ZOOLONE Module 08-10 (Long Exam 2)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Integumentary System, Musculoskeletal System, Digestive System *Module 7 (Animal Form and Function) not part of set*
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
1
New cards
Integumentary System
organ system whose functions are:
- protects the underlying organs and tissues
- maintains body temperature
- synthesizes vitamin D3
- stores lipids
- detects touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
- excretes salt, water, and organic wastes
- protects body against infection
- protects the underlying organs and tissues
- maintains body temperature
- synthesizes vitamin D3
- stores lipids
- detects touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
- excretes salt, water, and organic wastes
- protects body against infection
2
New cards
hypodermis
- aka subcutaneous layer
- thick layer of fat underneath the skin
- thick layer of fat underneath the skin
3
New cards
epidermis
layer of skin:
- thinner
- protected by hair
- some areas thickened with keratin
- where the glands are embedded
- made up of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
- thinner
- protected by hair
- some areas thickened with keratin
- where the glands are embedded
- made up of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
4
New cards
keratin
fibrous protein that constitute the nails, claws, hooves, hair, and feathers
5
New cards
Layers of the Epidermis
stratum:
corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, & basale/germinativum
corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, & basale/germinativum
6
New cards
stratum corneum
layer of the epidermis:
- outermost layer
- keratinized layer
- dry, dead layer that prevents skin from dehydration
- outermost layer
- keratinized layer
- dry, dead layer that prevents skin from dehydration
7
New cards
stratum lucidum
layer of the epidermis:
- seen only in thick skin
- ex. palms, fingers, soles
- seen only in thick skin
- ex. palms, fingers, soles
8
New cards
stratum granulosum
layer of the epidermis:
- grainy in appearance
- due to generation of keratin
- grainy in appearance
- due to generation of keratin
9
New cards
stratum spinosum
layer of the epidermis:
- thickest layer of epidermis
- spiny in appearance
- due to protruding cell processes that join cells via desmosomes
- thickest layer of epidermis
- spiny in appearance
- due to protruding cell processes that join cells via desmosomes
10
New cards
stratum basale
layer of the epidermis:
- aka stratum germinativum
- nearest to the dermis
- deepest layer
- mitosis of skin cells
- aka stratum germinativum
- nearest to the dermis
- deepest layer
- mitosis of skin cells
11
New cards
Dermis
layer of skin:
- made up of connective tissues
- location of nerve endings, blood vessels, and hair follicles
- made up of connective tissues
- location of nerve endings, blood vessels, and hair follicles
12
New cards
Hair
characteristic of mammals:
- epidermal structure BUT lies in the dermis
- grows continuously
- rapid proliferation of cells in the follicle
- pushed upwards away from source of nourishment
- accumulate keratin then die
- stops at a certain length
- remains in the follicle until new growth pushes it out
- epidermal structure BUT lies in the dermis
- grows continuously
- rapid proliferation of cells in the follicle
- pushed upwards away from source of nourishment
- accumulate keratin then die
- stops at a certain length
- remains in the follicle until new growth pushes it out
13
New cards
Hair Growth Cycle
Anagen, Catagen, Telogen (ACT)
14
New cards
Anagen
stage in the hair growth cycle:
- growth phase
- nourishment of hair follicle via blood supply
