Psychology Unit 5 Flashcards: Understanding Anxiety and Mood Disorders
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Personality
An individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
Classic Perspectives on Personality
Psychoanalytic theories, humanistic perspectives, trait theories, cognitive perspectives, behaviorist perspectives, and biological perspectives
Psychoanalytic theory
A theory developed by Freud that attempts to explain personality, motivation, and mental disorders by focusing on unconscious determinants of behavior - includes id, ego, and superego
Id (Freud)
Innate biological instinct and urges; self serving, irrational, and totally unconscious
Ego (Freud)
Rational thought; controls & channels the id; reality principle
Superego (Freud)
Represents the conscience, holds rules, values for socially acceptable behavior
Reality principle (Freud)
Tendency of the ego to postpone gratification until it can find an appropriate outlet
Sigmund Freud
Austrian physician whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
Humanistic perspective
The psychological view that assumes the existence of the self and emphasizes the importance of self-awareness, subjective experiences, and personal growth
- Contrasts with deterministic views
- Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers are principle humanistic perspective psychologists
Abraham Maslow
Humanistic psychologist known for his "Hierarchy of Needs" and the concept of "self-actualization"
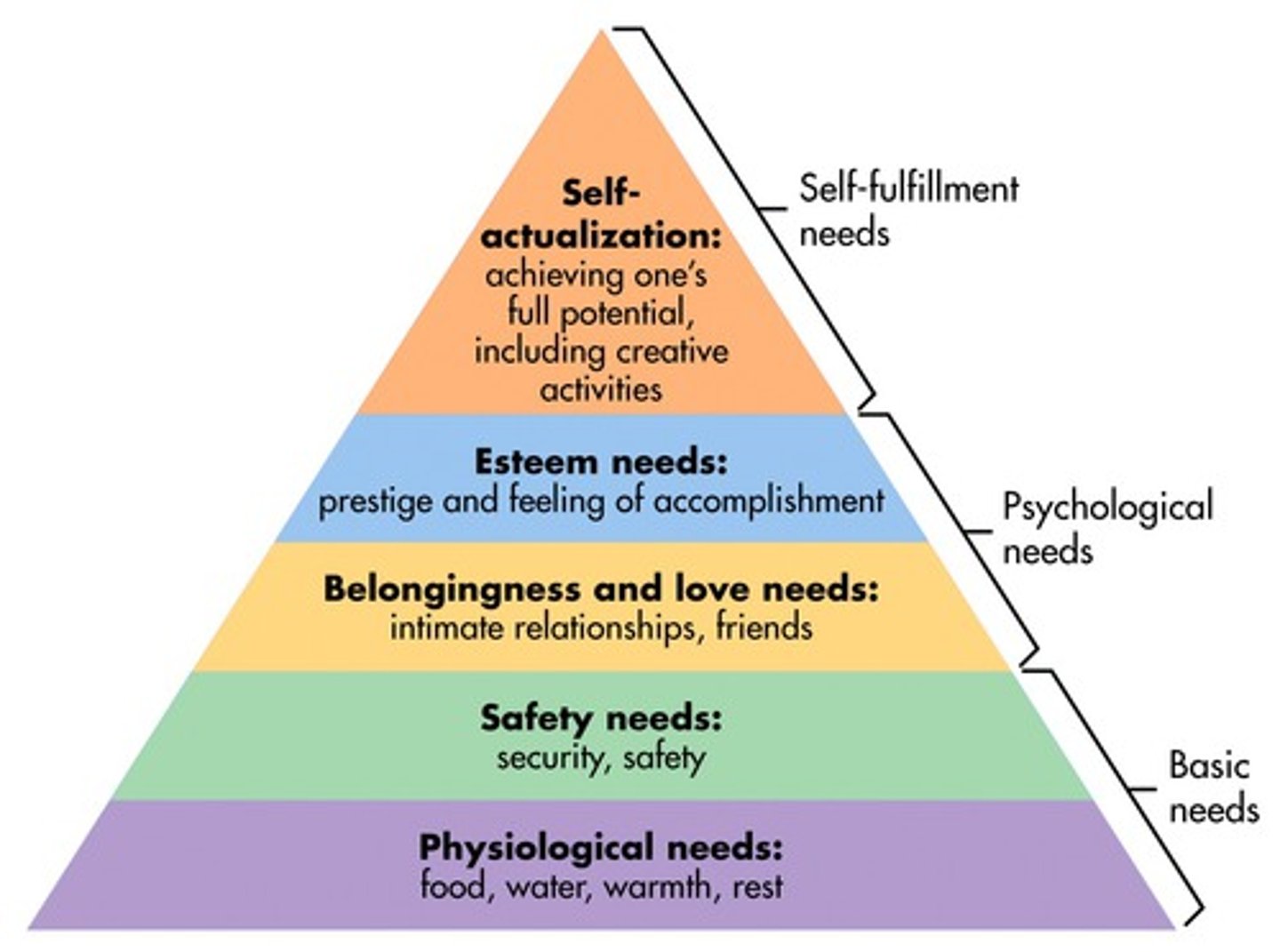
Hierarchy of Needs (Maslow)
Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with physiological needs that must first be satisfied before higher-level safety needs and then psychological needs become active
Hierarchy of Needs Representation (Maslow)
