herps vocab and diagrams
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
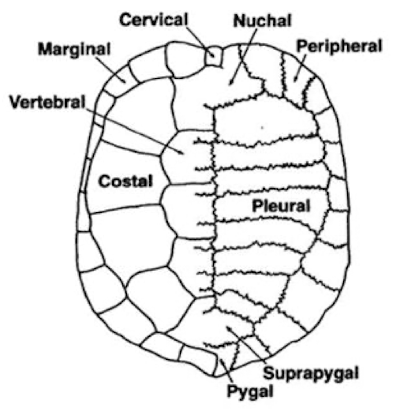
Top
Carapace
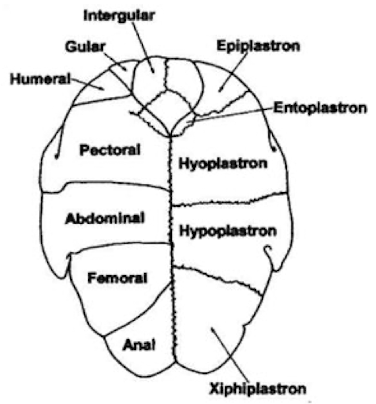
Bottom
Plastron
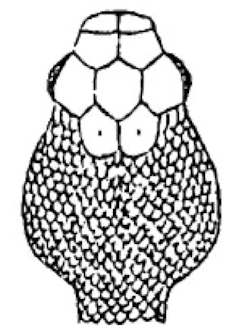
Pouched cheeks
Venomus
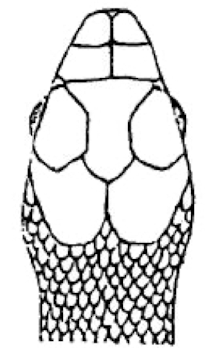
Non-pouched cheeks
Nonvenomous
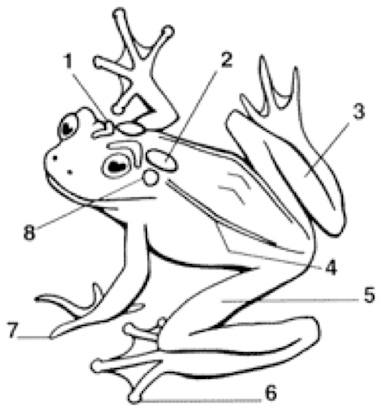
1
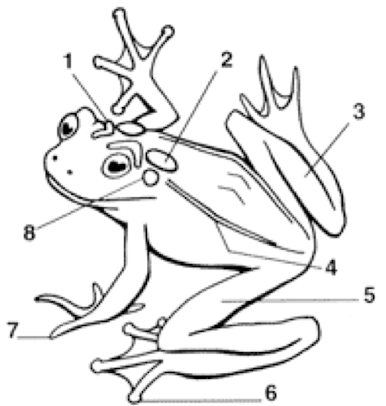
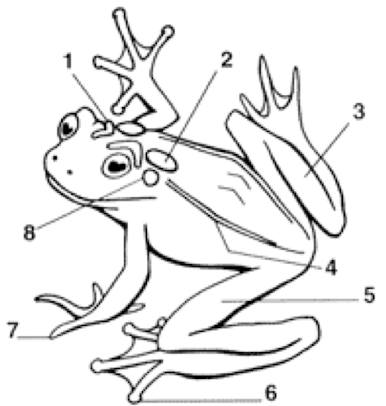
