Acid-Base Balance Chapter
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What does a weak acid do?
releases H+
What does a weak base do?
binds excess H+
where are protein buffer systems found?
in cells and blood
Where are phosphate buffer systems found?
within cells
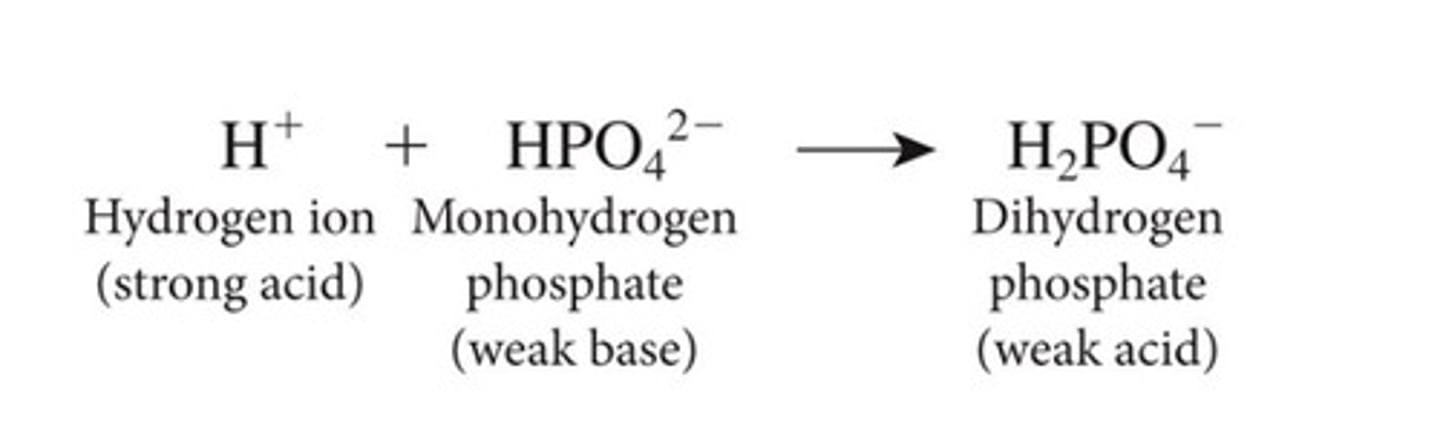
Whats the weak base for phosphate?
hydrogen phosphate(HPO2-)
Whats the weak acid for phosphate?
dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4)
Whats a strong acid buffer?
produces weak acid
strong acid buffer
weak base
HPO24- weak base picture
Where are bicarbonate buffer systems found?
within ECF and blood
Weak base for bicarb?
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) mops a proton
Weak acid for bicarb?
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) donates a proton
whats buffering capacity?
limit of acid or base a chemical buffering system can buffer
Protein buffer system
3/4 in body fluids
contains: intracellular protein, plasma proteins, hemoglobin
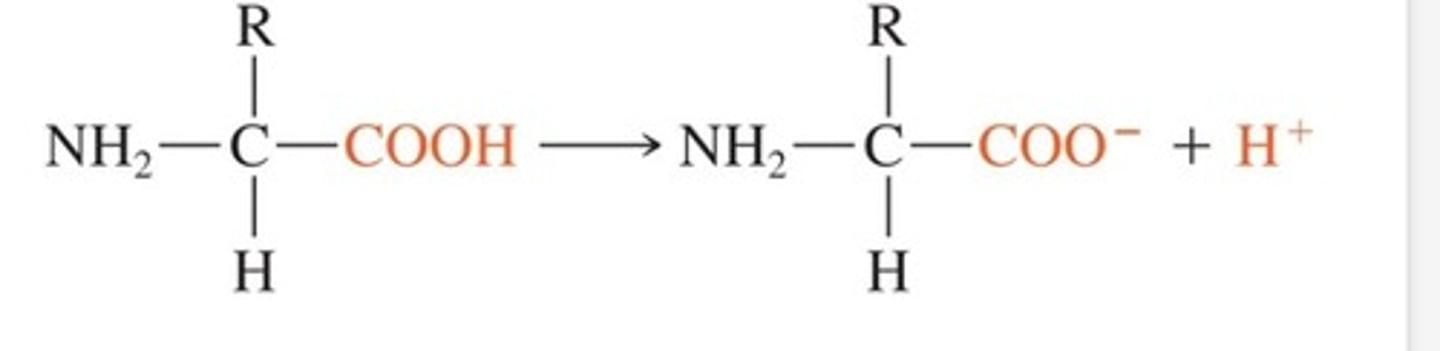
When pH rises in a protein buffer system what happens?
