knee injuries and assessments
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
selective tissue test
Girth measurements
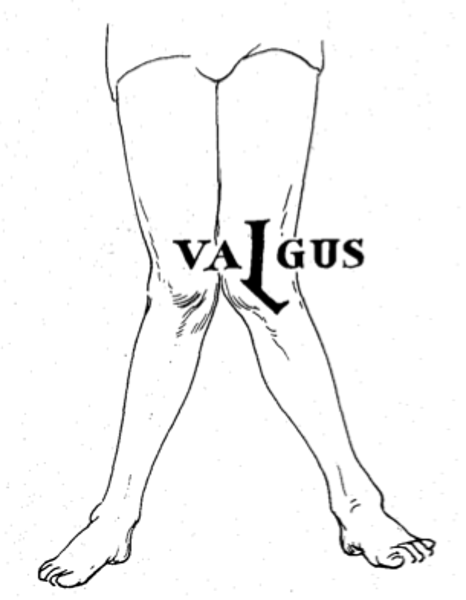
Genu Valgum
-Knock knees
-due to abnormal hip structure and hyper pronation
-Puts compression stress on lateral and distraction stress on medial structures
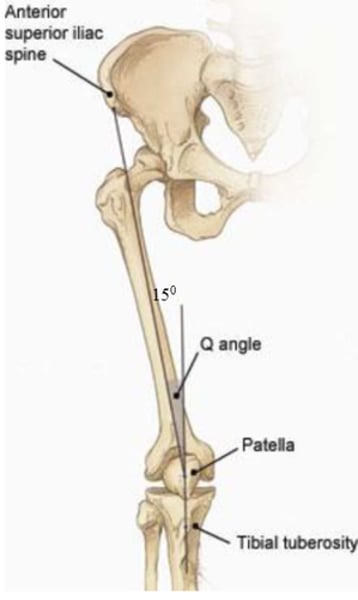
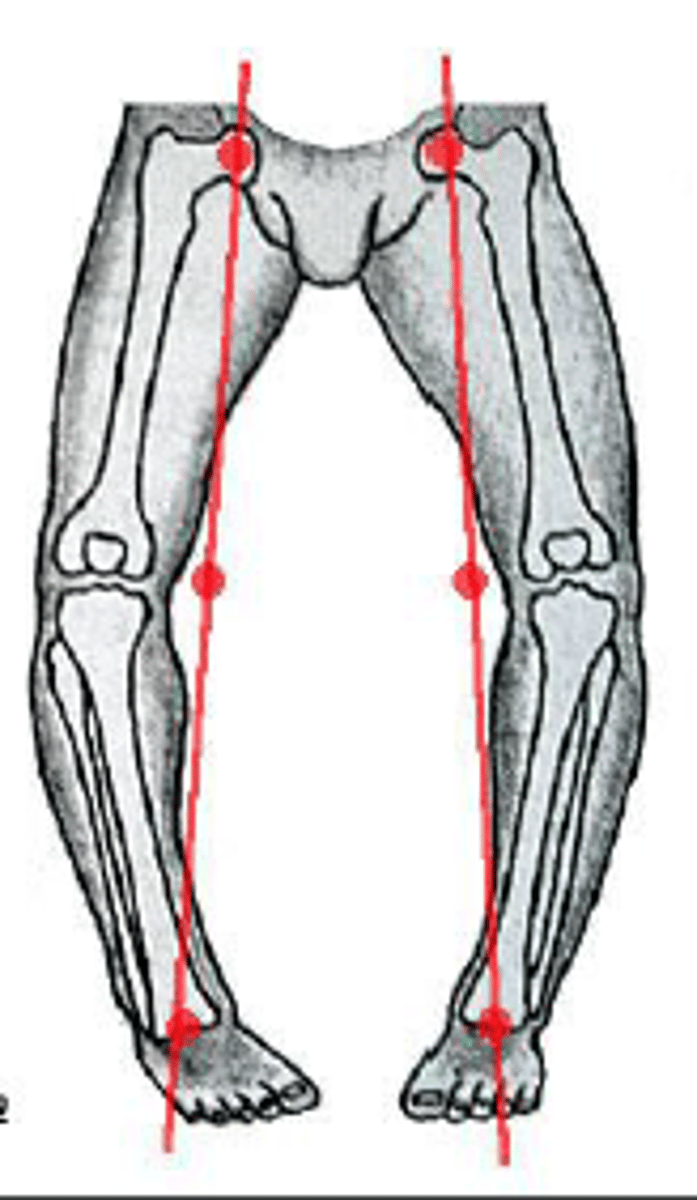
Q Angle
Patient should be laying supine (on back) with knee fully extended, Center fulcrum over midpoint of patella, align the movement arm with ASIS, align the stationary arm with tibial tuberosity, have patient produce flexion,
-abnormal <13 in men & <18 in women
MCL injuries
MOI: valgus force
-When knee is straight, force dissipated by; both MCL layers, joint capsule, tendons of pes anserine
-Knee flex <20=superficial fibers of MCL
MCL injury signs and symptoms
-Pain and swelling over the medial joint
-pain over med. epicondyle or med. tibia or lig.
-pain w/ extreme flex & ext.
-+ valgus stress test (straight=MCL+ joint capsule)
-+ cruciate's (maybe)(25/30 deg.=MCL
-Do Slocum Drawer to rule out capsule
LCL injuries
MOI: Blow to inside of leg, excessive tibia internal rotation
-Additional affected structures= ACL/ capsules
-HOPS; pain over lateral joint, diffuse swelling if any
-Pain over lat. epicondyle or fib. head/ lig.
