HA Exam 4
1/468
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
469 Terms
Stubby
Type of dendritic spine

Mushroom
Type of dendritic spine

Thin
type of dendritic spine
Multipolar
Most abundant in the body. Major neuron type in the CNS. CNS —> target area
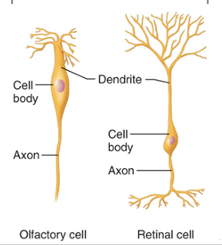
Bipolar
Rare. Found in some special sensory organs (olfactory mucosa, eye, ear). Sensory receptors —> CNS
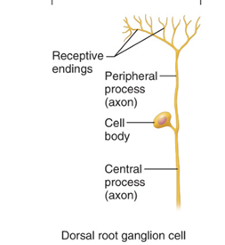
Unipolar (Pseudounipolar)
Found mainly in the PNS. Common only in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord and the sensory ganglia of cranial nerves. Cells or tissues —> CNS
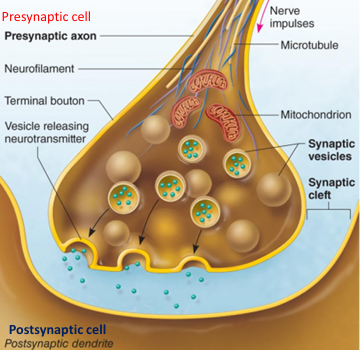
Chemical synapse
Vesicular (axon and dendrite)
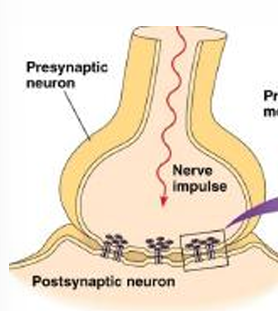
Electrical synapse
Nonvesicular
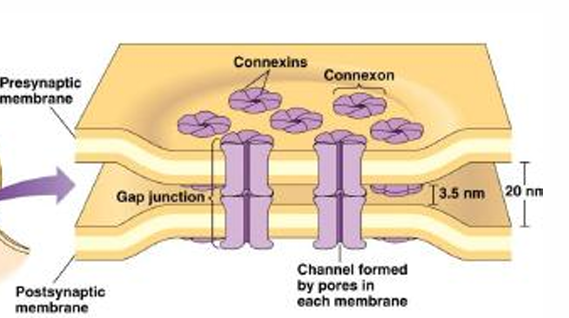
Gap Junctions
Pass an electrical signal or current directly from the cytoplasm of one cell to another through ____ (electrical synapse)
Ependymal cells
Create barriers between compartments. Source of neural stem cells. (CNS)

