Leukocytes, plasma, and Platelets
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Leukocytes Structures
Also called white blood cells (WBC’s)
Less numerous than RBC’s
Crucial to body defenses
Leukocytes Functional Characteristics
Form protective mobile army against bacteria, viruses, parasites, toxins, & tumor cells.
Can slip into & out of blood vessels by DIAPEDESIS.
Pinpoint areas of tissue damage & destroy foreign substances or dead cells
2 Main Types of Leukocytes
Granulocytes and Agranulocytes
Granulocytes
Have a granular cytoplasm
Originate from bone marrow
65% of leukocytes
Multi-lobed nuclei
Agranulocytes
No granules in cytoplasm
Originate from lymphoid
35% of leukocytes
Nucleus has single lobe
Granulocytes -> Neutrophils
-Most Numerous.
-Nuclei consist of 3-5 lobes.
-Attracted to sites of inflammation & active phagocytes
Granulocytes >Basophils
-u or s-shaped nucleus
-causes cells to release heparin & histamine.
-histamine: vasodilator
-heparin: prevents blood clotting
-enhance migration of wbc’s
Granulocytes >Eosinophils
-nucleus has two lobes like figure 8 (sort of)
-reside in intestinal & pulmonary mucosae
-phagocytic
Agranulocytes > Lymphocytes
-2nd most numerous
-found in lymph tissue
-major cells of immunity
-yield antibodies
-nucleus is spherical & takes up most of cell
Agranulocytes > Monocytes
-nucleus is kidney shaped
-highly mobile macrophages
-Phagocytic
Production of WBCs
Leukopoiesis: production of wbc’s
Life span from a few days to several years
Blood plasma contains over 100 solutes:
Proteins, Organic Nutrients, Electrolytes, Respiratory gases and Plasma Proteins
Proteins
albumin, globulins, clotting proteins, and others (Lactic acid, urea, creatinine)
Organic nutrients
glucose, carbohydrates, amino acids
Electrolytes
sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate
Respiratory gases
oxygen and carbon dioxide
Plasma Proteins
Albumins – blood pressure
Globulins (alpha, beta, gamma) – transport lipids and antibodies for immunity
Fibrinogen – important for blood clotting
Hemostasis
The process of stopping blood flow. Involves coagulation and clotting.
3 Events of Hemostasis
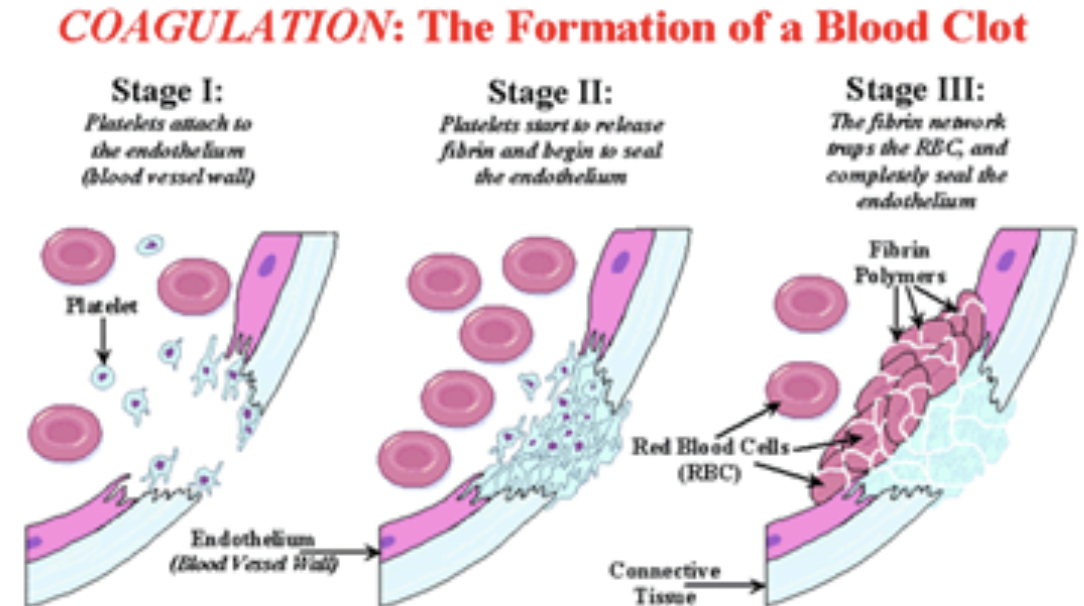
Stage 1
When the blood vessel wall is broken, thrombocytes (platelets) in the blood (which are easily damaged) disintegrate and release an enzyme called thromboplastin. Thromboplastin then converts a protein in the blood plasma called prothrombin into an active enzyme called thrombin. Calcium is needed for this process to work. (So: thromboplastin + calcium + prothrombin = thrombin). This makes the platelets stickier so they start to bind directly over the site of injury.
Stage 2
Thrombin then changes another plasma protein, fibrinogen into fibrin. Fibrin is insoluble and forms a netlike covering across the damaged vessel. (Thus thrombin + fibrinogen = fibrin).
Stage 3
As blood tries to flow through the net, red and white blood cells and platelets are trapped and form a clot. (Thus fibrin + blood cells = clot).
I read it!
Disorders of hemostasis
Thrombus, Embolus, Thrombocytopenia, Hemophilias
Thrombus
Clot that develops & persists in an unbroken blood vessel
if too large may block circulation
Embolus
Thrombus that breaks away from vessel wall & floats freely in bloodstream
will block circulation if encounters small artery
Thrombocytopenia
Condition in which number of circulating platelets is reduced, causes bleeding
Hemophilias
Inability for blood to clot properly