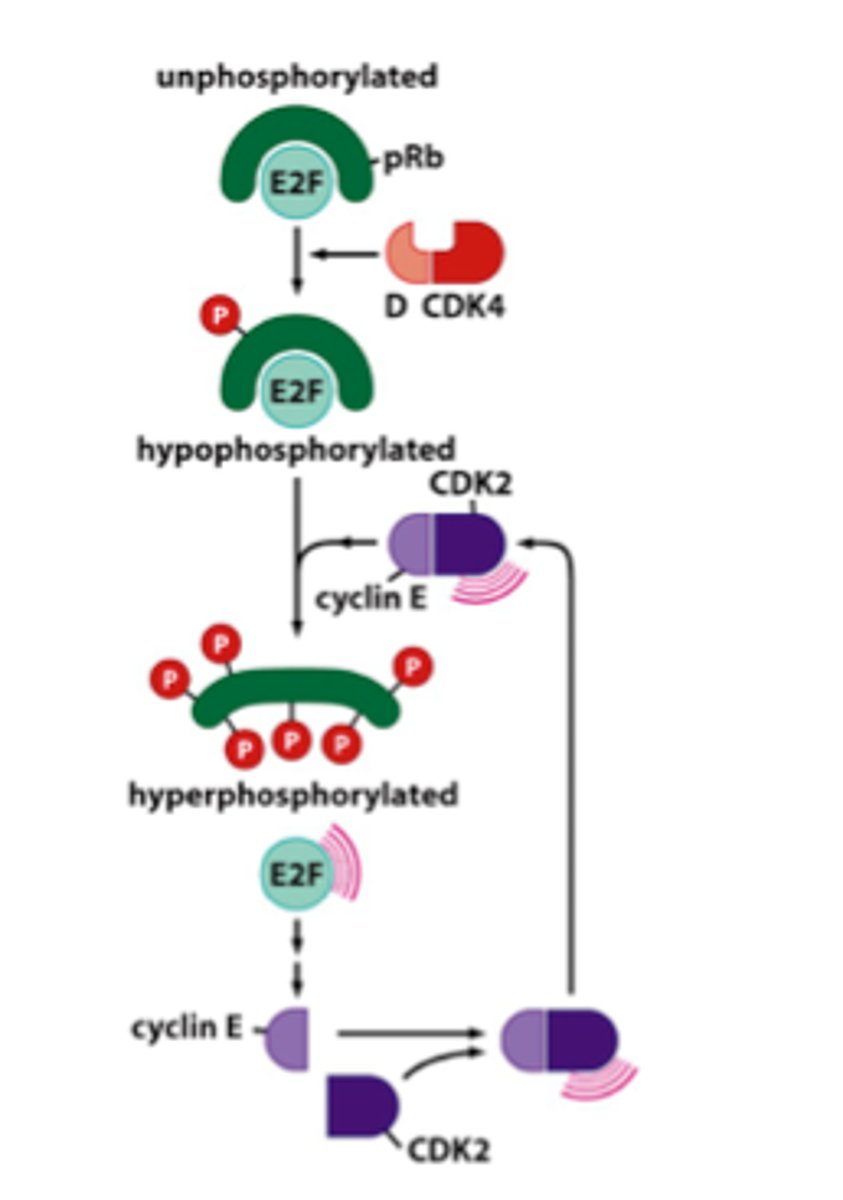
negative feedback loop
what type of feedback
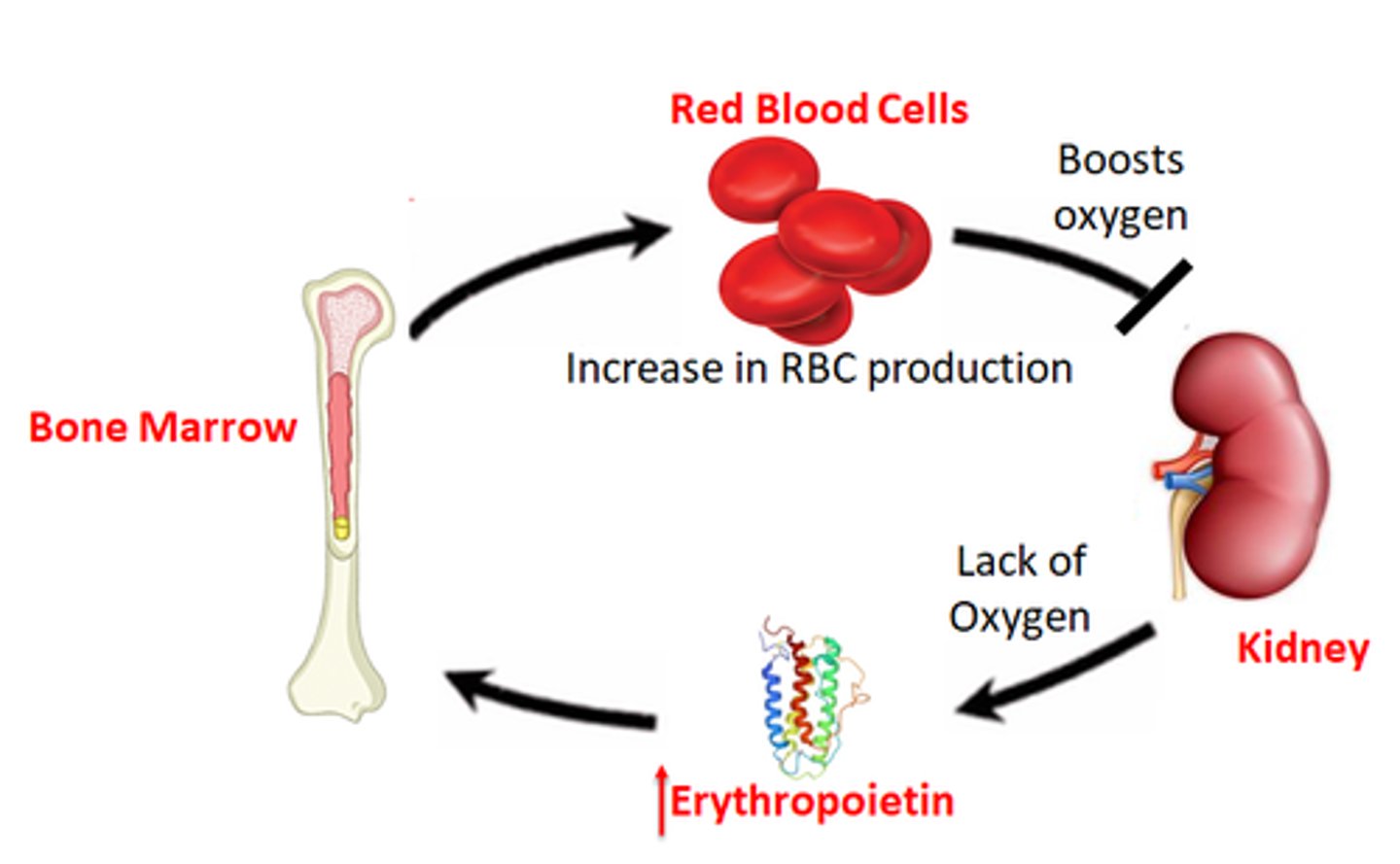
differentiation or apoptosis
examples of why a cell would want to inhibit a pathway
cell signaling networks aren't regulated correctly
cancers, developmental disorders, endocrine issues can be linked to what issue
G1, S, G2, M
what 4 stages are in the cell cycle
no growth factor (and other factors)
what causes cell to go into quiescence
false
true or false: if the growth factor is removed during any point of interphase, the cell cycle will stop
restriction point
what is the stage in which cell cycle could stop depending on presence of certain proteins
false
true or false: once the cell cycle has begun, it cannot be stopped
DNA damage and spindle assembly checkpoints
what 2 check points regulate the cell cycle
checks chromosome alignment during metaphase
what does the spindle assembly checkpoint do
M phase (mitosis)
MPF increases Cdk activity which induces entry into what phase
steadily, rapidly
cyclin B is expressed _______ while Cdk1 is expressed _______
interphase
what phase does the cell enter into after mitosis
cohesin proteins
primary proteins that contribute to chromosome segregation
false, they are still bound at the centromere
true or false: when cohesins are phosphorylated they are completely unlinked to chromatids
condensins
what proteins drive chromosome condensation
cohesin, condensins
_______ link sister chromatids together and ________ pack chromatin into loops
CycB/Cdk1
what activates condensin
true
true or false: condensin requires ATP hydrolysis to function
center of chromosome
where are condensin stacks located
proteins of nuclear pore complex
Cdk1/cyclin B phosphorylates what
disassembly of pore complex and detachment of inner nuclear membrane
what does phosphorylating proteins of the nuclear pore complex cause
prometaphase
during what phase does breakdown of nuclear lamins occur