Renal Physiology - Physiology
5.0(1)Studied by 10 people
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:22 AM on 9/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
Functions of the Kidney
Regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance
Regulation of plasma osmolarity
Removal of metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs
Endocrine functions (Renin & Erythropoietin)
Metabolism
Ensuring long-term acid-base balance
Regulation of plasma osmolarity
Removal of metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs
Endocrine functions (Renin & Erythropoietin)
Metabolism
Ensuring long-term acid-base balance
2
New cards
Two major classes of Nephrons
Cortical (superficial, located in cortex) - 80%
Juxtamedullary (deep) - 20%
Juxtamedullary (deep) - 20%
3
New cards
Renal corpuscle
Comprised of Glomerulus and Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
4
New cards
Glomerular (Bowman's) Capsule
Consist of Capsular outer layer, visceral layer (podocytes), Bowman's space (separates two layers)
5
New cards
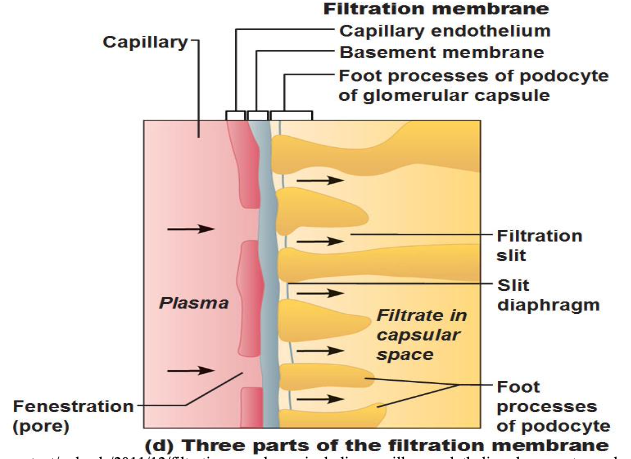
Filtration membrane
Fenestrated endothelium of glomerular capillaries, Basement membrane (negatively charged), and foot processes of podocytes (w/ filtration slits)
*No macromolecules, ONLY H2O, glucose, AAs, nitrogenous wasters, solutes smaller than plasma proteins pass (NO blood cells pass)
*No macromolecules, ONLY H2O, glucose, AAs, nitrogenous wasters, solutes smaller than plasma proteins pass (NO blood cells pass)
6
New cards
Glomerulus
specialized for filtration
afferent arteriole --> glomerulus --> efferent arteriole
afferent arteriole --> glomerulus --> efferent arteriole
7
New cards
Peritubular capillaries (cortical nephron)
Low-pressure capillaries adapted for absorption of H2O and solutes; cling to adjacent renal tubules in cortex
8
New cards
Vasa recta (Juxtamedullary nephron)
Long (thin-walled) vessels parallel to long nephron loops of juxtamedullary nephrons
9
New cards
Jutaglomerular Apparatus (JGA)
one per nephron
Has three cell populations:
- Macula densa
- Granular cells
- Extraglomerular mesangial cells
Has three cell populations:
- Macula densa
- Granular cells
- Extraglomerular mesangial cells
10
New cards
Macula densa
Epithelial cells of DCT (near renal corpuscle)
Function as chemoreceptors
Function as chemoreceptors
11
New cards
Granular cells
Granules contain Renin
Function as mechanoreceptors (sense blood press. in afferent arteriole)
Function as mechanoreceptors (sense blood press. in afferent arteriole)
12
New cards
Extraglomerular mesangial cells
B/w afferent & efferent arterioles
May pass signals b/w macula densa & granular cells
May pass signals b/w macula densa & granular cells
13
New cards
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Volume of plasma that is filtered across the glomerular per unit time
- The amt of filtrate kidneys produce each minute (average: 125 mL/min)
- The amt of filtrate kidneys produce each minute (average: 125 mL/min)
14
New cards
Two Major Forces of GFR
- Hydrostatic pressure (forces fluids & solutes thru filtration membrane)
- Oncotic pressure
- Oncotic pressure
15
New cards
Outward pressures promoting filtrate formation
Hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries (HP (GC)) = glomerular blood pressure (55 mm Hg)
16
New cards
Inward forces stopping filtrate formation
1) Hydrostatic pressure capsular space (HP (BS)) - 15 mmHg
2) Colloid oncotic pressure in capillaries (OP (GC)) - 30 mmHg
2) Colloid oncotic pressure in capillaries (OP (GC)) - 30 mmHg
17
New cards
Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Sum of forces, pressure responsible for filtrate formation
Main factor controlling glomerular filtration rate
Main factor controlling glomerular filtration rate
18
New cards
Net Filtration Pressure Equation
NFP = (HPgc - HPbs) - (onocGC - onocBS)
NFP = outward pressures - inward pressures
NFP = (55 - 15) - (30 - 0) = 40 - 30 = 10 mm Hg
(onocBS is negligible)
NFP = outward pressures - inward pressures
NFP = (55 - 15) - (30 - 0) = 40 - 30 = 10 mm Hg
(onocBS is negligible)
19
New cards
GFR is directly proportional to...
