B2.1 Membranes + membrane transport
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Another name for plasma membrane
Cell membrane
Basis of cell membranes
Lipid bilayers
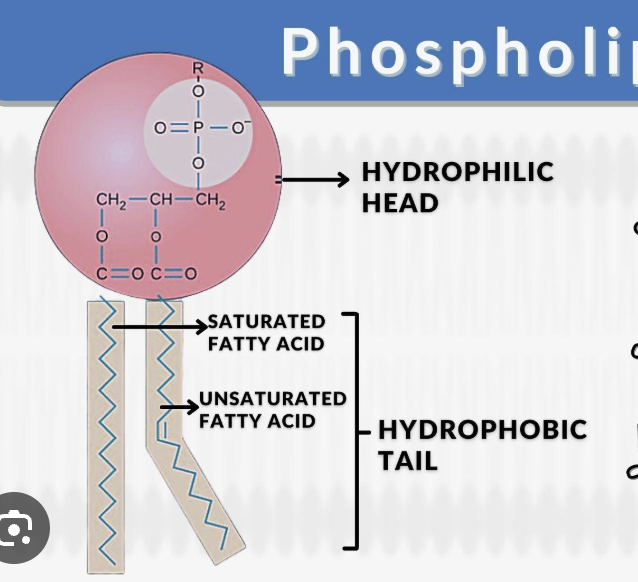
Structure of a phospholipid
Hydrophobic fatty acid tail
Hydrophilic phosphate head
Are phospholipids hydro phobic or phyilic?
Amphipathic
Amphipathic
Contains polar, hydrophilic regions AND non-polar, hydrophobic regions
What do phospholipids + other amphipathic lipids naturally form in water?
Naturally form continuous sheet-like bilayers in water
Function of cell membrane (lipid bilayer)
Control what materials enter + leave the cell
Selectively permeable
Act as barriers
Loction of lipid bilayers
Plasma membrane
Organelle membranes (eg mitochondria)
Vesicles + lysosomes
Membranes are effective barriers between…
Aqueous solutions
Permeability
Ability of a molecule to pass thru a membrane
What is permeability based on?
Size of molecule
Charge of molecule
What forms the core of the membrane (lipid bilayer)?
Hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains
Fatty acid tails
Permeability of hydrocarbon chains (FA tails)
Low permeability to large molecules + hydrophilic particles (incl ions + polar molecules)
How do lipid bilayers make effective barriers?
Core of membrane = hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains
Have low permeability to large molecules + hydrophilic particles (ions, polar molecules)
What is the membrane not permeable to?
These have low permeability:
Large molecules
Hydrophilic particles- ions, polar molvules
What types of molecules can pass thru the membrane (high permeability)?
Small, non-polar molecules
Eg O2
Why can’t glucose go thru the membrane?
Small but polar
Needs alternative method
Qualities of cell membranes
Semi-permeability
Only certain materials can freely cross the CM
Selectivity:
Cell can control the passage of any material that cannot freely cross the membrane
Passive transport
No energy (ATP) required
Relies on CG
Methods of passive transport
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Simple diffusion
Passive net movement of particles from an area of high to low conc down a CG until a dynamic equilibrium is reached
Equilibrium = same conc on either side of the membrane
Does simple diffusion require a membrane?
No
Can happen w or w/o a membrane
What type of molecules can simple diffusion occur for?
Small, non-polar
Eg O2, CO2
Example of simple diffusion across membranes
Movement of O2 + CO2 molecules betw phospholipids
Concentration gradient
Shows the difference in conc betw 2 areas
Factors affecting diffusion
Temp
Higher temp = more KE
Steepness of CG
Higher CG = faster diffusion
Molecule size + charge
Faster for small, uncharged molecules
SA
Higher SA = faster diffusion
Diffusion distance
Shorter DD = faster diffusion
Do all membrane proteins have the same structure, location, function?
