31: Terrestrial ecosystems - deserts, tundra and peatlands
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
pattern of movement of air masses
descending dry air absorbs moisture
ascending moist air releases moisture
2 multiple choice options
descending dry air _____ moisture creating _____ conditions
absorbs, arid
desert location is determined by
- global atmospheric circulation
- rain shadows
- continental interiors
physical characteristics of deserts
- low and unpredictable rainfall
- high evaporation
- hot or cold temperature
- large diurnal variation in temperature
deserts can be ___ or ___
hot or cold
deserts have _____ and _______ rainfall
low and unpredictable
deserts have high _______
evaporation
deserts have large ______ variation in temperatures
diurnal
desert plant adaptations
1. avoid drought: carefully timed phenology (annual life cycle, seasonal flowering)
2. tolerate drought
how do desert plants avoid drought?
carefully timed phenology (annual life cycle and seasonal flowering)
how do desert plants tolerate drought?
intensification of water absorption & reduced transpiration
how do desert plants increase water absorption?
shallow spreading succulents roots, deep tap roots, dew/fog traps
how do desert plants reduce water loss?
sunken stomata, reduced stomatal opening, hairy/rolling leaves, retain dead leaves around stem, deciduous shed leaves
CAM
crassulacean acid metabolism photosynthesis
how does CAM work?
stomata remain closed during the day to reduce water loss.
during the night, organic acids accumulate in chlorophyll and are converted to carbon dioxide during the day.
this increases photosynthesis and reduces transpiration.
desert raunkiaer plant life forms
highest = therophytes
lowest = phanerophytes
tundra climate
cold, low precipitation, permafrost, short growing season
tundra has ___ precipitation
low
permafrost is characteristic of
tundra
tundra has a ___ growing season
short
tundra has ___ botanical diversity
low
tundra has ___ trees
no - all plants are low in stature (<30cm)
tundra has ____ rooting
shallow
biome raunkiaer plant life forms
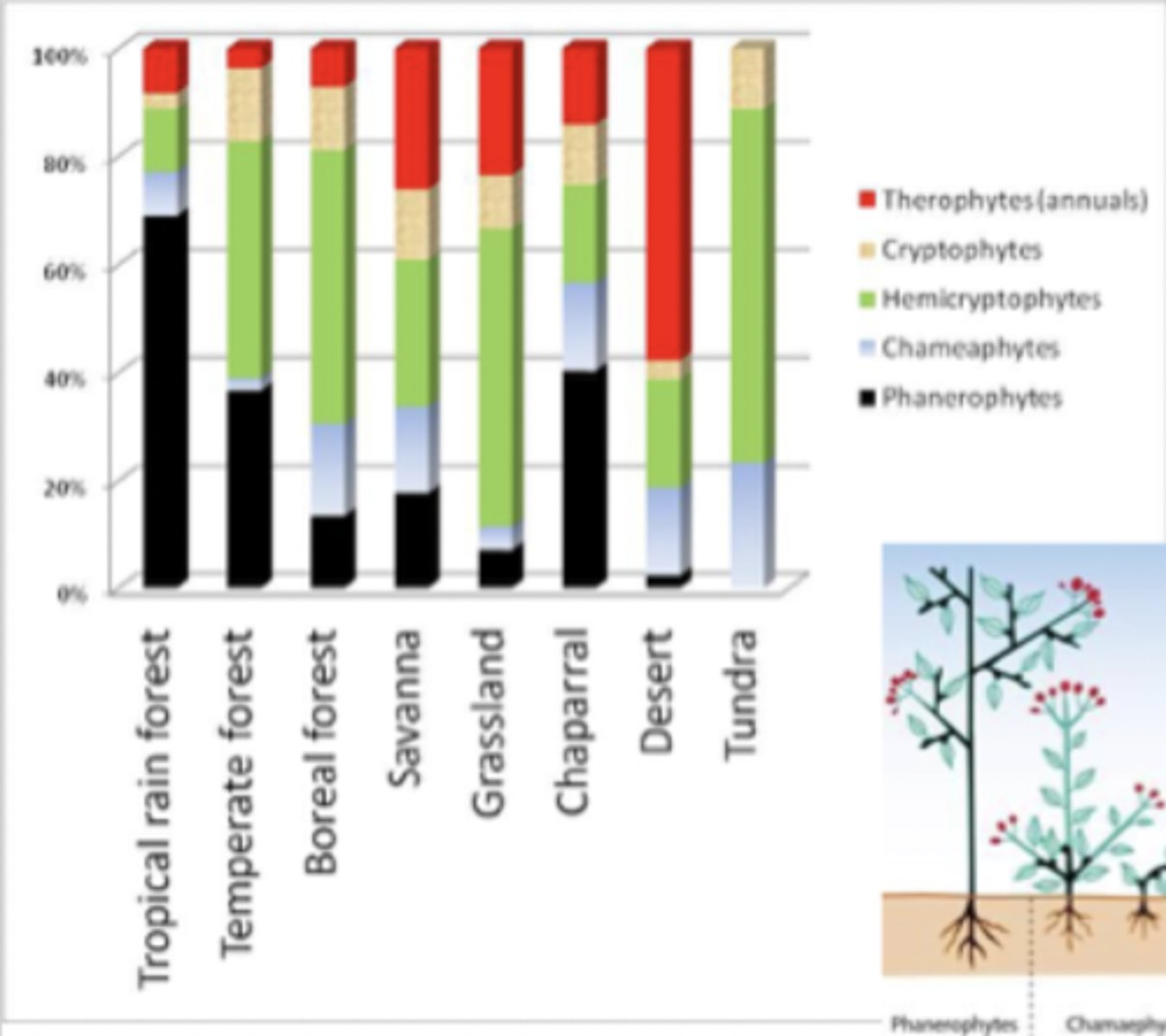
tundra has ____ nutrient system due to low temperature and low precipitation
low
the ______ has the lowest nutrient cycling rates of any ecosystem
arctic
peatlands
partially decayed organic matter of plant origin formed under wet, anaerobic conditions
in peatlands, production of organic matter is greater than
decomposition
peatland distribution
areas of high rainfall and impeded drainage - natural wetlands
examples of peatlands
bogs, lakes, swamps, reedswamps, fens
raised bog development
lake -> reedswamp -> fen -> raised bog
raised bogs and blanket bogs are
ombrotrophic
fen bogs are
minerotrophic
blanket bogs are found in regions where
>1200mm rain and >200 rain days
ombrotrophic
water and nutrients supplied by rain water
minerotrophic
water and nutrients supplied by groundwater
ombrotrophic bog system is very
acidic
(low in nutrients and bases)
peatlands are exploited for
fuel, horticulture, waste water treatment, forestry, agriculture
peatlands are conserved for
wildlife, regional water table, landscape, tourism, archives, carbon sink
irish peatland carbon storage
4 Gt Co2
1 Gt
1 billion tons
carbon storage has _____ over the last 1,000 years
increased