The COOH disassociates to act like acid= COO- +H+
When pH falls in a protein buffer system what happens?
the free amine group picks up a proton to act as a base
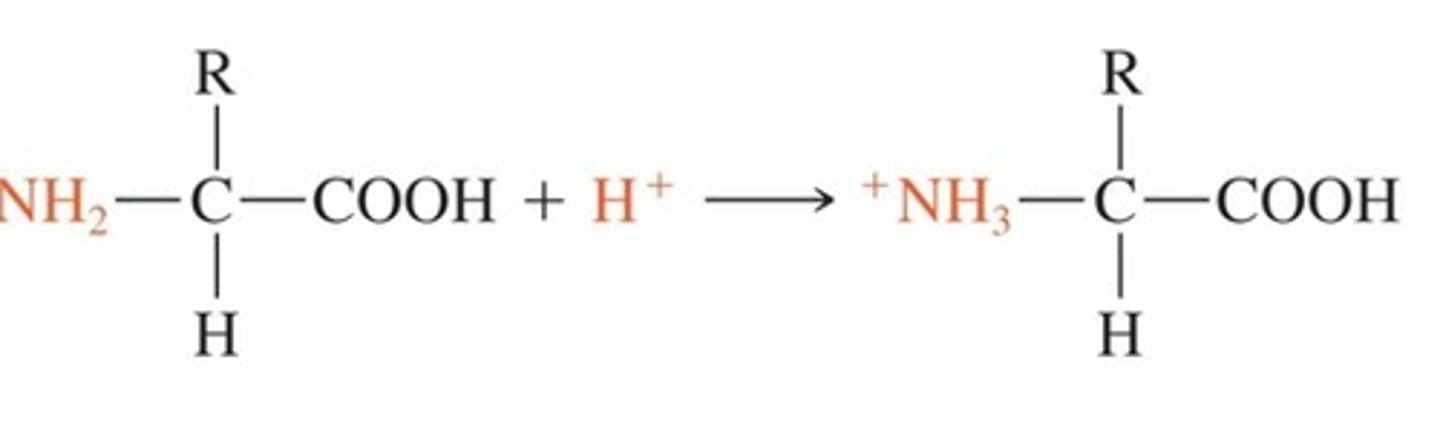
What is an amine group for?
acts as a weak base to buffer acid
What does carboxylic acid do?
acts as a weak acid to buffer base
Whats impaired respiratory function?
holding on to breathing forces a reaction to the right
Whats abnormal rates in respiratory rates?
hyperventilation
reduced amount of CO2, pulls reaction to the right
Kidneys do what for moving HCO3-?
pump H+ in urine, bicarb is reabsorbed in blood and kept as a buffer
What happens during respiratory acidosis ?(most common)
cant eliminate CO2, above 45 mm Hg
What causes respiratory acidosis?
hypoventilation, airway obstruction, emphysema, respiratory membrane has too much water
What causes respiratory alkalosis?(reaction goes to the left)
severe anxiety attack, hypoxia, aspirin overdose, kidneys aren't pumping H+
Metabolic acidosis caused by?
Loss of HCO3- or gain of H+
What causes metabolic acidois?
ketoacidosis, excessive alc intake, renal dysfunction, diarrhea
What happens during metabolic alkalosis?
too many protons about binded up
What are the effects of metabolic alkalosis?
excessive vomiting, overdose of alkaline drugs, kidneys with diuretic overuse, taking a lot of tums
solution for metabolic alkalosis?
hypoventilation (breathing deeper and slower to hold on to CO2)
What is an ABG for?
diagnose and monitor acid base disturbances
How do the kidneys compensate for respiratory acidosis?
increased H+ secretion and reabsorption of HCO3-
What is ketoacids?
produced from fat metabolism
Ketoacidosis
excessive production of ketones, making the blood acidic