No
Diverse structure, location, function
2 types of membrane proteins
Integral
Peripheral
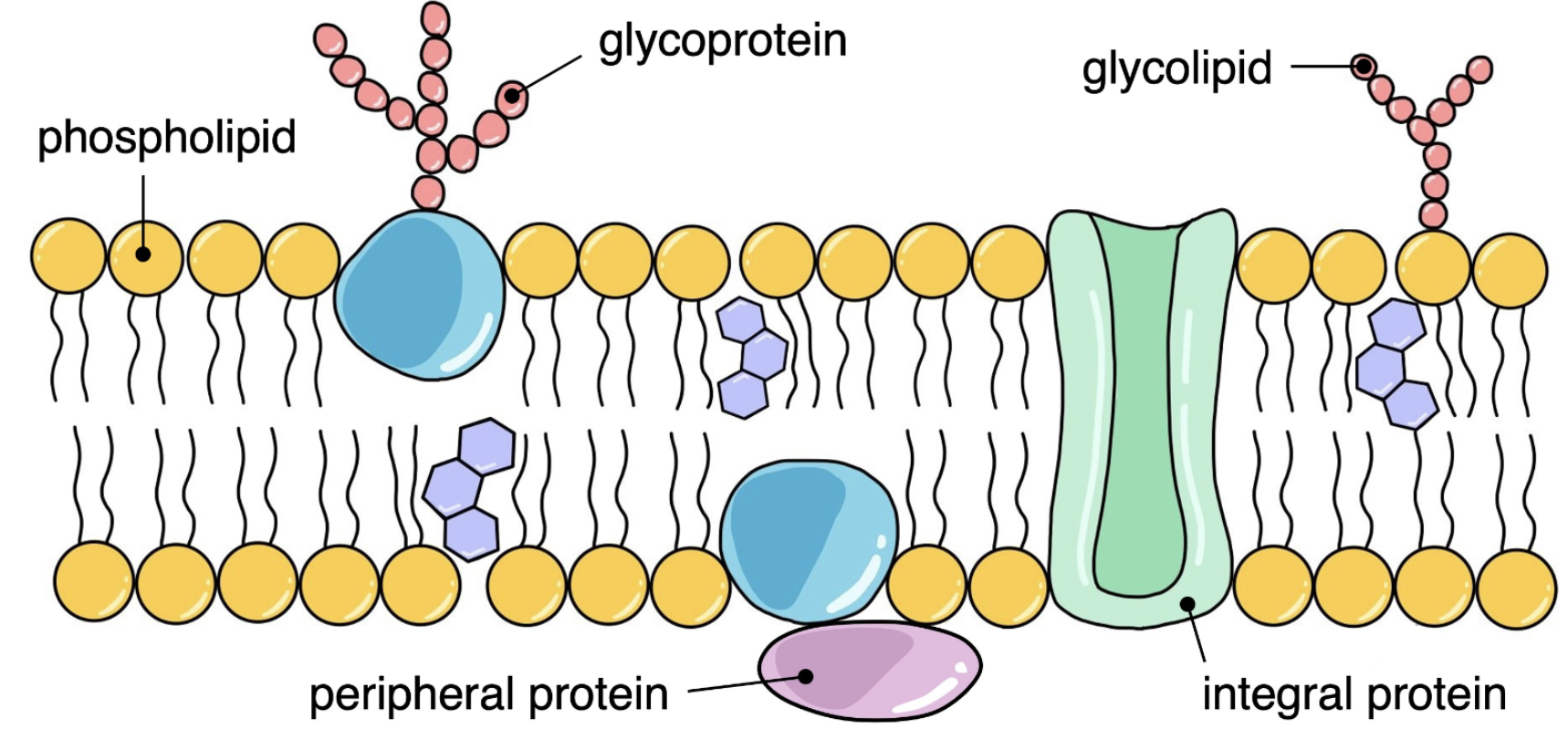
Integral proteins
Embedded in 1 or both of the lipid layers of a membrane
Transmembrane
Amphipathic
Examples of integral proteins
ATP synthase
Channel proteins
Protein pumps
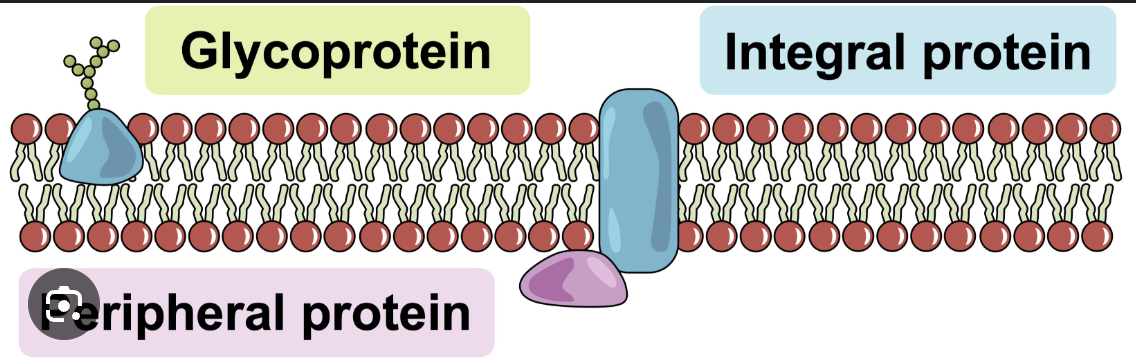
Peripheral proteins
Attached to 1 or other surface of the bilayer
Inner or outer membrane
Hydrophyllic
Examples of peripheral proteins
Glycoproteins
Cytochrome c (electron transport chains)
6 functions of membrane proteins (JETRAT)
Junction
Enzymes- ATP synthase
Immobilised enzymes
Transport- channel proteins, protein pump
Recogniton- glycoproteins
Attachment
Transduction of hormone signals
Hormone binding sites (receptors)
What does diffusion happen due to?
The random movement of particles
Movement of water molecules across membranes by osmosis
Osmosis
Passive net movement of water from an area of high water conc to an area of low water conc thru aquaporins thru a partially permeable membrane
Until equilibrium is reached
Low solute conc → high solute conc
3 reasons for osmosis
Random movement of particles
Impermeability of membranes to solutes
Differences in solute concentration
Aquaporins
Channel proteins which specifically allow water to pass thru
Greatly increases the permeability of water
Integral protein
Where are lots of aquaporins found?
Kidneys
Root hair cells
Define osmosis based on hypo / hypertonic
Water moves from low solute (hypotonic) to high solute (hypertonic) environments
In osmosis, why is the net movement of water from low to high solute conc?
Substance dissolves, it is surrounded by water molecules