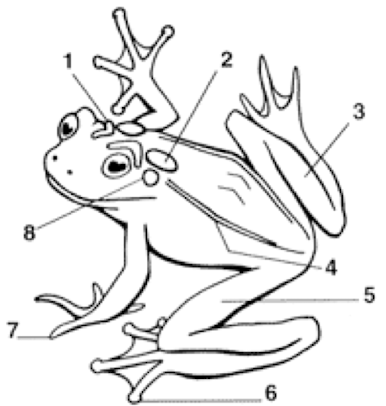
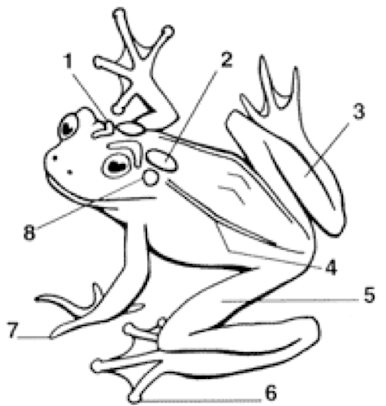
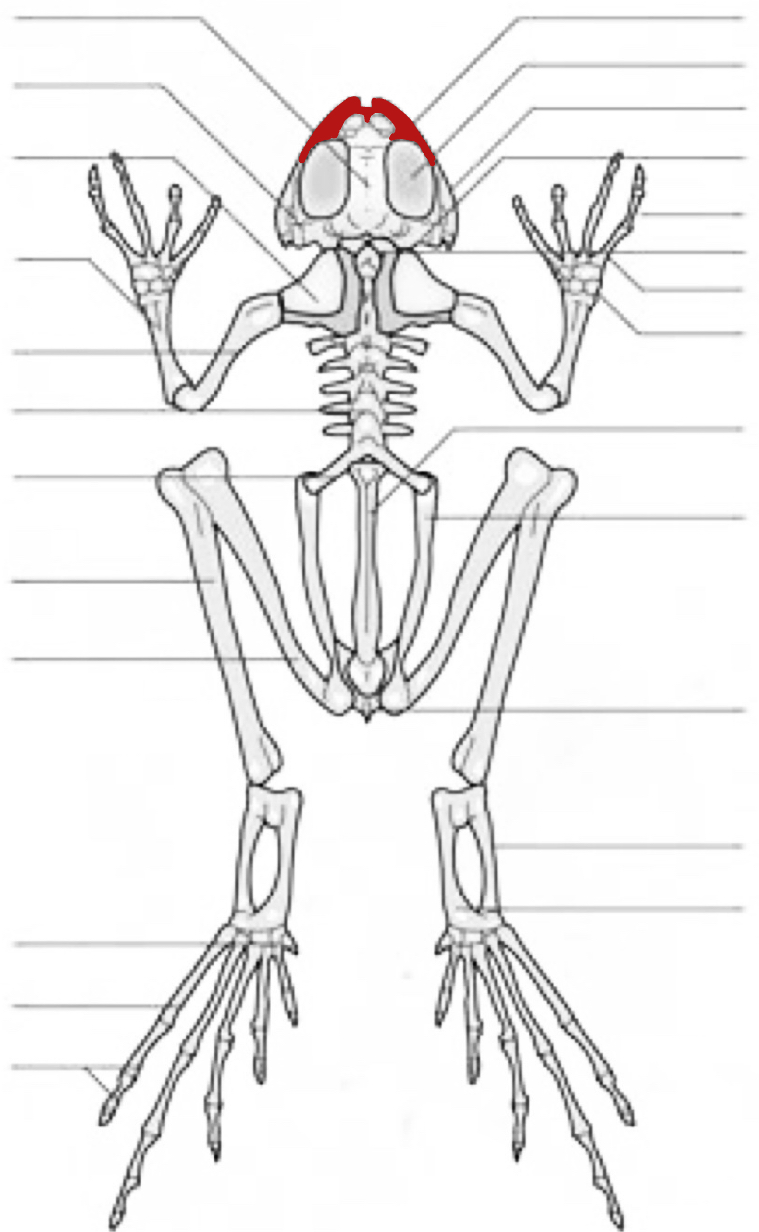
Cranial Crests
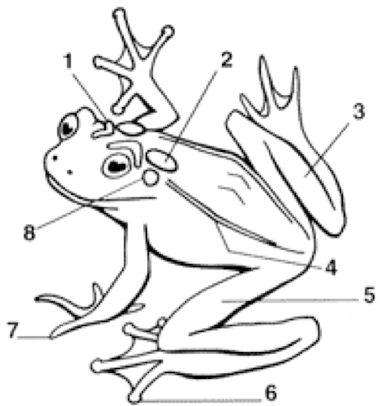
2
Parotoid Gland
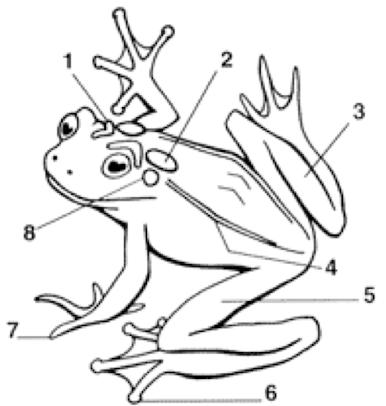
3
Tarsus (shank)
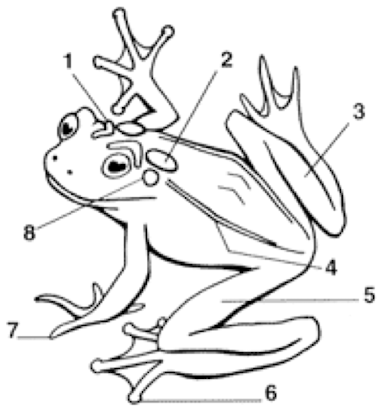
4
Dorsolateral folds
5
Femoral area (thigh)
6
Toes with digital discs
7
Toes without digital discs
8
Tympanum
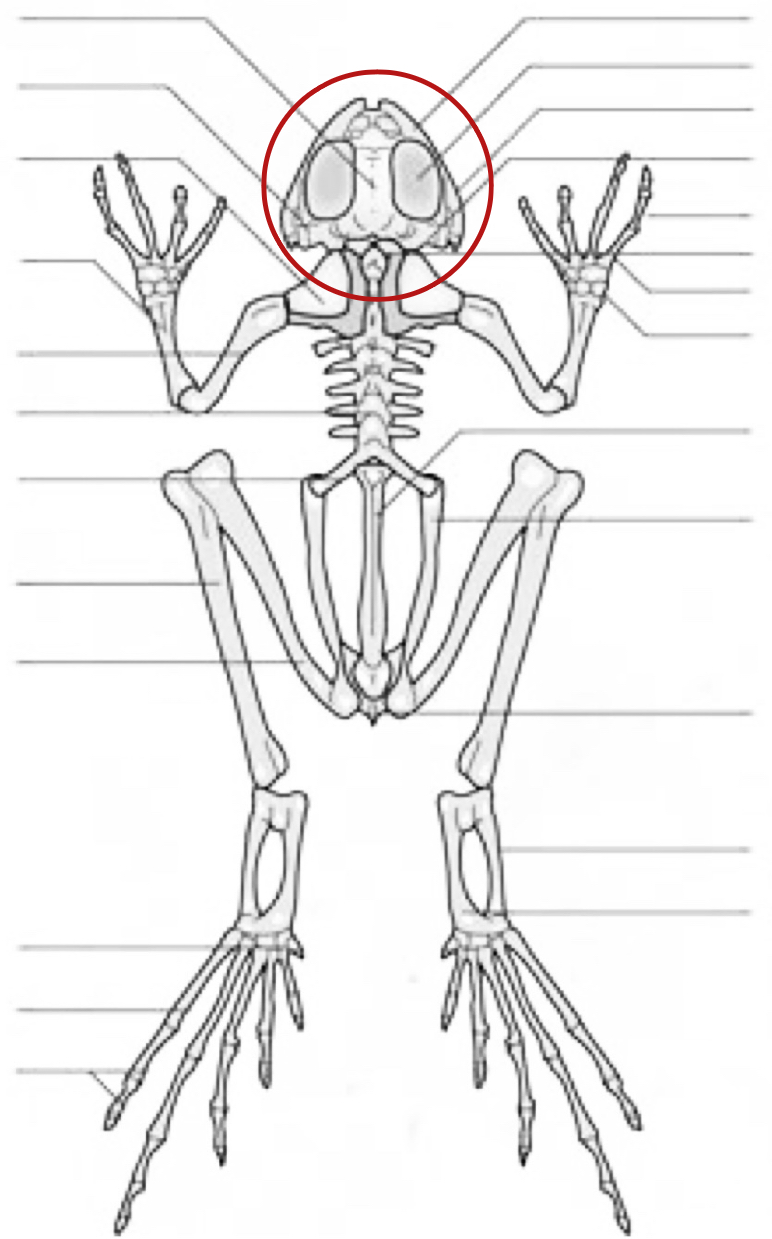