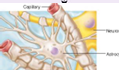
Astrocytes
Take up K+, water, and neurotransmitters. Secrete neurotrophic factors. Help form the blood-brain barrier. Provide substrates for ATP production (CNS)
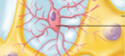
Microglia
Modified immune cell. Act as scavengers (CNS)
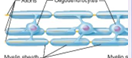
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheaths (CNS)
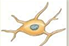
Schwann cells
form myelin sheaths. Secrete Neurotrophic factors. (PNS)

Satellite cell
Support cell bodies (PNS)
Myelin
Multiple concentric layers of phospholipid membrane
Schwann
_____ cell wraps around the axon many times
Node of Ranvier
a section of unmyelinated axon membrane between two Schwann cells
Ganglion
A collection of nerve cell bodies found outside of the CNS
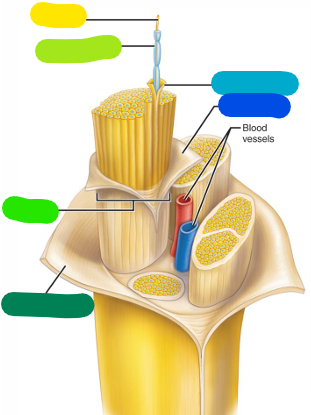
Axon
yellow
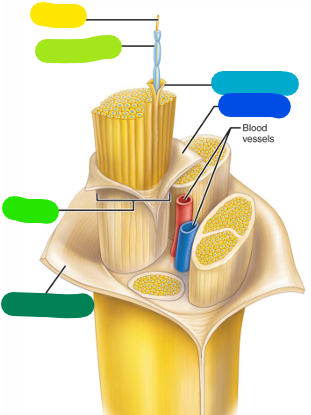
Myelin sheath
lime green
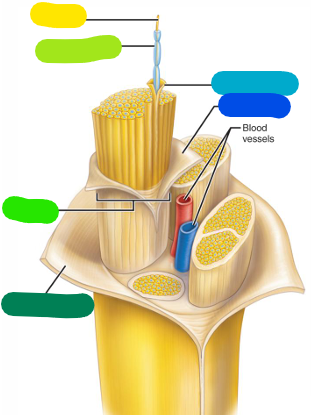
Fascicle
A bundle of axons (bright green)
