APH CH 13 Cardiovascular system
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Cardiovascular System
Function
- Homeostasis by transportation
- Transports: oxygen, nutrients, electrolytes, heat, CO2
Cardiovascular System
3 Parts
heart (central)
blood vessels (peripheral)
blood (transport median)
Arteries-
carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
Veins-
carries deoxygenated blood to the heart
Right side-
Pulmonary circuit- gets rid of CO2 and picks up O2 (gas exchange)
Left side-
Systemic circuit- pumps blood to the body (with O2), works harder, BP
Pericardium –
Thick fibrous membrane that encloses the heart and the proximal ends of the large blood vessels
Visceral pericardium –
Thin membrane directly covers the heart
Epicardium-
outer layer
Myocardium-
thick, muscular middle layer
Endocardium-
Inner layer
Atria (atrium: singular)-
thin wall, receives blood from body or lungs (right and left)
Ventricle-
thick, muscular wall, delivers blood to body (right and left)
Valves-
Allows blood to flow in only one direction
Bicuspid / Mitral Valve-
Left side, between left atrium and left ventricle
Tricuspid Valve-
Right Side, between right atrium and right ventricle
Semilunar:
Pulmonary Valve-
Right side, allows blood to leave right ventricle to lungs via pulmonary artery
Semilunar:
Aortic Valve-
Left side, allows blood to leave the left ventricle to body via aorta
left ventricle has _____ walls
thicker
Apex-
bottom point of the heart
Base-
top portion of the heart
Resting heart rate range ______ BPM
40 - 90
Average resting heart rate _____ BPM
60-70
Maximum pulse (heartbeat) is
220 – age
Exercise should be between _________ of your max HR to work your cardiovascular system for 30-45 mins
60% - 85%
Systole –
“SQUEEZE”
Diastole –
“DIALATE”
Ventricles and Atria work in
opposition
When the atria contract,
the ventricles relax
When the ventricles contract,
the atria relax
The measurement of atria systole and
ventricle diastole is called
blood pressure
Equipment used for measuring blood pressure is a __________ and __________
stethoscope ; sphygmomanometer
The Heart Sounds
– caused when valves ________!
close
1st “Lubb” –
A/V Valves (Bi and Tri) closes
2nd “Dubb” –
Semilunar Valves (pulmonary and aortic) closes
A ______ ______ is when one or more of your valves don’t close properly causing the backward flow of blood. The sound can be heard while using a stethoscope.
heart murmur
ECG / EKG =
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram records electrical changes that occur in the ________ during the cycle
myocardium
P Wave-
Atrial systole
depolarization of the atria
initiated by the SA node