skull
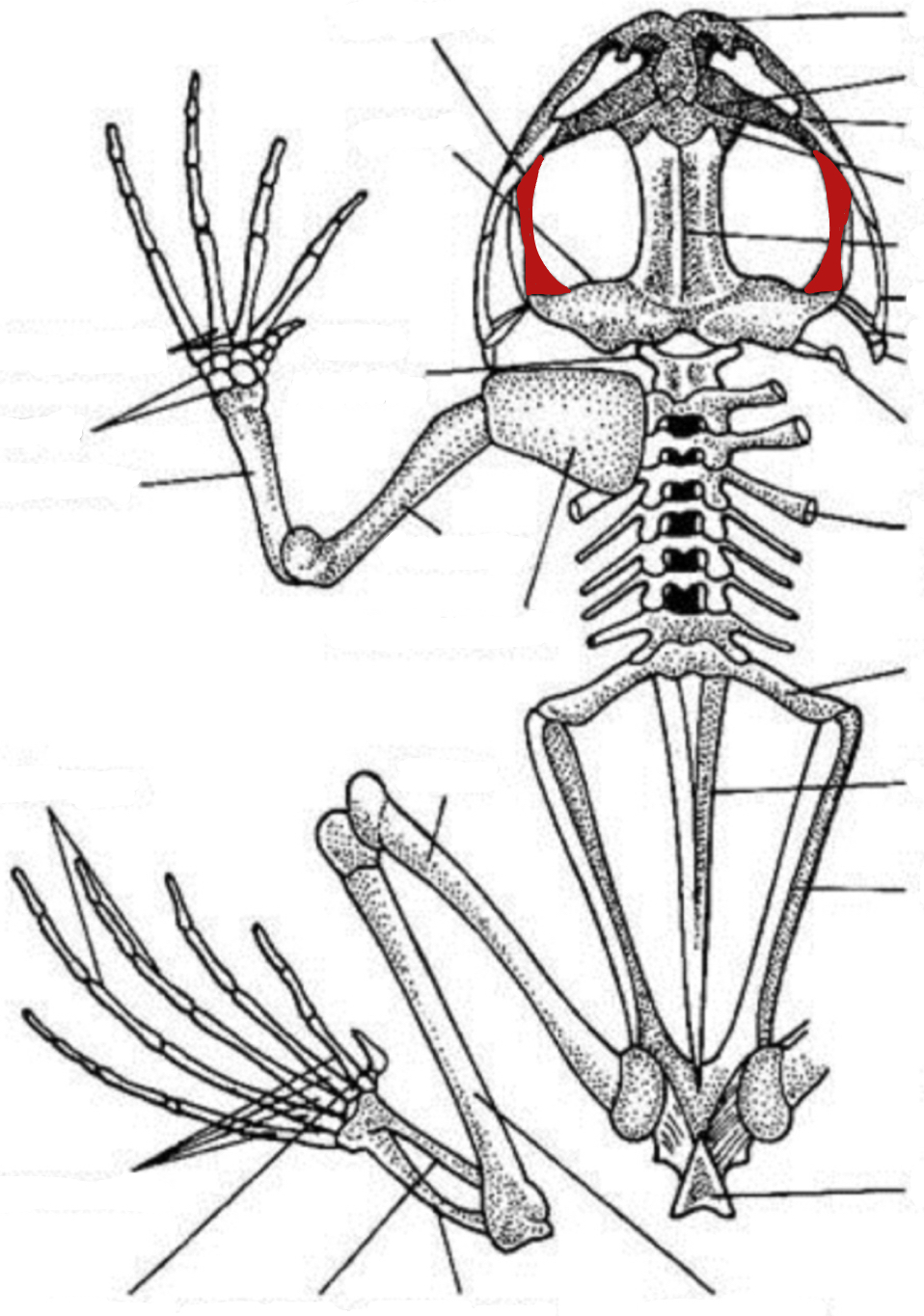
pterygoid
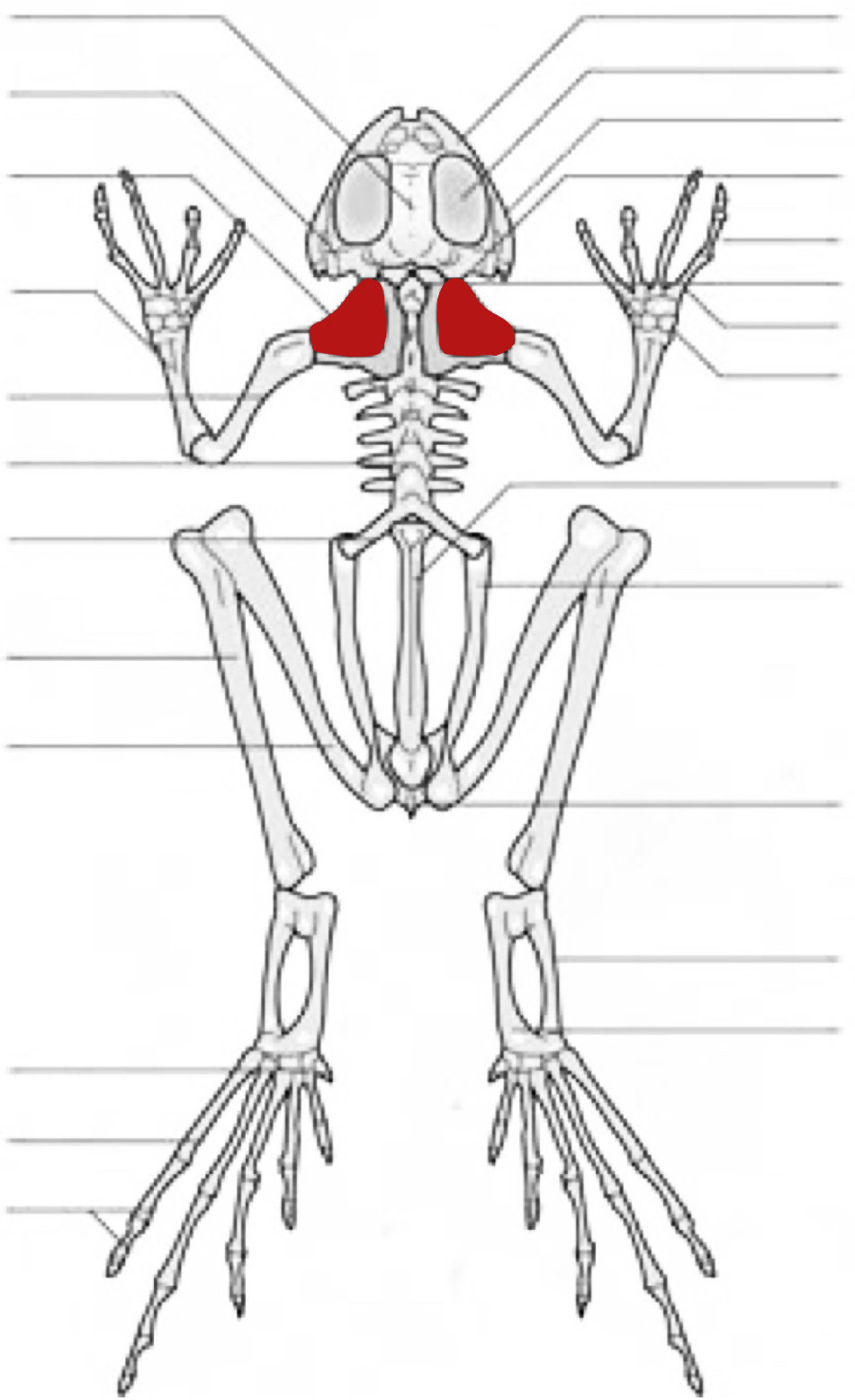
scapular
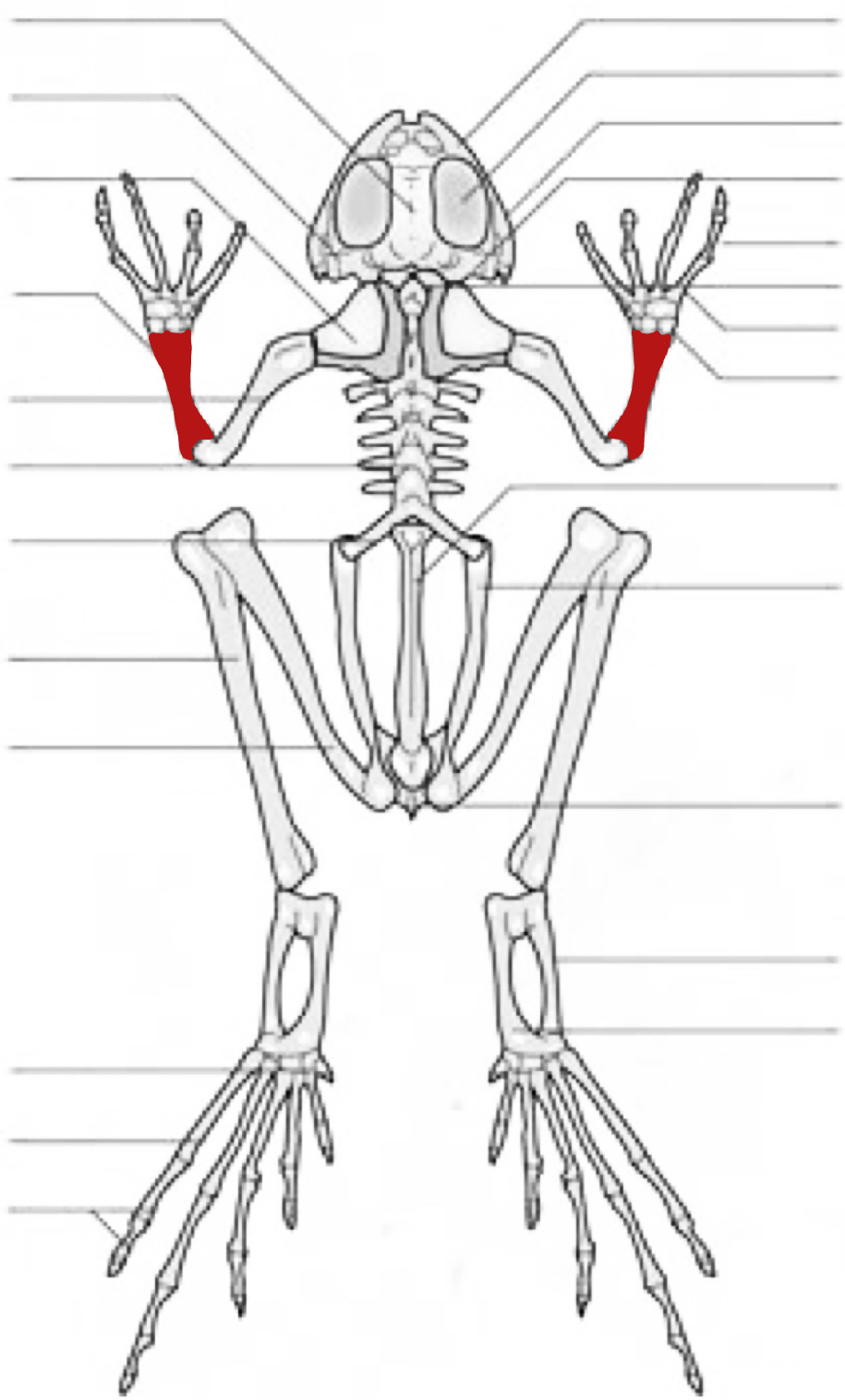
radio-ulna
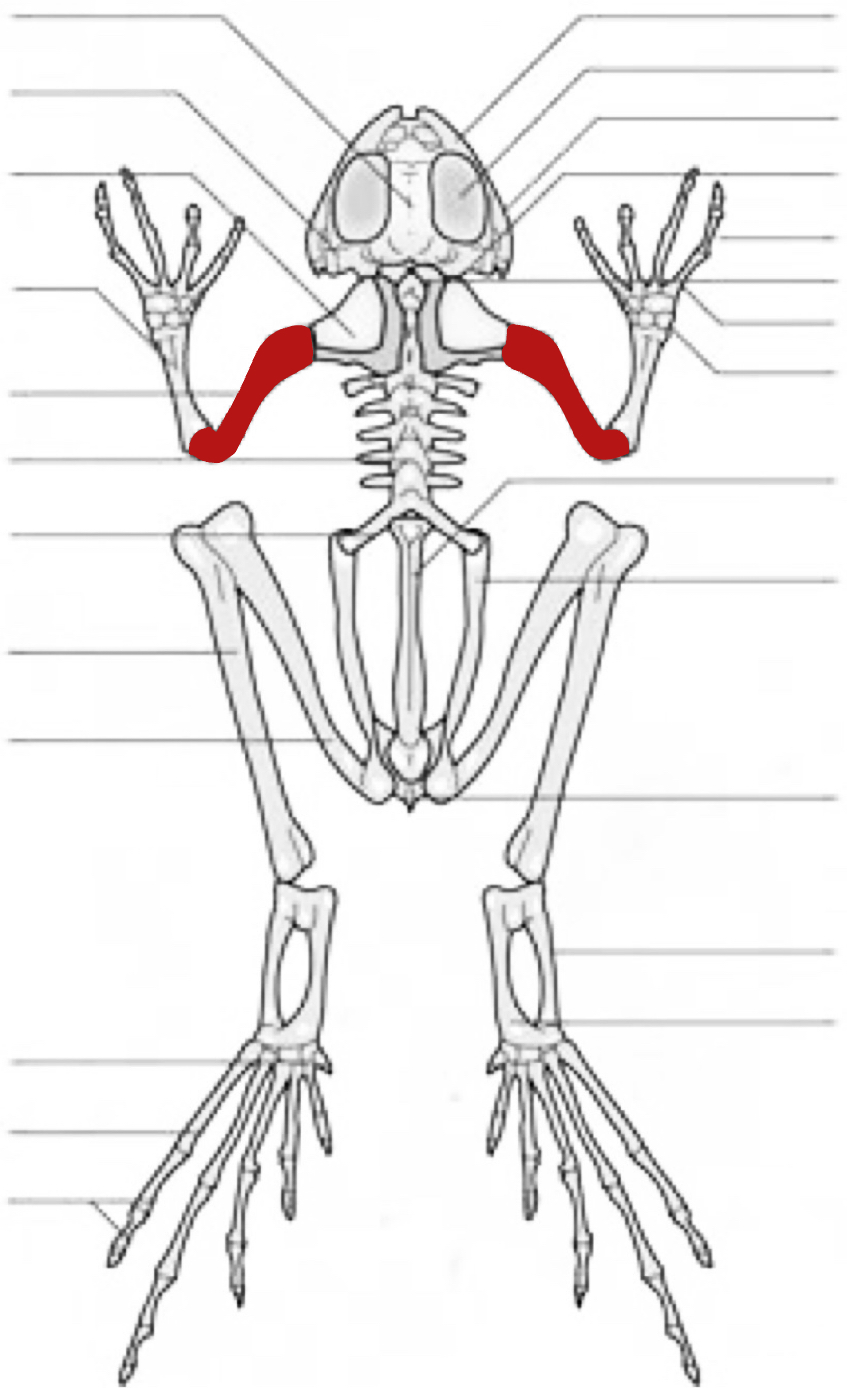
humerus
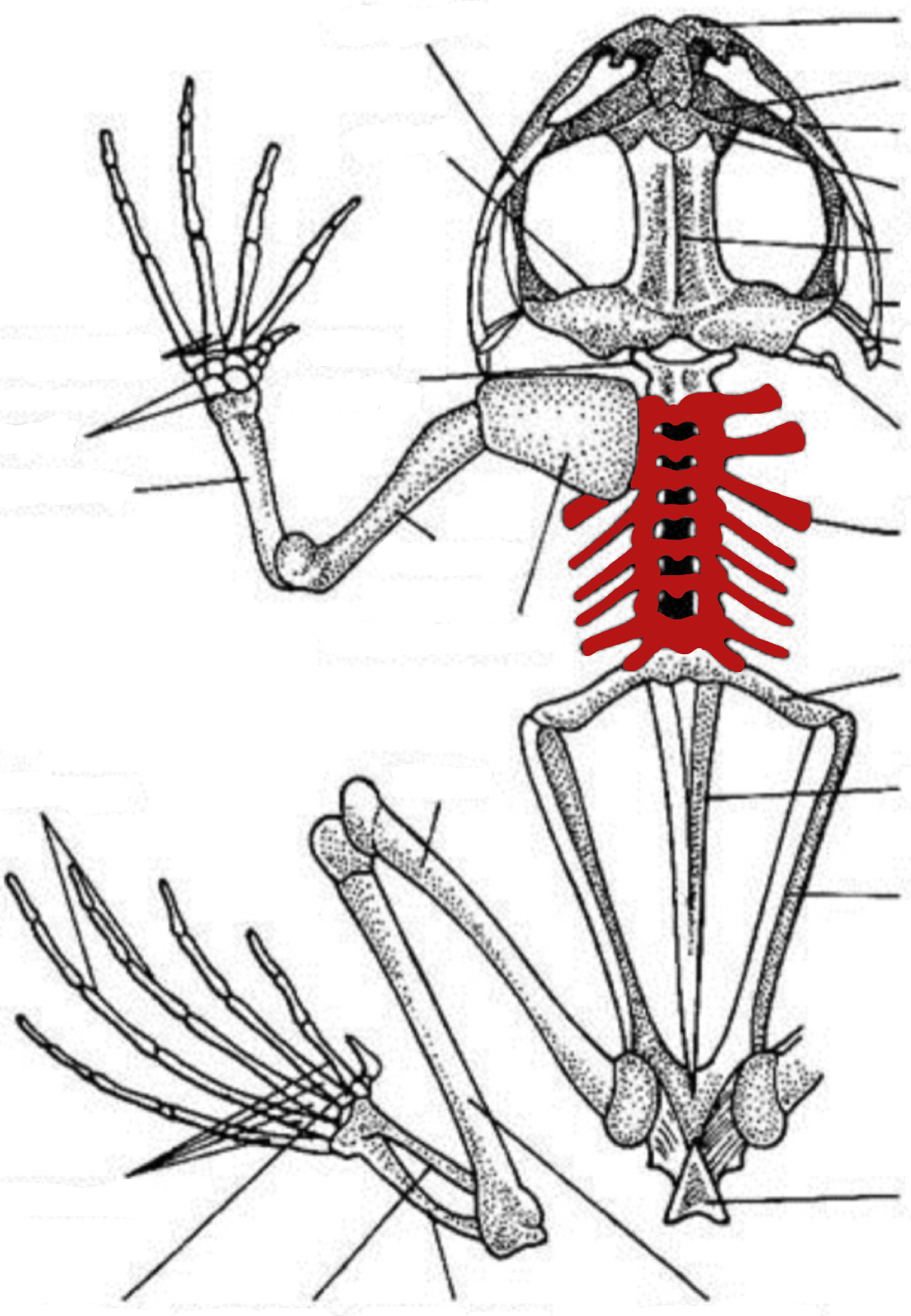
vertebra
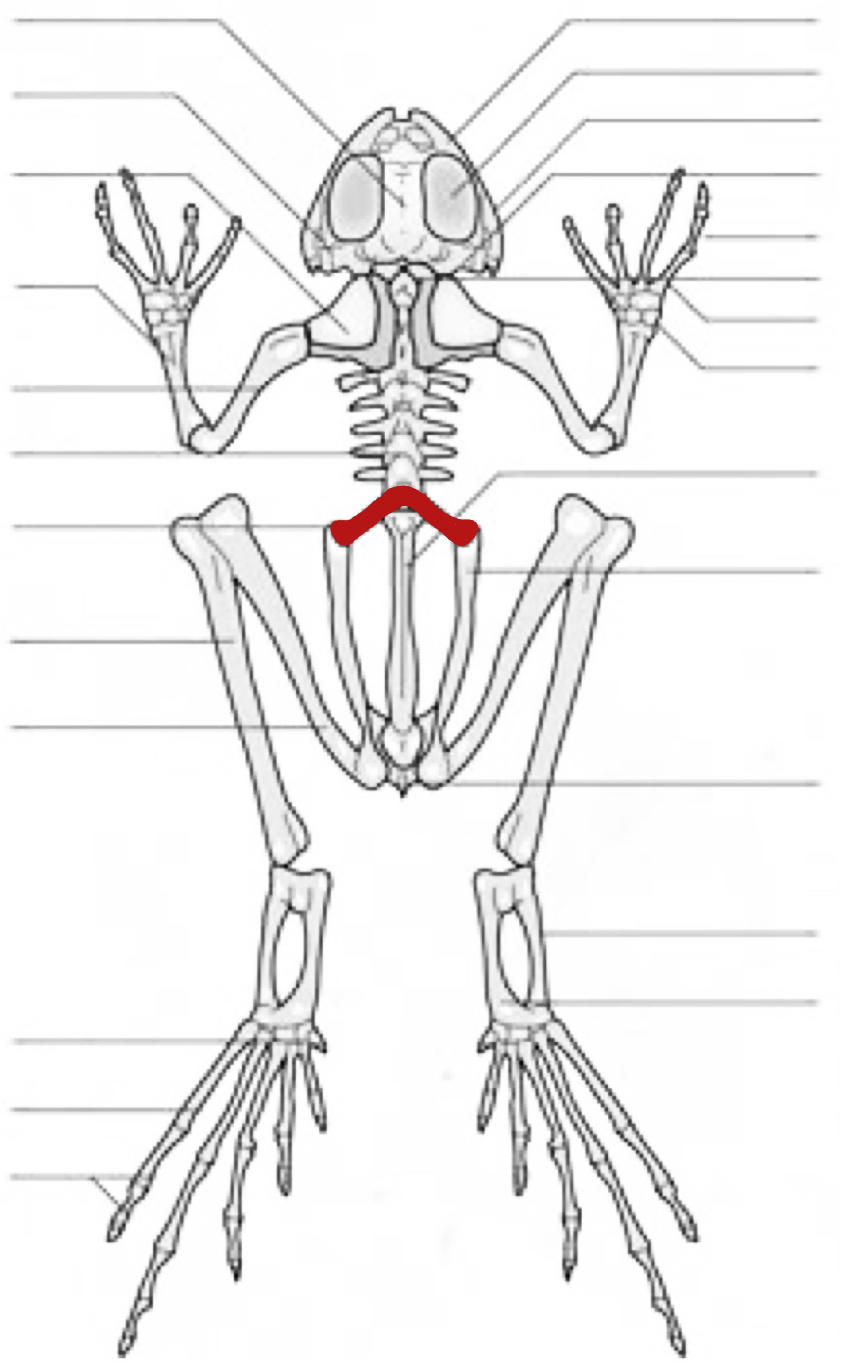
sacral vertebra
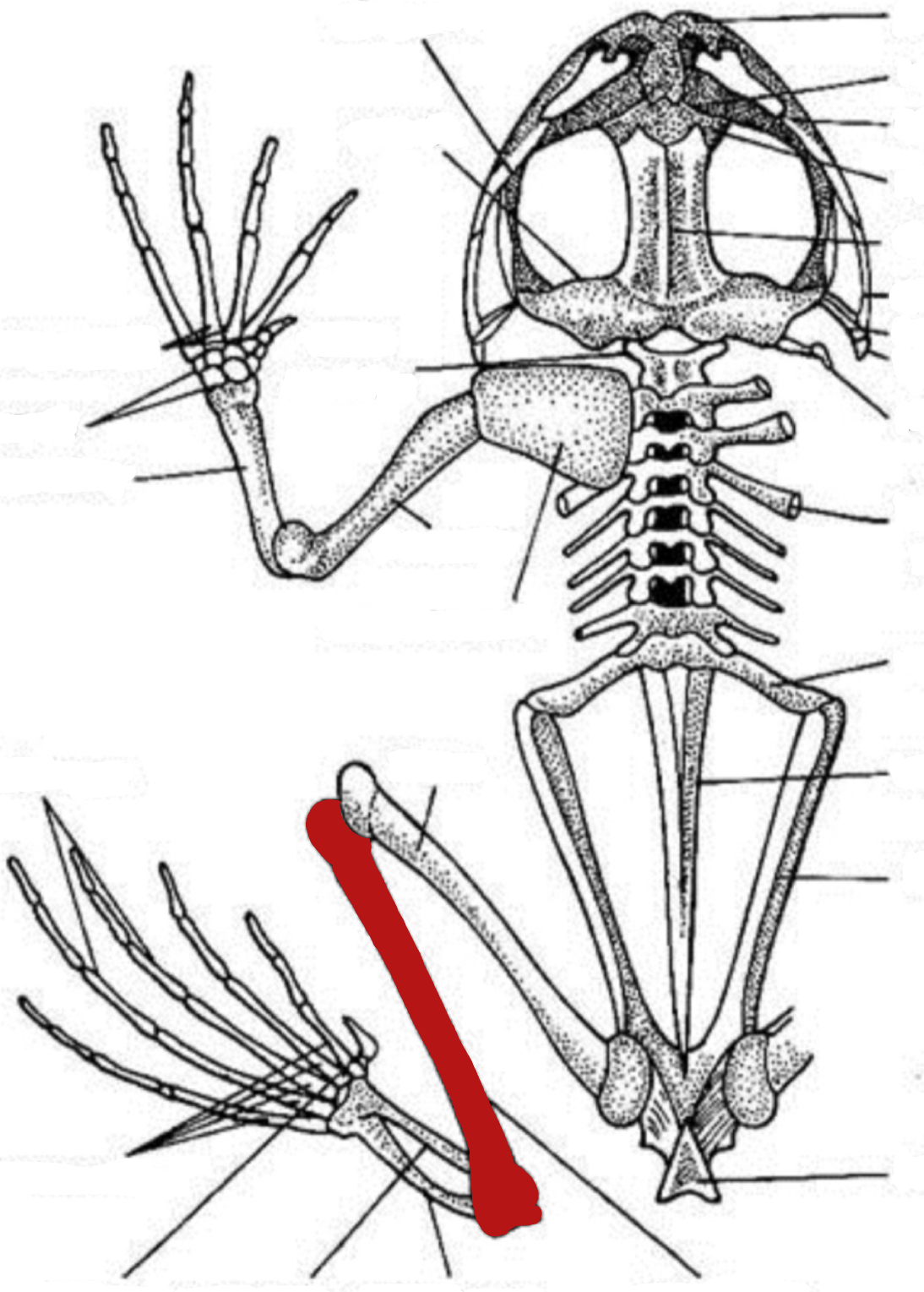
tibiofibula
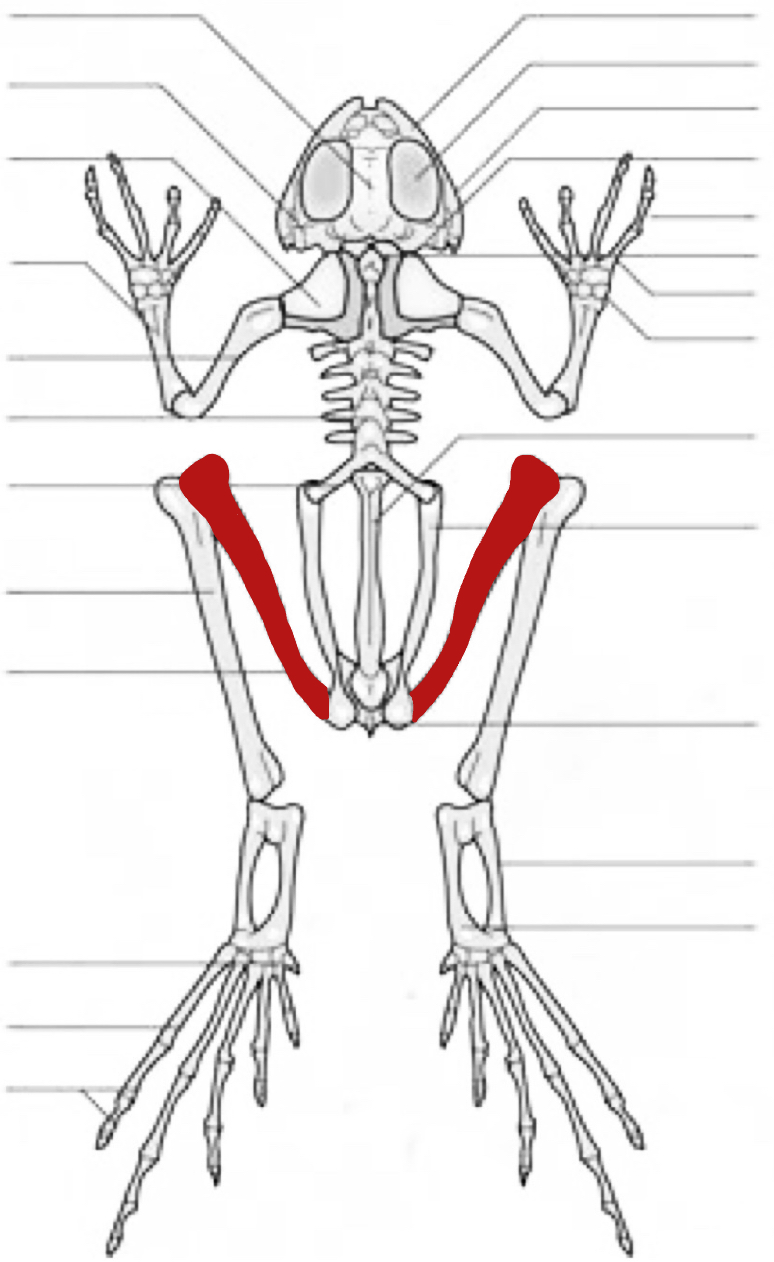
femur
tarsus
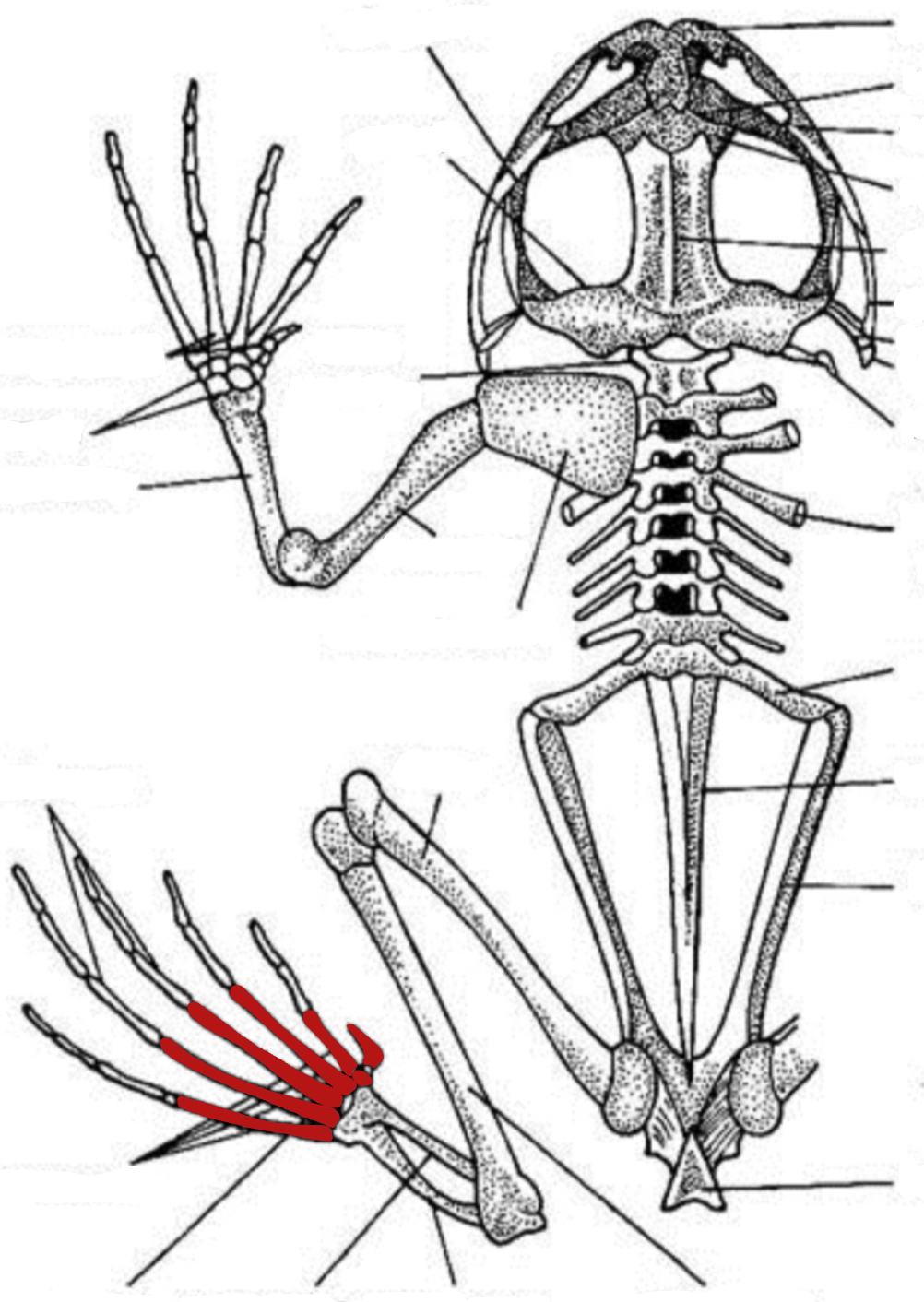
