Data Analysis
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Descriptive statistic
procedures for describing individual variables and relationships between variables
eg. describing characteristics of study sample
Inferential statistics
procedures used to analzye data after an experiment is completed
procedures used to determine if an IV has a significant effect
allow for the making of extrapolations from a sample to the population from which it was drawn
Three levels of measurement
nominal
ordinal
ratio
0 has a true value (can go above)
Nominal measurement
involves no continuum
assignment of numeric values is arbitrary
discrete categories
Ordinal measurement
implies underlying continuum
values are ordered but intervals are not equal
community size
likert items etc
Ratio
involves a continuum
numeric values are assigned and reflect equal intervals
0 is a true 0
weight, age in years, etc
Tendency
simple statistics that typify a set of values
convey a sense of the data
Mean, median, mode
mean
calculated by summing values and dividing by number of cases
average
used for ratio data
median
calculated by ordering values then using the middle most value (mean of the two values if there are two middle values)
half cases will fall above the median and half will fall below
ratio or ordinal data
mode
most frequently occuring value
category of a variable with the most cases
used for ratio, ordinal and nominal data
dispersion
the variability of measures
range
standard deviation
variance
Range
subtracting the lowest score from the highest in a set of values
can be described as indicating the highest and lowest values
Standard deviation
reflects the average amount of deviation from the mean value in a set of values
related to the normal distribution curve
Sqrt of the sum of squares divided by N-1
Standard error of the mean
the standard deviation relative to the sample size
Varience
measure of SD squared
this is a single number that represents the total amount of variate in a distribution
lots of this is not good
Standardizing data
ensuring that units match up to allow for comparisons between units of different sizes
5 types of data standardization
proportions
percentages
percentage change
rates
ratios
Proportions
standard method of designating a portion of the total
0-1 (none → all of the total)
can be used instead of percentages
Batting average is usually a proportion
Percentage
proportion can be converted to this
how often something happens per 100 times
Percentage change
the amount tha tsomethign changes overa period of tiem
T2-T1/T1
Rates
Represents the frequency of somthing for a standard sized unit
Eg. divorce suicide, crime rates
Ratios
represent a comparison of one thing to another
one thing over another
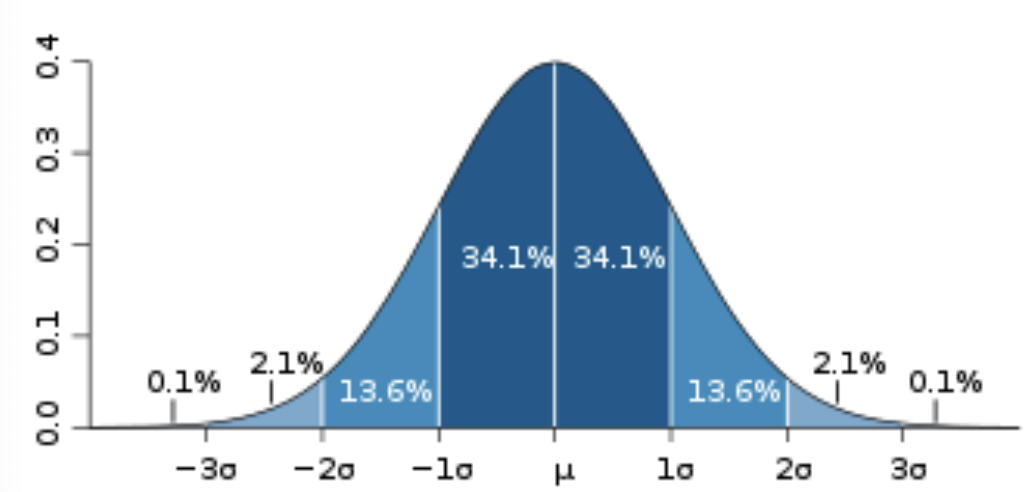
Normal distribution
bell curve
distribution pattern of a set of data follow this curve
much data in the social and physical world is normally distributed
symetrical will have half above and half below
Normal distribution and standard deviations
2/3 of cases are +- 1 sd of mean
95.6% of cases are +- 2 sd by definition
scores in 1 sd
68.2% will be within 1 sd to the right and left of the mean
z-scores
standardized score
represents the distance above or below the mean in standard deviation units of any raw value in a distribution
+3→-3 range in vlaues
Crosstabular analysis
used with nominal DV
data is cross classified and sorted into categories within the IV and DV to show relation between an IV and a DV
Comparing means
when the DV is ratio and the IV is nominal or ordinal
compare the mean values of the DV for each category of the IV
both T-test and ANOVA can be used as tests of significance
comparisons of the means
Correlations
used to describe the relationship between ratio level variables
describes how close two ratio level variables co-vary together
allows exploration
what is the equation describing the relationship between two variables
what is the strength of the relationships between two variables
equation for correlation
y= a + bX
estimates how much the IV has to change to produce a unit of change in the DV
a = constant
b = slope
Regression line
offers the best linear description of the relation between two variables
Correlation coefficient
r demonstrates the strength of correlation between the two variables
from -1 → +1
-1 is a perfect negative correlation
an increase of 1 unit in one variable is associated with a proportional decrease in the other variable
+1 is a perfect positive correlation
inferential statistics
used to determine the probability that a conclusion based on an analysis of data from a sample is true and not due to sample fluctuations
Test of significance
tests used to test a hypothesis
chi square
t-test
anova
Hypothesis
null hypothesis - prediction of no relationship between variables
this is what test of significance tests
alternative research hypothesis - prediction of relationships
Testing the null hypothesis
you either accept the null or reject the null
to accpet the null it concludes that there is no difference between variables
rejecting th enull concludes that there is probably a difference between the variables
Publication bias
occurs if results from studies which have not been published are different than those that are published
affects inerpretations of reviews and meta analysis that includes only publihsed literature
favourable results are published more than non significant
Main effect
