Chp 7 - Arrays and Vectors
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Array
A variable that can store multiple values of the same type
values are stored in adjacent memory locations
declared using [ ] operator
int tests[5];
the size of an array is the total number of bytes allocated for it: (number of elements) * (size of each element)
Accessing Array Elements
each element in an array is assigned a unique subscript (starting at 0 to n - 1)
array elements can be used as regular variables
arrays must be accessed via individual elements
can access element with a constant or literal subscript
can use integer expression as subscript

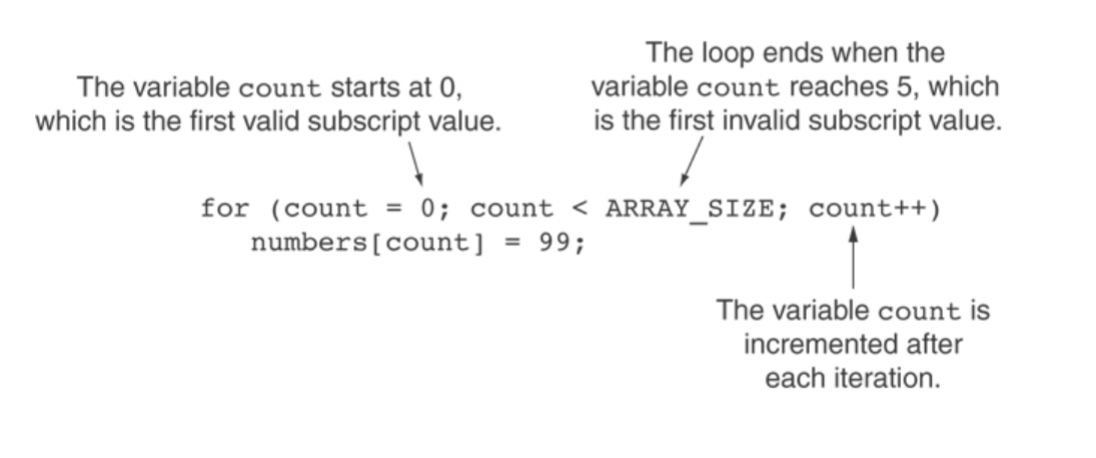
Using a Loop to Step Through an Array
Array Initialization
global array ➡ all elements initialized to 0 by default
local array ➡ all elements uninitialized by default
arrays can be initialized with an initialization list
int tests[5] = {79, 82, 91, 77, 84};
you can also determine the array size by the size of the initialization list
No Bounds Checking in C++
when you use a value as an array subscript, C++ does not check it to make sure it is a valid subscript
you can use subscripts beyond the bounds of the array, doing so can corrupt other memory locations, crash program, lock up computer, cause elusive bugs…BE CAREFUL!
The Range-Based for Loop
C++ 11
a loop that iterates once for each element in an array
each time the loop iterates, it copies an element from the array to a built-in variable, known as the range variable
the range-based for loop automatically knows the number of elements in an array, you do not have to:
use a counter variable
worry about stepping outside the bounds of the array
can be used in any situation where you do not need to use the element subscripts