-Pain & AROM loss (extreme)
-+ varus test
-Do slocum drawer to rule out capsule
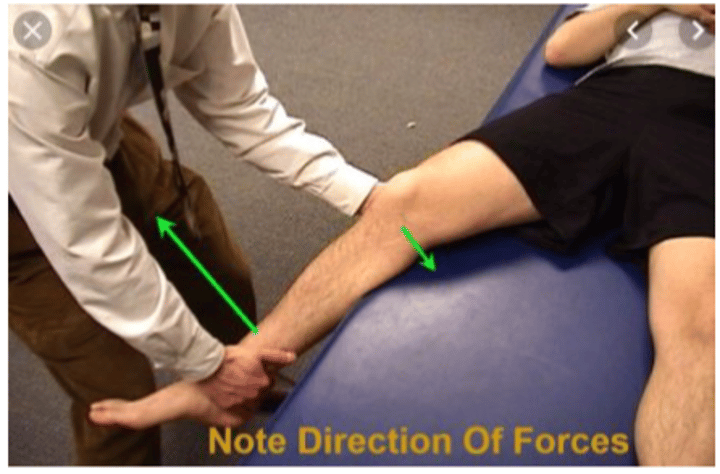
Varus stress test
-Patient lies in supine with injured leg next to edge of table
-abduct patients leg and position yourself between the table and the leg, flex knee to 25 deg.
-One hand supporting Lat. distal tibia while other hand grabs knee at medial joint line
-Apply lateral force to knee while moving tibia medially.
-Redo test at 0 deg. ext.
Varus stress test positive signs
-A positive test increased pain, laxity, lack of endpoint
-Positive test with knee bent 25 deg. is for LCL sprain
-Positive test with knee straight=LCL sprain, lat. joint capsules, and or cruciate lig.
-Sensitivity = 25%
cause of ACL sprain/rupture
-Extreme valgus (foot fixed)
-extreme rotation at knee (can be int. or ext. rotation.
-excessivly strong quad contraction with valgus or rotation (esp. when knee reaches full ext.
-Severe hyper extension (femur goes back, tibia goes foward.
-Sudden deceleration adds force and increases likelihood
ACL injuries MOI
- sudden deceleration
-blow to lat. leg with knee bent and foot fixed
-blow drives femur back
-rotational forces w/ fixed foot
-More common from non-contact than other knee lig.
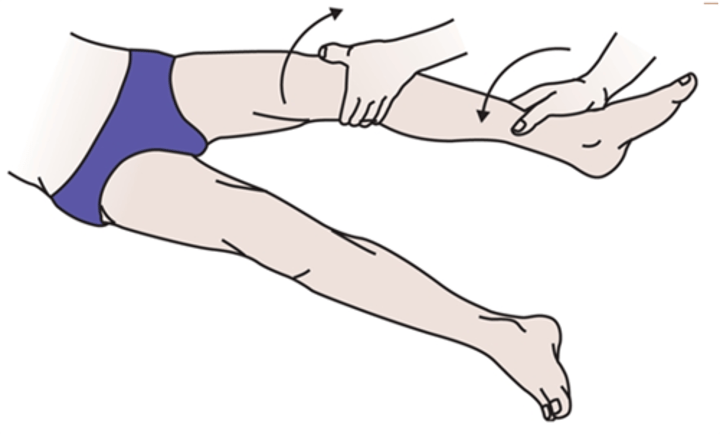
Anterior drawer test described
Patient lays on back, hip flexed at 45 deg. knee at 90 deg.
Tell patient to relax hamstrings, sit on exam table infront of knee, grabing tibia below knee joint line. Place thrumbs on joint like of patellar tendon