→ forms H bonds → restricts movement of water molecules
So areas w high solute conc have fewer water molecules free to move to areas w lower solute conc
Water is polar but it can pass thru membranes (lipid bilayer)- how?
It is small enough
Osmolarity
A measure of solute concentration.
High osmolarity = lots of solute
Low osmolarity = little solute
Water potential
The tendency of water to move from one area to another due to osmosis
What type of transport are channel proteins needed for?
Facilitated diffusion

Facilitated diffusion
Passive net movement of particles from an area of high to low conc thru a channel protein embedded in the membrane
What types of particles use facilitated diffusion to pass thru the membrane?
Polar, charged molecules
Eg glucose
Are channel proteins generic to all molecules?
No- specific to molecules
Eg K+ channels
Most allow only 1 type of molecule to diffuse thru
How does the structure of channel proteins make it selectively permeable?
Allows specific ions to diffuse thru when channels are open but not when they are closed
Diameter + specific shape allows for transport of specific molecules
Can protein channels open + close?
Yes
They are gated
Eg voltage gated
Allows for selective permeability w/o using energy
Similarities betw simple + facilitated diffusion
Both:
Passive (no energy)
Move particles down CGs
Differences betw simple + facilitated diffusion
Molecule charge
Molecule size
Need channel proteins?

Active transport
Active movement of particles from an area of low to high conc thru pump proteins
Needs ATP (produced by mitochondria in AR)
Against CG
Why does AT need energy?