- growth phase
- nourishment of hair follicle via blood supply
15
New cards
Catagen
stage in the hair growth cycle:
- transition phase
- follicle detaches from nourishing blood supply
- transition phase
- follicle detaches from nourishing blood supply
16
New cards
Telogen
stage in the hair growth cycle:
- resting phase
- without nourishment, hair dies and falls out
- resting phase
- without nourishment, hair dies and falls out
17
New cards
2 Types of hair in Mammals
Under hair & Guard hair
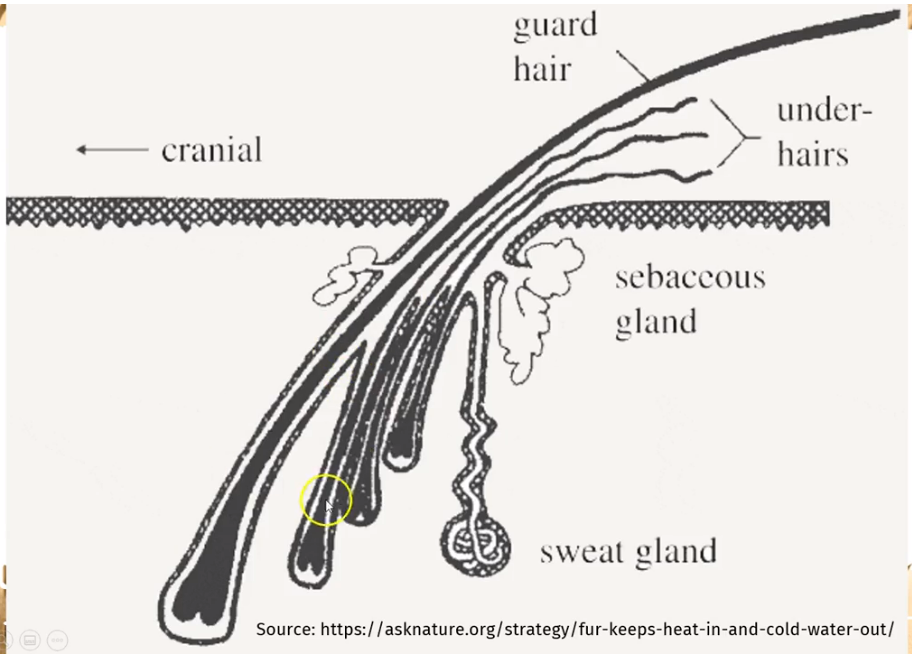
18
New cards
Under hair
type of hair:
- Dense and soft
- for insulation
- below guard hair
- Dense and soft
- for insulation
- below guard hair
19
New cards
Guard hair
type of hair:
- course and longer
- protect against wearing
- provide coloration
- under water, they become wet and adhere to each other
- course and longer
- protect against wearing
- provide coloration
- under water, they become wet and adhere to each other
20
New cards
3 Layers of Hair
Medulla, Cortex, Cuticle
21
New cards
Medulla
layer of hair:
- center of the hair
- center of the hair
22
New cards
Cortex
layer of hair:
- with pigment granules that lie outside the medulla
- with pigment granules that lie outside the medulla
23
New cards
cuticle
layer of hair:
outermost layer
outermost layer
24
New cards
arrector pili muscle
muscle in the dermis that causes the hair to "stand" thus causing chicken skin or goosebumps
25
New cards
Molting
- process of shedding hair or fur
- can happen periodically
- can happen periodically
26
New cards
Structural and Functional Adaptation
- types of adaptation that are present in fur having different patterns
- ex. spots, stripes, salt-and-pepper patterns conceal the animals
- camouflage for survival
- ex. spots, stripes, salt-and-pepper patterns conceal the animals
- camouflage for survival
27
New cards
Integumentary Derivatives
Vibrissae, Quills, Horns, Antlers, Glands
28
New cards
Vibrissae
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- whiskers
- sensory hairs that provide a tactile sense to many mammals
- long in length for nocturnal and burrowing animals
- whiskers
- sensory hairs that provide a tactile sense to many mammals
- long in length for nocturnal and burrowing animals
29
New cards
quills
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- effective and dangerous spiny armor
- porcupines, hedgehogs, and echidnas (sea urchins)
- NOT embedded in the skin
- effective and dangerous spiny armor
- porcupines, hedgehogs, and echidnas (sea urchins)
- NOT embedded in the skin
30
New cards
True Horns
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- antelopes, sheep, cattle
- hollow sheath of keratinized epidermis that embraces a core of bone arising from the skull
- NOT shed and NOT branched, but continuously grow
- antelopes, sheep, cattle
- hollow sheath of keratinized epidermis that embraces a core of bone arising from the skull
- NOT shed and NOT branched, but continuously grow
31
New cards
Antler
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- deer
- branched and composed of solid bone when mature
- velvet
- shed after breeding season
- deer
- branched and composed of solid bone when mature
- velvet
- shed after breeding season
32
New cards
velvet
high vascular soft skin that covers the antlers during annual spring growth
33
New cards
Rhinoceros Horn
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- Hair-like keratinized filaments arise from dermal papillae and are cemented together
- NOT attached to the skull
- Hair-like keratinized filaments arise from dermal papillae and are cemented together
- NOT attached to the skull
34
New cards
Glands in the Integumentary System