-pull tibia anteriorly
-+ test =ACL sprain
-Sensitivity 22-99%
-Specificity 78-97%
positive ligament test
-pain
-inreased laxity
-lack of endpoint
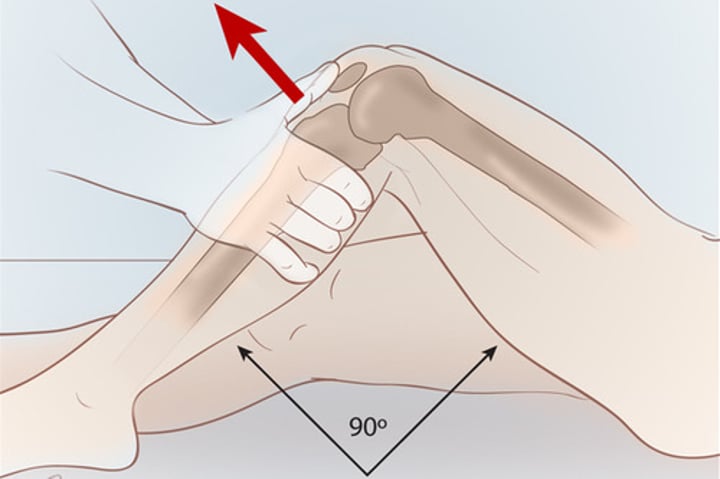
Prone Lachmans described
Patient lays prone (on stomach) with knee passively flexed at 30 degrees
-Support ankle between your arm and body
-One hand palpate anterior joint line on either side of patellar tendon
-Place pressure downward on proximal posterior tibia (pay attention for tibia translation
-+ test = ACL sprain
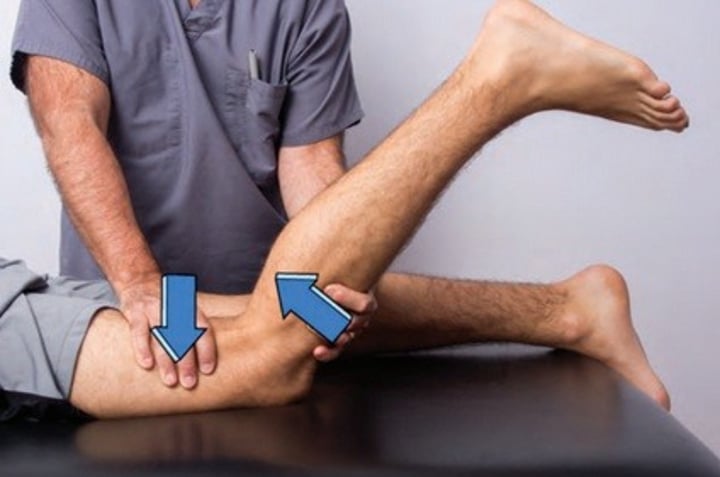
Posterior drawer
Patient lays in supine, hip flexed at 45 deg. knee flexed at 90 deg. Sit on table in front of knee grabing tibia below the knee joint line. Place thumbs on joint line of patellar tendon. Push tibia posteriorly
-+ test = sprain of PCL
-Sensitivity 86-90%
-Specificity 99%
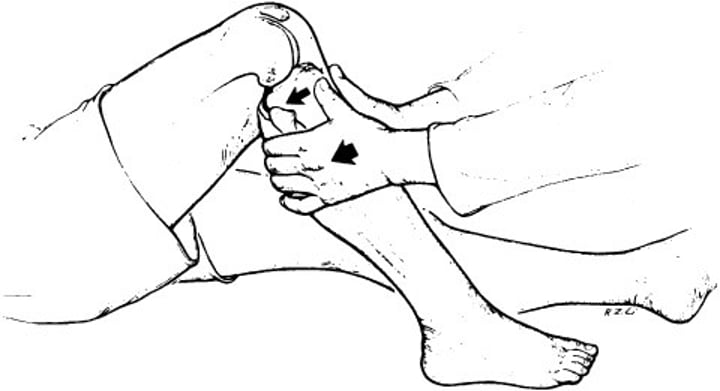
Meniscus Injuries MOI & HOPS
-Twisting with foot fixed
-Pain over joint line, catching or knee giving out, popping or clicking in joint line, swelling after activity with little heat
-+ McMurray's, Apley compression, distraction
Thessaly Test for... & describe
Meniscal tears
-Patient stands flat footed on injured leg with opposite leg flexed at 45 deg. Stand in front to support arms. Tell patient to flex planted knee to 5 deg. and IR & ER the tibia
-Repeat test 3 times
-Have patient flex knee at 20 deg. & IR and ER the tibia
-Sensitivity and specificity vary.
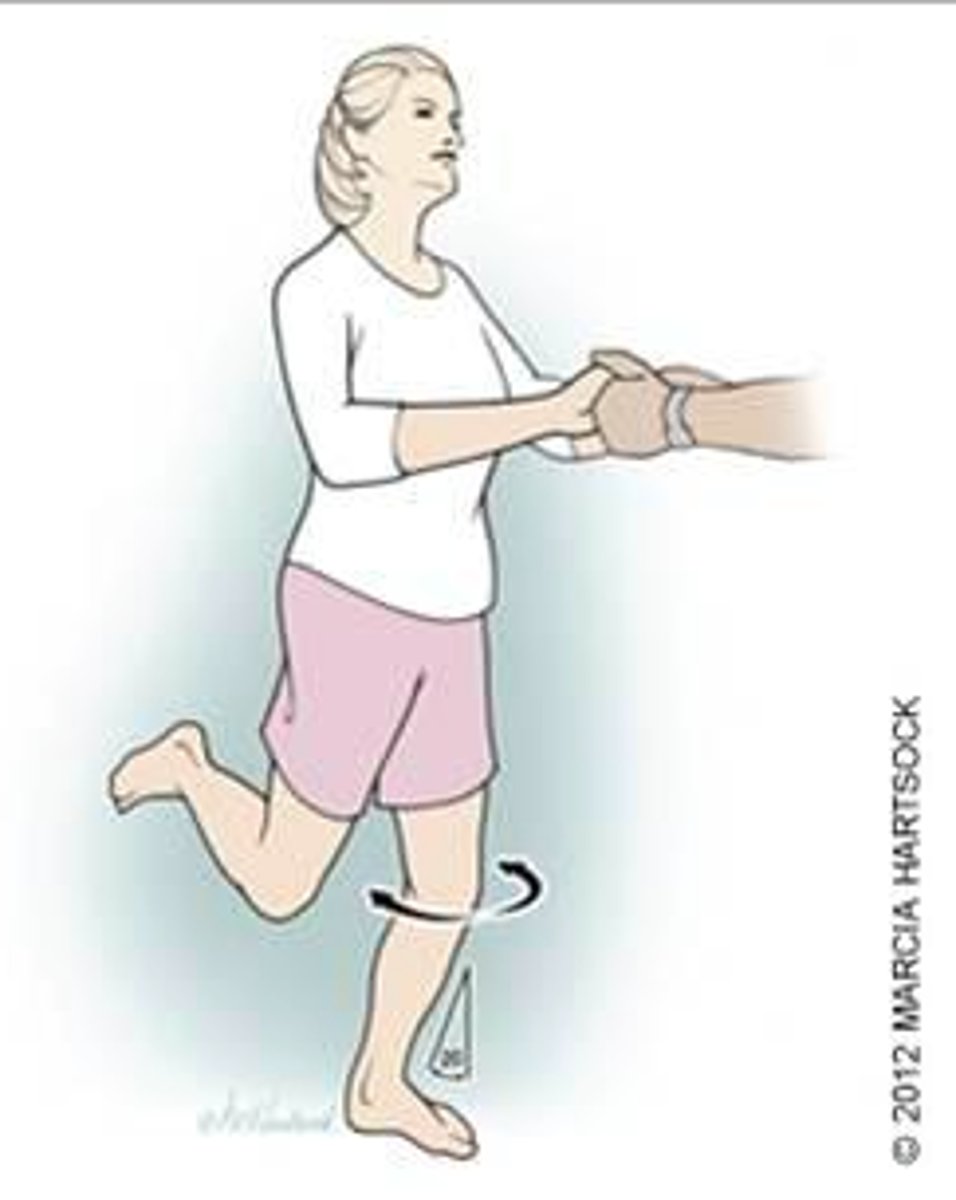
Thessaly test is performed at...