Copying one array to another
assign element-by-element

Printing an array
print element-by-element

Structured Binding Declarations
defines a set of variables and initializes them with the values that are stored in an array
auto [variable1, variable2, etc…] = array;
![<p>defines a set of variables and initializes them with the values that are stored in an array</p><ul><li><p><strong>auto [variable1, variable2, etc…] = array;</strong></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d8c82664-6f46-403e-9b32-abc78ed1c38c.png)
Parallel Arrays
two or more arrays that contain related data
a subscript is used to relate arrays (elements at the same subscript are related)
arrays may be of different types
Arrays as Function Arguments
to pass an array to a function, use the array name
showScores(tests);
to define a function that takes an array parameter, use empty [] for array argument
void showScores(int []);
it is common to pass array size so that the function knows how many elements to process
showScores(tests, ARRAY_SIZE);
array size must be reflected in prototype header
Two-Dimensional Arrays
First declarator is number of rows, second is number of columns.
const int ROWS = 4, COLS = 3;
int exams[ROWS][COLS]
initialized row-by-row
some values in a row will be set to 0 or NULL
in a parameter
void getExams(int exams[][COLS], int rows)
![<ul><li><p>First declarator is number of rows, second is number of columns.</p><ul><li><p><strong>const int ROWS = 4, COLS = 3;</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>int exams[ROWS][COLS]</strong></p></li></ul></li><li><p>initialized row-by-row</p></li><li><p>some values in a row will be set to 0 or NULL</p></li><li><p>in a parameter</p><ul><li><p><strong>void getExams(int exams[][COLS], int rows)</strong></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/68a7d2ce-ebff-4e91-8235-571378f3f148.png)
Arrays with 3+ Dimensions
you can define arrays with any number of dimensions
when used as a parameter, specify all but 1st dimension in prototype heading
void getRectSolid(short [][3][5])
STL vector
A data type defined in the Standard Template Library
can hold values of any type
automatically adds space as more is needed - no need to determine size at definition
can use [ ] to access elemets
Declaring Vectors
#include<vector>
declare a vector to hold int element:
vector<int> scores;
declare a vector with initial size 30 (only starting size)
vector<int> scores(30);
declare a vector and initialize all elements to 0
vector<int> scores(30, 0);
declare a vector initialized to size and contents of another vector
vector<int> finals(scores);
adding elements to a vector
you can initialize a vector with a list of values (C++ 11)
vector<int> numbers {10, 20, 30, 40};
use push_back member function to add element to a full array or to an array that had no defined size:
scores.push_back(75);
use size member function to determine size of a vector
howbig = score.size();
removing vector elements
use pop_back member function to remove last element from vector
scores.pop_back();
to remove all contents of vector. use clear member function
scores.clear();
to determine if vector is empty, use empty member function
while (!scores.empty())
Range-Based for Loop with a vector

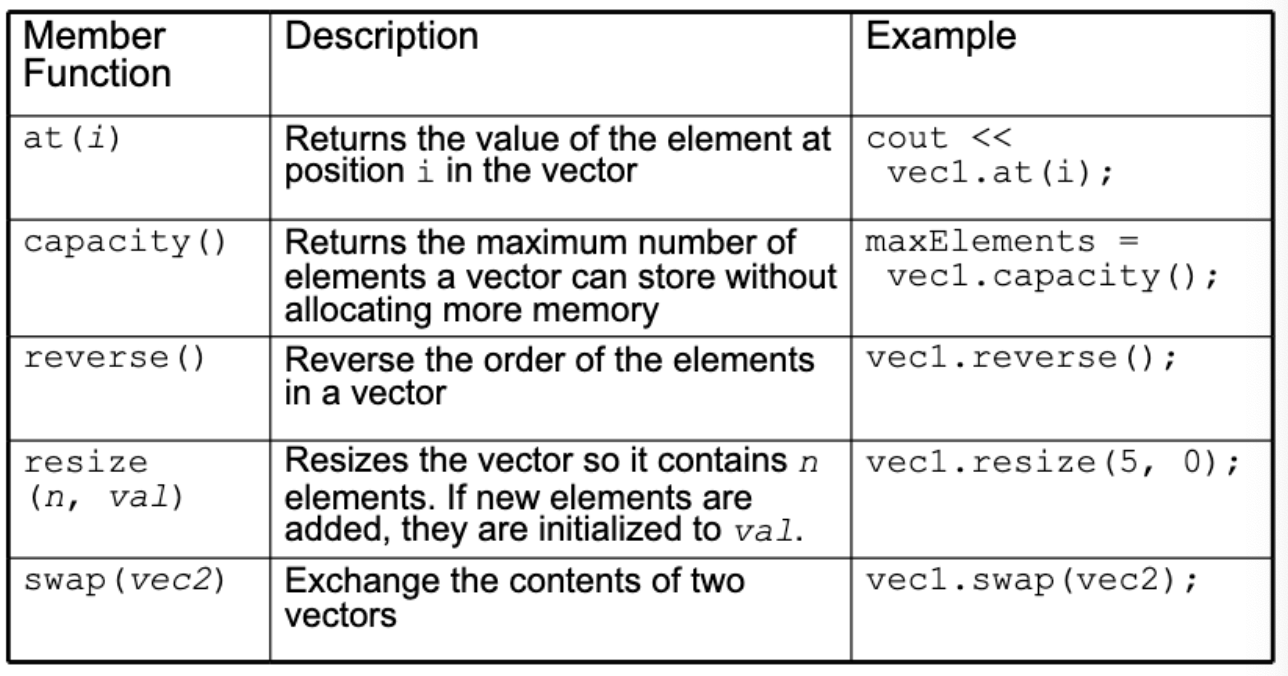
Other Useful Member Functions