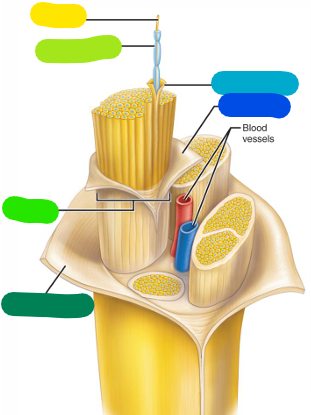
Epineurium
Outer layer — becomes continuous with the dura mater (dark green)
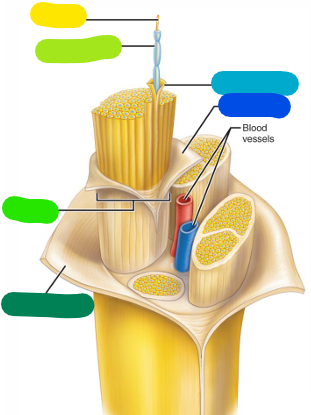
Perineurium
Layer surrounding a fascicle (dark blue)
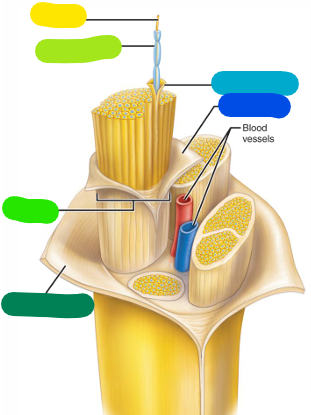
Endoneurium
Layer surrounding a single axon (light blue)
Afferent signals
—> CNS
Efferent signals
CNS —>
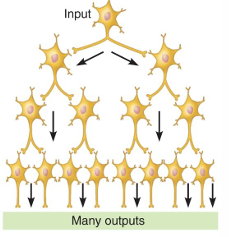
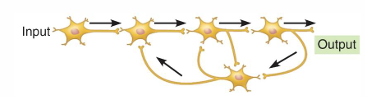
Diverging circuit
One presynaptic neuron branches to affect a larger number of postsynaptic neurons
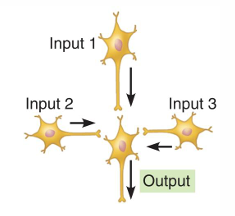
Converging circuit
Many presynaptic neurons provide input to influence a smaller number of postsynaptic neurons
Reverberating circuit
One neuron receives feedback from another neuron in the same circuit
Neural cortex
purple
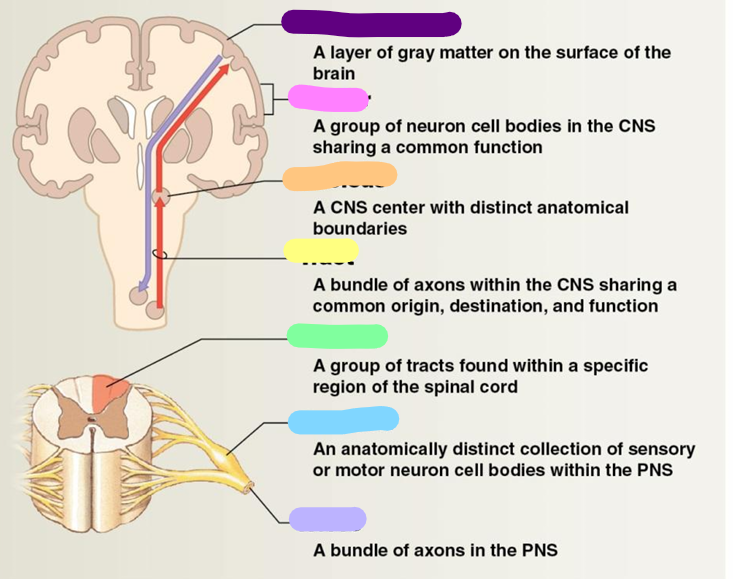
Center
pink
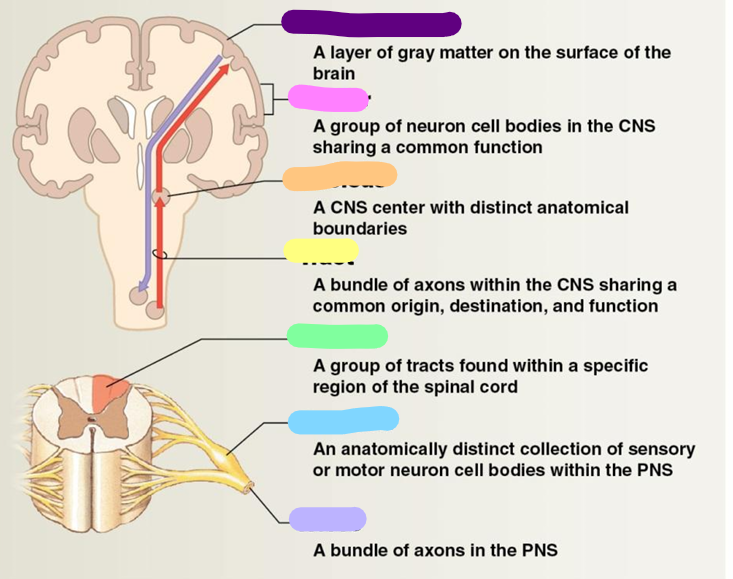
Nucleus
orange
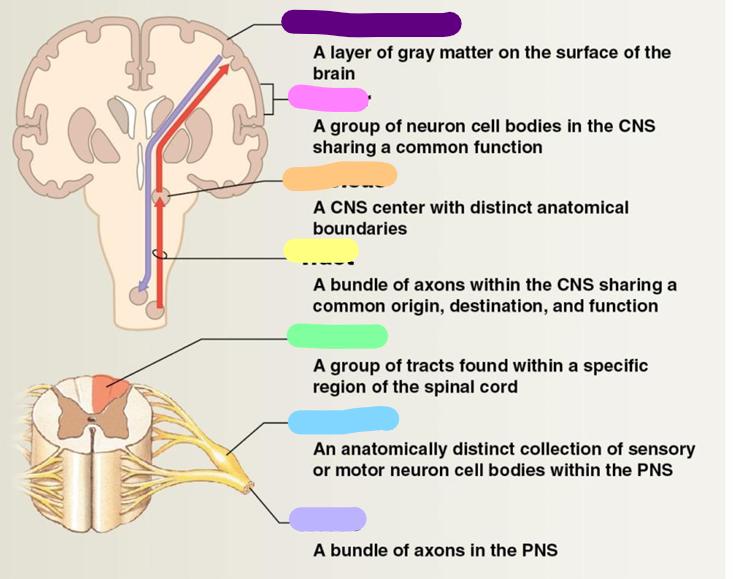
Tract
yellow
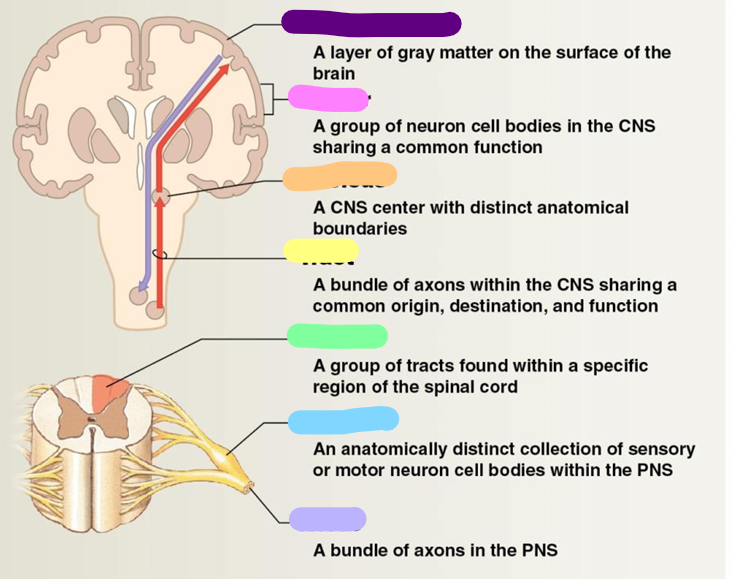
Column
green
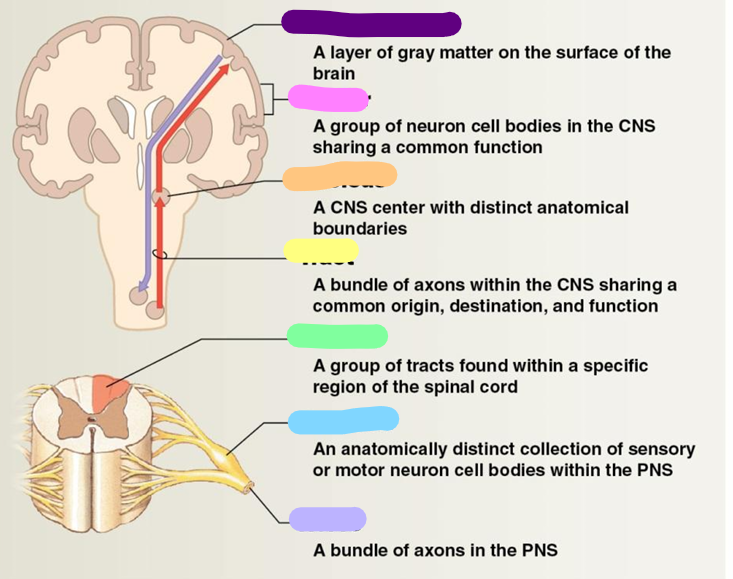
Ganglion