5 degrees then 20 degrees
Thessaly test positive sign
-Joint line discomfort
-Sensation of locking or catching
-+ test = meniscal tear
IT band friction syndrome precursor & MOI
- distance runners, cyclers, large Q angle, genu varum, pronation, leg length discrepancy
-MOI: overuse
Ottawa knee rule
X-ray required if; 55 y/o and up, isolated patella tenderness, tenderness of fibula head, inability to flex more than 90, inability to bear weight(4 steps)
Ottawa sensitivity and specificity
Adult sen= 98-100%, spec=19-54%
Child sen= 92%, spec=49%
genu varum
Bowlegs
-Foot supination, external tibial rotation, lateral patella position, external femoral rotation
-Places stress on lateral structures and compresses medial structures
Genu Recurvatum
-Abnormal hyperextension
-Stretches posterior capule, ACL tension
MCL injuries rule-outs
-Meniscus and capsule (can be injured w/ valgus force)
-IN adolescents rule out growth plate fracture
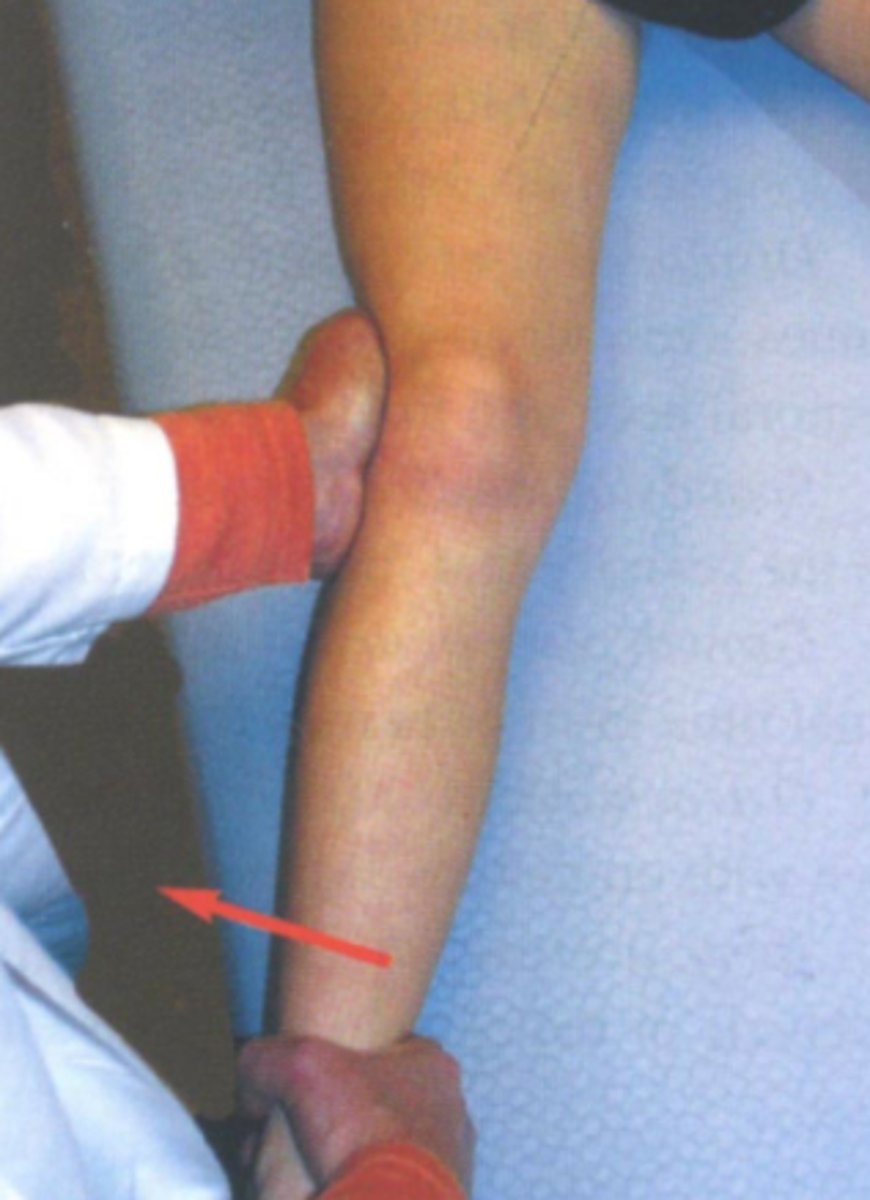
Valgus stress test described
Patient lays in supine. Stand on outside of patients leg, ensre it is at the edge of the table. Lift leg and bend knee to 25 degrees (sprain of MCL), one hand on medial distal tibia and the other along to knees lateral joint line, apply a valgus (medial) force to knee with distal tibia is moved laterally.