QRS Complex-
- Ventricular systole
Depolarization of the ventricle
repolarization of atria
T Wave-
Repolarization of ventricle
ventricular diastole
Normal ECG below
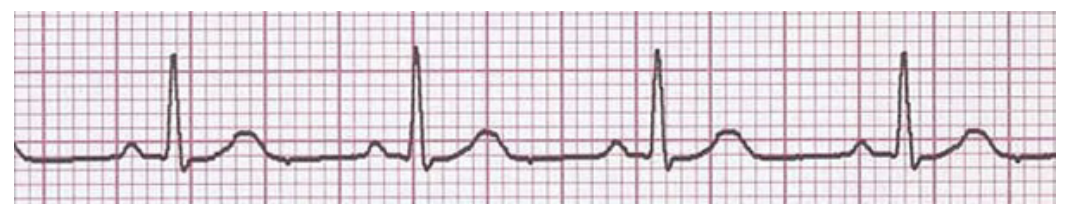
An ECG with Tachycardia (fast)
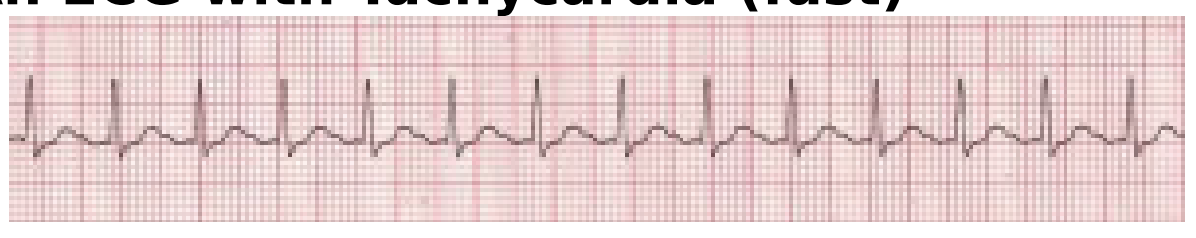
An ECG with Bradycardia (slow)

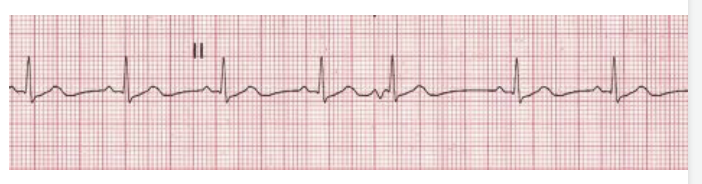
PAC – premature atrial contraction
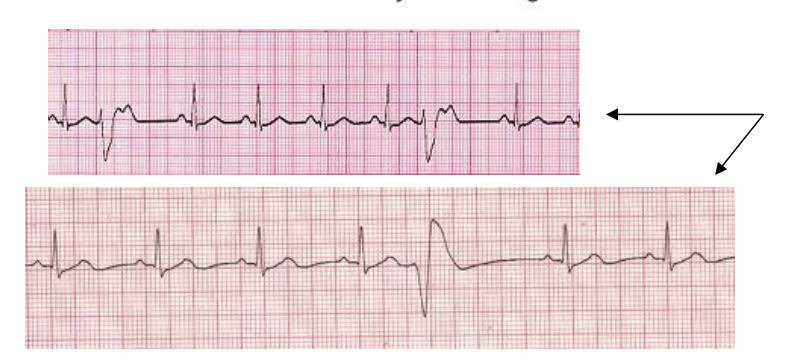
PVC- Premature ventricular contraction
Natural Pacemaker –
S-A Node
(sinoatrial node)
Parasympathetic Nervous System –
Regulates HR – depending on the body’s needs
Cardiac Control Center –
Medulla Oblongata (brain stem)
- Also impulses from cerebrum (entire brain) & hypothalamus (diencephalon)
Arteries
Thick walls - 3 layers
Tunica interna
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Arteries
High Pressure
(except for Pulmonary Artery)
Arteries
Carry oxygenated blood
(except for Pulmonary Artery)
Arteries
Middle tunica layer has
thick walls due to smooth muscles
Vasoconstriction
Diameter reduces as smooth muscles contract
Vasodilation
Diameter increases as smooth muscles relax
Arterioles
Arteries eventually give rise to smaller, finer branches
Arterioles
Larger arterioles have three layers similar to arteries
Arterioles
Walls become thinner as they approach capillaries
Capillaries
Smallest diameter blood vessel
Capillaries
Where gas exchange (diffusion) takes place, extremely thin walls
Capillaries
Denser areas of capillaries occur where metabolism rates are higher
- Muscles and nerves have more capillaries
- Cartilage, cornea, epidermis lack capillaries
Capillaries
Connects arterioles (lead away from the heart) to venules (lead back to the heart)
Venules
Small branches leading from capillaries that supply blood to veins
Veins
Bring blood back to the heart under low pressure
Veins
Carry deoxygenated blood (except for pulmonary vein)
Veins
Has three distinct layers like arteries, but the middle layer is poorly developed
Veins
Veins have thinner walls, less smooth muscle, less elastic tissue
Veins
have valves to prevent back flow
Veins
Lumen (hole) has greater diameter
Arteries
1. Common Carotid (rt/lf)
2. Subclavian (rt/lf)
3. Brachiocephalic
4. Aortic (arch)
5. Common Iliac (rt/lf)
6. Brachial (rt/lf)
7. Radial (rt/lf)
8. Ulnar (rt/lf)
9. Axillary (rt/lf)
10. Femoral (rt/lf)
11. Popliteal (rt/lf)
12. Anterior / Posterior Tibial (rt/lf)
Veins
1. Internal Jugular (rt/lf)
2. Brachiocephalic (rt/lf)
3. Subclavian (rt/lf)
4. Vena Cava (superior/inferior)
5. Axillary (rt/lf)
6. Brachial (rt/lf)
7. Radial (rt/lf)
8. Ulnar (rt/lf)
9. Common Iliac (rt/lf)
10. Femoral (rt/lf)