blue
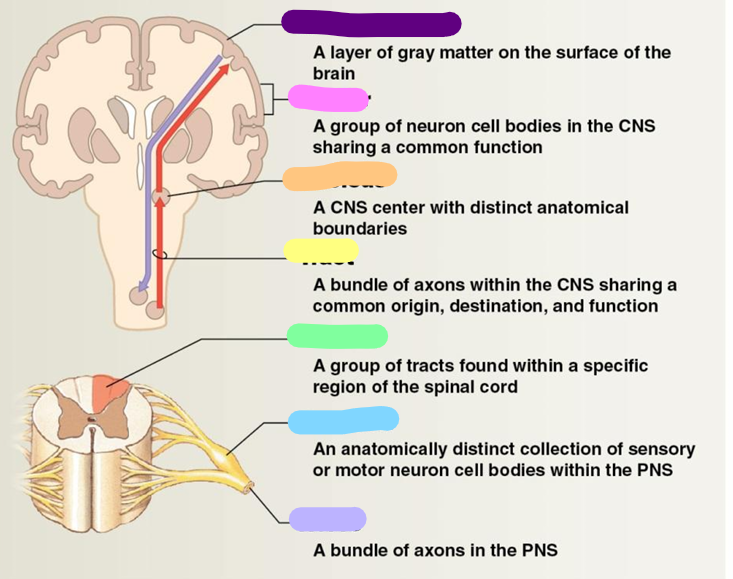
Nerve
Lavender
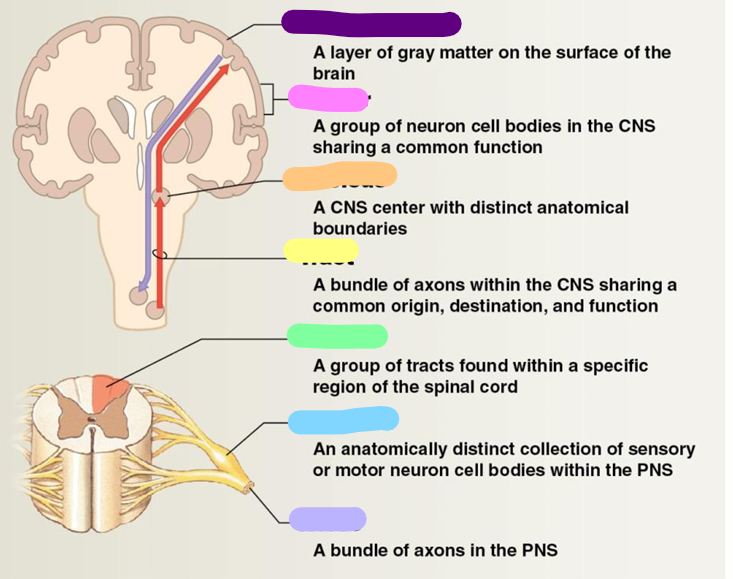
White matter
Mostly myelinated axons and contains very few cell bodies
Gray matter
Nerve cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals
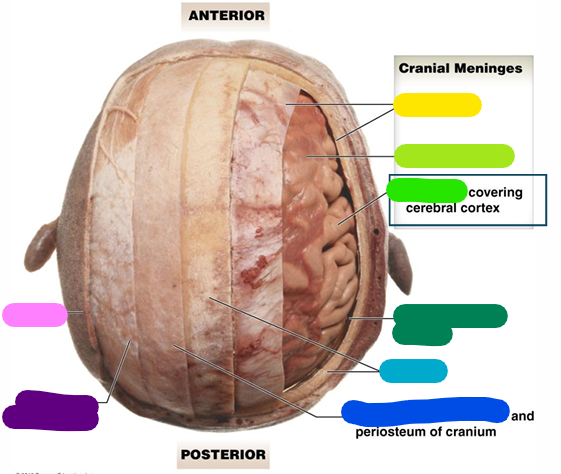
cranium
The brain is encased in the ____
Dura mater
Outer most layer; lavender
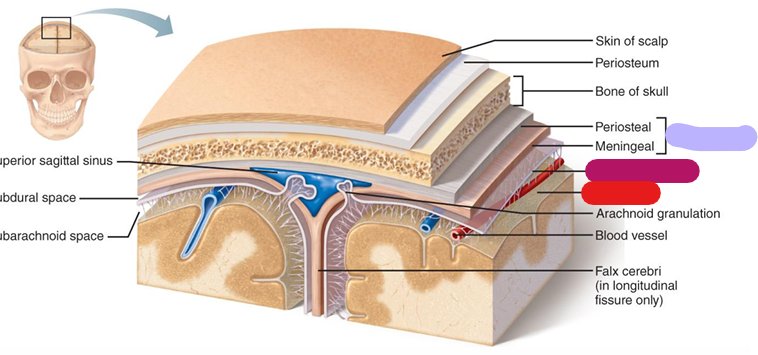
Arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid space between the two layers (magenta)
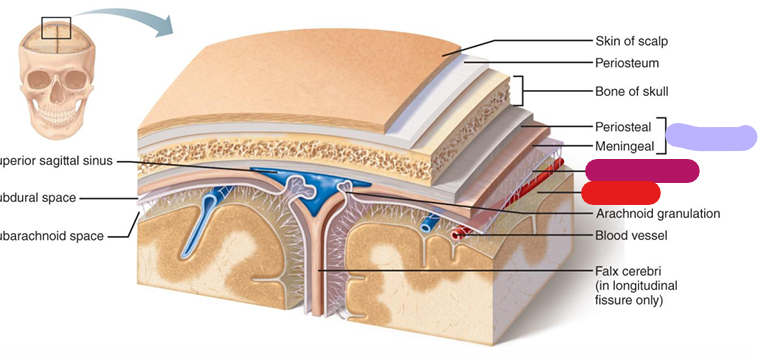
Pia mater
Arteries are associated with this layer; red
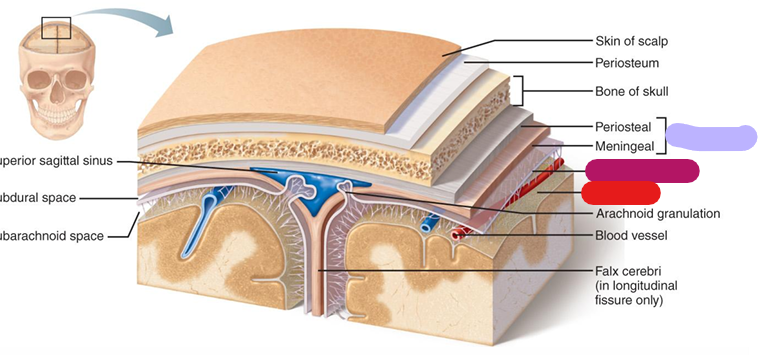
Meninges
They stabilize the neural tissue and protect it from bruising against the bones of the skeleton. (Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater)
Falx cerebri
between cerebral hemispheres; red (dura mater)
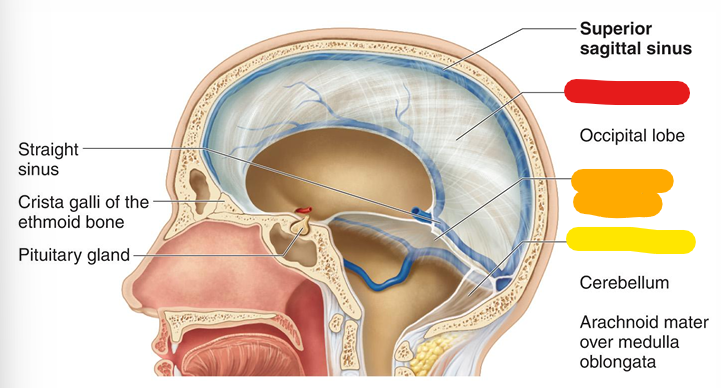
Tentorium cerebelli
Separates cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum; orange (dura mater)
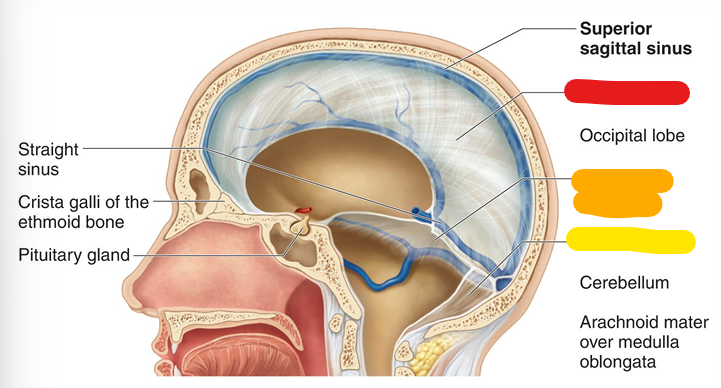