1) NFP
2) Total surface area available for filtration
3) Filtration membrane permeability
2) Total surface area available for filtration
3) Filtration membrane permeability
20
New cards
Mechanisms of Urine Formation
Three renal processes:
Tubular absorption
Tubular secretion
Glomerular filtration
Tubular absorption
Tubular secretion
Glomerular filtration
21
New cards
Renal Clearance
Cx = Ux * V/ Px
22
New cards
Cx = C inulin
Filtered, but not Reabsorbed or Secreted
23
New cards
Cx < C inulin
Filtered and Reasbored
Ex: Na+, Cl-, HCO3-, phosphate, urea, glucose, and amino acids
Ex: Na+, Cl-, HCO3-, phosphate, urea, glucose, and amino acids
24
New cards
Cx > C inulin
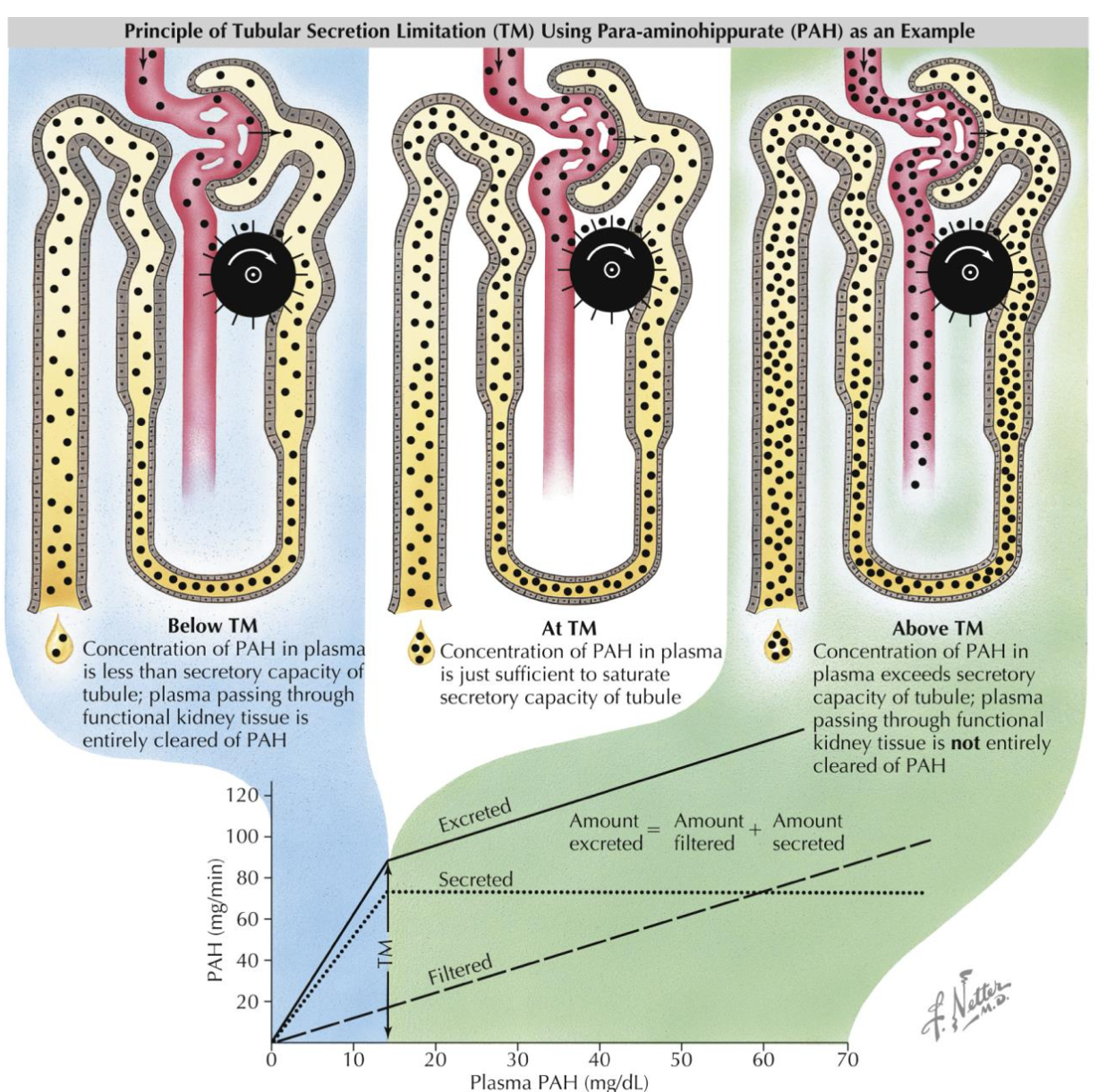
Filtered and Secreted
Ex: para-aminohippuric acid (PAH), creatinine, urea, NH4+, and morphine
Ex: para-aminohippuric acid (PAH), creatinine, urea, NH4+, and morphine
25
New cards
Cx < or > C inulin
Filtered, Reabsorbed and Secreted
Ex: H+ and HCO3-
Ex: H+ and HCO3-
26
New cards
Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)
RBF - (1 - HCT)
Normal adult male: RBF = ~1L/min, HCT = ~40%
Ex: Renal Handling of PAH (effective RPF)
Normal adult male: RBF = ~1L/min, HCT = ~40%
Ex: Renal Handling of PAH (effective RPF)
27
New cards
Constriction of Afferent arteriole
Decrease RPF
Decrease HP (Glomerular Cap) --> Decrease GFR
Decrease HP (Glomerular Cap) --> Decrease GFR
28
New cards
Constriction of Efferent arteriole
Decrease RPF
Increase HP (Glomerular Cap) --> Increase GFR
Increase HP (Glomerular Cap) --> Increase GFR
29
New cards
Control of GFR
1) Autoregulation (local level) intrinsic
2) Hormonal regulation (by kidneys)
3) Autonomic regulation (sympathetic division)
2) Hormonal regulation (by kidneys)
3) Autonomic regulation (sympathetic division)
30
New cards
Renal autoregulation
Two types:
1) Myogenic mechanism
2) Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism
1) Myogenic mechanism
2) Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism
31
New cards
Countercurrent multiplier