Moves particles against the CG
Role of pump proteins in AT
Pumps use energy ATP to transfer specific particles across membranes
So they can move particles against a CG
In how many ways can protein pumps move particles in?
Only 1
Are protein pumps specific or general?
Specific to diff molecules
Eg Na pump
What types of molecules can be actively transported?
Molecules
Ions
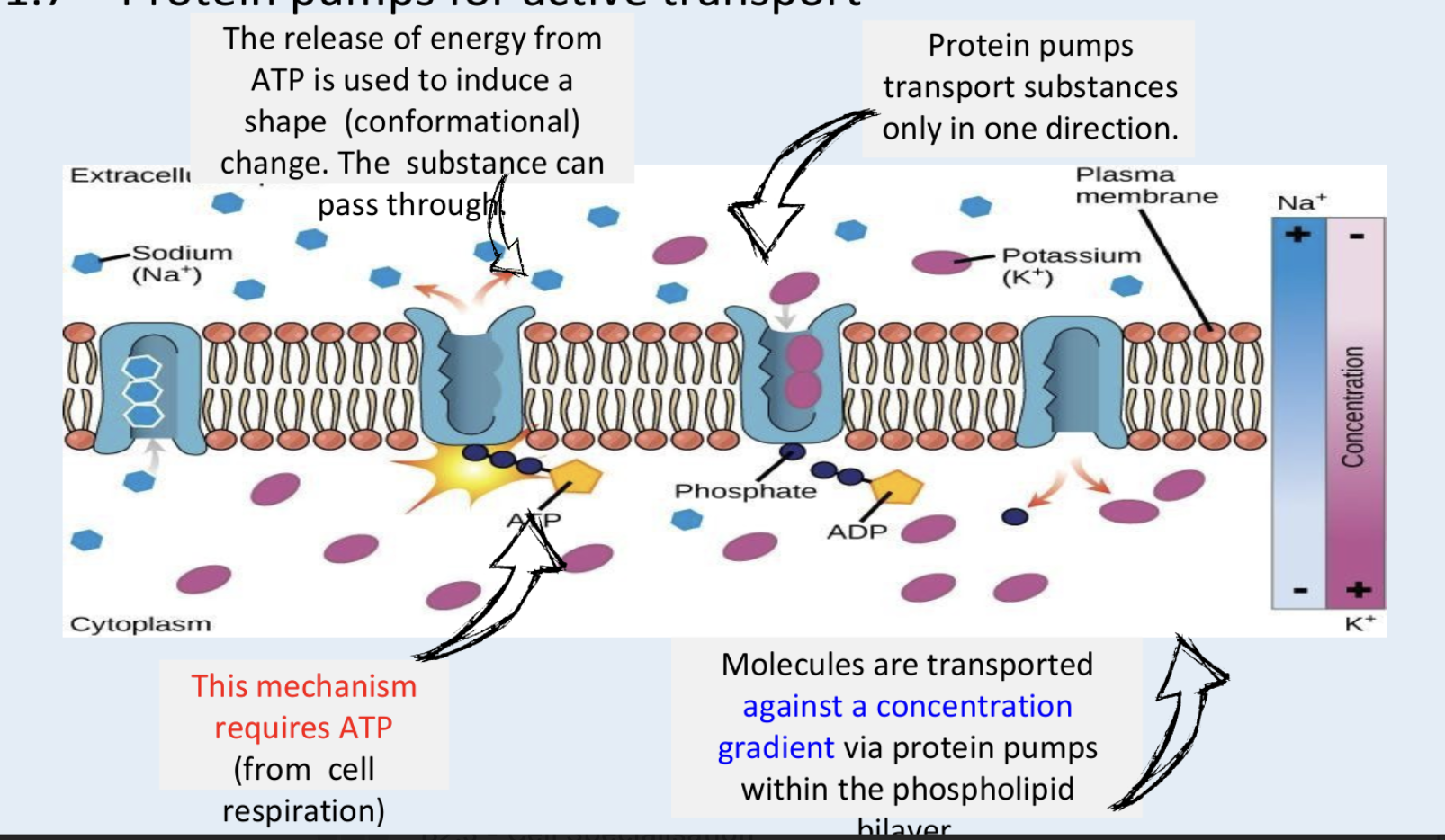
How do pump proteins work?
