Psychopathology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
definitions of abnormality
* **Statistical Infrequency**
* **Deviation from social norms**
* **Failure to function adequately**
* **Deviation from ideal mental health**
* **Deviation from social norms**
* **Failure to function adequately**
* **Deviation from ideal mental health**
2
New cards
statistical infrequency
behaviour is rare or statistically unusual
3
New cards
deviation from social norms
behaviour or thinking violates unwritten rules about what is expected or acceptable in a particular social group (objective)
4
New cards
failure to function adequately
if they are unable to cope with demands of everyday life (subjective)
5
New cards
deviation from ideal mental health
* Positive view of self
* Capability of growth and development
* Autonomy and independence
* Accurate perception of reality
* Positive friendships and relationships
* Capability of growth and development
* Autonomy and independence
* Accurate perception of reality
* Positive friendships and relationships
6
New cards
phobias
* type of anxiety disorder characterised by irrational and extreme fears
* Specific phobias
* Social phobias
* Agoraphobia
* Specific phobias
* Social phobias
* Agoraphobia
7
New cards
specific phobias
suffers have fears of specific things
\-> animal phobias, injury phobias, situational phobias, natural environment phobias
\-> animal phobias, injury phobias, situational phobias, natural environment phobias
8
New cards
social phobias
involve being over anxious in social situations
\-> performance phobias, interaction phobias, generalisation phobias
\-> performance phobias, interaction phobias, generalisation phobias
9
New cards
agoraphobia
fear of leaving home, occurs with panic attacks and can be brought on by simple phobias
10
New cards
behavioural characteristics of phobias
* **Panic** (crying in response to the phobic stimulus)
* **Avoidant/anxiety response** (Panic (crying in response to the phobic stimulus)
* **Disruption of functioning** (not going to school)
* **Endurance** (remaining through the phobic stimulus)
* **Avoidant/anxiety response** (Panic (crying in response to the phobic stimulus)
* **Disruption of functioning** (not going to school)
* **Endurance** (remaining through the phobic stimulus)
11
New cards
Emotional characteristics of phobias
* **Persistent, excessive fear and anxiety**
* **Fear from exposure to phobic stimulus** (immediate unpleasant response)
**Emotional response is unreasonable and disproportionate** to the danger or threat posed by the phobic stimulus
* **Fear from exposure to phobic stimulus** (immediate unpleasant response)
**Emotional response is unreasonable and disproportionate** to the danger or threat posed by the phobic stimulus
12
New cards
Cognitive characteristics of phobias
* **Selective attention to the phobic stimulus**
* **Irrational beliefs** -> increase the pressure to perform well
* **Cognitive distortions** (perception of phobic stimulus is distorted)
* **Recognition of exaggerated anxiety** -> phobics are constantly aware that the anxiety levels they experience are overstated
* **Irrational beliefs** -> increase the pressure to perform well
* **Cognitive distortions** (perception of phobic stimulus is distorted)
* **Recognition of exaggerated anxiety** -> phobics are constantly aware that the anxiety levels they experience are overstated
13
New cards
Behavioural explanation to phobias
**The Two Process Model - Mowrer (1960)**
* **Acquisition of phobias is seen as directly occurring through classical conditioning**
* Found that by making a few presentations for an electric shock to rats immediately following the sound of a buzzer, he could produce a fear response just by sounding the buzzer
* **Maintenance of phobias is seen as occurring through operant conditioning, where avoiding the phobia acts as a negative reinforcer and reinforces the avoidance response.**
* Trained the rats to escape electric shocks by making the avoidance response of jumping over a barrier when the buzzer sounded, negatively reinforcing the phobi
* **Acquisition of phobias is seen as directly occurring through classical conditioning**
* Found that by making a few presentations for an electric shock to rats immediately following the sound of a buzzer, he could produce a fear response just by sounding the buzzer
* **Maintenance of phobias is seen as occurring through operant conditioning, where avoiding the phobia acts as a negative reinforcer and reinforces the avoidance response.**
* Trained the rats to escape electric shocks by making the avoidance response of jumping over a barrier when the buzzer sounded, negatively reinforcing the phobi
14
New cards
King et al (1998)