interaction of filtrate flow in descending/ascending limbs of nephron loops of juxtamedullary nephrons --> creates gradient
32
New cards
Countercurrent exchanger
blood flow in descending/ascending limbs of vasa recta --> maintains gradient
33
New cards
Thin descending limb
Permeable to water, impermeable to solutes
34
New cards
Thick ascending limb
Impermeable to water
35
New cards
Medullary osmotic gradient
Concentration gradient created in peritubular fluid of medulla
- Na+, K+, 2 Cl- moves out of ascending limb (via Na+-K+/2Cl- transporter) into interstital fluid and then water diffuses out of descending limb --> raising osmolality of intersititial fluid (to max 1200 mL/min)
- Na+, K+, 2 Cl- moves out of ascending limb (via Na+-K+/2Cl- transporter) into interstital fluid and then water diffuses out of descending limb --> raising osmolality of intersititial fluid (to max 1200 mL/min)
36
New cards
Vasa recta - Countercurrent exhcanger
- Highly permeable to water and solutes
a. Descending limb: water out, NaCl in --> at bottom of loop reaches 1200
b. Ascending limb: water in, NaCl out --> ends @ 325 (slightly higher than 300 start)
a. Descending limb: water out, NaCl in --> at bottom of loop reaches 1200
b. Ascending limb: water in, NaCl out --> ends @ 325 (slightly higher than 300 start)
37
New cards
Urea Recycling
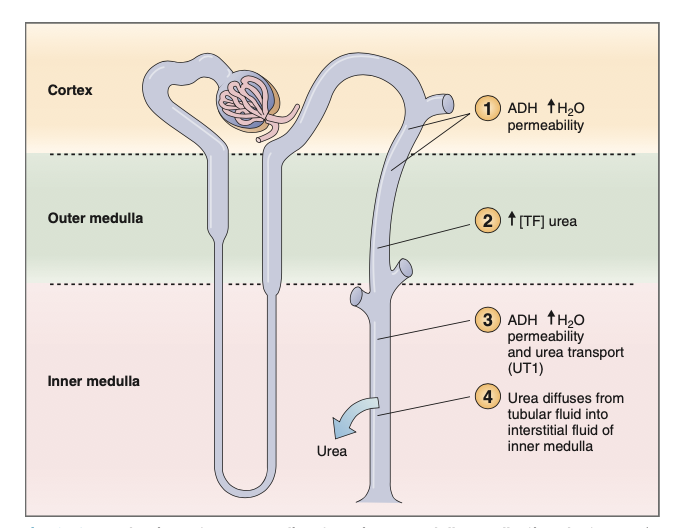
Cortical and outer medullary collecting ducts: ADH increases water permeability but NOT urea permeability --> water is absorbed but urea remains --> urea increase
Inner medullary collecting ducts: ADH increases water permeability & facilitated diffusion of urea (UT1) --> helps maintain gradient
Inner medullary collecting ducts: ADH increases water permeability & facilitated diffusion of urea (UT1) --> helps maintain gradient
38
New cards
Anitidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Prevents excessive water loss in the urine and increases water absorption
*Targets kidney's collecting ducts
*Targets kidney's collecting ducts
39
New cards
Aldosterone
Determines rate of Na+ reabsorption and K+ loss in kidneys
