APSC 530 Repro Exam 3 SG
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
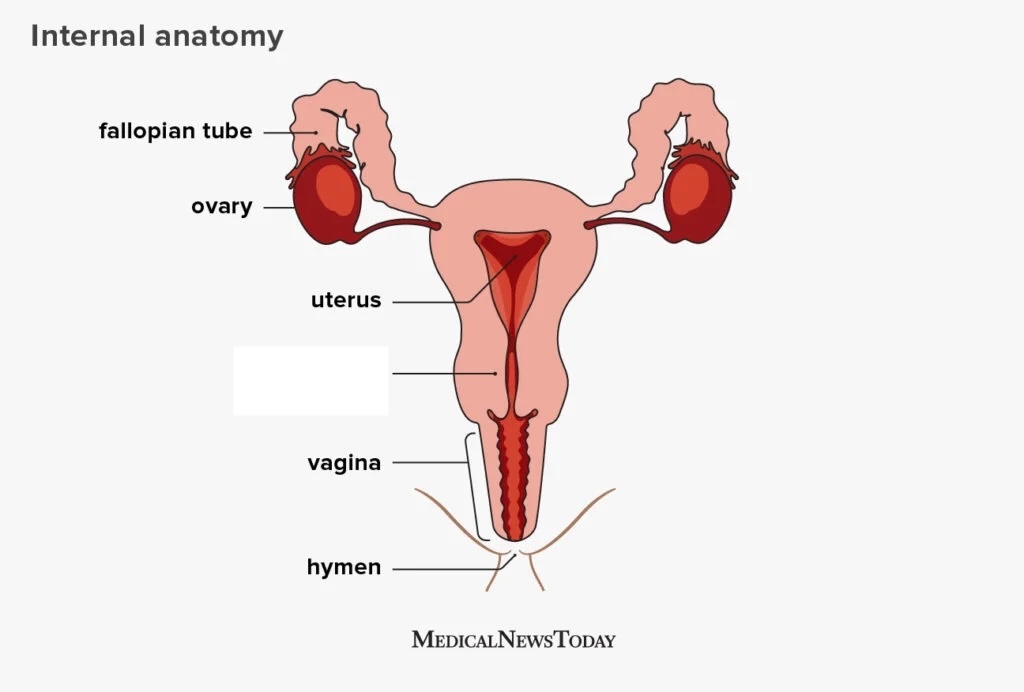
Cervix
Separates the UTERUS from the VAGINA
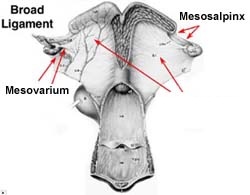
Broad Ligament
-Sling-like structure that suspends the tract in the abdominal cavity
-Specifically suspends: Uterus, Oviduct, Ovaries
Mesovarian
*Broad Ligament Anatomy*
-attaches and suspends the ovary
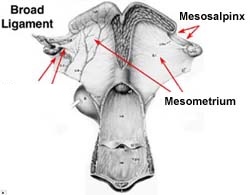
Mesoalpinx
*Broad Ligament Anatomy*
-attaches to oviduct
-part of the lining of the abdominal cavity in higher vertebrates
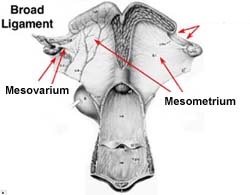
Mesometrium
*Broad Ligament Anatomy*
-largest section of BL
- attaches to uterus and stretches as fetus grows
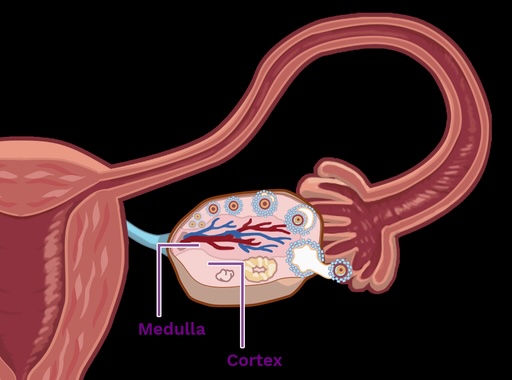
Medulla
Cortex
The Two Gross Anatomy Regions of the Ovary:
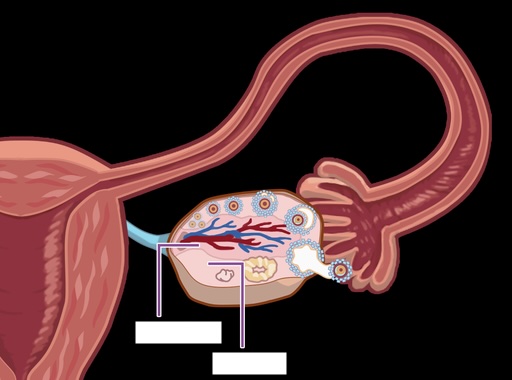
Cortex
Ovary Gross Regional Anatomy
–where follicles are housed
–peripheral region
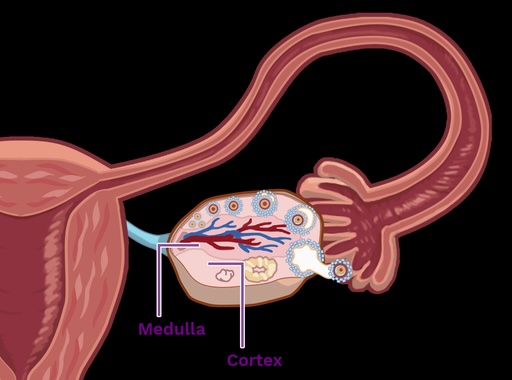
Medulla
Ovary Gross Regional Anatomy
--numerous vessels enter here
–central region
Oocytes
Estradiol (E2) Progesterone (P4)
Ovary Functions
The EXOCRINE function of the ovary is that it produces ________ (HINT: cells)
The ENDOCRINE function of the ovary is that it produces __________
Endocrine hormones are secreted into the bloodstream to act on other parts of the body, while exocrine hormones are eventually excreted outside on any epithelial surface
Estrous Cycle
Cyclic Changes of the Ovary
—limited period of time when females are sexually receptive to male, aka “in heat”
—defined by changes in hormonal patterns, many of which occur because of structures on the ovary
-If no pregnancy occurs, the cycle resumes without menstruation
Menstrual Cycle
Cyclic Changes of the Ovary
-period from start of one menses to the next
