The Scientific Revolution and The Enlightenment
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
According to Locke, what is the purpose of government?
To protect people’s rights
2
New cards
What did Locke say has ruined cities and depopulated countries?
The issue of who should have power
3
New cards
What inherent and sacred rights do all men have according to John Locke
Life, Liberty, and Property
4
New cards
According to Hobbes, what forces us to obey the laws of nature?
The laws themselves
5
New cards
According to Hobbes, what do men desire that is only ended in death?
Power
6
New cards
How did Hobbes describe man?
Solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, short, wicked.
7
New cards
What is the purpose of religion according to Voltaire?
To deceive men and to comfort them
8
New cards
“I detest what you write, but I would give my life to make it possible for you to continue to write“
Voltaire
9
New cards
“There are truths that are not for all men, nor for all occasions“
Voltaire
10
New cards
“For the laws of nature (as justice, equity, modesty, mercy, and in sum, doing to others as we would be done to) of themselves, without the terror of some power, to cause them to be observed, are contrary to our natural passions that carry us to partiality, pride, revenge, and the like.“
Thomas Hobbes
11
New cards
“Man is free the moment he wants to be“
Voltaire
12
New cards
What did Montesquieu devote himself to?
The study of political liberty
13
New cards
What three bodies did England split its power into?
* Parliament (legislative/lawmaking)
* English Court (Judicial/Carrying Laws Out)
* King (Executive/Interpreting Laws)
* English Court (Judicial/Carrying Laws Out)
* King (Executive/Interpreting Laws)
14
New cards
Why did Montesquieu believe in the separation of powers?
It prevented one individual from gaining to much power
15
New cards
What idea did Rousseau believe in?
* Individual Freedom
* Abolishing the nobility so that everyone would be equal
* Abolishing the nobility so that everyone would be equal
16
New cards
What ideas did Voltaire believe in?
* freedom of expression
* religious freedom
* religious freedom
17
New cards
What idea did Wollstonecraft believe in?
Women’s rights
18
New cards
What idea did Beccaria believe in?
Governments should seek greatest goods for the greatest number of people
19
New cards
How did most philosophes view women?
* Traditional views
* Different/unequal to men
* Different/unequal to men
20
New cards
Which 3 ideas did Wollstonecraft argue?
* Women & men need the same education to be virtuous & useful
* Women can be nurses & doctors
* Women should be able to participate in politics
* Women can be nurses & doctors
* Women should be able to participate in politics
21
New cards
What was the title of Wollstonecraft’s book?
*A Vindication of the Rights of Women* (1792)
22
New cards
Salon
A social gathering of wealthy women to discuss philosophy
23
New cards
Which 3 principles were examined by enlightenment thinkers?
* Divine Right of Monarchs
* Union of Church & State
* Social Class Division
* Union of Church & State
* Social Class Division
24
New cards
What was inspired by the theories of the Enlightenment?
The French & American revolutions
25
New cards
What did people begin to question during this time?
The Church’s teachings
26
New cards
Where did people turn for guidance in place of the Church?
Themselves
27
New cards
What took the center stage during the enlightenment?
Reason
28
New cards
Why did philosophers admire Newton?
He used reason to explain Natural Laws
29
New cards
What did people begin to look for during this time?
Laws governing human behavior
30
New cards
What did people want to apply the scientific method to?
All aspects of society:
* government
* religion
* economics
* education
* government
* religion
* economics
* education
31
New cards
What was the title of Hobbes’ book?
*Leviathan* (1651)
32
New cards
According to Hobbes, what would there be without absolute government?
“war of every man against every man“ life would be “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, short“
33
New cards
What “social contract“ did Hobbes propose?
People gave up their rights to a strong, absolute ruler
34
New cards
How did Locke view men?
As reasonable beings who could govern themselves and were all born free and equal
35
New cards
What did Locke believe you should do to a government who fails to protect your rights?
Overthrow it
36
New cards
Who were the philosephes?
French social critics (philosophers in French)
37
New cards
According to the philosophes, what is reason?
the absence of intolerance, bigotry, or prejudice
38
New cards
How did philosophers believe you could achieve happiness?
By living nature’s laws
39
New cards
Who was the most influential philosophe?
Voltaire (a.k.a. François Marie Arouet)
40
New cards
Which three groups did Voltaire target for ridicule?
The Clergy, Aristocracy, and the Government
41
New cards
Natural Laws
Unchanging laws that exist within nature created by the Creator (God) to govern creation (e.g. gravity, inertia/momentum, natural rights)
42
New cards
The Watchmaker Analogy
William Paley/1802- The idea that, like a watch, the universe and everything in it is too complex to exist without a creator (a watchmaker)
43
New cards
Deism
The religious belief that a creator made the world and made natural laws to run the world, then left (Deists don’t believe in a God listening to their prayers)
44
New cards
Why was Hobbes opposed to a democracy?
