Unit 11- Focal Disease, Trauma and Cysts
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
A splenic abscess is _______ and typically from ______ ______
Uncommon
Other organs
What are the signs/symptoms of a splenic abscess?
+ blood culture
High WBC
Fever
LUQ Tenderness
Splenomegaly
US appearance of a splenic abscess:
Splenomegaly
Solid/Complex
Hypoechoic, septations
Irregular, ill-defined borders
Low level echoes
Hyperechoic foci
Debris or gas
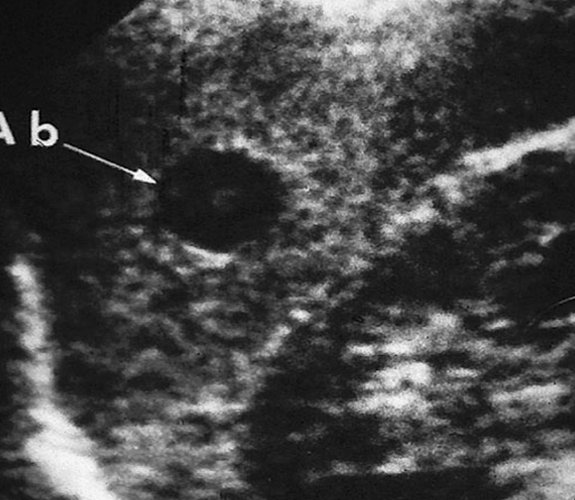
What is this image showing?
Splenic Abscess
What are the different types of Splenic Infection?
Hepatosplenic candidiasis
Mycobacterial infections
Active Tuberculosis
Splenomegaly
US appearance of Hepatosplenic Candidiasis:
Irregular masses within spleen
Wheel within a wheel
Bull’s eye
Hypoechoic nodule
Hyperechoic nodule
Splenomegaly
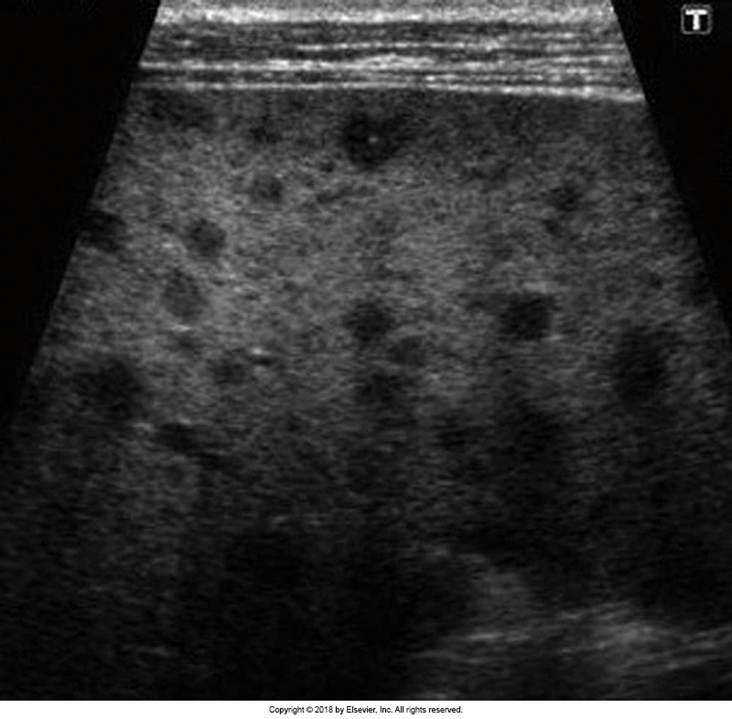
What is this image showing?
Hepatosplenic Candidiasis
What do patients show on ultrasound with Mycobacterial infections?
Tiny diffuse echogenic foci
What do patients show on ultrasound with Active Tuberculosis?
Echo-poor or cystic masses = small abscess lesions
What are these images showing?
Active Tuberculosis Abscess
What is the definition of AIDS?
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
With AIDS, what are the focal lesions involved with the spleen?
Infectious processes
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Lymphoma
US appearance of AIDS in the spleen:
Splenomegaly (most common)
Small round lesions
Liver lesions with hepatomegaly
Retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
Ascites
What is the most common cause of focal splenic lesions?
Splenic Infarction
What is a Splenic Infarction caused by?
Occlusion of splenic artery or any of its branches
What are other causes of Splenic Infarction and in what patients does this occur?