-if pregnancy doesn’t occur, the endometrial lining is shed as menstrual blood
Folliculogenesis
Follicular Development
-the process by which immature ovarian follicles develop into mature (Graafian) follicles, which are capable of ovulating an oocyte
True
T/F: Ducts are generally created by epithelial cells
Corpus Luteum
Ovarian Structures
-created from remnants of cells that used to make up the follicle
-1st recorded in cow and it was yellow; most species it’s actually white
Corpus Albicans
Ovarian Structures
- dead version of Corpus Luteum
Superficial Epithelium
Ovarian Structures
-outermost surface of ovary
-typically squamous or cuboidal in shape
Tunica Albuginea
Ovarian Structures
-dense connective tissue layer that covers ovary’s surface
-located beneath superficial epithelium
Stroma
Ovarian Structures
-connective tissue surrounding follicles
Primordial Follicle
Follicular Development
-forms when primordial Germ Cells (PGC) move into genital ridge
-surrounded by pregranulosa cells (squamous ep.)
-stimulation of development is unknown
Primary Follicle
Follicular Development
-–Oocytes surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal granulosa cells
Secondary Follicle
Follicular Development
-More than 1 layer of cuboidal granulosa. cells
-no cavity (antrum) formation
-still have oocyte and eggs in the middle
Tertiary Follicle
Follicular Development
–Get pockets of follicular fluid
–Increased follicular size
–Cavity (antrum) formation begins
–Antrum filled with follicular fluid
•Follicular fluid – produced by granulosa cells
Graafian Follicle
–Cavity (antrum) formed
–These follicles can be palpated
–Wall of follicle thins and erupts at ovulation
False: CUBOIDAL CELLS
T/F: SQUAMOUS CELLS are referred to as granulosa cells when they start to produce estrogen.