Input of energy (ATP)
→ conformational change (pump protein changes shape)
So particle moves thru + transported against CG
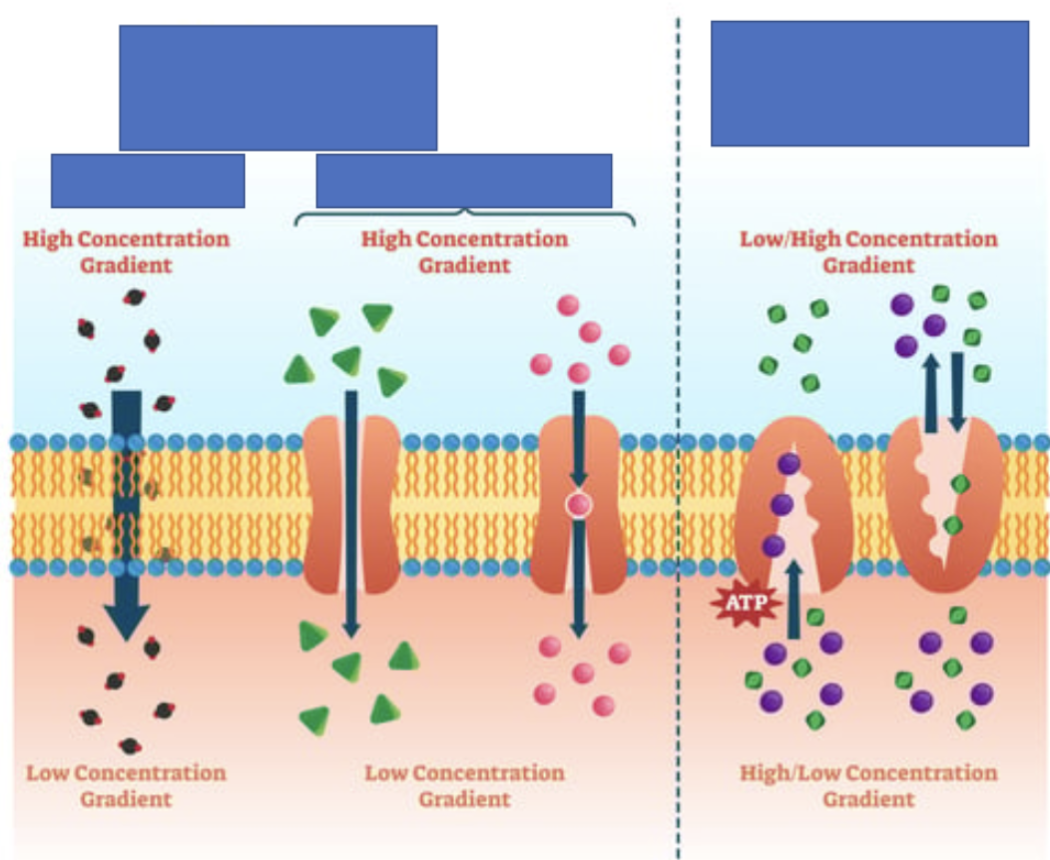
What makes membranes selectively permeable?
Facilitated diffusion (channel proteins)
Active transport (protein pumps)
Examples of molecules that are always permeable
Water
Small, non-polar eg O2
Is permeability by simple diffusion selective?
No
Only depends on the size + hydrophilic / hydrophobic properties of particles.
