Physics midterm one electric charge and Coulomb’s law
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
neutral atom
A neutral atom has the same number of protons as electrons.
positive ion
A positive ion is an atom with one or more electrons removed.
negative ion
A negative ion has gained one or more electrons.
Two positive or two negative charges …… each other.
repel
A positive
charge and a negative charge ……. each other.
attract
Note when an object for ex a rod gets rubbed to a carpet they would attract since each one would gain its own different charge when they were in contact
A …….. permits the
easy movement of charge
through it. An ……
does not. Ex:
conductor….insulator Most metals and humans
are good conductors, while
most nonmetals are
insulators.
….,…..are
intermediate in their
properties between good
conductors and good
insulators.
Semiconductors …..
Semiconductors are special materials that can act like both conductors and insulators, but it depends on certain conditions, like temperature or if they’re given energy.
• When there’s low energy (like at low temperatures), semiconductors act more like insulators—they don’t conduct electricity well.
• When there’s more energy (like when you heat them or apply an electric field), they act more like conductors—they let electricity flow better.
So, it’s not the material changing from conductor to insulator, but rather how it behaves under different conditions that makes it unique.
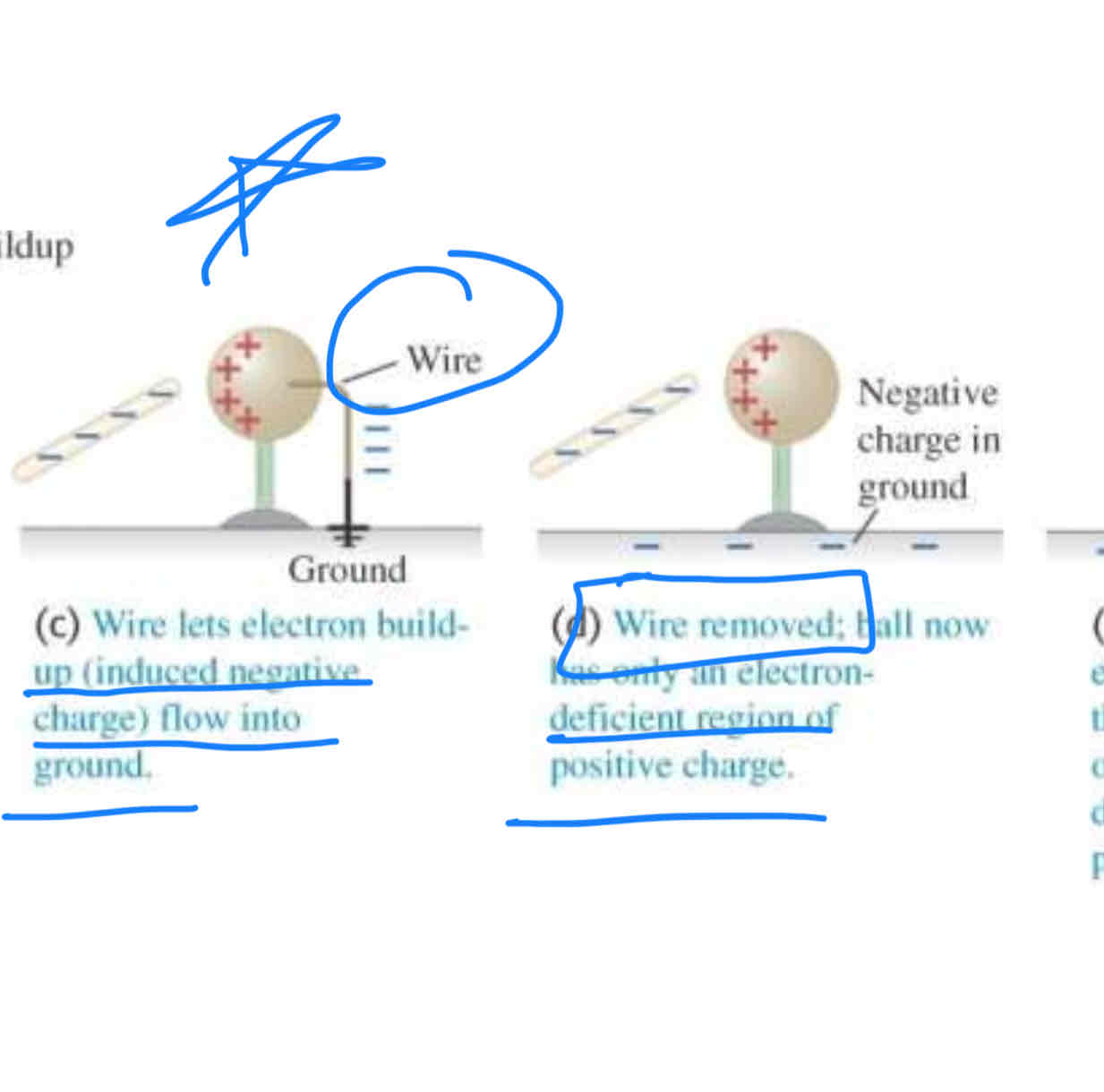
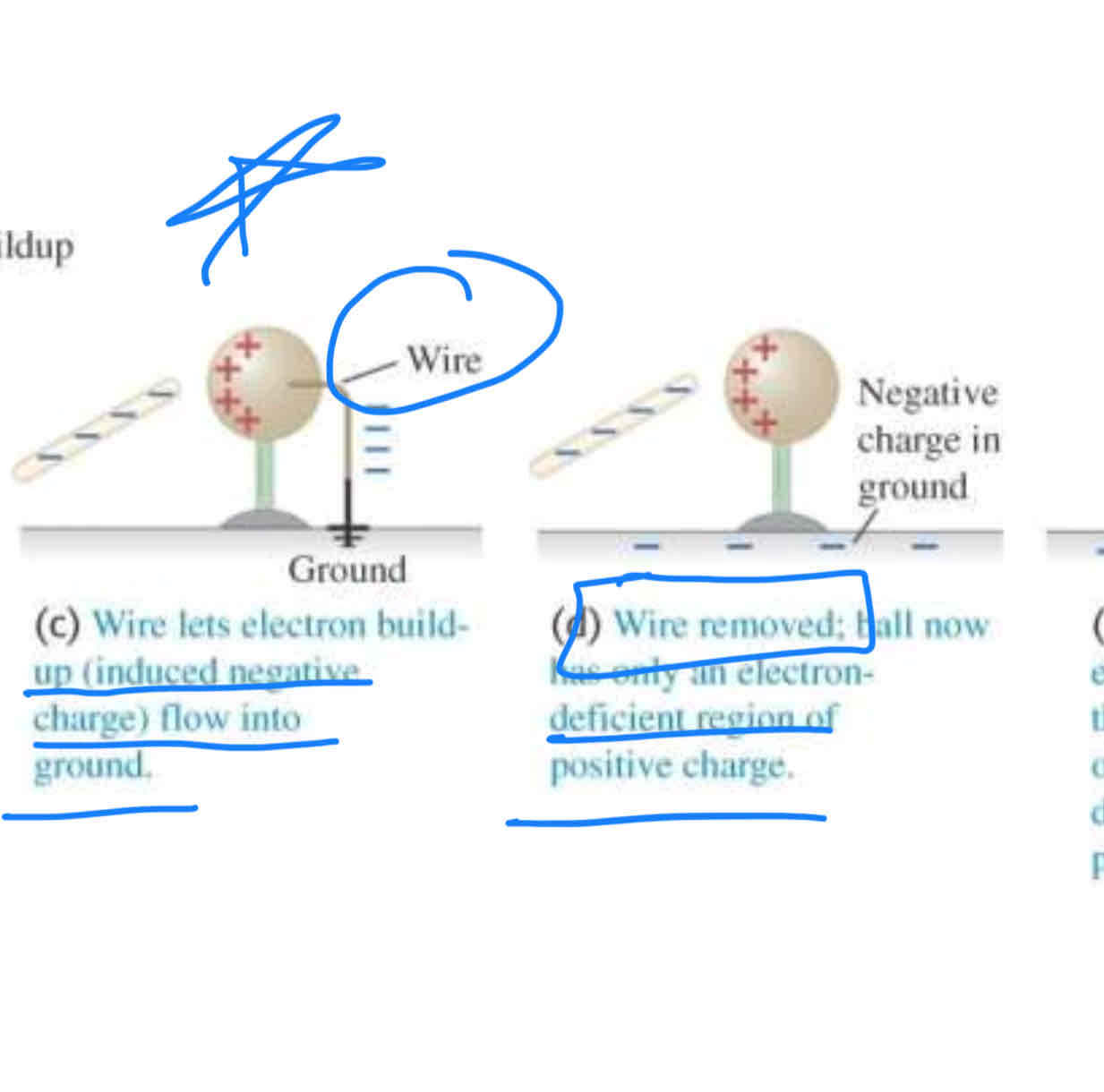
the negative rod is able to charge the metal ball
without losing any of its own charge. This process is called
charging by induction.
Imp note
Electric forces on uncharged objects
The charge within an insulator can shift slightly. As a result, a
charged object can exert electric forces on neutral objects
………. is particle of “zero” size carrying a charge, e.g.