metatarsus
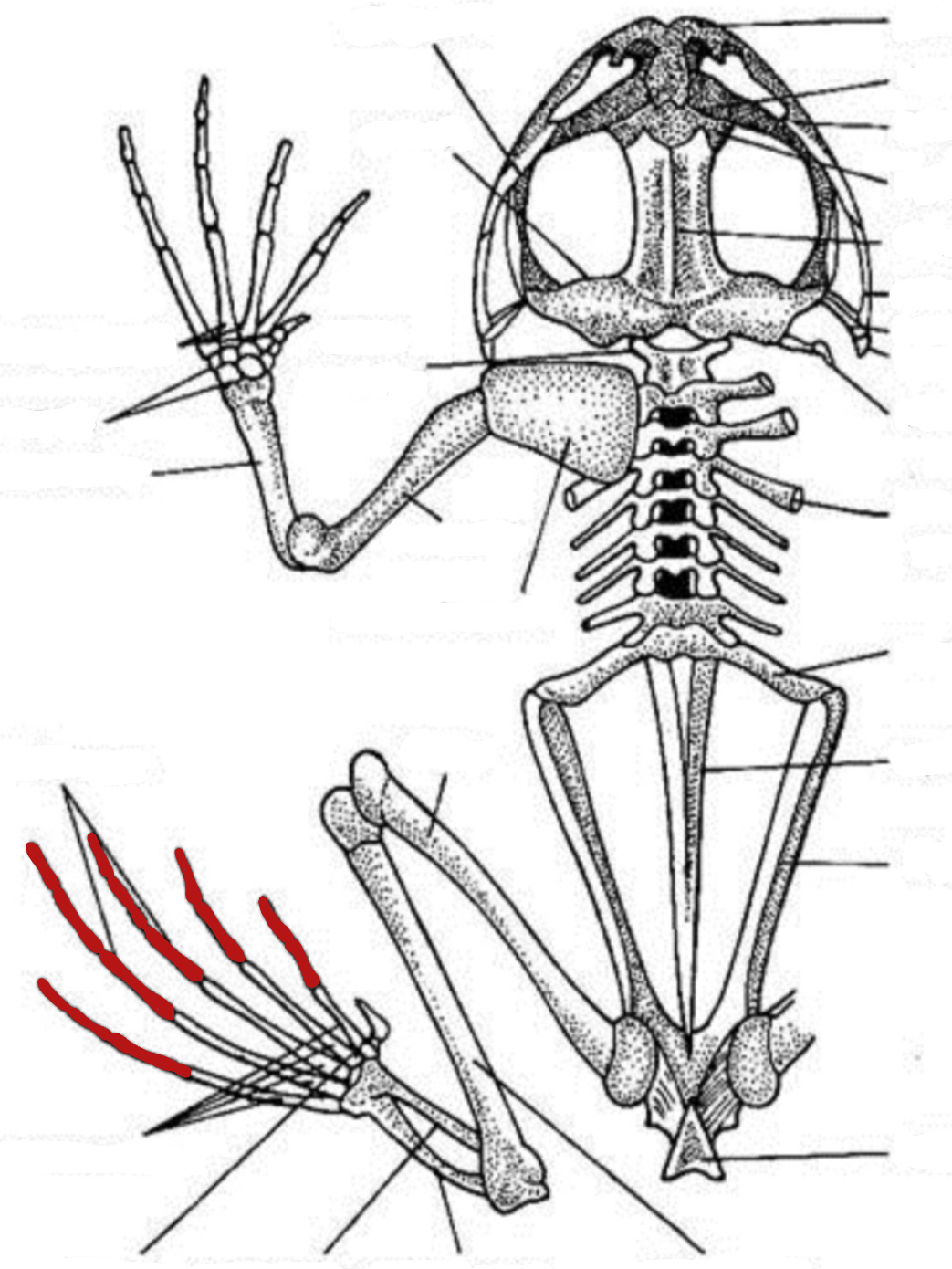
phalanges
maxillary
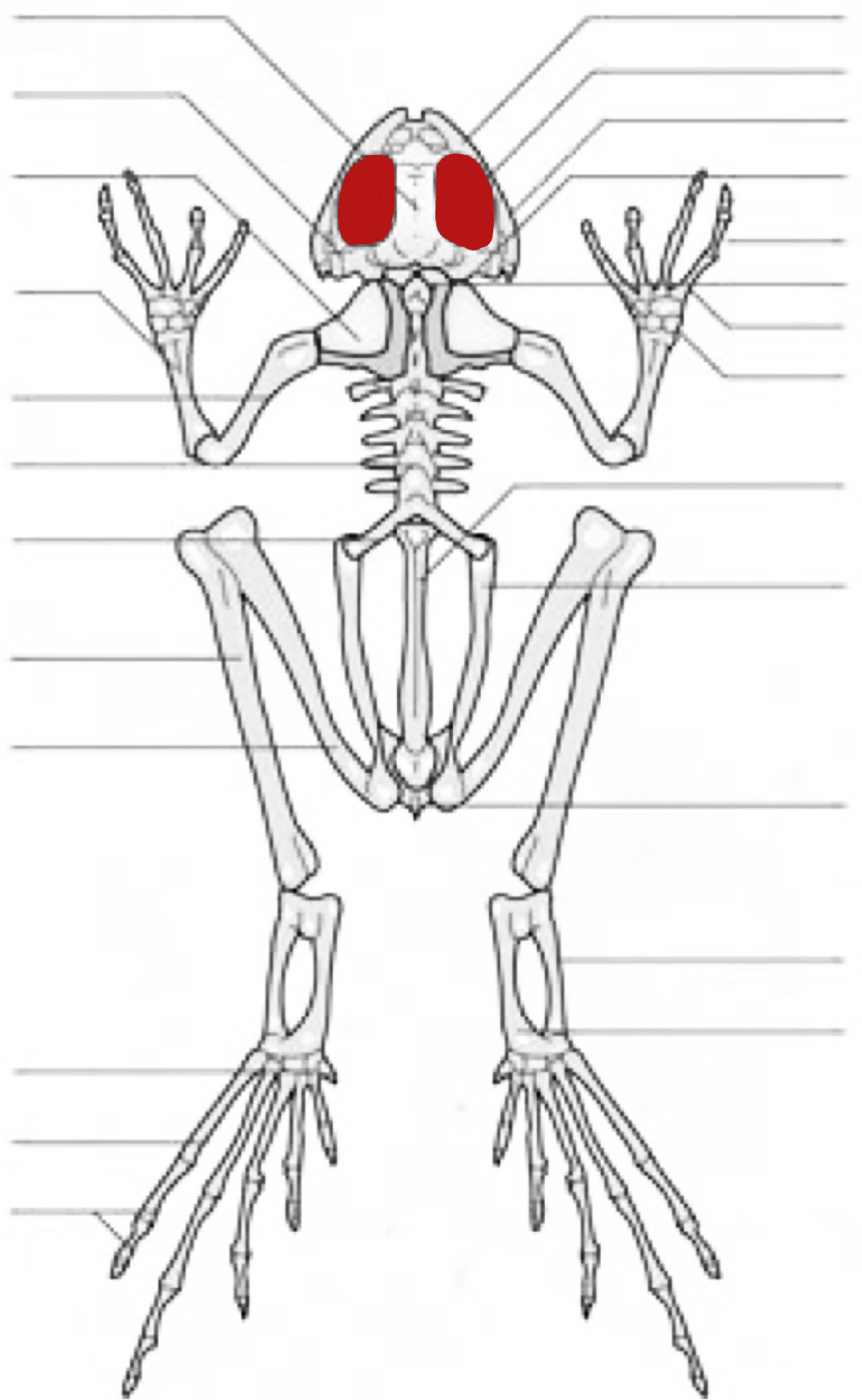
orbital cavity
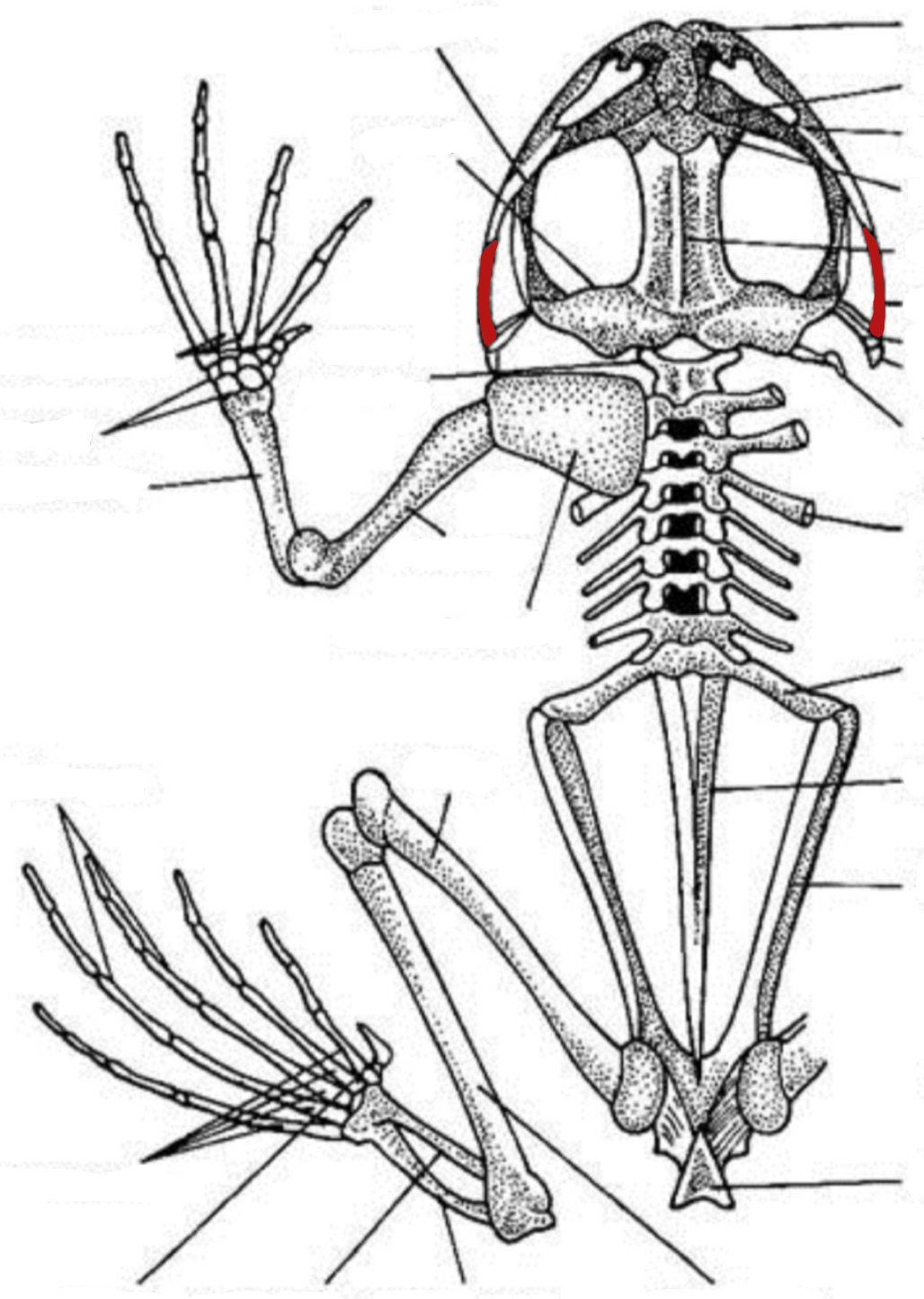
quadratojugal
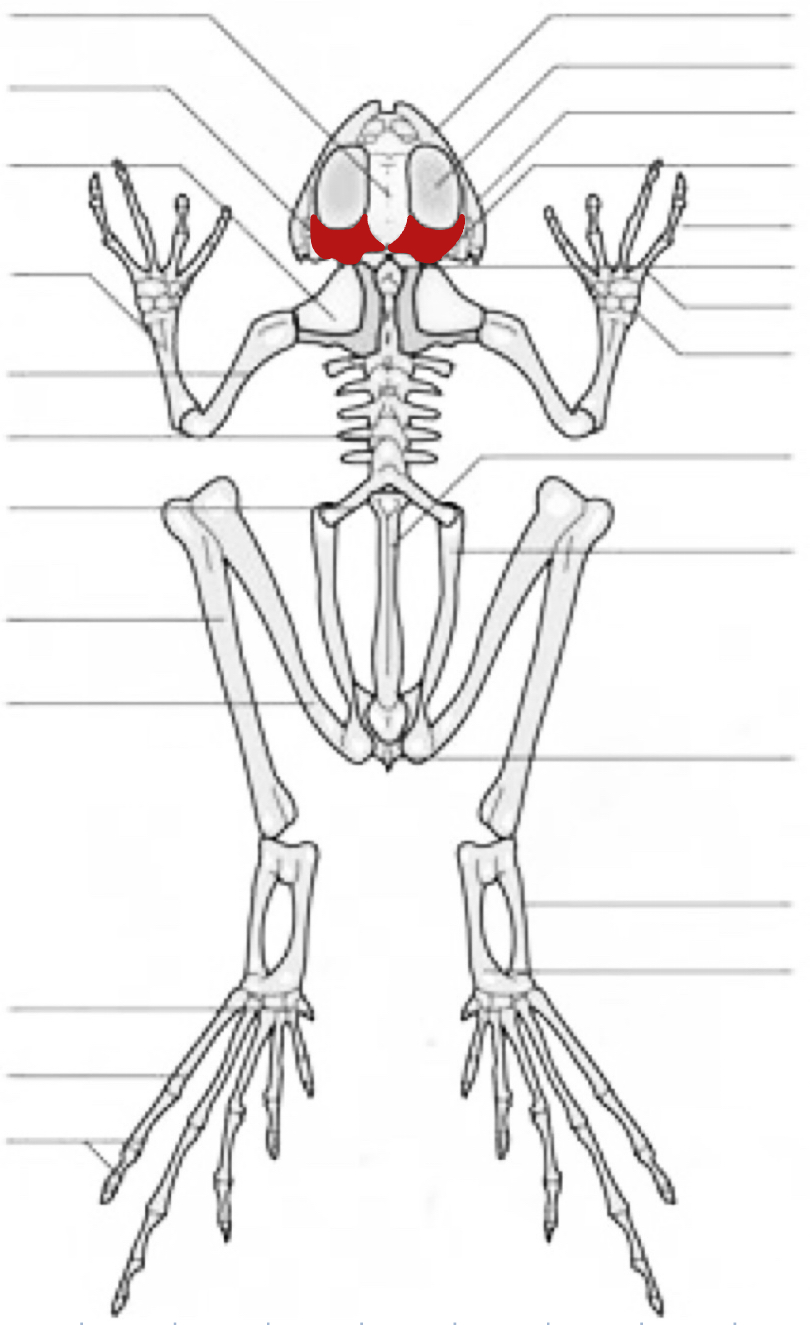
prootic
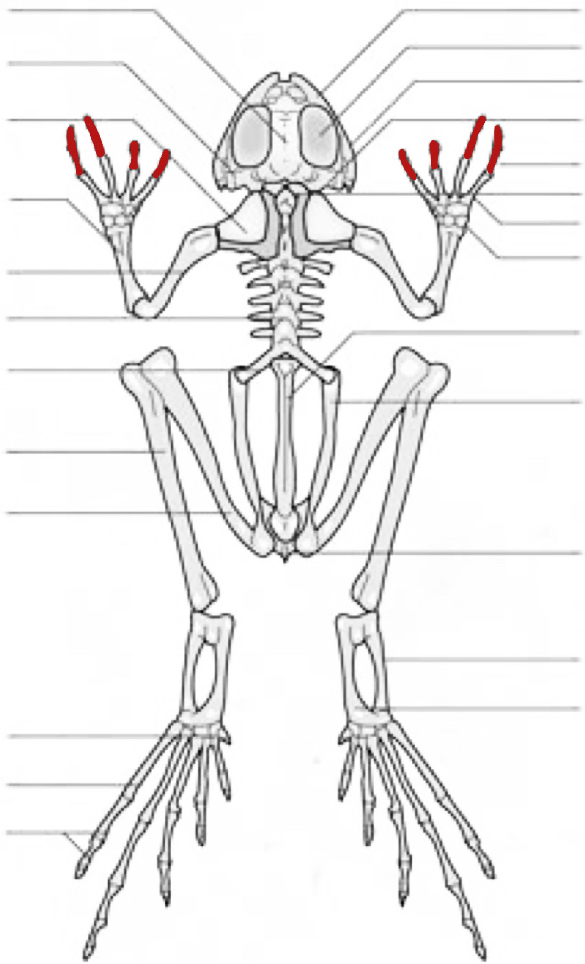
phalange
occipital lateral
carpus
metacarpus
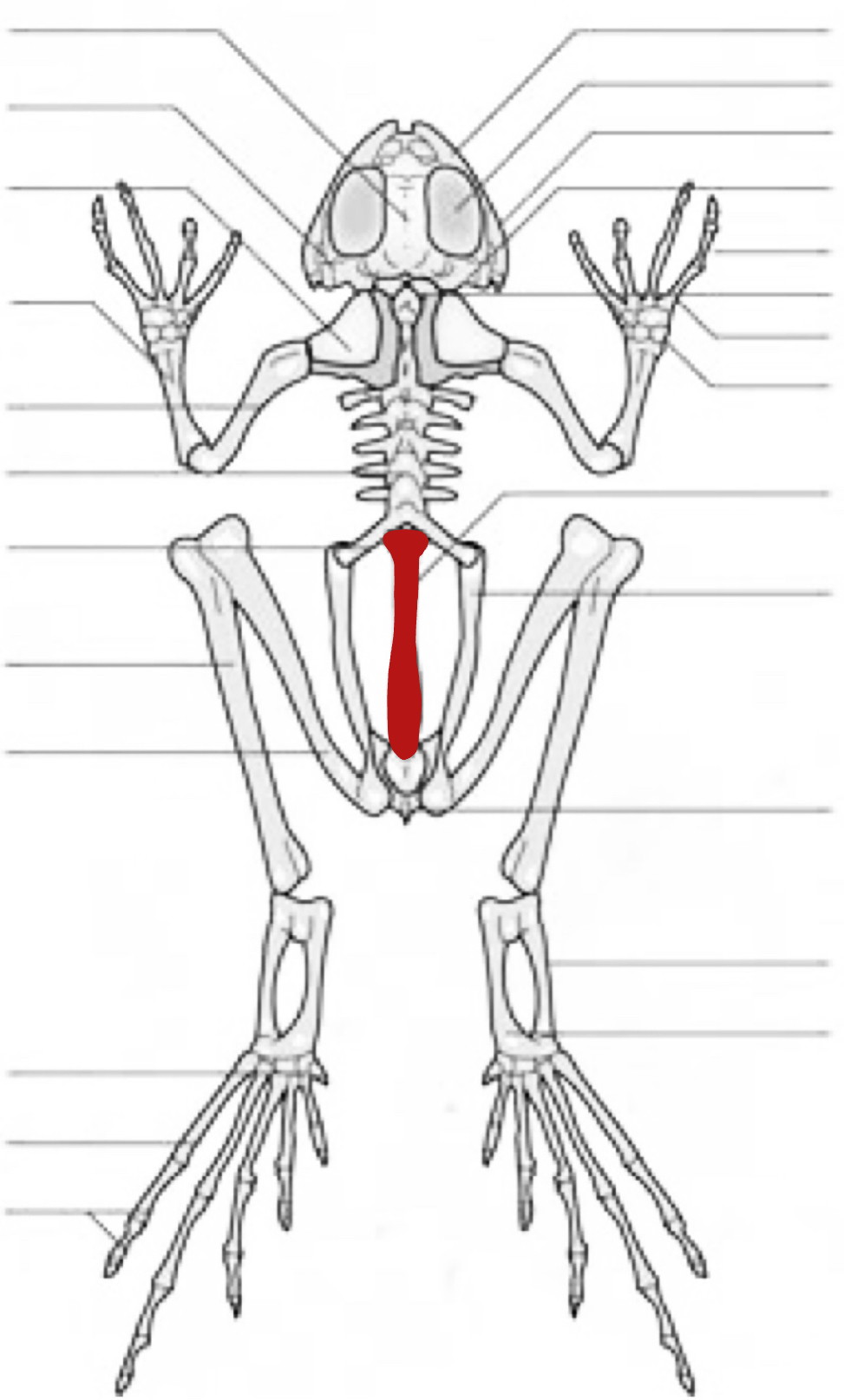
urostyle
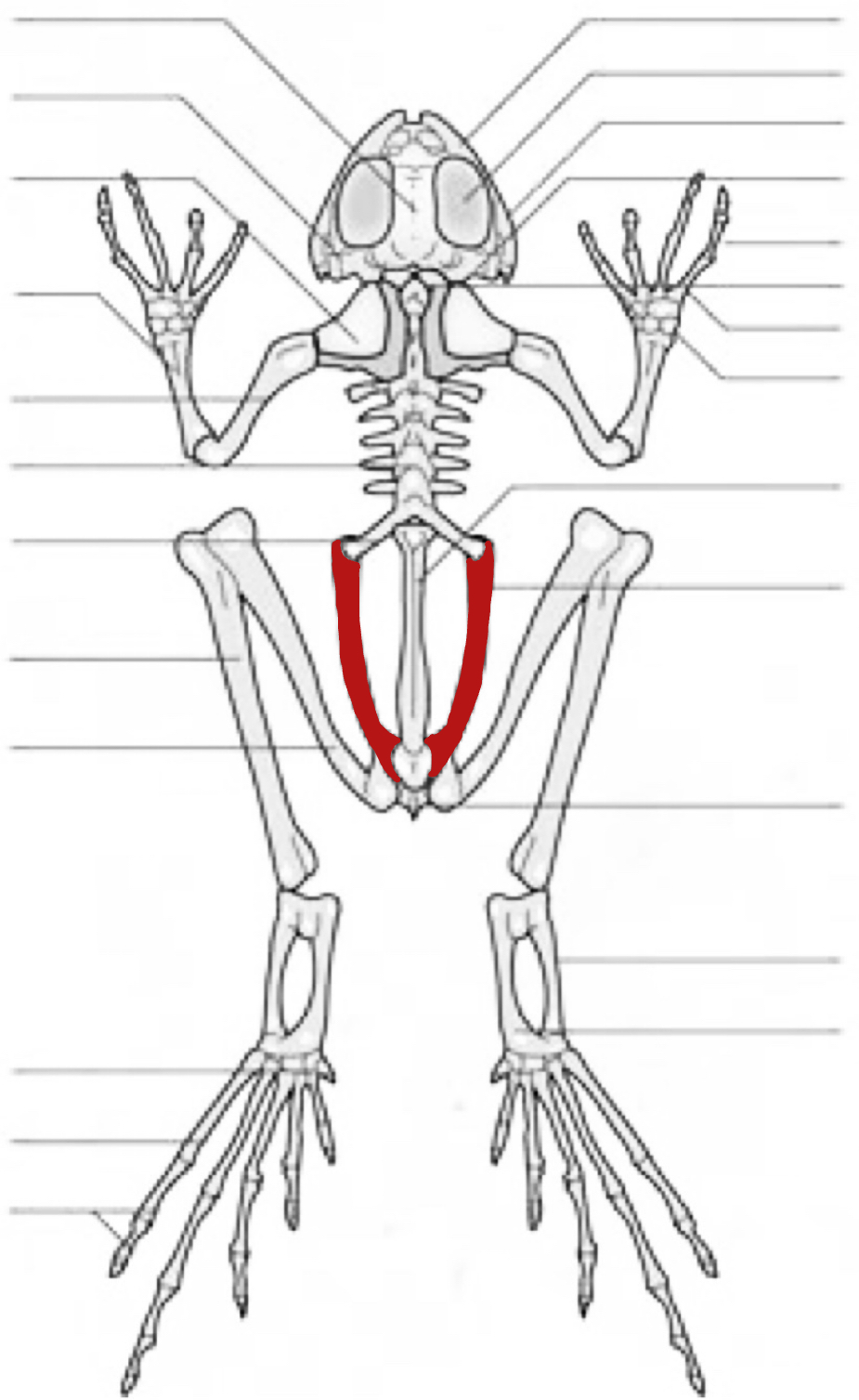
ilium