Diaphragm sellae
lines the sella turcica of the sphenoid (dura mater)
Falx cerebelli
divides two cerebellar hemispheres; yellow (dura mater)
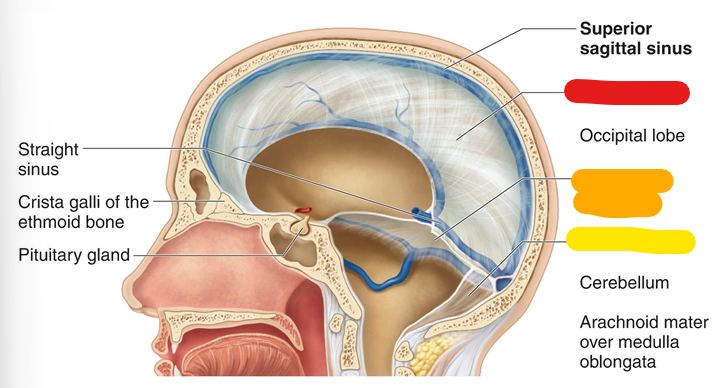
pia mater
Attached to the surface by astrocytes; highly vascularized membrane
Dura mater
yellow
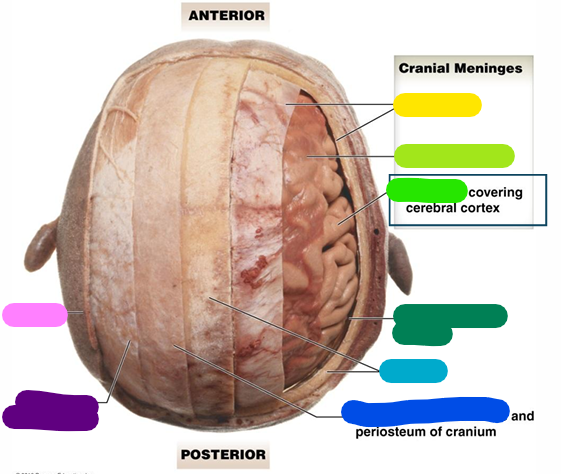
Arachnoid mater
lime green
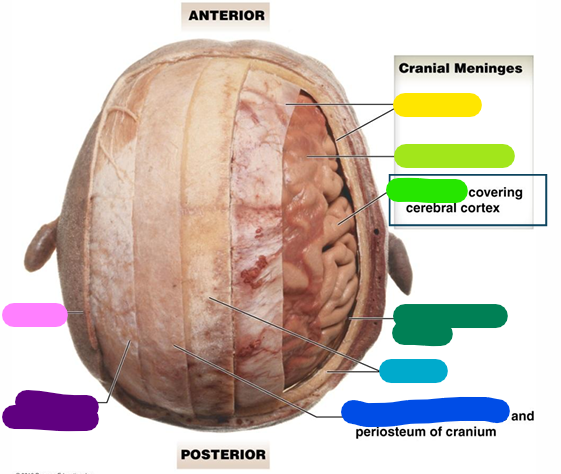
Pia mater
bright green
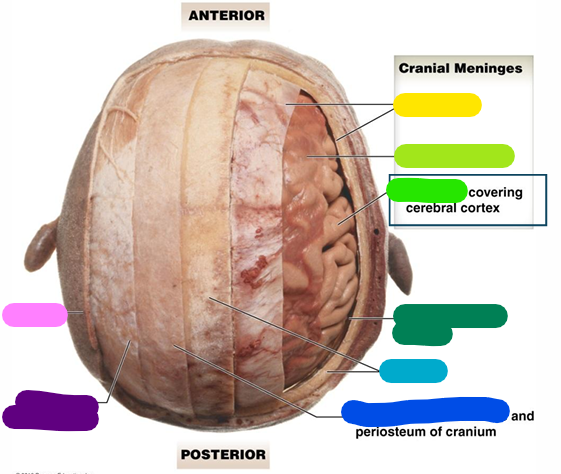
Subarachnoid space
dark green
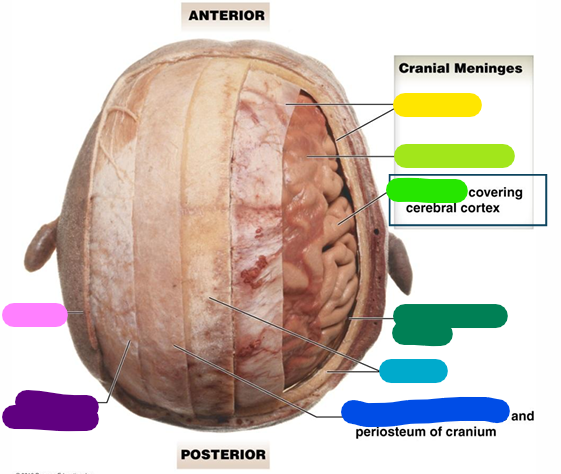
Cranium
light blue
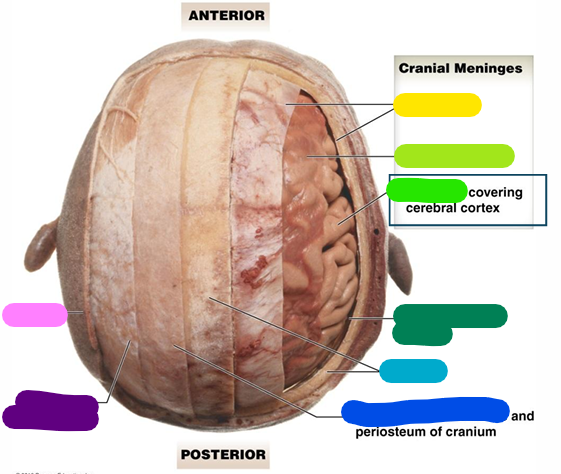
Loose connective tissue
dark blue
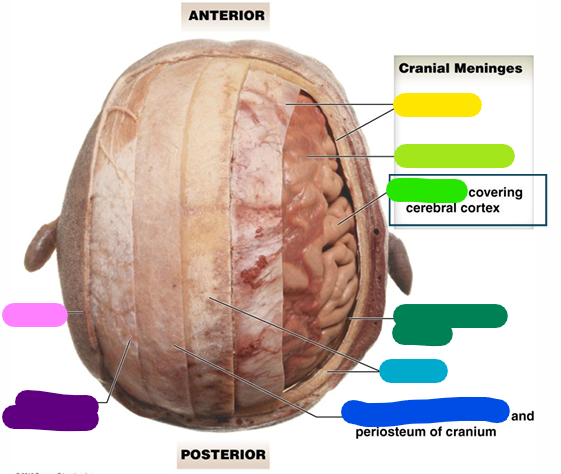
Epicranial aponeurosis
purple
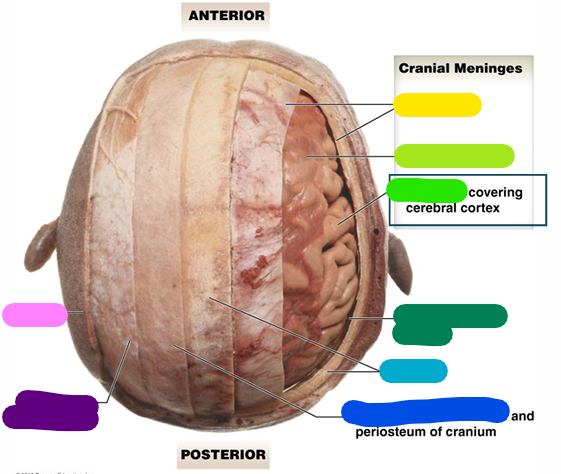
Scalp
pink
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Formed by tight junctions that seal together endothelial cells of brain capillaries. Lipid soluble substance Oxygen, carbon dioxide, alcohol, and anesthetic agents penetrate easily. Glucose can cross slowly. Hypothalamus, pineal gland, pituitary, choroid plexus, and medulla oblongata with highly permeable capillaries