Carl Rogers
Humanistic; self-concept and unconditional positive regard drive personality
Person-centered perspective (Rogers)
People are basically good, and given the right environment their personality will develop fully and normally
Trait theory of personality
Personality consists of a set of traits which are characteristics that vary between people and are stable over the course of the lifetime.
Key: NO ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES. Very little personal control over personality, personality is hereditable and predictable
- Gordon Allport is principle trait theory of personality psychologist
Gordon Allport
Trait theory of personality; 3 levels of traits: cardinal, central, and secondary
Cognitive perspective
Role of thought processes and cognitive patterns on shaping personality
How individuals perceive, interpret, and make sense of experiences
Behaviorist perspective
Observable behaviors and the impact of the environment on personality
- Downplays role of internal mental processes
- B.F Skinner and John B. Watson are principle Behaviorist perspective psychologists
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorist that developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats
Operant Conditioning (Skinner)
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
John B. Watson
Behaviorism; emphasis on external behaviors of people and their reactions on a given situation; famous for Little Albert study
Little Albert Study
Little Albert learns to make associations between stimuli in the environment and reflexes; Albert shows little fear with dog, monkey, or burning newspaper, neutral stimuli since he hasn't learned to fear anything; Shows Albert a white rat while making loud clanging noise, which upsets Albert, who eventually associates white rat with being upset; Proves fear is learned.