It would give a wicked, nasty population control over each other
45
New cards
Tabula Rasa
Latin- “Scraped Tablet” (i.e. blank slate)
* Locke believed that everyone was a blank slate and their character was determined by their environment
* Locke believed that everyone was a blank slate and their character was determined by their environment
46
New cards
What impact did the Renaissance have on the scientific revolution?
people placed less importance on the church
47
New cards
What impact did the Reformation have on the scientific revolution?
Religious leaders influenced people to think about God in different ways.
48
New cards
What primary texts did Europeans use to understand the world?
* Ancient Greek & Roman texts
* The Bible
* The Bible
49
New cards
Scientific Method
Problem/Question → Hypothesis → Experiment → Interpret Data
50
New cards
Copernicus
* **heliocentric theory**- he reasoned that the sun was the center of the universe
* Wrote a book titled *On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Bodies*
* Wrote a book titled *On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Bodies*
51
New cards
Galileo
* Built a telescope and observed the universe
* Also studied motion, discovered the Law of Falling Bodies & that the trajectory of a projectile is a parabola
* Published *Starry Messenger* (1610), describing Saturn’s moons, the Sun’s dark spots, and heliocentricity
* Also studied motion, discovered the Law of Falling Bodies & that the trajectory of a projectile is a parabola
* Published *Starry Messenger* (1610), describing Saturn’s moons, the Sun’s dark spots, and heliocentricity
52
New cards
Francis Bacon
Developed and pushed for scientific theory
53
New cards
Isaac Newton
* **Law of Universal Gravitation**- Every object is attracted to every other object
* **Law of Attraction**- The attraction is determined by Mass and Distance
* He believed that all parts of the universe worked together like a giant clock with God at the center
* **Law of Attraction**- The attraction is determined by Mass and Distance
* He believed that all parts of the universe worked together like a giant clock with God at the center
54
New cards
Leeuwenhoek
Used a microscope to observe bacteria in tooth scrapings as well as red blood cells
55
New cards
Fahrenheit
* Made a mercury thermometer that showed 32º as freezing
* Also worked on an alcohol thermometer
* Researched how atmospheric pressure affected a liquids boiling point
* Also worked on an alcohol thermometer
* Researched how atmospheric pressure affected a liquids boiling point
56
New cards
Andreas Vesalius
Proved Galen’s theory on anatomy wrong by dissecting human corpses
57
New cards
William Harvey
Performed vivisections to learn about the circulation of blood
58
New cards
Edward Jenner
Treating smallpox using inoculation
59
New cards
Robert Boyle
* The founder of modern chemistry, also studied medicine, physics, alchemy, etc.
* Studied the relationship of pressure & Volume with his and Robert Hooke’s air pump
* Proposed that matter could be made up of smaller primary particles
* Studied the relationship of pressure & Volume with his and Robert Hooke’s air pump
* Proposed that matter could be made up of smaller primary particles
60
New cards
Boyle’s Law
Regarding the relation concerning the compression and expansion of a gas at constant temperature.
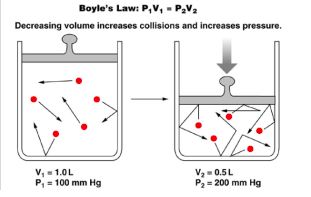
61
New cards
Law of Falling Bodies
All falling objects fall at the same speed regardless of their size, shape, or mass (Galileo)
62
New cards
Science
The systematic study of the structure and behavior of the physical and natural world through observations and experimentation, and the testing of theories against the evidence obtained
63
New cards
What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment?
All things must be questioned, old ways of doing things should be rethought
64
New cards
“Dare to know, Dare to use your reason, Dare to think for yourself“
Immanuel Kant
65
New cards
“Power corrupts (,) Absolutely“
Montesquieu
66
New cards
Parliament
The British government’s legislative (lawmaking) branch, which consists of the **house of congress** & the **house of lords**
67
New cards
America’s government- Executive Branch
The president enforces laws over a 4 year term
68
New cards
America’s government- Legislative Branch
Law making
* The senate- 100 senators (2 per state), 6 year terms
* The House of Representatives- 435 members (based on state population), 2 year terms
* The senate- 100 senators (2 per state), 6 year terms
* The House of Representatives- 435 members (based on state population), 2 year terms
69
New cards
America’s government- Judicial Branch
The Supreme Court (9 justices) interprets laws until death, retirement or conviction by the senate