Granulosa
Tachycardia cells have multiple layers of ________ cells and an antrum cavity filled w/ follicular fluid that’s produced by these cells.
Gap Junctions
Follicle Anatomy
-granulosa cells are interconnected allowing oocyte to give and receive info
-granulosa cells communicate via these
Growth Differentiation Factor 9 (GDF-9)
Follicle Anatomy
-1st oocyte protein discovered
- Directs oocyte growth
- In “Knocked out animals”; follicles cease
developing at primary follicle stage
Knockout Animal
-a genetically modified animal where a specific gene has been intentionally inactivated or removed
-CRISPR can knock genes out or in
Connective Tissue Cells
These are always found under the basement membrane
Theca Externa
Follicle Anatomy
-Cells that are outside Basement Membrane
-outermost layer of granulosa cells
-don’t produce hormones
Theca Interna
Follicle Anatomy
-The inner-most layer that is closest to the granulosa cells
-has many blood vessels; produce Testosterone leaves vessels and stimulates theca and granulosa cells
Basement Membrane
separates theca interna and granulosa cells
Ovulation
-defined as: purposeful degradation of tissue
-occurs due to enzymatic digestion of the preovulatory follicular wall (STIGMA)
-occurs on very specific area on oocyte
Induced
Spontaneous
______ ovulation requires mating for ovulation to occur. (EX: rabbit, camel, cat)
_____ ovulation ovulate whether mated or not (EX: human, livestock)
Angiogenesis
-occurs rarely outside of ovary
-important part of CL development
-movement of the blood vessels of the theca interna into the GC layer
-granulosa cells produce factors that draw the blood vessles
-ensures follicle and CL have the nutrients they need
Corpus Hemorragicum
–Blood filled remains of ruptured follicle
–Very little P4 production
Corpus Luteum
–Formed from tissue of ruptured follicle
–Increased P4 production
Leteotropic Signal
CL signals
-CL maintenance and growth
Leuteolytic Signals
CL signals
-CL regression and degeneration
Leuteolysis
CL undergoes this as a result of prostaglandin F2 alpha which produces progesterone
pituitary gland
The _____ ______ controls the function and formation of the CL
sows
In _____ after the LH surge (which triggers ovulation), the corpus luteum can form and function without further help from the pituitary.
So, even if you removed the pituitary after ovulation, the CL would still work and produce progesterone.
Guinea Pigs
In ____ ____ The initial LH surge from the pituitary is needed, but ongoing pituitary support is not
-pituitary needed until like day 3 or 4 of the cycle
ewes
In ______:
The CL always depends on LH from the pituitary throughout the entire luteal phase.
If you remove the pituitary at any point, the CL will regress and stop producing progesterone.
Ampullary-isthmic Junction
Area on the oviduct where fertilization takes place
Horses
•In ______, only a fertilized egg can pass on from the ampullary-isthmic junction to the uterus
Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy
How do we distinguish between a fertilized and unfertilized egg?