-Redo test at 0 deg. extension (sprain of MCL, medial joint capule, and/or cruciate ligaments)
-sensitivity 86-96%
ACL functions to prevent...
-Anterior tibia translation
-Internal tibia rotation on femur
-External tibia rotation on femur
-Hyperextension of tibiofemoral joint
Females and ACL
-5% higher chance than males
Theories; increased hyperextension, increased internal & valgus force with landing, hormonal changes during menstration, femoral notch size, decrease hamstring activation, don't typically stiffen their knee.
ACL signs and symptoms
-immediate pain, swelling, hot knee
-Pain "inside knee", knee "falling apart"
-ROM may be limited due to swelling, PROM pain increase w/ INT. & EXT . rotation of knee
-+ Anterior drawer test
-+lachman's
Lachmans described
Patient in supint with knee passivly flexed 20-25 deg. Grab tibia at tibial tuberosity level and grasp femur just above condyles. pull tibia foward while applying posterior femur pressure
-+ test= ACL sprain
PCL injuries MOI & HOPS
-Driving femur posterior/ hyperextension
-Pain in popliteal fossa; knee "falling apart"
-Overtime PCL deficency causes ACL issues
-+ posterior drawer, posterior sag, external rotation dial test.
Godfreys test for PCL
Patient lays in supine with knees extended and together. Stand on side of patient and lift their legs parallel to the table, knees bent to 90 deg. Hold leg near the ankle