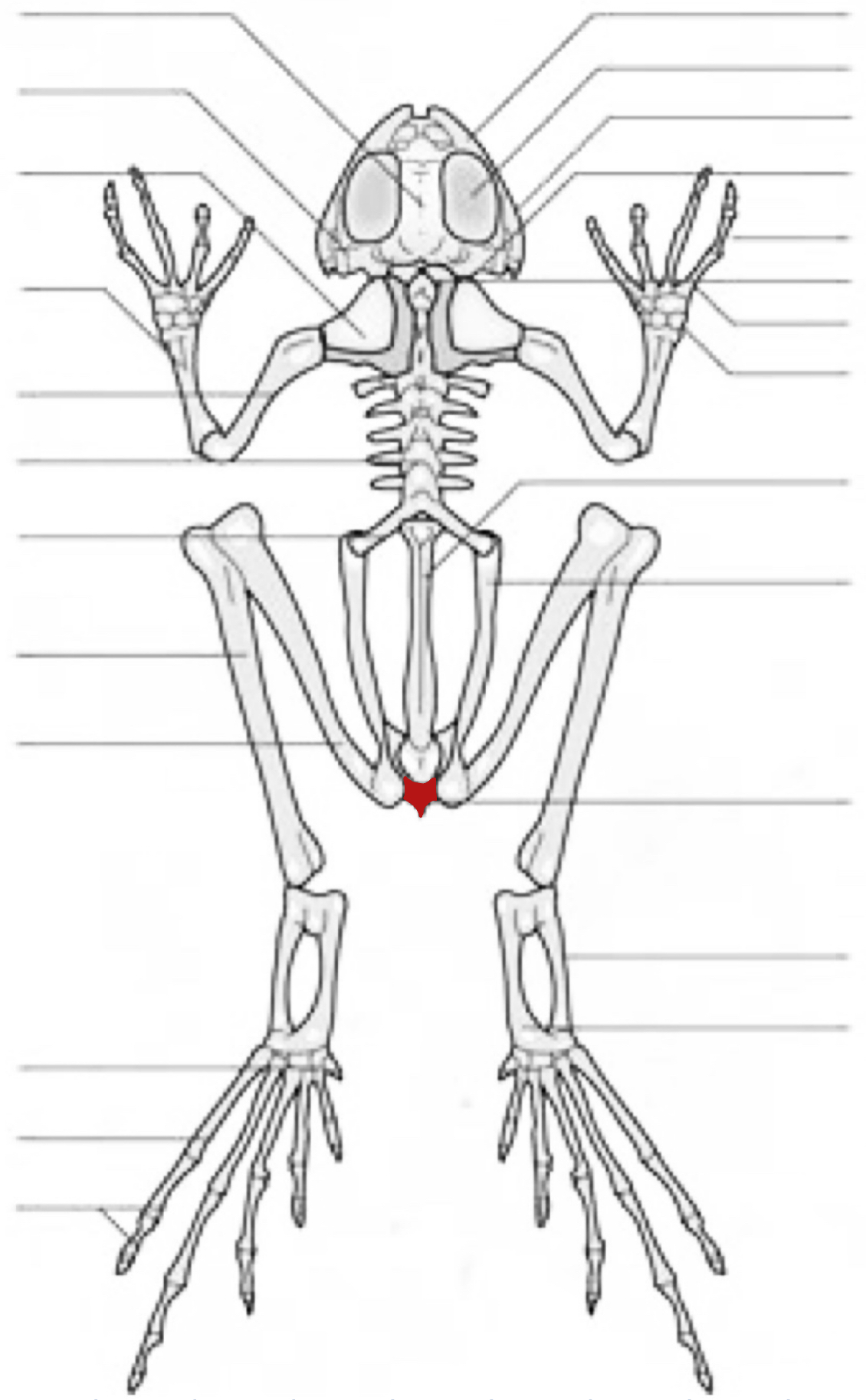
ischium
calcanium
talus

Form?
Paedomorphic

Form?
Non-Padeomorphic
“normal”
Clade Lissamphibia Characteristics
non-amniotes
scaleless
cold-blooded, amphibious animals
larvae mature in water & breathe through gills
undergo metamorphosis
adults breathe air through lungs AND skin (sub-cutaneous respiration)
oviparous, ovoiviparous
Order Urodela
Salamanders
Order Anura
Frogs & Toads
Clade Sauropsida includes