* Reported that case studies showed that children tended to acquire strong phobias through a traumatic experience, which further supports the idea of phobias being acquired through classical conditioning
15
New cards
evaluation of behaviourist explanations of phobias
\+ real life applications
* Effectiveness of behaviourist treatments in addressing phobic symptoms
\- viewpoint is weakened by the fact that not everyone experiencing traumatic events go on to develop a phobia
\- Bounton (2007) argues that the model neglects the influence of evolution theory, where avoidance responses are learned more quickly if the required response resembles an animal’s natural defensive behaviour
* Effectiveness of behaviourist treatments in addressing phobic symptoms
\- viewpoint is weakened by the fact that not everyone experiencing traumatic events go on to develop a phobia
\- Bounton (2007) argues that the model neglects the influence of evolution theory, where avoidance responses are learned more quickly if the required response resembles an animal’s natural defensive behaviour
16
New cards
Ways to treat phobias
* **Systematic desensitisation** (Anxiety hierarchy, Gradual exposure)
* **Counterconditioning**
* **Flooding**
* **Counterconditioning**
* **Flooding**
17
New cards
systematic desensitisation
* Based on classical conditioning, with patients learning in stages to replace fear responses with feelings of calm
* Can take about a month to advance through the entire desensitisation hierarchy
* **McGarth et al (1990)** found that 75% of patients with phobias were successfully treated using SD, when using in vivo techniques
* Can take about a month to advance through the entire desensitisation hierarchy
* **McGarth et al (1990)** found that 75% of patients with phobias were successfully treated using SD, when using in vivo techniques
18
New cards
Evaluation of systematic desensitation
\+ supporting evidence Jones (1924) used SD to eradicate Little Peter’s phobia of white fluffy animals and objects Eventually, he developed affection for the rabbit which generalised onto similar animals and objects
\+ effective
* Gilroy et al. (2003) examined 42 patients with arachnophobia, each was treated with three 45min sessions -> when examined 3 months and 33 months later, the SD group was less fearful than the control group who were only taught relaxation techniques
\+ preferred by patients (has relaxation techniques, low refusal rates and low attrition rates)
\- SD is mainly suitable for patients who are able to learn and use relaxation techniques and who have vivid imaginations enough to conjure up images of feared objects -> No guarantee this will work with actual objects
\+ effective
* Gilroy et al. (2003) examined 42 patients with arachnophobia, each was treated with three 45min sessions -> when examined 3 months and 33 months later, the SD group was less fearful than the control group who were only taught relaxation techniques
\+ preferred by patients (has relaxation techniques, low refusal rates and low attrition rates)
\- SD is mainly suitable for patients who are able to learn and use relaxation techniques and who have vivid imaginations enough to conjure up images of feared objects -> No guarantee this will work with actual objects
19
New cards
counterconditioning
phobic stimulus is paired with a relaxing stimulus until it triggers relaxation not anxiety
\-> 2 opposing emotions of anxiety and relaxation are perceived as incapable of coexisting simultaneously (reciprocal inhibition)
\-> 2 opposing emotions of anxiety and relaxation are perceived as incapable of coexisting simultaneously (reciprocal inhibition)
20
New cards
Flooding
* Aim is to remove the learned association between the stimulus and response
* Involves inescapable exposure to the feared object/situation that lasts until the fear response disappears
* If flooding session ends too soon, when anxiety levels are still high, it may have the opposite of the desired effect
* Informed consent is crucial
* Involves inescapable exposure to the feared object/situation that lasts until the fear response disappears
* If flooding session ends too soon, when anxiety levels are still high, it may have the opposite of the desired effect
* Informed consent is crucial
21
New cards
Evaluation of flooding
\+ supporting evidence
* **Ost (1997)** found that flooding often delivers rapid immediate improvements
* **Solter (2007)** reported on case study of a 5 month old who showed signs of traumatic stress after a 3 day hospital stay to correct his head shape
Flooding was used, and a positive outcome was produced, with him having no remaining symptoms after 2 months
\+ cost effective, due to its rapid nature, fewer sessions are needed
\- traumatic