-Observe tibial tuberositie levels
-+ test is a unilateral displacement of tib. tuberosity
-+ test = PCL sprain
-Sen-79%, Spec- 100%
Meniscus zones
Red zone= outer 1/3
Red-white zone= middle 1/3
White zone= inner 1/3
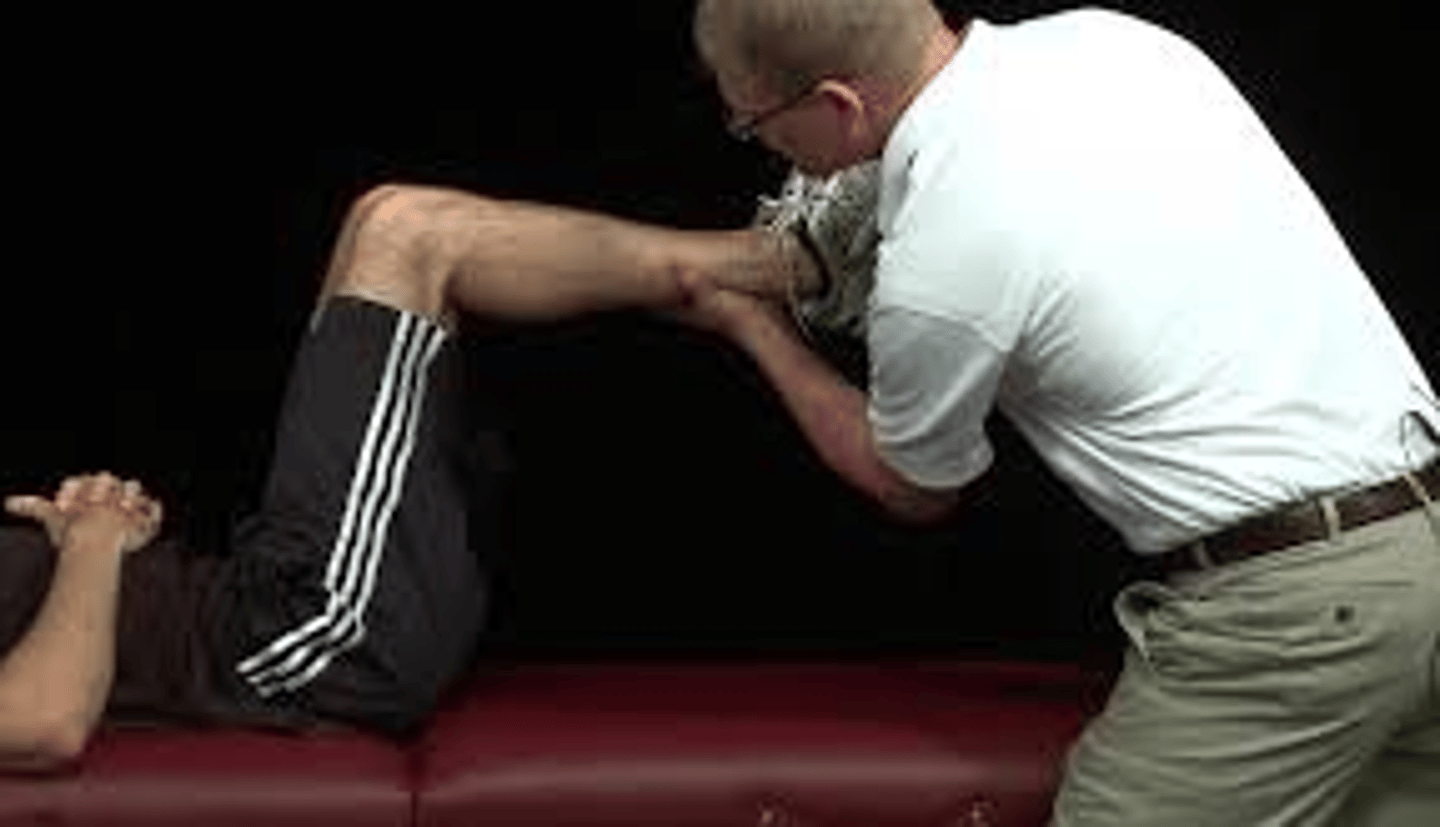
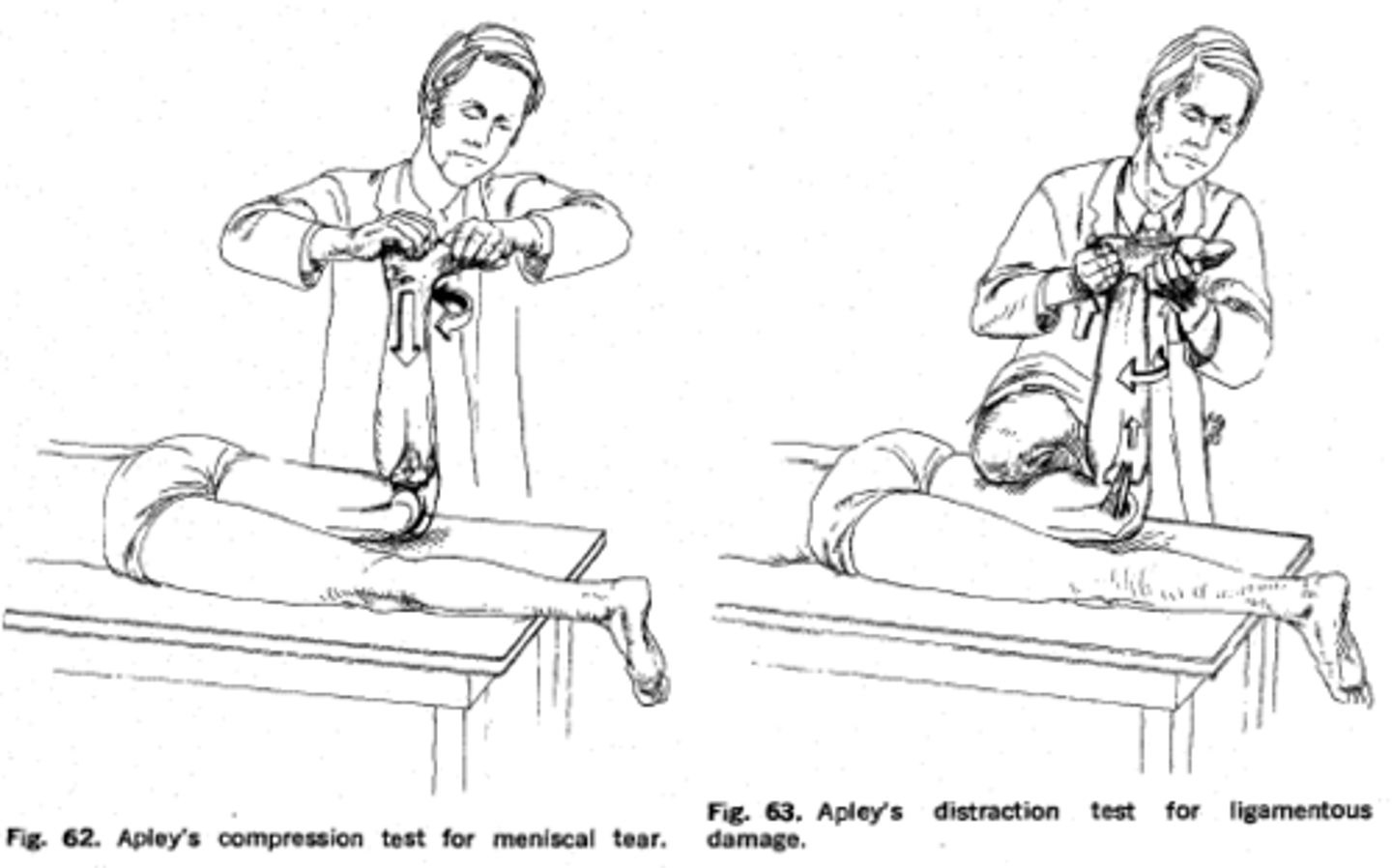
Apleys compression and distraction
Meniscal tears
-Patient lays prone, knee bent 90 deg. stand on outside of testing leg. Apply pressure to plantar heel surface while INT & EXT rotating the tibia
-Grab lower leg and stabilize knee proximal to femoral condyles. distract tibia away from femur while INT & EXT rotating tibia
-+ sign is pain during compression or distraction(meniscal tear), or pain relief during distraction (trauma to collateral lig. the joint capsule, or cruciate ligaments
-+ test = meniscal tear
IT band friction syndrome & HOPS
-IT band snaps over the lateral condyle
-Pain with up and downhill running
-point tender over lateral femoral condyle
-burning pain
-pain w/ RROM at 30 deg.
-+ obers & nobles test
Nobles test
Patient in supine with knee flexed. stand outside of testing knee. Place hand over joint line with thumb or superior to lateral femoral condyle, other hand on distal tibia
-Passively extend and flex the knee while applying pressure to lat. femoral condyle with thumb
-+ test= pain under thumb (common at 30 deg.)