ATP
Half of the body glucose is necessary to produce ___
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
The extracellular environment of the neurons. It is a salty solution that is continuously secreted by the choroid plexus.
Cerebrospinal fluid
Provides an optimal chemical environment (neuronal signaling). Allows exchange of nutrients and waste between blood and nervous tissue. It is a shock-absorbing fluid to prevent the brain from bumping against the interior of the skull.
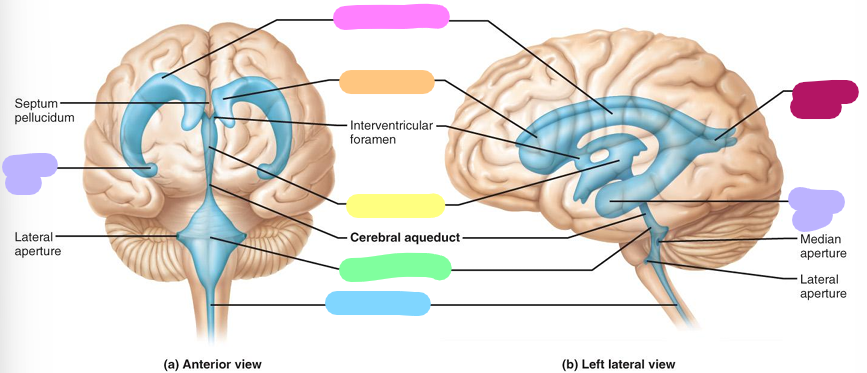
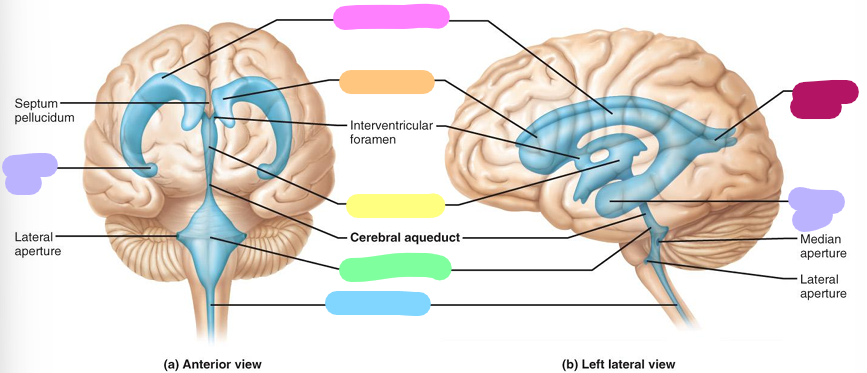
Ventricles
Four fluid filled chambers within the brain. They are filled with cerebrospinal fluid and lined by ependymal cells
Inferior horn
lavender
Gray matter
Includes: Nuclei that control blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, and vomiting
White matter
Somatosensory tracts and corticospinal tracts (from the cerebellum to the spinal cord)
pyramids