Sweat Gland
Scent Gland
Sebaceous Gland
Mammary Gland
Scent Gland
Sebaceous Gland
Mammary Gland
35
New cards
Sweat Glands
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- Tubular, highly coiled glands that occur over much of the body surface in most mammals
- absent in other vertebrates
- 2 types: eccrine & apocrine
- Tubular, highly coiled glands that occur over much of the body surface in most mammals
- absent in other vertebrates
- 2 types: eccrine & apocrine
36
New cards
eccrine gland
type of sweat gland:
- secrete watery fluid
- occur in hairless regions (foot pads)
- seen all around the body
- involved in heat regulation
- either reduced or absent in rodents, rabbits, and whale
- secrete watery fluid
- occur in hairless regions (foot pads)
- seen all around the body
- involved in heat regulation
- either reduced or absent in rodents, rabbits, and whale
37
New cards
apocrine glands
type of sweat gland:
- ALWAYS open to hair follicle
- larger, longer, more convoluted ducts
- secretory coil is in the dermis and extends deep into hypodermis
- glands may be present in dermis or hypodermis
- develop near puberty
- seen in ear canal, chest, underarm, scrotum
- secrete milky fluids (whitish or yellow)
- NOT involved in heat regulation
- correlated with the reproductive cycle
- ALWAYS open to hair follicle
- larger, longer, more convoluted ducts
- secretory coil is in the dermis and extends deep into hypodermis
- glands may be present in dermis or hypodermis
- develop near puberty
- seen in ear canal, chest, underarm, scrotum
- secrete milky fluids (whitish or yellow)
- NOT involved in heat regulation
- correlated with the reproductive cycle
38
New cards
Scent Glands
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- location and function vary greatly
- present in nearly all mammals
- for communication with members of the same species
- marking territorial boundaries
- warning or defense
- location and function vary greatly
- present in nearly all mammals
- for communication with members of the same species
- marking territorial boundaries
- warning or defense
39
New cards
Sebaceous Glands
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- associated with hair follicles
- gland cells are secreted in their entirety & are continuously renewed by cell division
- cells become distended with fatty accumulation then die
- cells expelled as greasy mixture
- associated with hair follicles
- gland cells are secreted in their entirety & are continuously renewed by cell division
- cells become distended with fatty accumulation then die
- cells expelled as greasy mixture
40
New cards
sebum
- “polite fat”
- greasy mixture expelled by sebaceous glands
- does NOT turn rancid
- keeps hair pliable and glossy
- greasy mixture expelled by sebaceous glands
- does NOT turn rancid
- keeps hair pliable and glossy
41
New cards
Mammary Glands
example of an Integumentary Derivative:
- modified apocrine gland
- occur in ALL female mammals
- rudimentary form in all male mammals
- increase in size at maturity
- large during pregnancy and subsequent nursing of young
- milk is secreted via the nipples
- modified apocrine gland
- occur in ALL female mammals
- rudimentary form in all male mammals
- increase in size at maturity
- large during pregnancy and subsequent nursing of young
- milk is secreted via the nipples
42
New cards
Monotremes
type of mammal:
- ex. platypus
- LACK nipples
- secrete milk onto the fur of the mother’ belly
- ex. platypus
- LACK nipples
- secrete milk onto the fur of the mother’ belly
43
New cards
musculoskeletal system
made up of the muscular and skeletal systems
44
New cards
3 Types of Muscle
Smooth, Cardiac, and Skeletal Muscles