electrons and protons.
Point charge
More precisely , particles’separation is much larger than
particle dimension.
Note to the note we mean that the distance between individual particles is much greater than the size of each particle itself.
We can have few charges separated by large distances, or
many charges spread like touching each other:
Which is called
Continuous Charge Distribution
………… The magnitude
of the electric force between two
point charges is directly proportional
to the product of their charges and
inversely proportional to the square of
the distance between them.
Coulomb’s law
Coulomb’s law Formula
F=k |q1.q2|/r2
k” is a constant called Coulomb constant
In empty space (Air) and in SI system The number is
9×10^9 Nm²/c²
……………………….When two
charges exert forces simultaneously on a third
charge, the total force acting on that charge is the
vector sum of the forces that the two charges would
exert individually.
Principle of superposition of forces: ….. vector sum is the process of combining those forces to find the total effect of an object
Rules to set the equilibrium position point where the net
electrostatic force is zero:
1- if the two charges are like charges the position of equilibrium will
be between them and close to the small charge in magnitude.
2- if the two charges are unlike charge, the equilibrium position will
be out of the charges and close to the small one in magnitude
Vector has both
Magnitude and direction
Ke is also written as
1/4pieE0 or instead of E0 ke

The constant E0is called the…….
and it equals……
permittivity of free space. 8.85×10^-12

Fe and fg are both
Inverse square forces An inverse-square law means that the force gets weaker as the distance increases, specifically decreasing by the square of the distance (so if the distance doubles, the force becomes four times weaker).
The elementary charge e number is….
1.6×10^-19c