Thermal Energy, Specific Heat Capacity, and Heat Transfer Calculations in Physics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the guiding equation for heat transfer?
Q = mass × c × ΔT, where Q is heat transferred, c is specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the temperature change.
What does specific heat capacity (c) represent?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °K (or 1 °C).
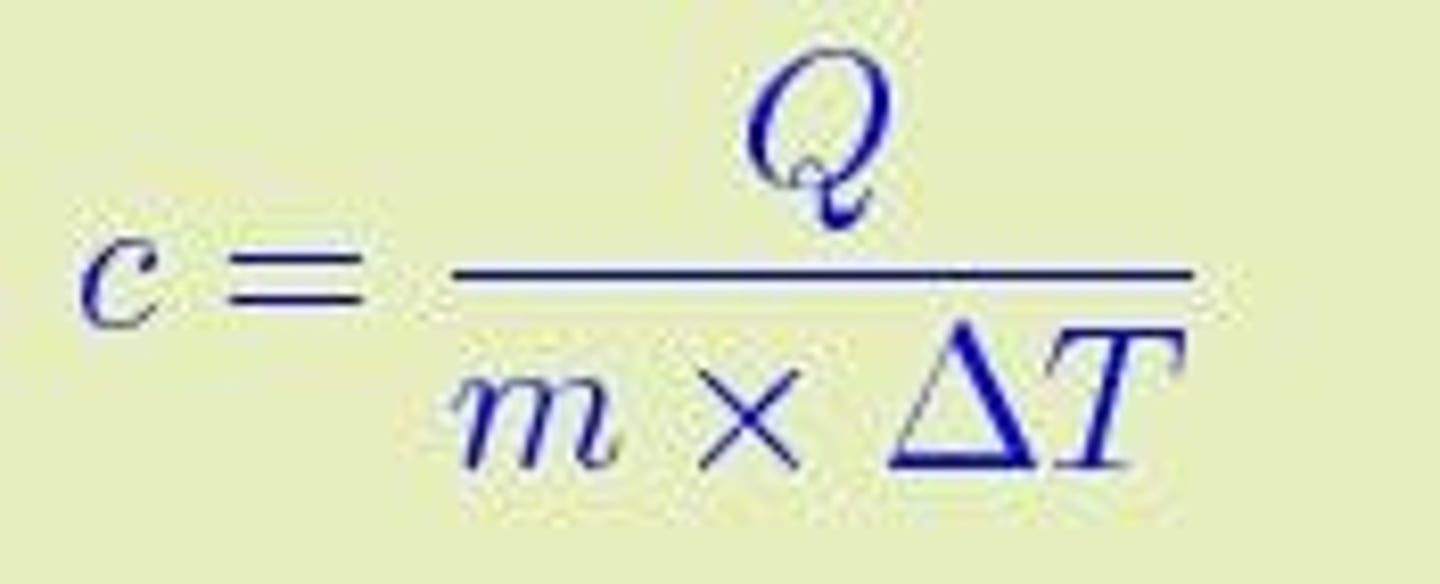
What is the specific heat capacity of water?
4.187 kJ kg-1 °K-1.
What is the specific heat capacity of ice?
2.108 kJ kg-1 °K-1.
What is the specific heat capacity of steam?
1.996 kJ kg-1 °K-1.
Why do different materials undergo different temperature changes when receiving the same amount of energy?
Due to differences in molecular interaction and mass, which affect their specific heat capacities.
What is thermal capacity?
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of an object by 1 °K.
How do you calculate the thermal energy needed to increase the temperature of an object?
Use the formula: Thermal Energy = Thermal Capacity × Temperature Change.
What is the thermal capacity of an object if it requires 4800 J to raise its temperature by 1 °K?
4800 J °K-1.
How much heat is absorbed by 0.375 kg of water to raise its temperature by 25° K?
Heat absorbed = mass × c × ΔT = 0.375 kg × 4.187 kJ kg-1 °K-1 × 25° K.
What mass of water can be heated from 25.0° C to 50.0° C by the addition of 2825 J?
Use the formula: mass = Heat / (c × ΔT).
What is the effective average power of a burner that raises the temperature of 500 g of water from 24 °C to 80 °C in 2 minutes?
Calculate power using: Power = Heat / time.
How much energy is required to raise the temperature of 3.87 kg of metal by 54 °C with a specific heat capacity of 456 Jkg-1°K-1?
Energy required = mass × c × ΔT = 3.87 kg × 456 Jkg-1°K-1 × 54 °C.
How do you determine the specific heat capacity of a liquid that requires 3840 J to raise the temperature of 156 g by 18.0 °K?
Use the formula: c = Heat / (mass × ΔT).
If the thermal capacity of a room is 3.5x10^5 JK-1, how long would it take a 2.5 kW heater to raise the temperature from 9°C to 22 °C?
Calculate time using: Time = Thermal Energy / Power.
What is the rise in temperature of brakes with a specific heat of 16 kJ/°K when a car descends a hill?
Calculate using the potential energy change converted to heat.
What is the relationship between specific heat capacity and temperature change?
Specific heat capacity determines how much temperature change occurs for a given amount of heat energy.
What does the temperature gradient refer to in heat transfer?
The difference in temperature between two objects or states.
What is the significance of thermal equilibrium in heat transfer?
It's the state where two substances reach the same temperature after energy transfer.