Isthmus
the narrow part of the oviduct closest to the uterus. It plays a key role in coordinating the transport of:
Sperm (from uterus → ampulla)
Ova (egg) (from ovary → ampulla)
-sperm travels up ovum travels down
Uterotubular Junction
In sow, regulates the number of sperm that can enter uterus to prevent polyspermy
Muscle Contraction
Secretory activity of non ciliated cells (oviductal fluid)
Cilia
Name 3 Primary Mechanisms for Gamete Transport
Duplex Uterus
Uterus that has two cervical openings
IN PIC
-Maruspials have 2 vaginal openings
-rabbits have single vaginal opening
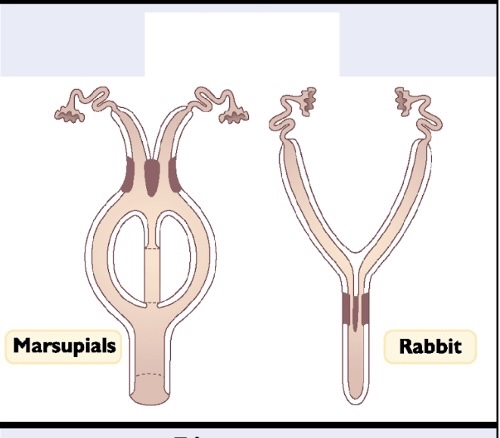
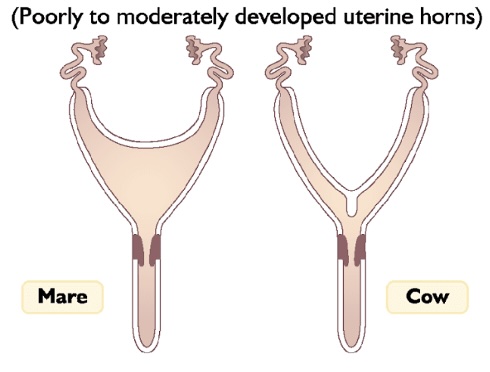
Bicornuate Uterus
-result of mullerian duct fusion to form Y shaoe
-Y-shaped, with two long horns and a common body and cervix, as in most carnivores
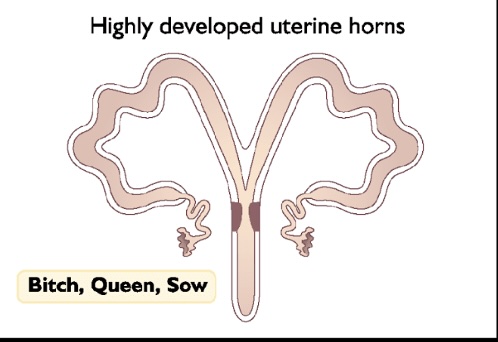
Bipartatite Uterus
-two separate uteri emptying into a common cervix
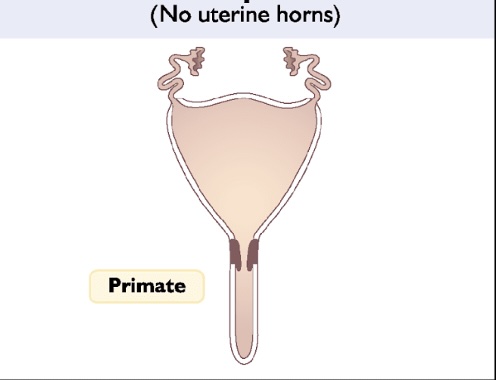
Simplex Uterus
-Result of nearly complete mullerian duct fusion
-no uterine horns
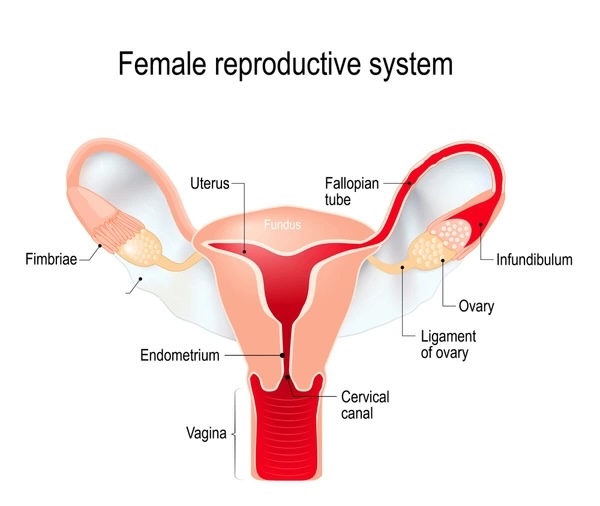
Serosa (Perimetrium)
-outermost layer of the uterus
-thin layer of connective tissue covered by a serous membrane
Muscularis (Myometrium)
-middle layer of uterus
-consists of smooth muscle
Mucosa (Endometrium)
-innermost lining of the uterus
-where embryo implants and develops
-cell types are simple columnar or pseudostratified epithelium
Uterine Glands
-embedded in endometrium
-secrete uterine milk (histotroph)