Biological perspective
The psychological perspective that emphasizes the influence of genetic and physiological factors on personality
- Includes role of brain structure, heritability of traits, and temperament
Contemporary Perspectives of Psychology
Cognitive-behavioral, psychodynamic, humanistic, physiological (biological), social-cognitive, and cultural
Cognitive-behavioral perspective
Combination of the role of thought processes and cognitive patterns on shaping personality with observable responses
Social-cognitive perspective
Views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people's traits (including their thinking) and their social context
- Albert Bandura is a principle social-cognitive perspective psychologist
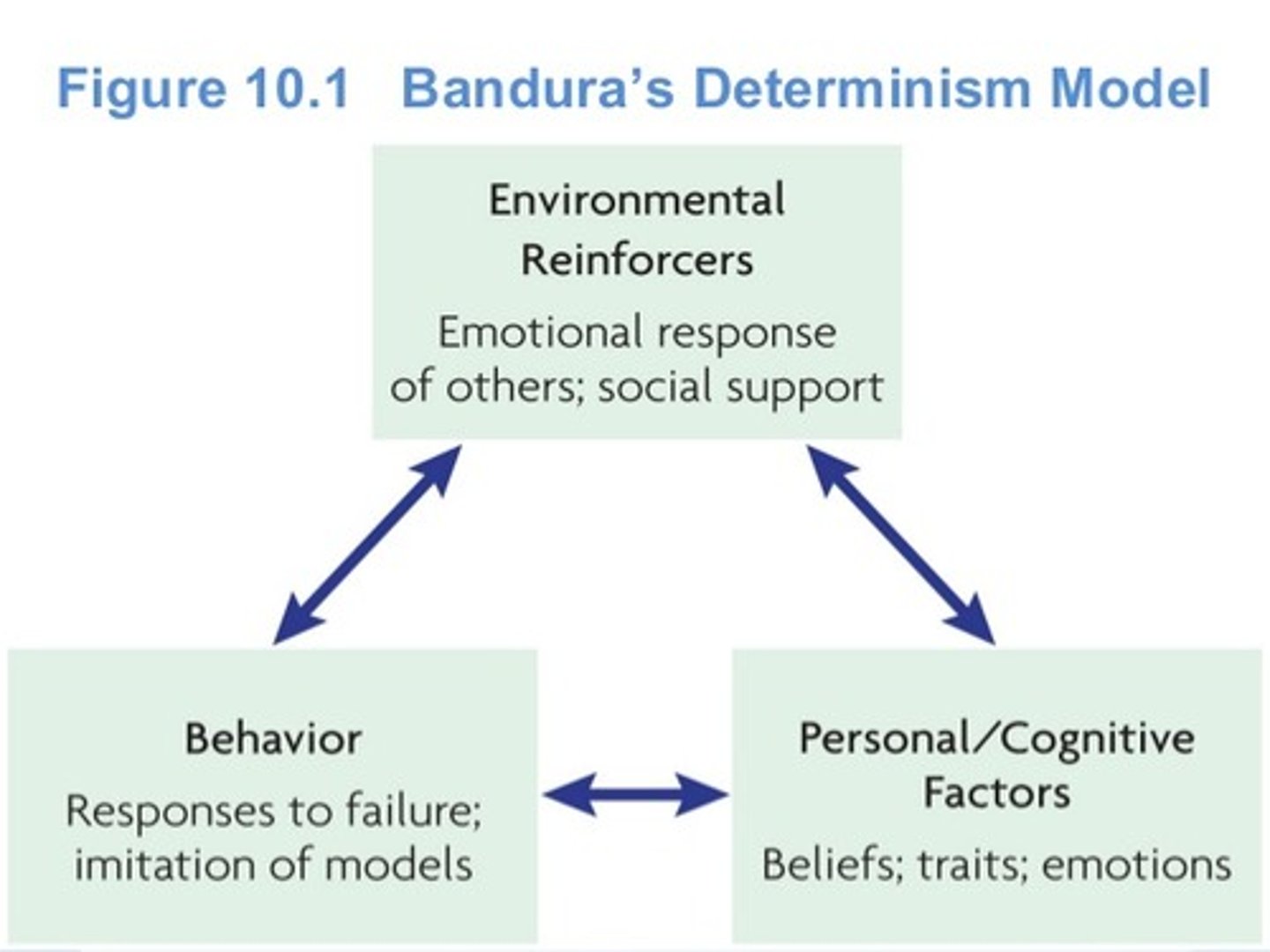
Albert Bandura Social Cognitive Theory
- Human behavior and personality are caused by the interaction of behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors (reciprocal determinism)
- Person's cognitive skills, abilities, and attitudes represent the person's self-system
- Most critical elements influencing the self-system are our beliefs of self-efficacy
Cultural perspective
A view that focuses on the influence of culture on thought, feeling, behavior, and personality development
How cultural norma, values, socialization, and practices contribute to variations in personality across societies
Rorschach inkblot test
The most widely used projective test, a set of 10 inkblots, designed by Hermann Rorschach; seeks to identify people's inner feelings by analyzing their interpretations of the blots
Recipirocal Determinism
The interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment
MMPI (Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory)
The most widely researched and clinically used of all personality tests. Originally developed to identify emotional disorders (still considered its most appropriate use), this test is now used for many other screening purposes
Spotlight effect
Overestimating others' noticing and evaluating our appearance, performance, and blunders (as if we presume a spotlight shines on us)
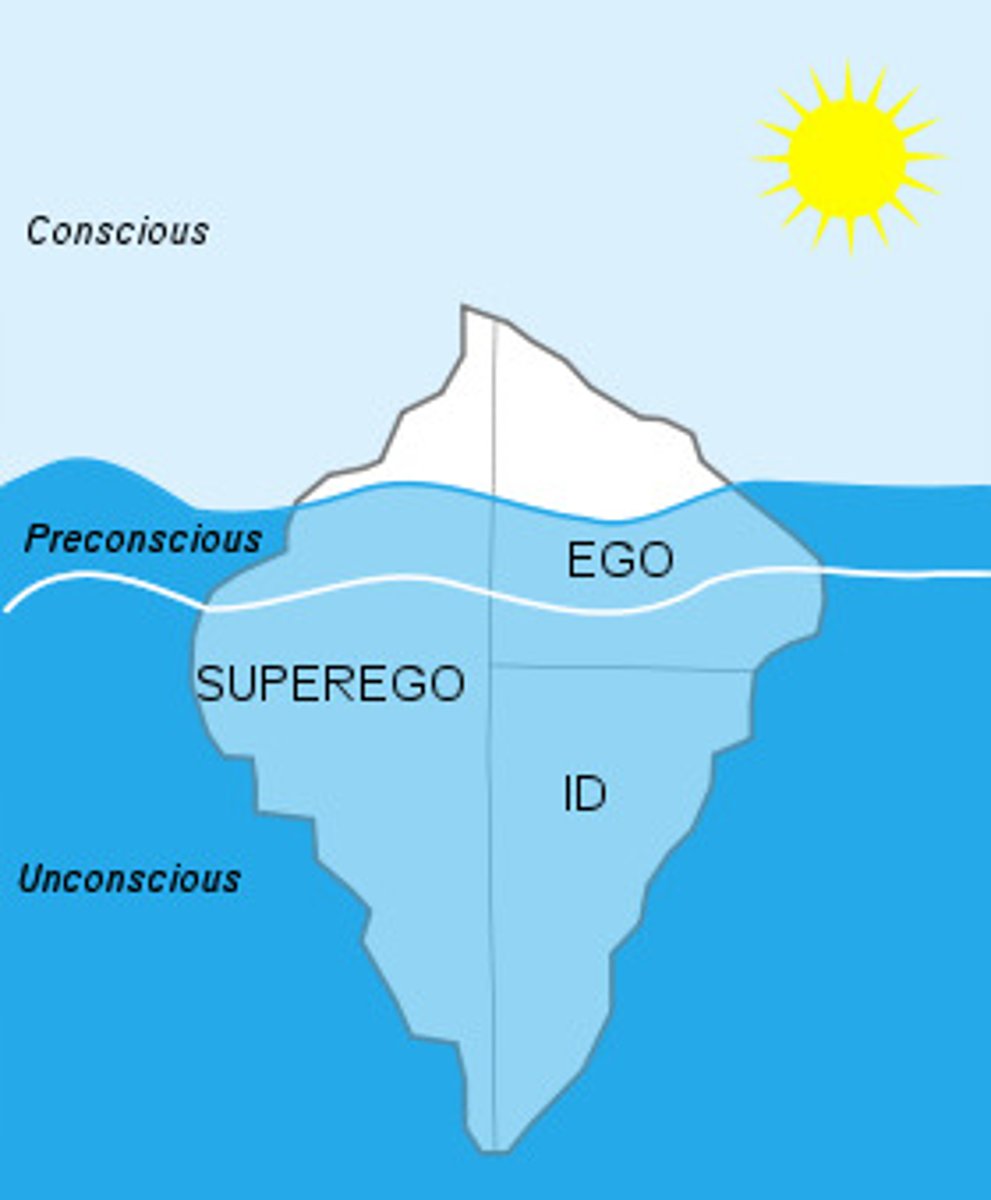
Three levels of consciousness
Conscious: mental events we are aware of
Preconscious: mental events that can be brought to our awareness
Unconscious: mental events inaccessible to our awareness
Three levels of consciousness iceberg
Mental conflict
Id impulses, superego demands, and reality often conflict with one another
-These conflicts can occur at any level of consciousness, and produce anxiety
-Anxiety will continue (and grow) until the ego resolves the conflict, often through compromise
Resolving mental conflicts
- Give in to id or superego
- Compromised between competing demands
- Keep conflict out of mind using defense mechanisms
Ego defense mechanisms
Largely unconscious mental strategies employed to reduce the experience of conflict or anxiety
Include repression, displacement, and rationalization
Repression (defense mechanism)
Blocking of unpleasant feelings and experiences from ones awareness
Displacement (defense mechanism)
The transfer of feelings from one target to another that is considered less threatening or that is neutral (often aggressive or sexual)
Rationalization (defense mechanism)
Attempting to make excuses or formulate logical reasons to justifying unacceptable feelings or behaviors
Mental energy (libido)
Psychoanalytic approach is that the apparatus of the mind needs energy to make it go.