The corticospinal tracts cross the middle line of the opposite side of the body in a region known as the _______
Pons
Relay station for information between the cerebellum and cerebrum
Mesencephalon or Midbrain
Small area that lies between the lower brain stem and the diencephalon
lateral ventricle
pink
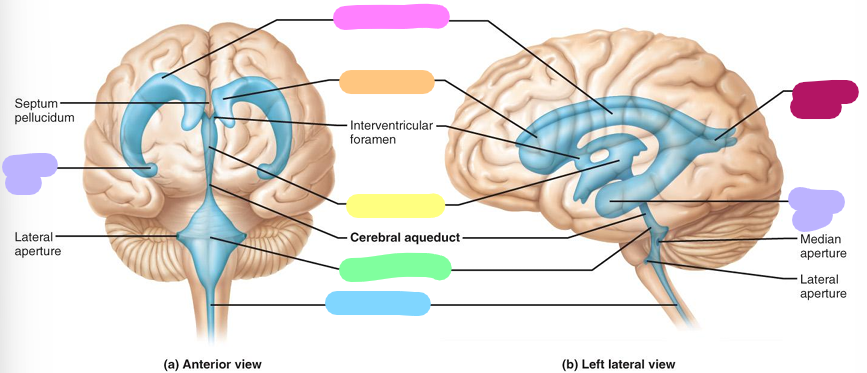
Anterior horn
orange
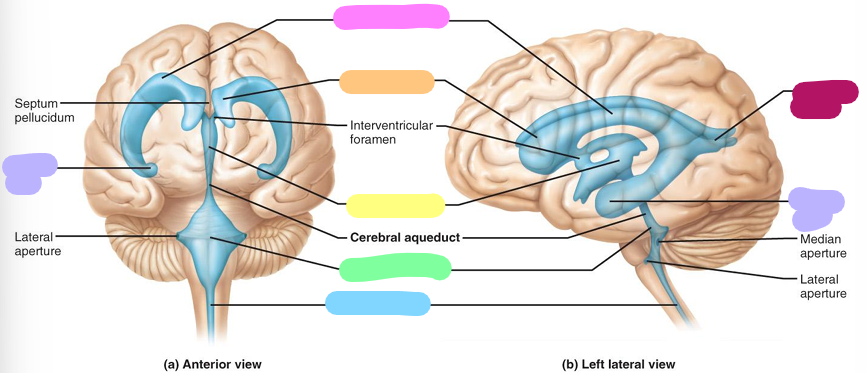
Third ventricle
yellow
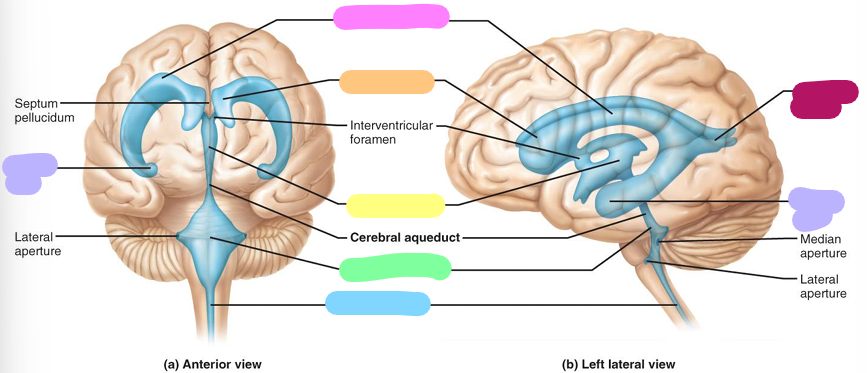
Fourth ventricle
pastel green
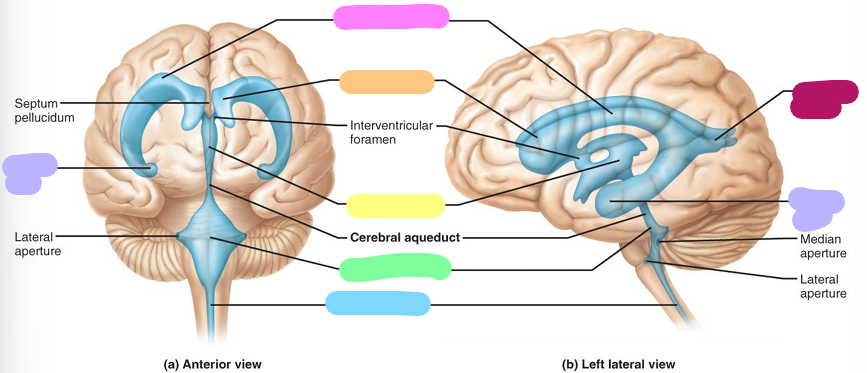
Central canal
blue
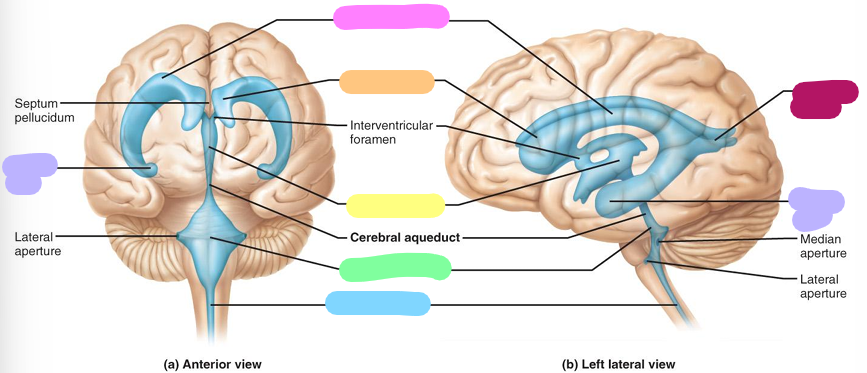
Posterior horn
magenta
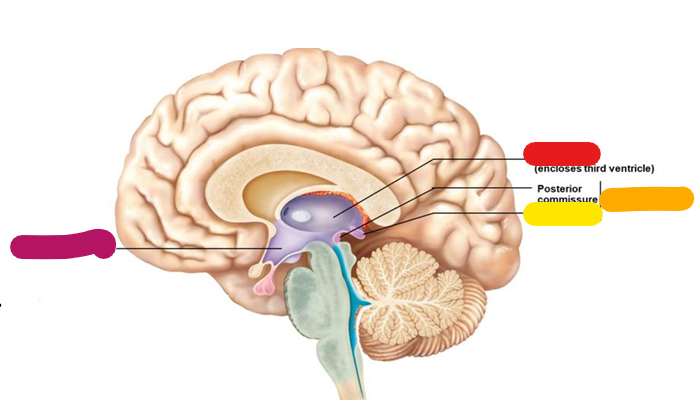
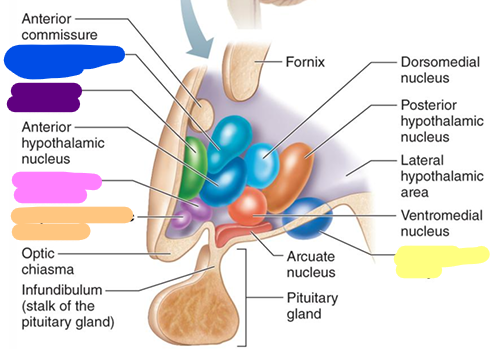
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis and behavioral drives; forms the floor of the third ventricle; links the nervous and endocrine system; magenta
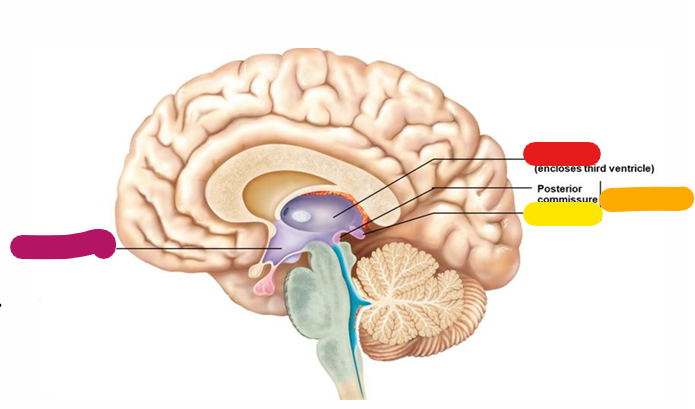
Thalamus
Coordinates motor activities; information filter; red
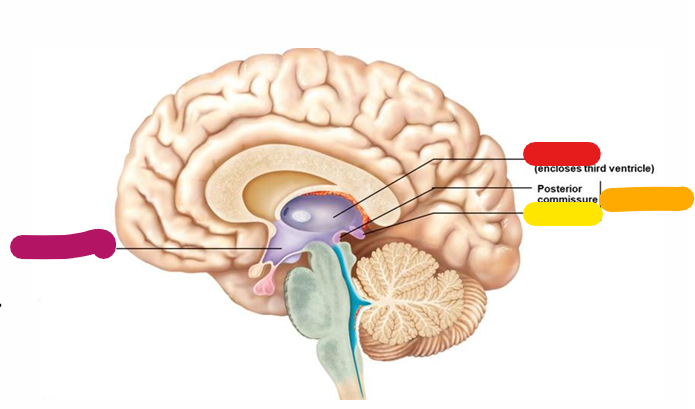
Epithalamus
orange
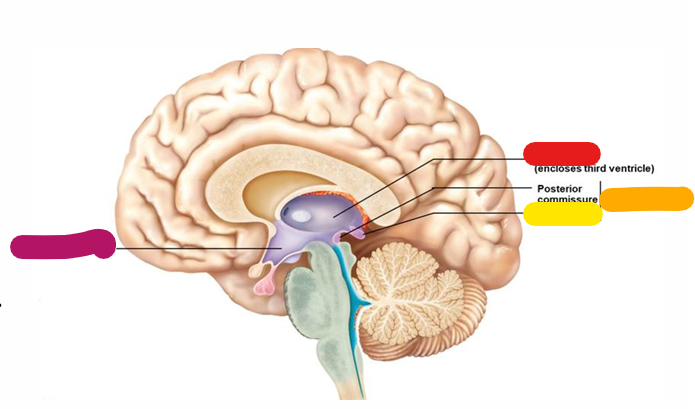
Pineal gland
yellow