Septic emboli
Local thrombosis
Pancreatitis
Leukemia
Lymphomatous disorders
Sickle cell anemia
Sarcoidosis
Polyarteritis nodosa
US appearance of Splenic Infarction:
Localized, wedge shaped, hypoechoic area
Dependent on time of onset
May become nodular or hyperechoic over time
Use color Doppler to evaluate lesion
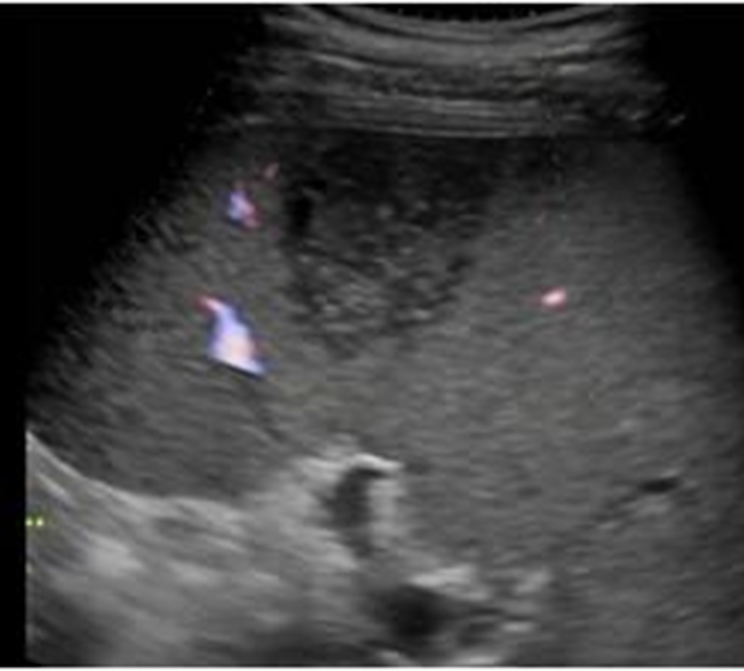
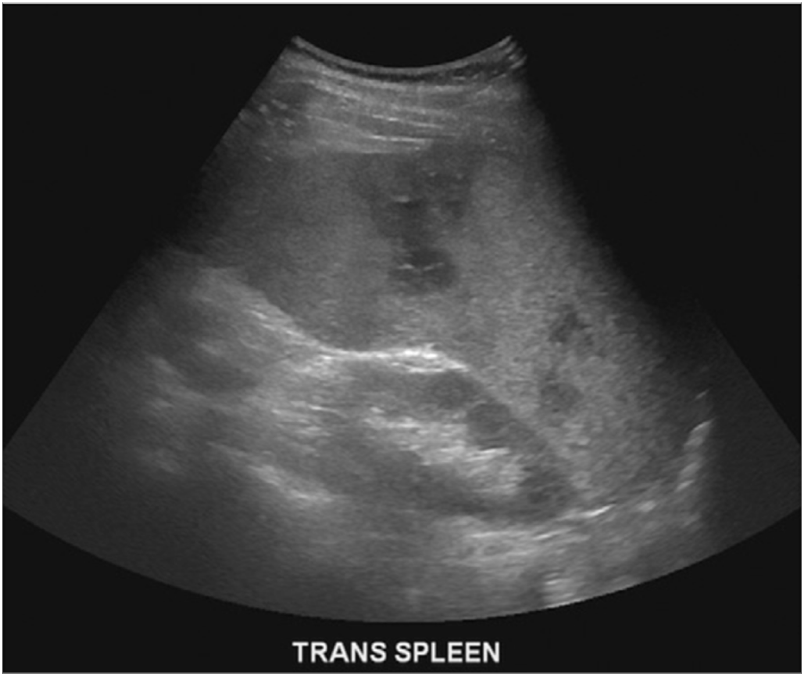
What are these images showing?
Splenic Infarct
With splenic trauma, what type is it usually?
Blunt trauma
What are the effectsofh blunt trauma?
Hematoma
Linear or stellate lacerations
Capsular tears
Puncture wounds (ribs, foreign bodies)
What are the possible outcomes of splenic trauma?
Intact capsule
Ruptured capsule
Delayed rupture
What are the common symptoms associated with splenic trauma?
LUQ pain
Left shoulder pain
Left flank pain
Dizziness
What are the clinical evaluation findings for a splenic trauma?
Hypotension
Decreased hemoglobin
Tenderness LUQ
If a patient has a splenic trauma that is an emergent situation what must be done?
Peritoneal lavage
Exploratory surgery
What is a FAST scan?
Sonographer quickly evaluates the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants (less than 5 min.)
What does the location of fluid in a FAST scan determine?