differences among groups for a single independent variable that are significant temporarily ignoring all other independent variables
effect of the variable averaging over all variables in the experiment
interaction effects
differences among groups of a single independent variable that are predictable only by knowing the level of the other independent variable
One tailed test
indicates a direction of the relationship in advance
if you preduct the direction of a relationship inadvance you do a one tailed test
Two tailed test
a test of any realtionship between variables
regardless of a direction of the relationship
Statistical significance
degree of risk you are willing to make a type 1 error
rejecting null when it is true
Level of significance
0.05
means there is a 5% chance of rejecting a true null hypothesis
less than 5% of the time the results that you are seeing wil be due to chance
statistical vs clinical significance
statistical
gives probability of a relationship existing
nothing about the magnitude or importance of the difference
clinical
the importance of the difference in the real world
this is determined by judgement
Statistical significance
is a precondition for considering clinical importance but says nothign about the effect
Three tests of significance
Chi-square test
T- test
ANOVA
extension of the T test
Chi-square test
used with crosstabular analysis
IV: Categorical - nominal or ordinal
DV: Usually nominal
Null: There is no significant difference between categories on the variable of interest
T-Test
small sample sizes
DV is measured at ratio level
IV has two categorical levels only
used to compare the means of two groups
Null: No significant difference between group means on the DV of interest
Between subjects T-test
two independent samples
used in experimental design
has an experimental and control group where the groups are independently established
Within subjects t-test
in these designs, the same person is subjected to different treatments and a comparison is made between the two treatments
ANOVA
family of tests that compares the group means to assess whether differences across means are reliable
post hock: compares the differences across levels of an IV when results are significant
ANOVA conditions
IV: 2+ categories
can be more than 1 IV at once
DV: ratio level
are there stat sig differences between groups on the characteristic of interest
how does the DV vary across categories of the IV
When are tests of significance not appropriate
if the total population is studied then there is no need to determine stat sig
any observed difference is the absolute difference not a statistically significant difference
Non-probability sampling procedures
if the sample was not random then results are more than likely not going to be significant
Non-experimental research which is not intended to generalize
High non-participation rates
if there are too many who do not participate it is hard to assume that those who do participate are similar to those who do not participate
research without a formal hypothesis
if there is no hypothesis even if a relationship is found it is not significant
F statistic
a higher F statistic there will be a lower p-value
higher F is more likely to be different
Mean square determines F statistic
between group means /
within group means
Degrees of freedom between groups
subtract 1 from the total number of groups
Degrees of freedom within groups
subtract the total number of groups from the number of observations
Degrees of freedom
represents the number of individual fragments of information usd to calculate a statistic
the number of values in a calculation which are free to vary after constraints are imposed
Anova test statistic
F ratio
compares 2 estimates of variability
within and between group variability
There is a sig difference when Vb is greater than Vw
this would show that the different conditions are resulting in different results on the DV
ANOVA limitation
does not pinpoint where the difference occurs it only tells you if there are differences between any group in the study
post hoc tests are required to actually determine which groups are statistically different from another
Two-way ANOVA
2 simultaneous IVs of 2+ categories each (nominal or ordinal IV)
Post-Hoc analysis
if significant main effect or interaction is foudn then you can conclude that there is a significant difference amongst the levels of your IVs somwehere
Tukeys, Duncan (too liberal do not use)
Bivariate correlation
how closely two ratio level variables co-vary together
Multiple regressions
analysis of more than 2 ratio level variables
used when we want to examine the impact of several IVs on a DV
may be used when you have a ratio level DV and preferably ratio level IVs
both bivariate correlations and multiple regression cannot prove causal relationships but they can provide evidence to support causal arguments
Multiple LINEAR regression
simplest multiple regression
considers the linear relationship among more than 2 variables
isolates the seperate effects of IVs on the DV
summarizes the relationship between a DV and 2+ IVS
3 m of data analysis
model
measurement
method
Model
determine whch variable is the DV and which will be the IVs
possible that 2 variables mutually influence one another
if possible specify in model > and < relationships between variables
Measurement of the.3 M approach
identify the level of measurement
method of 3 m approach
determine which method is appropriate for examining the relationships between variables
Crosstabs (chi-square)
means (ANOVA)
correlations