45
New cards
Smooth Muscle
type of muscle:
- LACKS striations
- cells are much smaller, tapering strands, with a single, centrally-located nucleus
- responsible for peristalsis, propelling, and regulating movement of substance
- contractions are involuntary and unconscious
- LACKS striations
- cells are much smaller, tapering strands, with a single, centrally-located nucleus
- responsible for peristalsis, propelling, and regulating movement of substance
- contractions are involuntary and unconscious
46
New cards
Cardiac Muscle
type of muscle:
- striated involuntary muscle
- found in the heart
- with presence of intercalated discs
- striated involuntary muscle
- found in the heart
- with presence of intercalated discs
47
New cards
intercalated discs
part that supports synchronized contractions of the cardiac muscle cells
48
New cards
Skeletal Muscle
type of muscle:
- striated muscle
- voluntary contractions
- attached to and interacts with skeletal elements
- makes up most of musculoskeletal system
- striated muscle
- voluntary contractions
- attached to and interacts with skeletal elements
- makes up most of musculoskeletal system
49
New cards
tendon
fibrous tissue that attaches the muscles to the bones
50
New cards
3 Connective Tissues surrounding the skeletal muscle
Epimysium, Perimysium, and Endomysium
51
New cards
Epimysium
type of connective tissue surrounding the skeletal muscle:
- outer layer
- surrounds the whole muscle tissue
- contains fascicle
- outer layer
- surrounds the whole muscle tissue
- contains fascicle
52
New cards
fascicle
bundles of muscle fibers
53
New cards
Perimysium
type of connective tissue surrounding the skeletal muscle:
surrounds each fascicle
surrounds each fascicle
54
New cards
Endomysium
type of connective tissue surrounding the skeletal muscle:
covers every muscle fiber in each fascicle
covers every muscle fiber in each fascicle
55
New cards
Sarcomere
- functional unit of muscle
- bordered by Z lines
- made up of myofibril
- bordered by Z lines
- made up of myofibril
56
New cards
myofibril
part in sarcomere that contains actin & myosin filaments
57
New cards
actin filaments
filaments that are connected to the Z lines in the sarcomere
58
New cards
myosin filaments
filaments found in the middle of sarcomere
59
New cards
A band
band where myosin filaments are found
60
New cards
I Band
band where actin filaments & Z lines are found
61
New cards
Sliding Filament Theory
theory that states that:
- actin & myosin filaments slide past each other longitudinally
- “head” of myosin binds to an actin filament, forming a cross-bridge and pulls the thin filament towards the center of the sarcomere
- works using ATP
- actin & myosin filaments slide past each other longitudinally
- “head” of myosin binds to an actin filament, forming a cross-bridge and pulls the thin filament towards the center of the sarcomere
- works using ATP
62
New cards
Tropomyosin and troponin complex
regulatory proteins that:
- bind to actin strands when a muscle fiber is at rest
- prevents the actin and myosin from interacting
- bind to actin strands when a muscle fiber is at rest
- prevents the actin and myosin from interacting
63
New cards
Calcium ions
ions that attach to the troponin complex & acts as a key to expose actin and contract the muscle
64
New cards
motor unit
made up of single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers that it controls
65
New cards
Skeletal System
organ system whose functions are:
- provides supporting framework
- surfaces for muscle attachment
- protection for vulnerable organs
- production of blood cells (hematopoiesis)
- storage of minerals
- provides supporting framework