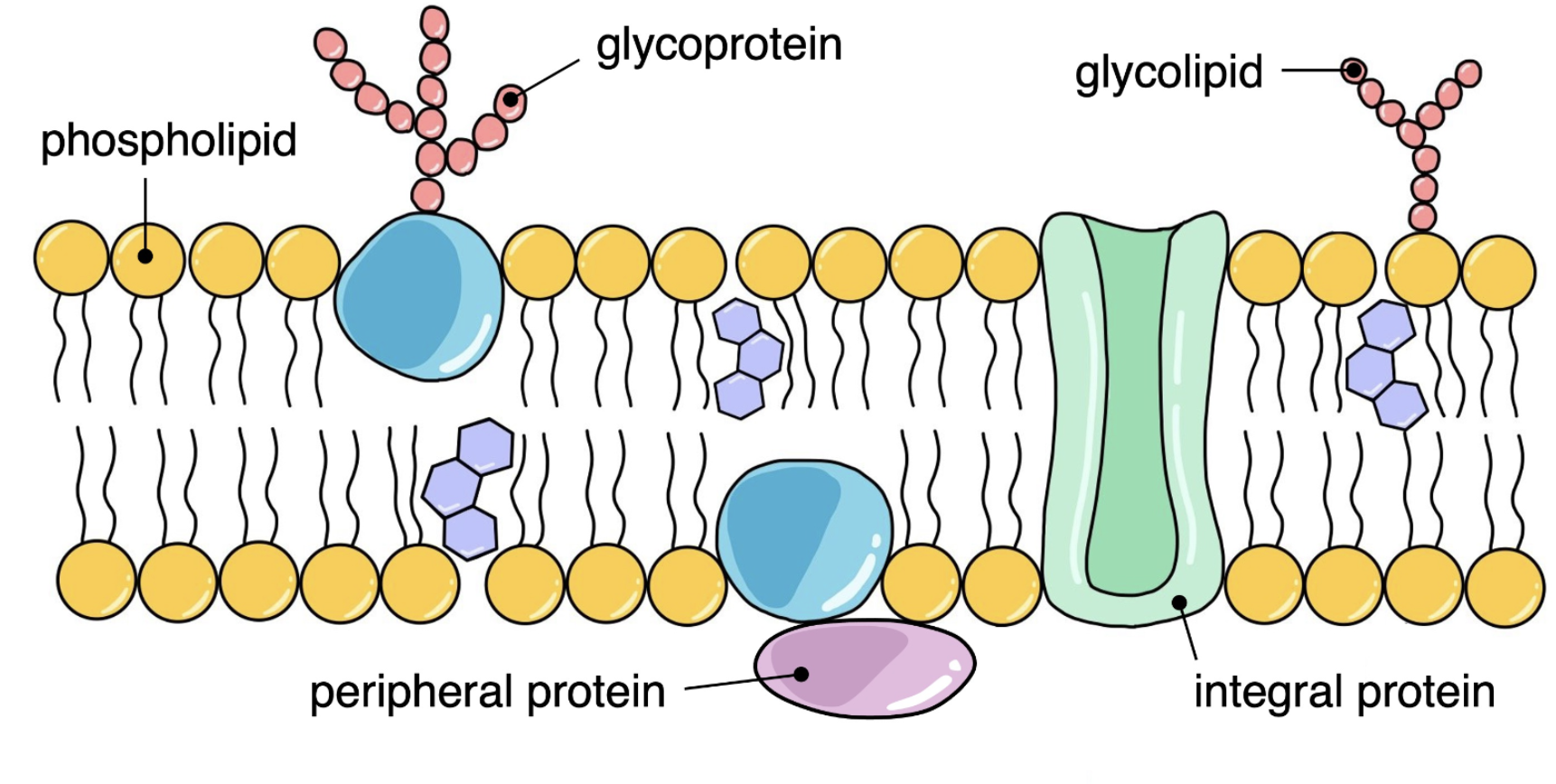
Glycoprotein
Membrane proteins with carbohydrate chains attached (on the outside)
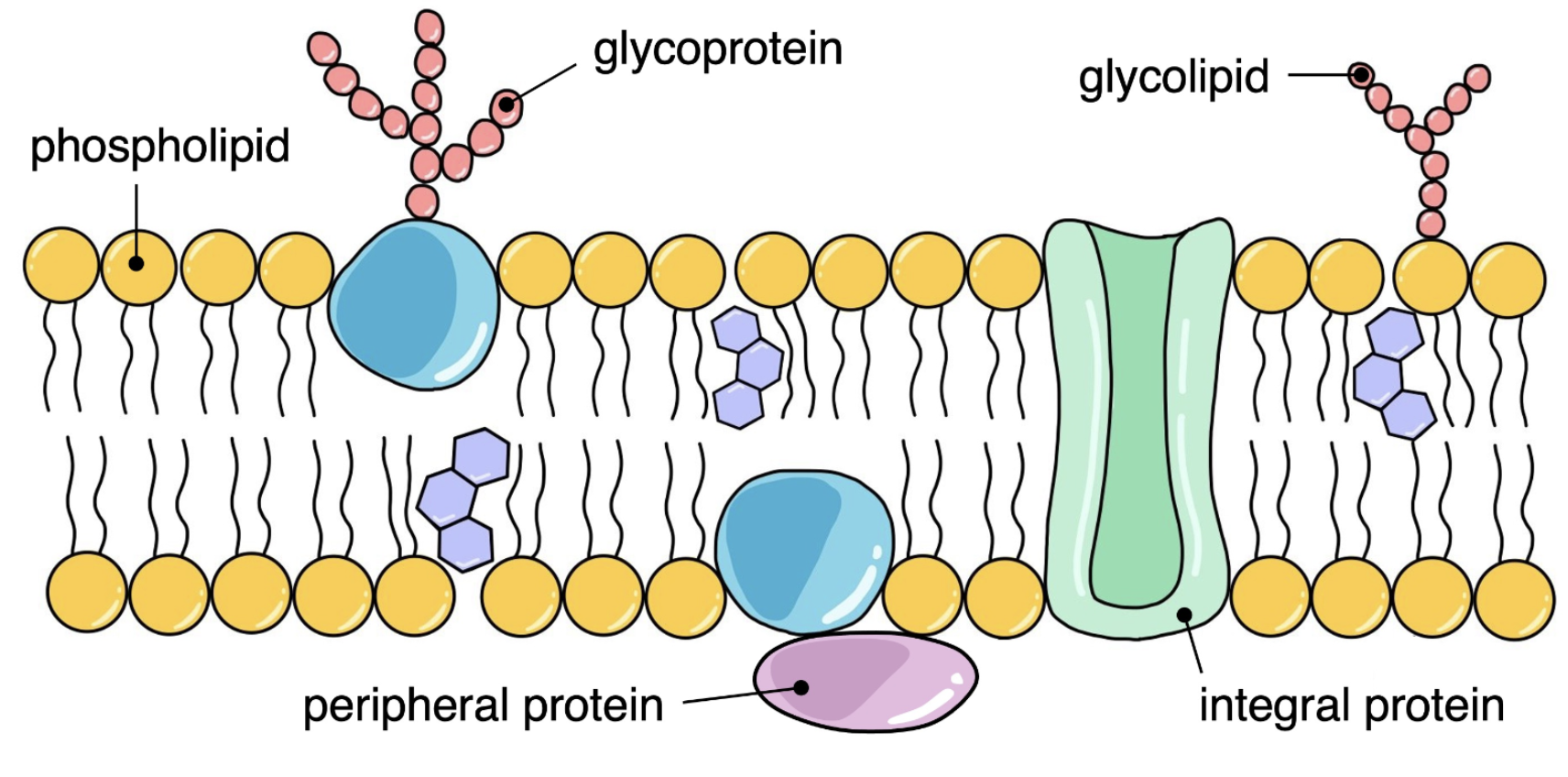
Glycolipids
Membrane lipids with carbohydrate chains attached (on the outside)
Where is the carbohydrate chain attached on glycoproteins + glycolipids?
On the extracellular side of membranes
Function of glycoprotein + glycolipid
Role in:
Cell adhesion
Cell recognition
In what cells are glycolipids found?