Location determines capsular or subcapsular hematoma
US findings of a Subcapsular Hematoma:
Splenomegaly if capsule intact
Progressively enlarges as bleeding continues
Irregular border
Hematoma
Subcapsular & Pericapsular fluid
Free intraperitoneal blood
Possible Left Pleural Effusion
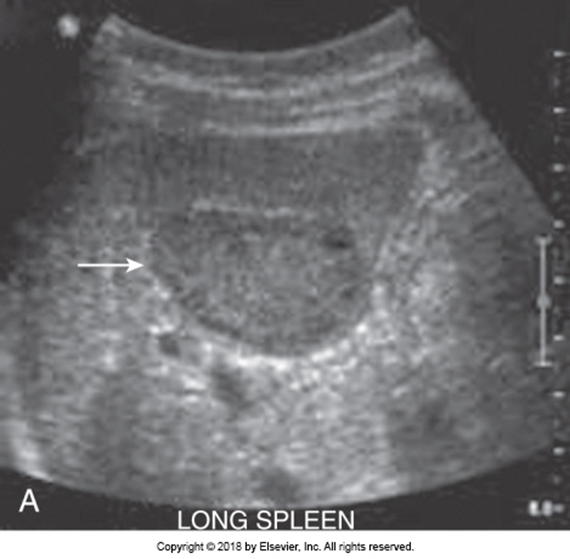
US finding of a focal hematoma:
Intrasplenic fluid collections
US findings of peri or subcapsular hematoma:
Perisplenic fluid collection
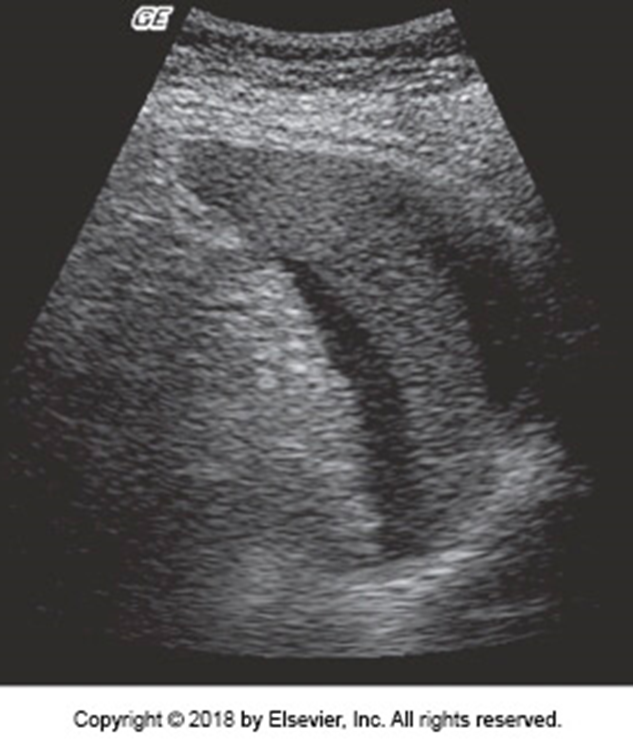
What is this image showing?
Splenic Hematoma
Pericapsular hematomas regress more than what?
Subcapsular hematomas or contusions
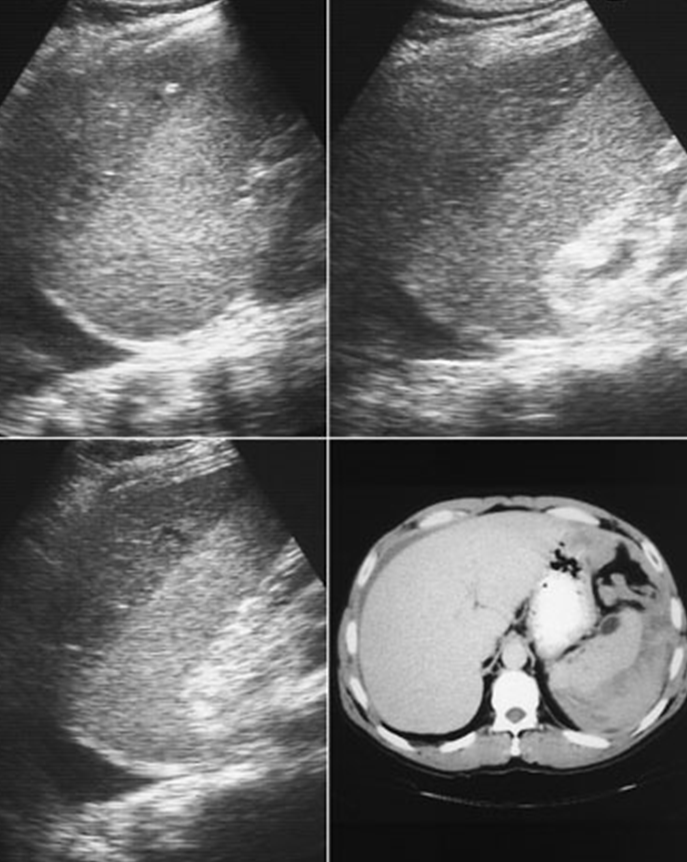
What is being shown in the images above?