* Not suitable for patients who are not in good physical health as extreme anxiety levels caused by confrontation, can be very stressful on the body (causing heart attacks etc)
\- less effective for some type of phobias
* Such as social phobias which could have cognitive aspects (might have irrational thoughts which are not tackled during flooding)
\- symptom substitution can occur, with new phobias replacing old ones
* **Ost (1997)** found that flooding often delivers rapid immediate improvements
* **Solter (2007)** reported on case study of a 5 month old who showed signs of traumatic stress after a 3 day hospital stay to correct his head shape
Flooding was used, and a positive outcome was produced, with him having no remaining symptoms after 2 months
\+ cost effective, due to its rapid nature, fewer sessions are needed
\- traumatic
* Not suitable for patients who are not in good physical health as extreme anxiety levels caused by confrontation, can be very stressful on the body (causing heart attacks etc)
\- less effective for some type of phobias
* Such as social phobias which could have cognitive aspects (might have irrational thoughts which are not tackled during flooding)
\- symptom substitution can occur, with new phobias replacing old ones
22
New cards
Depression
a mood disorder characterised by feeling of despondency and hopelessness
23
New cards
2 types of depression
* **Unipolar depression**: occurring without mania
* **Bipolar depression**: characterised by periods of heightened moods and periods of despondency and hopelessness
* **Bipolar depression**: characterised by periods of heightened moods and periods of despondency and hopelessness
24
New cards
behavioural characteristics of unipolar depression
* **Loss of energy**
* **Social impairment** (reduced levels of social interaction with friends etc)
* **Weight changes**
* **Poor personal hygiene**
* **Sleep pattern disturbance** (insomnia or hypersomnia)
* **Social impairment** (reduced levels of social interaction with friends etc)
* **Weight changes**
* **Poor personal hygiene**
* **Sleep pattern disturbance** (insomnia or hypersomnia)
25
New cards
emotional characteristics of unipolar depression
* **Loss of enthusiasm (lack of pleasure in daily activities)**
* **Constant depressed mood**
* **Worthlessness**
* **Constant depressed mood**
* **Worthlessness**
26
New cards
cognitive characteristics of unipolar depression
* **Delusions** (generally concerning guilt, punishment, personal inadequacy etc and some experience hallucinations)
* **Reduced concentration**
* **Thoughts of death**
* **Poor memory**
* **Reduced concentration**
* **Thoughts of death**
* **Poor memory**
27
New cards
behavioural characteristics of bipolar depression
* **High energy levels** (increased work output and social interactions/sexual activity)
* **Reckless behaviour**
* **Talkative** (fast, endless speech without regard for what others are saying)
* **Reckless behaviour**
* **Talkative** (fast, endless speech without regard for what others are saying)
28
New cards
emotional characteristics of bipolar depression
* **Elevated mood states** (intense feelings of euphoria)
* **Irritability** (frustrated when they don’t get their own way immediately)
* **Lack of guilt** (social inhibition and general lack of guilt concerning behaviour)
* **Irritability** (frustrated when they don’t get their own way immediately)
* **Lack of guilt** (social inhibition and general lack of guilt concerning behaviour)
29
New cards
cognitive characteristics of bipolar depression
* **Delusions** (can be delusional and grandiose or may believe others are persecuting them)
* **Irrational thought processes** (reckless and irrational decision making)
* **Irrational thought processes** (reckless and irrational decision making)
30
New cards
Cognitive explanations of depression
* **Beck’s Negative Triad (1987)**
* **Ellis’ ABC Model (1955)**
* **Ellis’ ABC Model (1955)**
31
New cards
**Beck’s Negative Triad (1987)**
**Negative schemas and cognitive biases maintain the negative triad:**
* Negative thoughts about **the self** (seeing themselves as helpless, inadequate etc)
* Negative thoughts about **the world** (obstacles are perceived within one’s environment that cannot be dealt with)
* Negative thought about **the** **future** (personal worthlessness is seen as blocking any improvements)
* Negative thoughts about **the self** (seeing themselves as helpless, inadequate etc)
* Negative thoughts about **the world** (obstacles are perceived within one’s environment that cannot be dealt with)
* Negative thought about **the** **future** (personal worthlessness is seen as blocking any improvements)
32
New cards
**Ellis’ ABC Model (1955)**
Believed that depressives mistakenly blame external events for their unhappiness