Also known as libido, only a fixed and finite amount is available at any given moment which when used impairs ego functions
Mental determinism (Freudianism)
All human mental life and behavior is determined by unconscious pleasure principles (food, shelter, sex) , which drive all decisions
Freudian slip
A verbal mistake that is thought to reveal an unconscious belief, thought, or emotion
Freud five stages of development
1. Levels of consciousness (Correct)
2. Parts of the mind (Sometimes correct)
3. Mental conflict (Correct)
4. Mental energy (Sometimes correct)
5. Mental determinism (Sometimes correct)
Hartshore & May (1928)
Using 8000 elementary-school students found:
Moral behavior consistent across similar situations
Moral behavior not as consistent across dissimilar situations
Concluded that behavior is jointly determined by personality and situation
Bandura's Reciprocal Determinism
Personality traits change
Personality traits can change based on life experiences, however genetic personality traits like eye color can not
5 big traits of personality (OCEAN)
Openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism (OCEAN)
Soto, John, Gosling, and Potter (2011)
Cross sectional study examining age differences in personality from childhood through middle age
Study was large and diverse providing accurate analysis.
Soto, John, Gosling, and Potter (2011) - Results
Found genes held a starting point for personality but life experiences shaped traits. Adolescence saw pronounced and curvilinear age trends and emergence of gender differences. Adults saw increase in agreeableness and conscientiousness with a decrease in neuroticism
Maturity principle
People become better equipped to deal with the demands of life as they acquire experience and skills
Allport and Odbert (1936)
Identified almost 18,000 words representing traits
Personality traits
Enduring tendencies to feel, think, and act in certain ways
Psychological traits
Genetic (nature) v. Environment (nurture)
Behavioral genetics
Studies the inheritance of traits related to behavior
Popular study found identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins, showcasing the impact of genetic, however twins were still different from one another, showing the impact of environment
Genes and the environment have equal influence over personality
Psychological (mental) disorder
A syndrome marked by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior
Not just unusual or conflicting behavior
Not an ordinary response to a negative event
Psychological diagnosis
The label given to psychological abnormality by classifying and categorizing the observed behavior pattern into an approved diagnostic system
Lifetime prevalence around 50%
DSM-5
the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders
Goal of psychological diagnosis
Define:
- Psychological disorder symptoms
- Relevant medical conditions
- Social and environmental stressors
- Overall functioning vs disability
Therapy
Safe and confidential treatment methods aimed at making people feel better and function more effectively
Big three approaches to psychotherapy
