16.3 Sexual reproduction in plants
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the function of the stigma?
It’s sticky surface catches pollen
What is the function of the style?
It links the stigma to the ovary
What’s the function of the ovary
It produced ovum(female sex cells)
What is the function of ovules?
It contains female sex cells
What is the function of the anther?
It contains pollen
What is the function of the filament?
It supports the anther
What is the function of the sepal?
It protects the unopened flower
What is the function of petals?
The bright colour of petals in insect-pollinated flowers attract insects
What is the male reproductive part of the plant called and what does it consist of?
Stamen
It consists of the anther and filament
What is the female part of the flower called and what does it consist of?
Carpel
It consists of the stigma, style and ovary
What is pollination?
The transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma
What are the features of insect-pollinated flowers?
Large and bright petals to attract insects
Moderate amount of pollen as insects r more efficient in pollination
Pollen grains are large, sticky and spiky to stick to insect body
Scent and nectar present to attract insects
Stigma is sticky and inside the flower
Anther is inside the flower and firmly attached
What are the structural adaptations of a wind-pollinated flower?
Petals are small and dull
Pollen is present in large amount to increase chances of successful pollination
Pollen grains are smooth, small and light so they can be blown easily by wind
No scent nor nectar
Stigma is feathery to catch drifting pollen grains and is outside the flower
Anther is outside the flower, swinging loose to release pollen grains easily
What is self pollination?
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower, or a different flower on the same plant
What is cross pollination?
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species
What are the effects of self pollination?
Reduces genetic variation
Limits the adaptability of offspring to changing environmental conditions
What are the effects of cross pollination?
Increases genetic variation
Relies on pollinators, can be a problem if they are missing
Wind pollinated plants are not affected by the absence of pollinators
When does fertilisation in a plant happen?
When a pollen nucleus fuses with a nucleus in an ovule
Describe the process of fertilization in a plant
A pollen grain lands on the stigma
Pollen tube begins to grow down the style until it enters the ovule through the micropyle
The pollen nucleus moves down pollen tube
Pollen nucleus fuses with ovum nucleus to form a zygote
Ovule eventually develops into a seed
Ovary wall eventually develops into a fruit
Which factors are essential for seed germination?
Water-causes seed to expand and activates enzymes within embryo to start growth
Oxygen-for respiration to release energy for growth
Suitable temperature-increases rate of germination, as enzyme-catalyzed reactions r temperature-dependent, up to an optimum
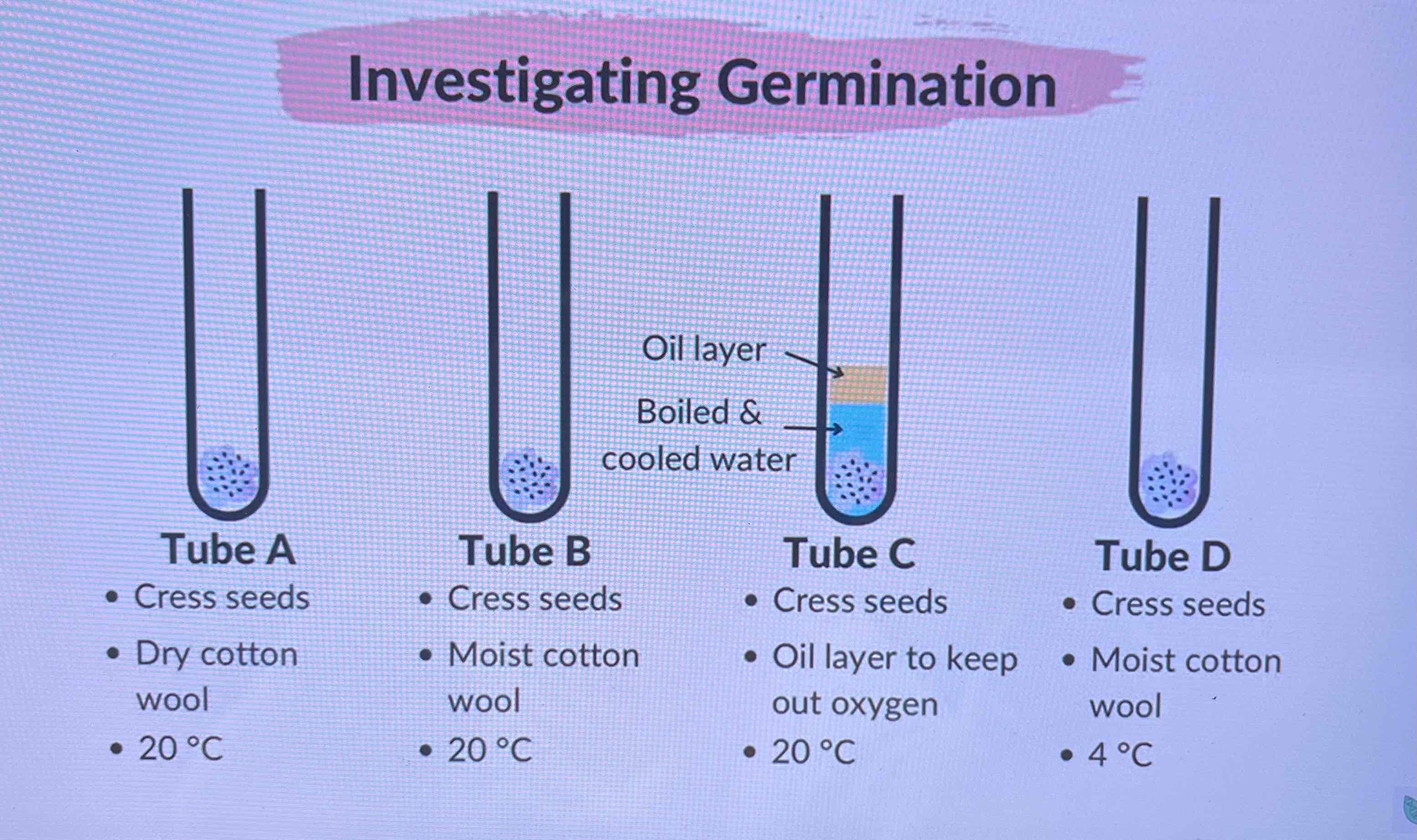
How to investigate germination?
Seeds don’t germinate in test tube A, due to lack of water
They germinate in test tube B as all factors are present
They don’t germinate in test tube C due to lack of oxygen
They don’t germinate in test tube D due to low temperature