\-> thought that their interpretation of these events is to blame for their distress
* **A: Activating event**
Something happens in the environment around you
* **B: Beliefs**
You hold a belief about the event
* **C: Consequence**
You have an emotional response to your belief
\-> thought that their interpretation of these events is to blame for their distress
* **A: Activating event**
Something happens in the environment around you
* **B: Beliefs**
You hold a belief about the event
* **C: Consequence**
You have an emotional response to your belief
33
New cards
Ways of treating depression
Cognitive behavioural therapy (REBT etc)
34
New cards
**Ellis’ Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy (1962)**
Extends the ABC model using:
* **D: Dispute**
If one has held an irrational belief which has caused unhealthy consequences, they must dispute that belief and turn it into a rational belief
* **E: New effect**
The disputation has turned the irrational belief into a rational belief and the person now has healthier consequences of their belief as a result
**Involves reframing which is challenging negative thoughts by reinterpreting the ABC in a more positive, logical way**
* **D: Dispute**
If one has held an irrational belief which has caused unhealthy consequences, they must dispute that belief and turn it into a rational belief
* **E: New effect**
The disputation has turned the irrational belief into a rational belief and the person now has healthier consequences of their belief as a result
**Involves reframing which is challenging negative thoughts by reinterpreting the ABC in a more positive, logical way**
35
New cards
Evaluation for treatments of depression
\+ CBT is most effective psychological treatment for moderate and severe depression
* **Lincoln et al (1997)** found that patients given CBT for 4 months, resulted in reduced symptoms
\+ not time consuming and cost effective; CBT occurs over a relatively short period of time
\- arguably too therapist centred, allowing them to possibly abuse their power of control (unethical)
\- For patients with difficulty concentrating (which depressives often do) can be unsuitable, leading to feelings of being overwhelmed and disappointed, which strengthens depressive symptoms rather than reducing them
* **Lincoln et al (1997)** found that patients given CBT for 4 months, resulted in reduced symptoms
\+ not time consuming and cost effective; CBT occurs over a relatively short period of time
\- arguably too therapist centred, allowing them to possibly abuse their power of control (unethical)
\- For patients with difficulty concentrating (which depressives often do) can be unsuitable, leading to feelings of being overwhelmed and disappointed, which strengthens depressive symptoms rather than reducing them
36
New cards
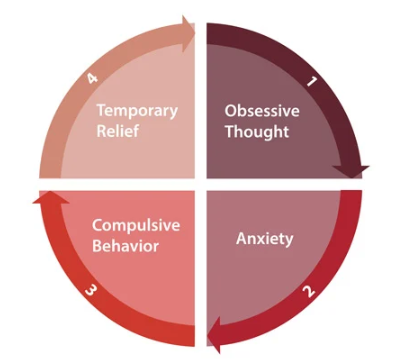
Obsessive compulsive disorder
an anxiety disorder where sufferers experience persistent and intrusive thoughts occurring as obsessions, compulsions or both
* Presence of obsessions or compulsions
* Are time consuming (1hr per day) and cause significant distress
* Obsessions/compulsions are not attributable to effects of a substance
* A different mental health disorder does not better explain the symptoms
* Presence of obsessions or compulsions
* Are time consuming (1hr per day) and cause significant distress
* Obsessions/compulsions are not attributable to effects of a substance
* A different mental health disorder does not better explain the symptoms
37
New cards
behavioural characteristics of OCD
* **Compulsions** (repetitive behaviours)
\-> physical (hand washing, ordering etc) or mental (counting, praying etc)
* **Hinder everyday functioning**
* **Social impairment** (anxiety levels are so high they limit ability to conduct meaningful interpersonal relationships)
\-> physical (hand washing, ordering etc) or mental (counting, praying etc)
* **Hinder everyday functioning**
* **Social impairment** (anxiety levels are so high they limit ability to conduct meaningful interpersonal relationships)
38
New cards
emotional characteristics of OCD
* **Anxiety**
* **Disgust** for some types of OCD
* **Disgust** for some types of OCD
39
New cards
cognitive characteristics of OCD
* **Obsessions** (repetitive/intrusive/irrational thoughts)
* **Attentional bias** (perception tends to be focused on stimuli)
* **Attentional bias** (perception tends to be focused on stimuli)
40
New cards
Biological explanations of OCD
* Genetic
* Diathesis stress model
* Neural
* Diathesis stress model
* Neural
41
New cards
Genetic explanation of OCD
OCD is polygenic, (up to 230 genes are responsible for symptoms) especially:
* **SERT gene: associated with production of serotonin**