1. Psychodynamic
2. Humanistic
3. Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Psychodynamic therapy
Therapy deriving from the psychoanalytic tradition that views individuals as responding to unconscious forces and childhood experiences, and that seeks to enhance self-insight
- Free association (encourage freudian slips_
- Transference (client treats therapist like important life figure)
- Dream analysis (manifest vs latent content)
Humanistic/Client-Centered Therapy
Treatment for psychological disorders where a therapist works with clients to help them develop their full potential for personal growth through greater self-understanding
Developed by Carl Rogers and believe that disorders occur when personal identity and self-actualization are disrupted
Self-actualization
The process by which people achieve their full potential
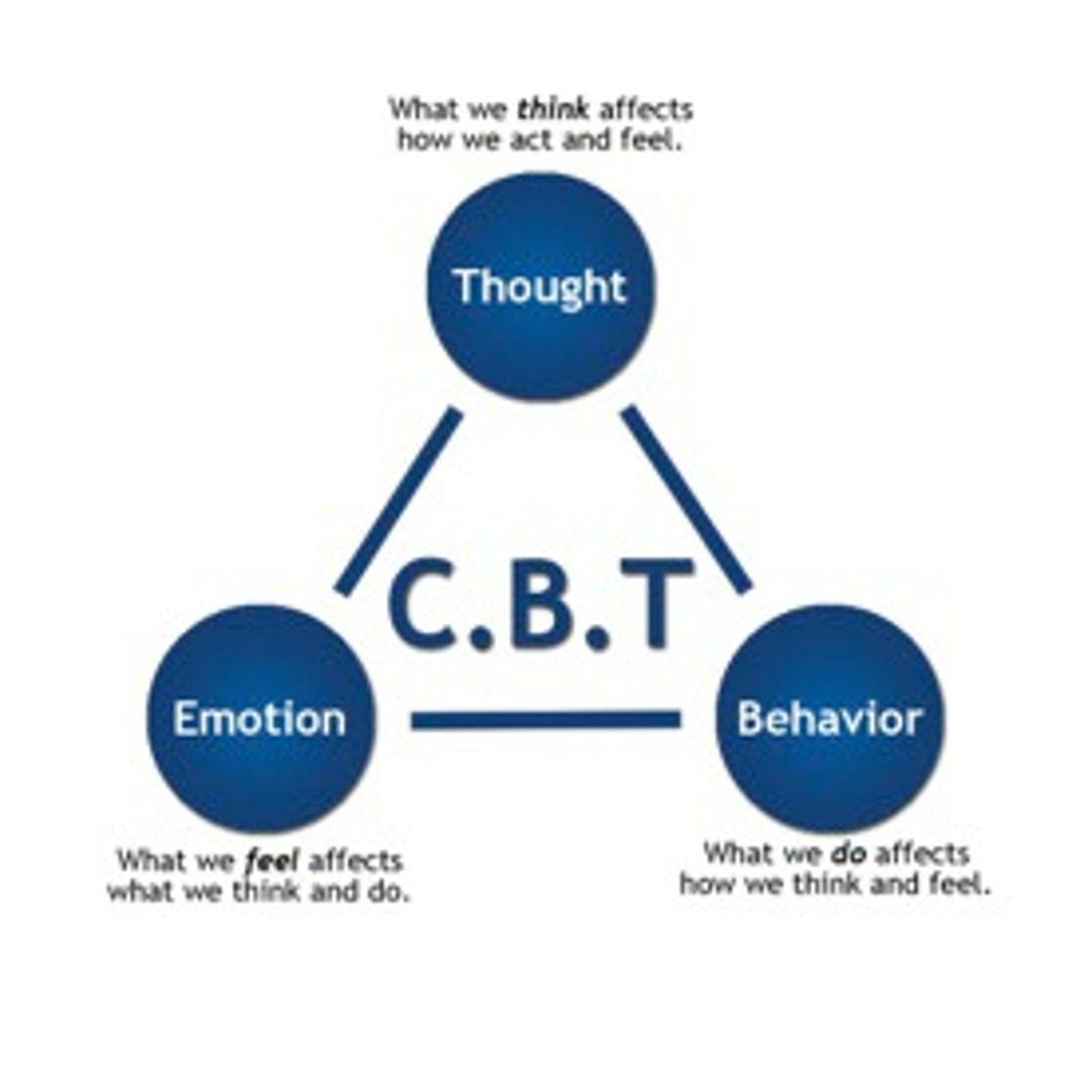
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
A popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
Believe disorders occur from learned patters of thinking, feeling, and behaving that are now maladaptive
Cognitive Triangle (CBT)
Biomedical approach
Proposes disorder stem from neurological abnormalities from brain structure or neurochemistry
Biomedical therapies
The use of medications, brain stimulation, psychosurgery or other medical treatments to treat the symptoms associated with psychological disorders
Brain stimulation
Applying electrical stimulation to specific brain areas to examine localization of brain function and observing how this affects behavior
Includes ECT, TMS, and rTMS
Therapeutic approach
CBT is more consistently effective, however this differs across disorders
Eclectic psychotherapy along with medication is key to help resolving issues
Anxiety-related disorders
A mental disorder involving overwhelming worry, anxiety, or fear that interferes with a person's daily functioning
Includes GAD, SAD, Panic disorder, OCD, PTSD
Depressive disorders
Mood disorders in which the individual suffers from depression
Includes MDD, Dysthymia, Bipolar disorder I/II
Schizophrenia
A group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional/hallucinatory thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions
Dissociative disorders
Disorders in which conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings
Includes multiple personality disorder, depersonalization, and dissociative amnesia
Personality disorders
Psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning
Includes BPD, ASPD, and NPD
Eating disorders
Severe disturbances in eating behavior characterized by preoccupation with weight concerns and unhealthy efforts to control weight
Neurodevelopmental disorders
A group of conditions manifested early in development that are characterized by developmental deficits that produce impairments of personal, social, academic, or occupational functioning
Includes ASD, ADHD, learning disabilities
Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
Treatment that strengthens social skills and targets interpersonal problems, conflicts, and life transitions