Top images are hematomas
Bottom left image is a pleural effusion
What do Congenital Cysts contain of?
Epithelial lining
Solitary
Unilocular
If simple = no clinical significance
US appearance of splenic cysts:
Anechoic - Hypoechoic
Well-defined walls
If complicated:
Septations with internal echoes
Thickened wall
Hemorrhage may produce a fluid level
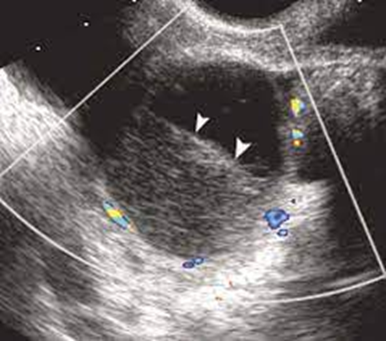
What is this image demonstrating?
A fluid filled level with a hemorrhage
What are splenic cysts secondary to?
Trauma
Infection
Infarction
What is a parasitic cyst?
Echinococcus parasite only
US appearance of a parasitic cyst?
Anechoic
Possible daughter cysts
Possible calcifications
Solid masses with fine internal echoes & poor enhancement
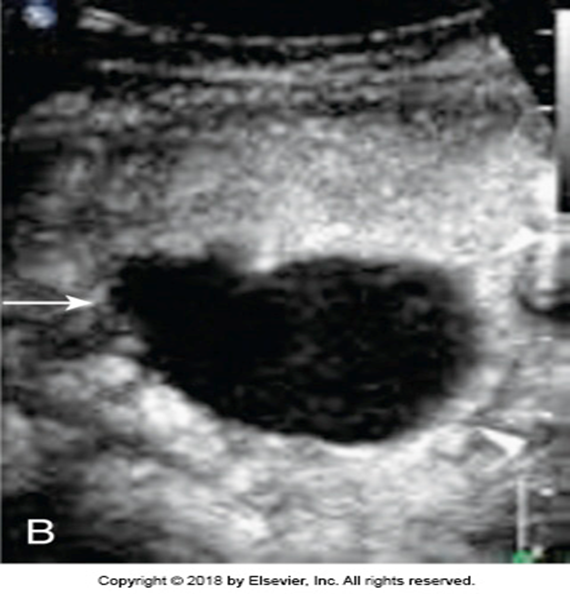
US appearance of a splenic cyst:
Anechoic or mixed homogeneity
Wall may be calcified
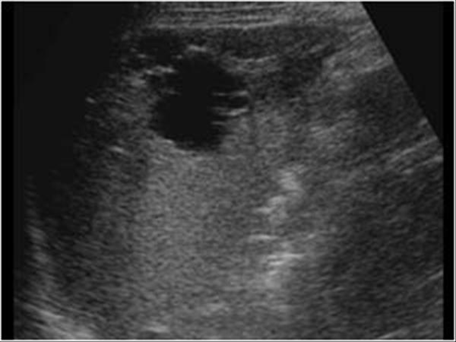
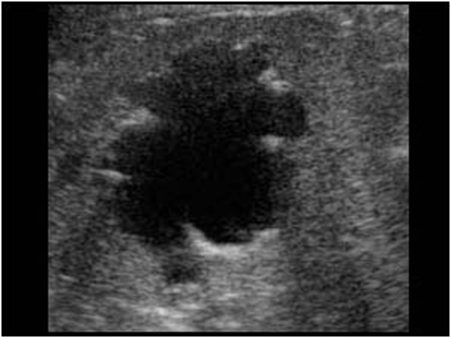
What is this image showing?
Splenic Cysts
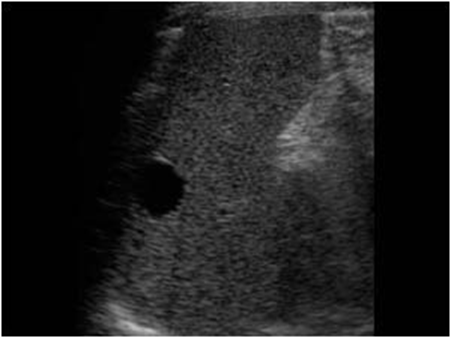
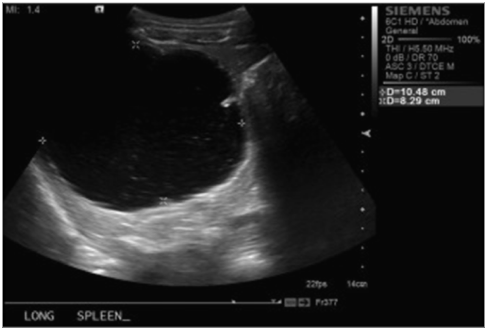
What are these images showing?
Splenic Cysts