-+ test= inflammation of IT band, its bursa, or lateral femoral condyle
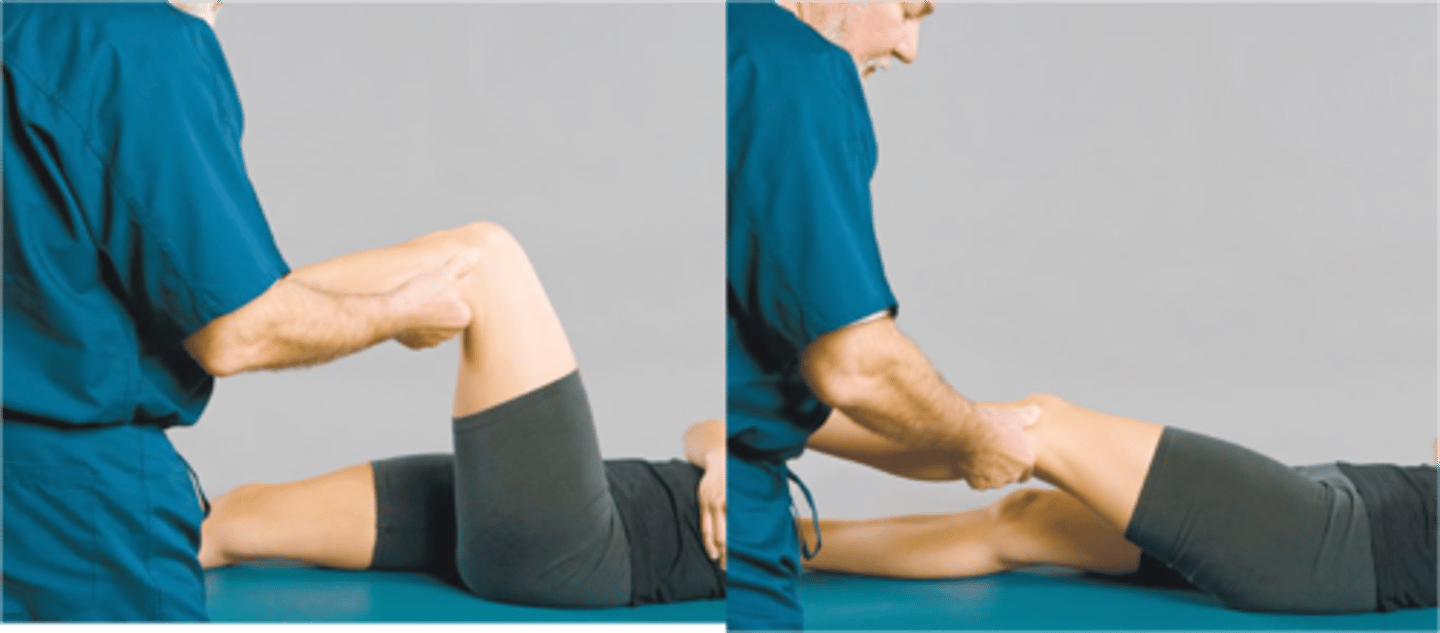
obers test
IT band tightness
Patient lays on side, bottom leg flexed foward to stabilize torso. stand behind patient with one hand under knee and one on distal tibia. Passively extend and abduct leg. remove hand from under knee allowing passive adduction.
-+ test= femur fails to allow passive adduction
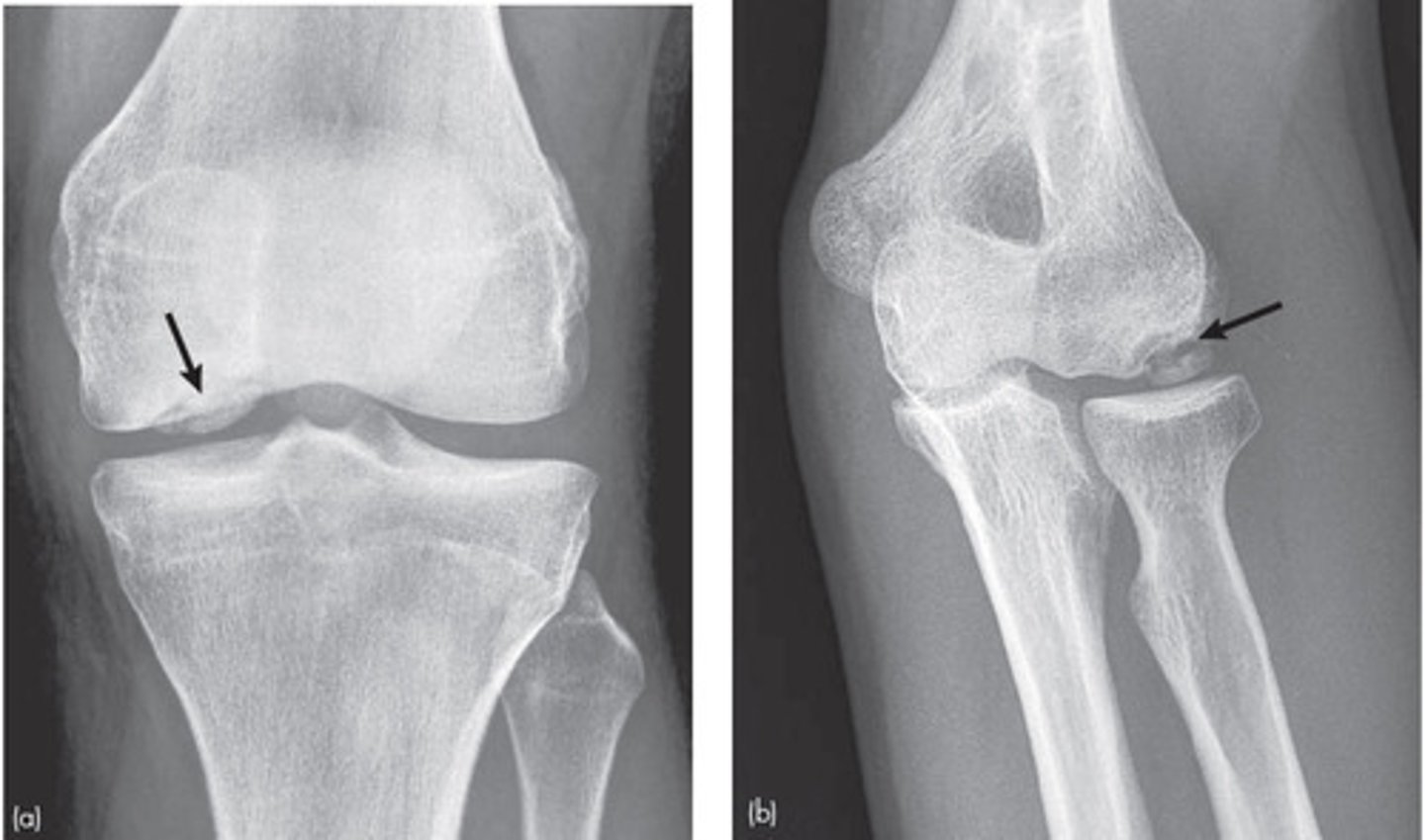
Osteochondral defects (OCDs) MOI & HOPS
-Fractures of the articular cartilage and underlying bone
-most involve medial femoral condyle
-MOI: compressive/ shearing force