11. Greater Saphenous (rt/lf)
12. Popliteal (rt/lf)
Dietary Fats
Not all fats are created equal
Ex: Saturated, Polyunsaturated, Monounsaturated and Trans fat
Your Body NEEDS Fats for
Energy
Protection/cushioning
Cell Membrane
Nervous system (myelin)
Carried Fat-soluble Vitamins- A, D, E, K
Hormones
Blood Clotting
Maintain healthy hair & skin
Protects organs
Body insulated
Sense of fullness after a meal
Extra calories =
weight gain and obesity
Obesity-
diabetes, heart disease, cancer, gallstones, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis
Increase blood cholesterol (sat and trans) =
Coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis
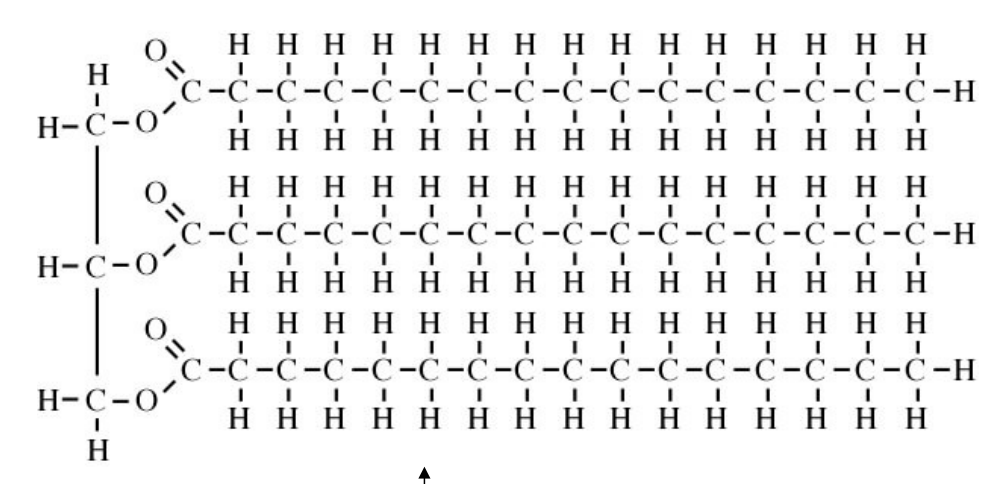
Saturated fats
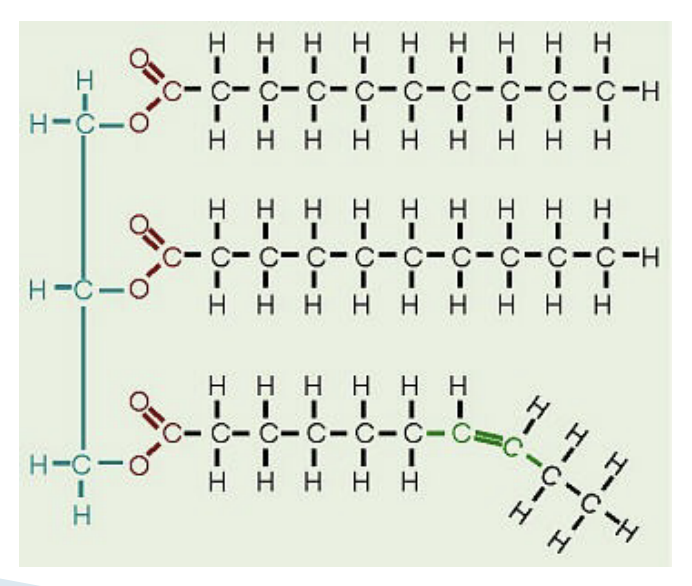
Unsaturated fats
Healthy Fats are
liquid at room temperature
Healthy Fats
Monounsaturated –
Ex- olive oil, peanuts, canola oils, avocados, most nuts
Healthy Fats
Polyunsaturated-
Ex- Vegetable oil (safflower, corn, sunflower, soy, and cottonseed oils)
Healthy Fats
Omega-3 fatty acids-
Cold water fish- salmon, mackerel, herring; flaxseed or flax oil, walnut oil, small amounts in soybean and canola oils
Harmful fats are
usually solid or waxy at room temp
Harmful fats
Saturated Fats-
ex: animal products (red meat, poultry, butter, whole milk) coconut, palm, other tropical oils
Harmful fats
Trans Fats-
Preserves foods longer; Adding hydrogen to vegetable oils through hydrogenation; Body’s enzymes unable to break down
ex: bake good (cookies, crackers, cakes), fried foods (doughnuts, french fries), margarine
Harmful fats
Dietary Cholesterol-
Body naturally makes it; also comes from animal products- meat, chicken, seafood, eggs, dairy products, butter
Total Cholesterol =
> 200
Blood Cholesterol
LDL (bad) =
> 100
can build up on the walls of your arteries and increase your chances of getting heart disease
Blood Cholesterol
HDL (good) =
< 60
protects against heart disease by taking the "bad" cholesterol out of your blood and keeping it from building up in your arteries. Exercise! & reduce trans fats
Blood Cholesterol
Triglycerides =
> 150
chemical form in which most fat exists in food and the body; contribute to atherosclerosis
Blood flows
right to left
Tricuspid valve has __ flaps
3
Bicuspid has ___ flaps
2
Systole number is ______ than diastole number
higher
Hypertension is when
walls of arteries start to break down
Hypotension is when there is
not enough blood flowing through the blood vessels
Heart is ______ of brain and spinal cord
independent
Arrhythmia -
abnormalities of heart beat
Purkinje fibers
activate muscles for a greater contraction embedded in myocardium and endocardium