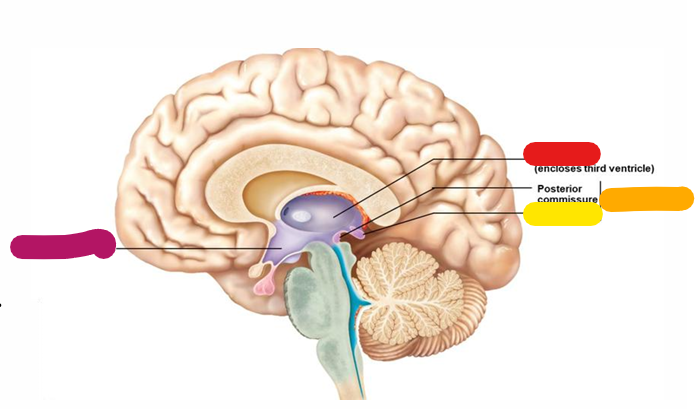
Diencephalon
Overall structure
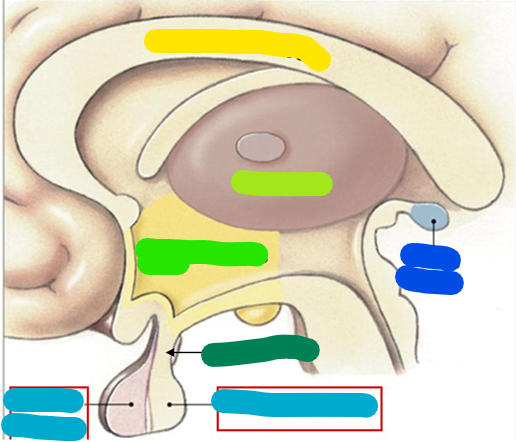
Corpus callosum
yellow
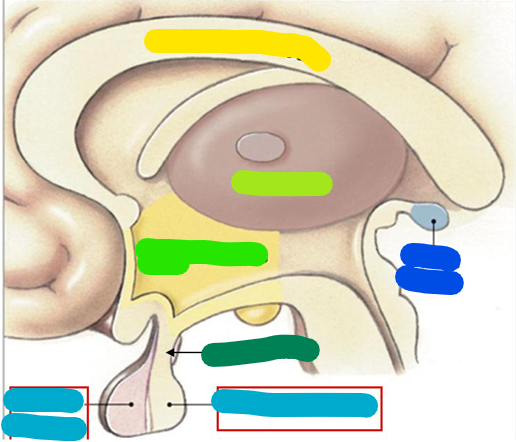
Thalamus
lime green
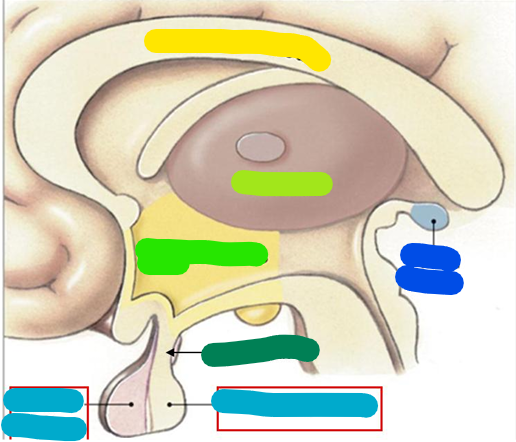
Hypothalamus
bright green
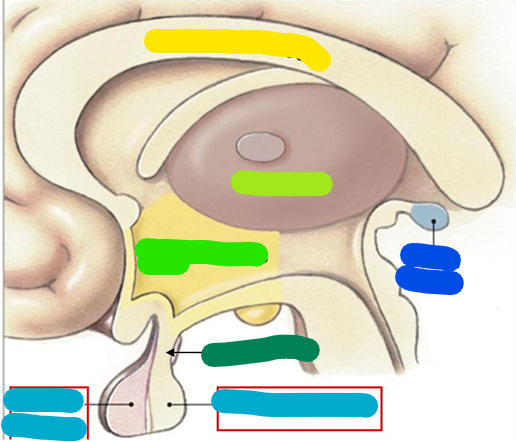
Infundibulum
dark green
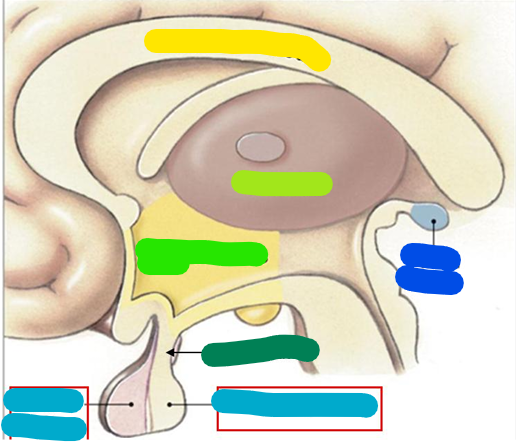
Pituitary gland
light blue
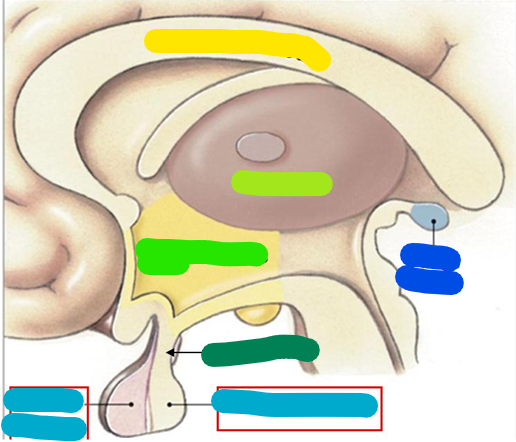
Pineal gland
dark blue
Hypothalamus

Paraventricular nucleus

Pre-optic area

Autonomic centers

Tuberal nuclei

Mammillary bodies

Suprachiasmatic nucleus

Supra-optic nucleus

Paraventricular nucleus
blue
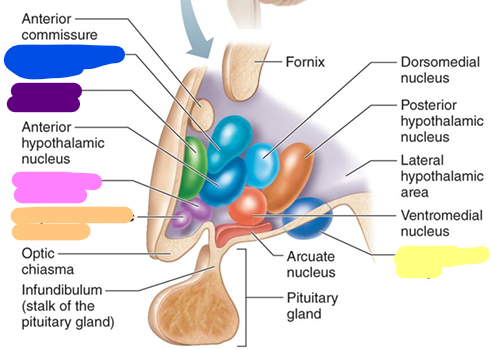
Preoptic nucleus
purple
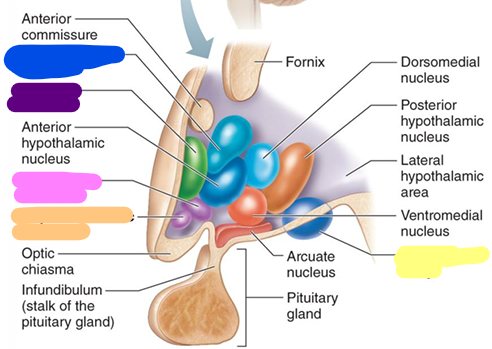
Supraoptic nucleus
pink
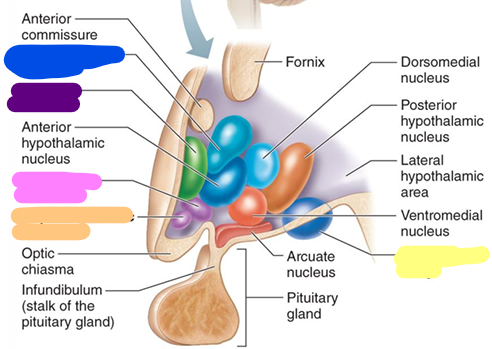
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
orange
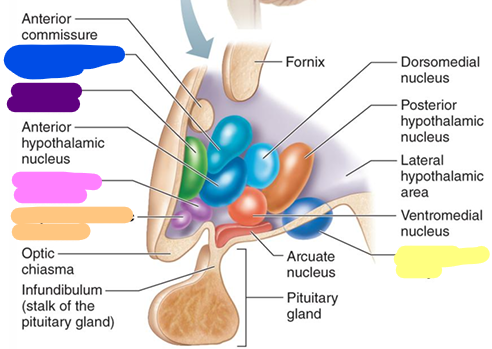
Mammillary body
yellow
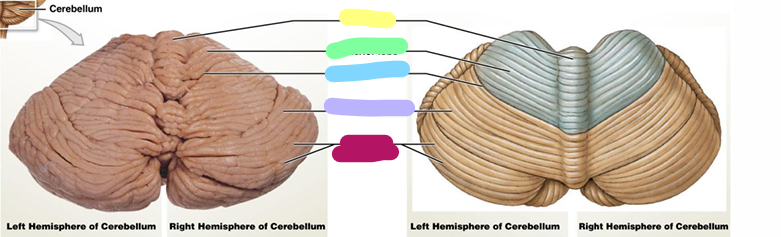
Vernis
yellow
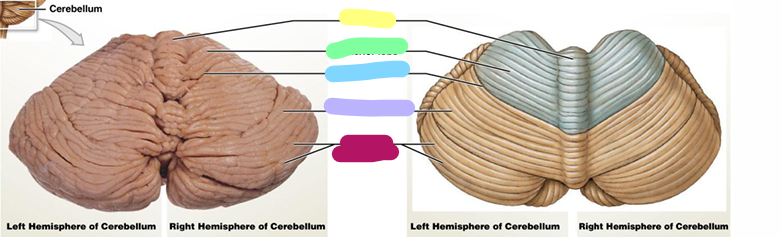
Anterior lobe
green