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy
An approach that combines elements of CBT with mindfulness meditation to help people with depression learn to recognize and restructure negative thought patterns
Family therapy
Therapy that treats the family as a system. Views an individual's unwanted behaviors as influenced by, or directed at, other family members
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
A treatment often used for borderline personality disorder that incorporates both cognitive-behavioral and mindfulness elements.
Group therapy
Therapy conducted with groups rather than individuals, permitting therapeutic benefits from group interaction
Preventing Psychological Disorders
- Support programs for stressed families
- Community programs to provide healthy activities and hope for children
- Relationship-building communication skills training
- Working to reduce poverty and discrimination
- Access to health services and assessments
- Psychoeducation
Motor system
Carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary
Somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls the body's skeletal muscles.
Sympathetic system
Fight or flight
Parasympathetic system
Rest and digest
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Microgenetics
Participants are presented with a novel task, and their mastery is followed over a series of sessions
Practical skills
Activities of daily living (personal care), occupational skills, healthcare, travel/transportation, schedules/routines, safety
Conceptual skills
The ability to analyze and diagnose a situation and to distinguish between cause and effect
Adaptive skills
Personal attributes or traits that enable a person to approach changing workplace situations with flexibility
Systematic desensitization
A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. Commonly used to treat phobias
Aversive conditioning
A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior (such as drinking alcohol)
Psychopharmacology
The study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior
Phobias
Excessive or irrational fears of specific objects or situations
- Recognition that fear is excessive or irrational
- Fear avoided or endured with intense distress
Phobias Treatment
- Biomedical approach is ineffective
- Psychodynamic approach fo uses on impulses or conflicts related to the fear but is typically ineffective
- Cognitive-behavioral approach recognizes how phobias are acquired by classical conditioning and maintained by operant conditioning -> solution is exposure therapies
Exposure therapies
- Graduated exposure uses fear hierarchies to slowly build up tolerance to stressful situations
- Intensive exposure uses sudden exposure at once to the biggest fear
- Both of these are effective (~80%)
Fear heirarchy
A list of feared objects or situations, ranked from least to most anxiety-producing
Fear and Anxiety Components
- Subjective (fear something bad will happen)
- Physiological component (sympathetic nervous system)
- Behavior component (Vigilance, avoidance, aggression)