- surfaces for muscle attachment
- protection for vulnerable organs
- production of blood cells (hematopoiesis)
- storage of minerals
66
New cards
2 Types of Skeletons
Hydrostatic & Rigid skeletons
67
New cards
Hydrostatic Skeletons
type of skeleton:
- “fluid-filled sac”
- earthworms
- alternate contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles in the body wall
- “fluid-filled sac”
- earthworms
- alternate contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles in the body wall
68
New cards
Exoskeleton
type of rigid skeleton:
- skeleton located outside the body
- ranges from very soft (shrimp) to very stiff (crab)
- typical of mollusks, arthropods, and many invertebrates
- skeleton located outside the body
- ranges from very soft (shrimp) to very stiff (crab)
- typical of mollusks, arthropods, and many invertebrates
69
New cards
Endoskeleton
type of rigid skeleton:
- skeleton inside the animal
- vertebrate animals, echinoderms, and some cnidarians
- made up of bone and cartilages
- skeleton inside the animal
- vertebrate animals, echinoderms, and some cnidarians
- made up of bone and cartilages
70
New cards
Bone
- major component of the skeleton
- well-vascularized tissue capable of responding to its environment
- categorized according to location and shape
- well-vascularized tissue capable of responding to its environment
- categorized according to location and shape
71
New cards
2 Types of Bone Location
Axial & Appendicular
72
New cards
Axial
bone location:
- in the middle of the body
- skull, vertebral column, ribs, & sternum
- in the middle of the body
- skull, vertebral column, ribs, & sternum
73
New cards
Appendicular
bone location:
bones of the limbs, shoulders, and pelvis
bones of the limbs, shoulders, and pelvis
74
New cards
5 Types of Bone Shape
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular, & Sesamoid bones
75
New cards
Long Bones
bone shape:
- found in limbs
- provide attachment site for limb muscles & levers for movement
- the ends are enlarged and smooth to avoid risk of dislocation
- found in limbs
- provide attachment site for limb muscles & levers for movement
- the ends are enlarged and smooth to avoid risk of dislocation
76
New cards
2 Main Parts of Long Bones
Epiphysis & Diaphysis
77
New cards
epiphysis
part of long bone:
- both ends of bone
- spongy
- smooth
- contains epiphyseal line/growth plate
- both ends of bone
- spongy
- smooth
- contains epiphyseal line/growth plate
78
New cards
epiphyseal line
- aka growth plate
- line in the long bone that separates metaphysis and diaphysis of growing animals
- line in the long bone that separates metaphysis and diaphysis of growing animals
79
New cards
diaphysis
part of long bone:
- middle
- contains marrow/medullar cavity
- contains Periosteum, Endosteum, & Nutrient Foramen
- middle
- contains marrow/medullar cavity
- contains Periosteum, Endosteum, & Nutrient Foramen
80
New cards
medullar cavity
cavity in the long bone that is surrounded by compact bone and produces RBCs
81
New cards
Periosteum
layer in the diaphysis:
- increase of diameter of bone
- aids in healing fractures
- made up outer fibrous layer and inner cell-rich layer (osteoblasts)
- increase of diameter of bone
- aids in healing fractures
- made up outer fibrous layer and inner cell-rich layer (osteoblasts)
82
New cards
Endosteum
layer in the diaphysis:
- lining tissue of the bone surfaces that faces the medullar cavity
- can also be found in spongy bone
- lining tissue of the bone surfaces that faces the medullar cavity
- can also be found in spongy bone
83
New cards
Nutrient Foramen
natural holes in bones in the diaphysis where nutrients go in
84
New cards
short bones
bone shape:
- found in carpus and tarsus
- highly irregular in size and shape relatively small
- ex. hands
- found in carpus and tarsus
- highly irregular in size and shape relatively small
- ex. hands
85
New cards
flat bones
bone shape:
- “squamous bones”
- found in most regions of the skull and ribs
- serve a protective or reinforcing function
- ex. ribs and skull
- “squamous bones”
- found in most regions of the skull and ribs
- serve a protective or reinforcing function
- ex. ribs and skull
86
New cards
irregular bones
bone shape:
- has jutting processes
- most from muscular & ligamentous attachments & some are for articulation
- bones of the vertebral column, pelvis, and skull that are not flat
- has jutting processes
- most from muscular & ligamentous attachments & some are for articulation
- bones of the vertebral column, pelvis, and skull that are not flat
87
New cards
sesamoid bones
bone shape:
- formed in between tendons near the freely mobile joints
- with one articular surface that glides on a flat or convex surface of one or more long bones
- protects tendons from stress & reduces friction between tendons
- ex. kneecap aka patella
- formed in between tendons near the freely mobile joints
- with one articular surface that glides on a flat or convex surface of one or more long bones
- protects tendons from stress & reduces friction between tendons
- ex. kneecap aka patella
88
New cards
2 Types of Bone Development
Intramembranous Ossification & Endochondral Ossification
89
New cards
Intramembranous Ossification
Type of Bone Development:
- fibrous membrane of some parts of the fetal skeleton are converted to bones
- skull and mandible
- fibrous membrane of some parts of the fetal skeleton are converted to bones
- skull and mandible
90
New cards
Endochondral Ossification
Type of Bone Development:
- conversion of (hyaline) cartilage to bone
- vertebrae, axial and appendicular bones, ribs, sternum
- conversion of (hyaline) cartilage to bone
- vertebrae, axial and appendicular bones, ribs, sternum
91
New cards
2 Types of Bone Structure
Compact & Spongy Bone
92
New cards
compact bone
Type of Bone Structure:
dense, appearing solid to the unaided eye
dense, appearing solid to the unaided eye
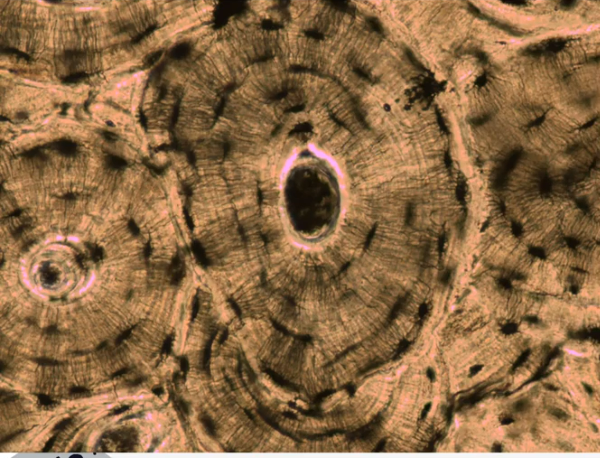
93
New cards
spongy bone
Type of Bone Structure:
- made up of open, interlacing framework of bony tissue, oriented to give maximum strength under normal stresses and strains that the bone receive
- found in epiphysis
- has adipose tissues or yellow bone marrow
- made up of open, interlacing framework of bony tissue, oriented to give maximum strength under normal stresses and strains that the bone receive
- found in epiphysis
- has adipose tissues or yellow bone marrow
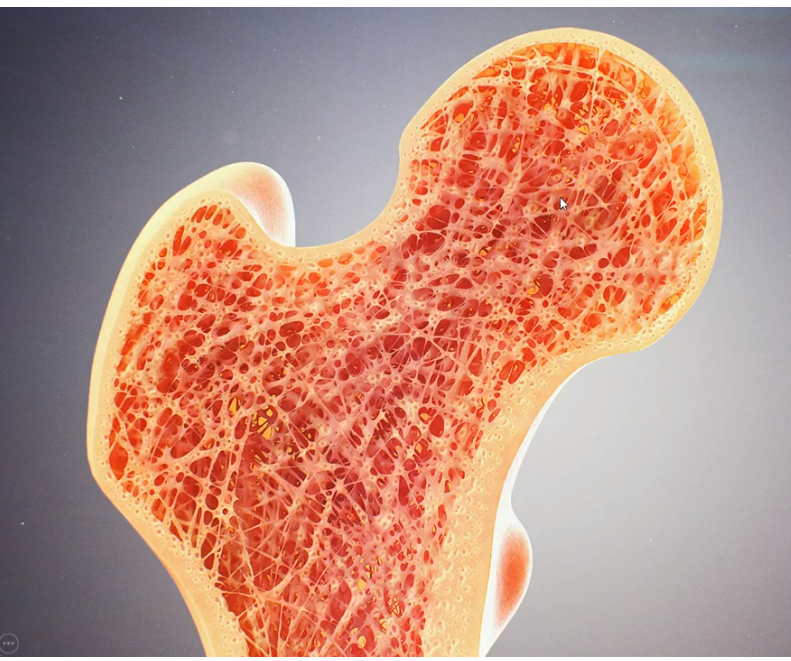
94
New cards
3 types of animals
herbivores, carnivores, omnivores
95
New cards
herbivores
type of animal that only eat plants and algae
96
New cards
carnivores
type of animal that eat meat / other animals
97
New cards
omnivores
type of animal that consume animals and plants/algae
98
New cards
Animal's Diet
must provide:
- chemical energy for cellular processes
- organic building blocks for macromolecules
- essential nutrients
- chemical energy for cellular processes
- organic building blocks for macromolecules
- essential nutrients
99
New cards
Essential Nutrients
Essential Amino Acids & Fatty Acids, Vitamins, and Minerals
100
New cards
Essential Amino Acid
type of essential nutrient:
- an amino acid that is required by animals but that they cannot synthesize
- 10 out of 20 must be supplied in the diet
- an amino acid that is required by animals but that they cannot synthesize
- 10 out of 20 must be supplied in the diet