Eukaryotes
Recognition (immune system)
Fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
Include:
Peripheral + integral proteins
Glycoproteins
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Indicate hydrophobic + hydrophilic regions
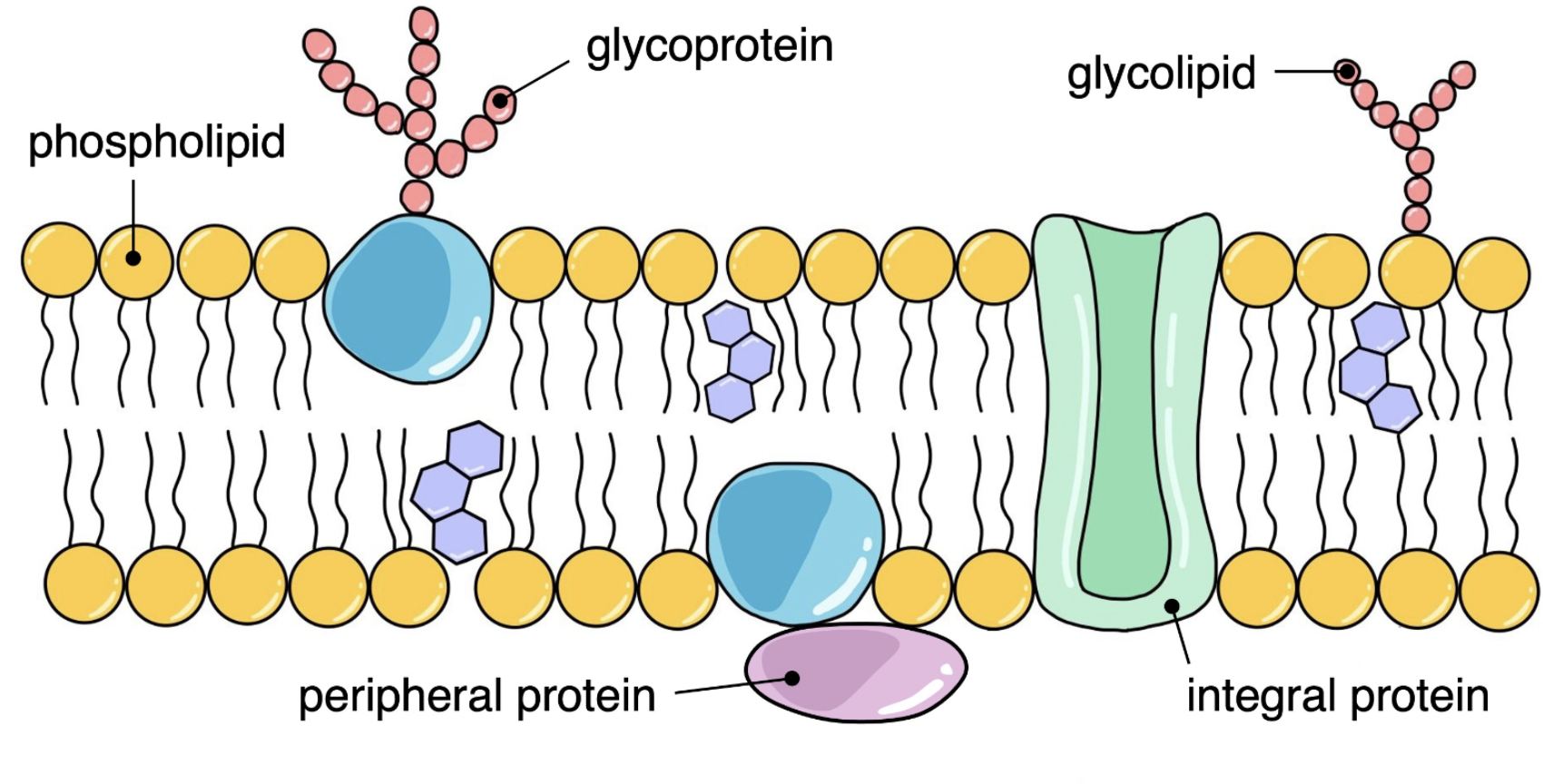
Are membranes flexible?
Yes