- secreted in response to rising K+ or falling Na+
- secreted in response to rising K+ or falling Na+
40
New cards
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Released by atrial cells in heart due to stretch (inc BP)
- Effects:
Decreases in blood pressure and volume
a. Decreased ADH, renin and aldosterone production
b. Inc excretion of Na+ and H2O
c. Promotes vasodilation directly and dec of angiotensin II
- Effects:
Decreases in blood pressure and volume
a. Decreased ADH, renin and aldosterone production
b. Inc excretion of Na+ and H2O
c. Promotes vasodilation directly and dec of angiotensin II
41
New cards
Alkalosis
arterial pH > 7.45
42
New cards
Acidosis
arterial pH < 7.35
43
New cards
Net gain of H+
Hyperventilation (Increase in CO2, slow breathing)
Diarrhea (loss of HCO3-)
Cell and protein metabolism
Ingestion of acid containing food
Diarrhea (loss of HCO3-)
Cell and protein metabolism
Ingestion of acid containing food
44
New cards
Net loss of H+
Hyperventilation (decrease in CO2)
Vomiting
Urinary acid excretion
Vomiting
Urinary acid excretion
45
New cards
HH equation
pH = Kidney / Lung = [HCO3-] / P(CO2)
46
New cards
Blood pH rises (alkaline)
Bicarbonate ions are excreted --> H+ ions retained by kidney tubules
47
New cards
Blood pH falls (acidic)
Bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed --> H+ ions are secreted
48
New cards
Respiratory acidosis w/ renal compensation
Indicated by:
LOW pH
HIGH P(CO2) (= cause of acidosis) and bicarbonate levels (compensation)
Kidneys reabsorb more bicarbonate --> create new bicarbonate and secrete more H+
LOW pH
HIGH P(CO2) (= cause of acidosis) and bicarbonate levels (compensation)
Kidneys reabsorb more bicarbonate --> create new bicarbonate and secrete more H+
49
New cards
Respiratory alkalosis w/ renal compensation
Indicated by:
HIGH pH
LOW P(CO2)
Decreasing HCO3- levels
HIGH pH
LOW P(CO2)
Decreasing HCO3- levels
50
New cards
Two mechanisms to generate bicarbonate ions
1) Excretion of buffered H+
2) Excretion of NH4+ (glutamine)
2) Excretion of NH4+ (glutamine)