Mutation leads to increase in reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neuron
Less serotonin flow = causes anxiety
* **COMT gene: regulates function of dopamine with COMT enzyme that breaks down dopamine**
Lower levels of COMT produced with mutation
Higher dopamine levels = temporary relief for performing a compulsion (rewards)
* **SERT gene: associated with production of serotonin**
Mutation leads to increase in reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neuron
Less serotonin flow = causes anxiety
* **COMT gene: regulates function of dopamine with COMT enzyme that breaks down dopamine**
Lower levels of COMT produced with mutation
Higher dopamine levels = temporary relief for performing a compulsion (rewards)
42
New cards
diathesis stress model
People gain a vulnerability towards OCD through genes but an environmental stressor is also required. This could be a stressful event etc
43
New cards
Neural explanation of OCD
Pathway involved in obsessive compulsive behaviour is a loop involving 3 anatomical brain regions:
* **Orbito-frontal cortex (OFC)**
* **Caudate nucleus (part of the basal ganglia)**
* **Thalamus**
1. OFC notices when something is wrong
2. When a danger is perceived, the OFC alerts the thalamus which directs signals back to the OFC
3. Caudate nucleus lies between the OFC and the thalamus and regulates signals between them
\-> dopamine and glutamate (neurotransmitters) are used to transmit signals
\n
In OCD, the caudate nucleus is thought to be damaged, **so it cannot suppress signals from the OFC, allowing the thalamus to become over excited**
If this occurs, the **thalamus sends strong signals back to the OFC, which responds by increasing obsessive thoughts, compulsive behaviour and anxiety**.
* **Orbito-frontal cortex (OFC)**
* **Caudate nucleus (part of the basal ganglia)**
* **Thalamus**
1. OFC notices when something is wrong
2. When a danger is perceived, the OFC alerts the thalamus which directs signals back to the OFC
3. Caudate nucleus lies between the OFC and the thalamus and regulates signals between them
\-> dopamine and glutamate (neurotransmitters) are used to transmit signals
\n
In OCD, the caudate nucleus is thought to be damaged, **so it cannot suppress signals from the OFC, allowing the thalamus to become over excited**
If this occurs, the **thalamus sends strong signals back to the OFC, which responds by increasing obsessive thoughts, compulsive behaviour and anxiety**.
44
New cards
Treatments for OCD
* Antidepressants
* SSRIs: Block the transporter mechanism that reabsorbs both serotonin and noradrenaline
* Tricyclics
* Anti- anxiety drugs
* Benzodiazepines: **Slow down the central nervous system by enhancing the activity of the NT GABA**
* SSRIs: Block the transporter mechanism that reabsorbs both serotonin and noradrenaline
* Tricyclics
* Anti- anxiety drugs
* Benzodiazepines: **Slow down the central nervous system by enhancing the activity of the NT GABA**
45
New cards
Evaluation of treatments for OCD
\+ placebo vs drug studies show that the drugs are effective
* Soomro et al (2008) meta analysis reviewed 17 studies of the use of SSRIs with OCD patients and found them to be more effective than placebos
\+ effective in the short term
* Little long term evidence exists (Koran et al. 2007)
\+ little effort required compared to CBT, is cheaper and requires little monitoring
* Suffers also benefit from talking to the GP about the symptoms and treatment
\- side effects
* SSRIs - headaches, nausea and insomnia#
* Tricyclics - hallucinations and irregular heartbeat
* BZ - aggression, long term impairment of memory and addiction
Should therefore only be used for a limited time
\- Turner et al (2008) publication is bias towards studies that show a positive outcome
* Much research is funded by drug companies
* Selective publication can lead doctors to make inappropriate treatment choices
* Soomro et al (2008) meta analysis reviewed 17 studies of the use of SSRIs with OCD patients and found them to be more effective than placebos
\+ effective in the short term
* Little long term evidence exists (Koran et al. 2007)
\+ little effort required compared to CBT, is cheaper and requires little monitoring
* Suffers also benefit from talking to the GP about the symptoms and treatment
\- side effects
* SSRIs - headaches, nausea and insomnia#
* Tricyclics - hallucinations and irregular heartbeat
* BZ - aggression, long term impairment of memory and addiction
Should therefore only be used for a limited time
\- Turner et al (2008) publication is bias towards studies that show a positive outcome
* Much research is funded by drug companies
* Selective publication can lead doctors to make inappropriate treatment choices