-Sudden diffuse pain in knee joint, locking, cluncking, giving away. pain increase when weight bearing, Loss of ROM, pain w/ AROM flex/ext
-Dec. strength in closed chain activities
-+ Wilsons test
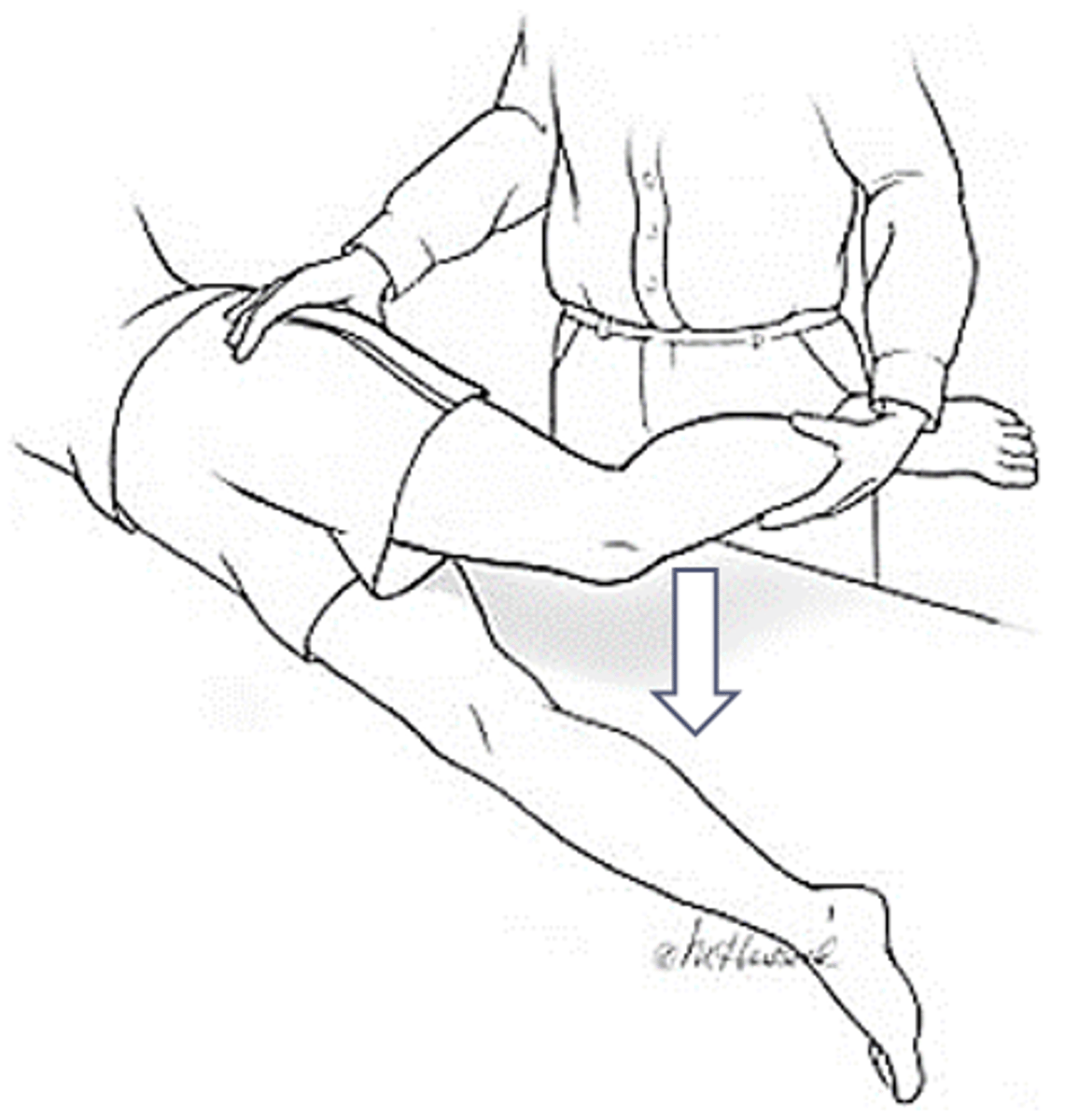
Wilsons test
Pupose- asses osteochondritis of medial femoral condyle
Position- supine with knee flexed to 90 deg.
Technique- extend knee with IR of tibia
-+ test= pain at 30 deg. FLEX in IR that lowers if the tibia is ER, rules out meiscal PX
Baker's cyst
-Popliteal cyst
-MOI: damage to med meniscus, hernia of semitendinosus sheath, deterioration of capsule, tumor
-Pain, loss of ROM, large soft tissue in the popliteal space