turtles, lizards, snakes, crocodilians, and birds
Order Testudines
Turtles
Clade Lepidosauromorpha
Order Squamata
Lizards & Snakes
Suborder Serpentes
Snakes
Clade Archosauromorpha
Order Crocodylia
Crocodiles & Alligators
Fossorial
ground dwelling
Paedomorphic
having traits of juvenile characteristics
usually in reference to external gills, fan-like tails
Costal Grooves
vertical skin flaps on sides of body
Nasolabial Grooves
narrow grooves between each nostril and upper lip
Dorsal-Lateral Folds
lateral ridges running parallel on body
Cranial Crest
ossified ridge surrounding eyes
Parotoid glands
poison glands on shoulder
Femoral Pores
emit pheromones, found on ventral side of body/on legs of some lizards
Caudal Anatomy
self-amputation of tail, used in escaping predators
Lamellae
thin plate like structures on feet for gripping
Spectacle
transparent scale over eye in some Squamates
Nictitating Membrane
transparent 3rd eyelid that covers the eye but still allows for vision in Testudines & Crocodylians
Hemipenes
paired male organ used in copulation in Squamates; many have hooks or lamallae, can be forked
Facultative Parthenogenesis
‘sometimes parthenogenic’; under appropriate conditions, some species are able to produce viable offspring without males
Oviparous
external egg-laying
Ovoviviparous
internal egg-laying and then give live birth