Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) Unit 3
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
annual interest rate (nominal yield) assigned to a bond at issuance; though, most bonds pay semiannually
coupon rate
price of par
$1000
premium to par
above $1000
discount to par
below $1000
interest assigned to a bond at issue
nominal yield
measure of a bond’s annual interest relative to its current market price; annual coupon payment / market price
current yield
annualized return of the bond if held to maturity taking into account the price paid; if bought at a discount, the yield is higher and the holder makes money at maturity; if bought at a premium, the yield is lower as the holder loses money at maturity
yield to maturity (basis)
allows a bond issuer to pay the principal of the bond prior to the maturity date; generally issued at a discount
call feature
allows investor to receive principal from the issuer prior to the maturity date; generally issued at a premium
put feature
bonds sold at deep discount paying no interest but maturing at par
zero-coupon bonds
true or false: owners of zero-coupon bonds are taxed on the year’s accumulated interest (phantom income)
true
AAA, AA, A, BBB
Standard & Poor’s four highest bond ratings (investment grade)
Aaa, Aa, A, Baa
Moody’s four highest bond ratings (investment grade)
high yield (junk bonds)
bonds with a rating of BB or Ba and lower
time to maturity
interest rates
coupon rate
these all contribute to a bond’s volatility measured by duration; a higher duration means more volatility
safest investment for US investors
treasury-backed securities
corporate debt securities pay interest based on this calendar:
7 days/week, 52 weeks/year
30 days/month, 360 days/year
30 days/month, 365 days/year
5 days/week, 52 weeks/year
30 days/month, 360 days/year
bonds backed by the corporation’s real estate assets
mortgage bonds
used to purchase large pieces of equipment; until debt is paid in full, equipment is collateral
equipment trust certificates
corporation deposits marketable securities it owns as collateral for a debt issue
collateral trust bonds
debt issue secured only by the word of the corporation; written promises to pay back the debt
debenture
these bonds are backed by a second corporation, such as a parent company; only as good as the word of the issuer and its backer
guaranteed bonds
these are issued by companies coming out of bankruptcy and only pay interest if they are profitable and the board declares interest is to be paid; they do NOT regularly pay interest and are not suitable for a bond investor seeking income
income bond
lowest level of unsecured debt; still senior to a stockholder
subordinated debt
Order of Liquidation
Secured Debtholders
Unsecured Debtholders and General Creditors (wages & taxes)
Subordinated Debtholders
Preferred stockholders
Common stockholders
A 6% bond trading on a 7% basis is trading
a. at a discount
b. with coupon rate below 6%
c. at a premium
d. with current yield above 7%
a. at a discount (when YTM is higher than coupon, the bond is trading at a discount)
True or False: Interest on Municipal bonds is tax free on a federal level
True
True or False: Interest earned from municipal bonds is tax free on the state level but only if the investor lives in the state of issuance
True
True of False: Municipal bonds accrue interest based on a 30-day month, 360-day year
True
these municipal bonds benefit the entire community and do not produce their own revenues; principal and interest are paid using taxes
general obligation (GO) bonds
these municipal bonds are used to finance a facility that generates its own income such as water, electric, sewer, toll roads
revenue bonds
True or False: interest from bonds by or from a territory of the US is tax free at ALL levels; territory meaning Guam, US Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico
True
municipal bonds to tide a city or town over for a short while until anticipated revenues arrive; mature in less than 12 months
Short-Term Municipal Obligations or Municipal Anticipation Notes
Tax Equivalent Yield
used to determine municipal bond investment’s tax benefit; divide the tax-free yield by 100% less the investor’s tax rate
30% tax bracket; mun bond at 7%; what must a corp bond yield to be equivalent?
7% / (100% - 30%) = 10%
30% tax bracket; corp bond yields 11%; what is equivalent mun yield?
11% x (100% - 30%) = 7.7%
True or False: the yield of a municipal bond will always be higher than that of an equivalent corporate bond
False: the yield of a municipal bond will always be lower than that of its corporate equivalent because of its tax advantages
these treasury securities are issued with maturities of 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 13 weeks, 26 weeks, and (monthly) 52 weeks; issued at discount paying par at maturity;
Treasury Bills
the only treasury securities issued without a stated interest rate
Treasury bills and STRIPS
the only treasury securities issued at a discount
treasury bills and STRIPS
used in market analysis as the stereotypical risk-free investment
13-week treasury bill
treasury notes
direct debt obligation of the US government; pay semiannual interest as a % of stated par value; mature at par value; maturities of 2 - 10 years
treasury bonds
direct debt obligations of US government; pay semiuannual interest as % of stated par value and mature at par; maturities greater than 10 years up to 30 years
type of bond created by brokerage firms made up of treasury securities; NOT backed by the US government
treasury receipts
issued with maturities of 5, 10, or 20 years having a fixed coupon rate and paying interest every 6 months; principal value is adjusted every 6 months based on inflation rate; interest rate payments adjust accordingly
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
Agency Securities (asset backed securities)
securities issued by federal agencies
Farm Credit Administration
Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA)
Federal Home Loan Mortgage Association (Freddie Mac)
Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae)
Student Loan Marketing Association (Allie Mae)
provide very short-term funds to corporations, banks, BDs, municipalities, and federal government
money market securities
has a fixed interest rate and minimum face value of $100,000 though values of $1 million or more are common; longer maturities pay interest every 6 months
Jumbo Certificate of Deposit
postdated check or line of credit issued by a bank and provided to certain corporations in import-export business; payment date never more than 270 days; may be referred to as bill of exchange or letter of credit
Bankers’ Acceptances
promissory notes used to raise cash; 270 days or less
Commercial Paper, Prime Paper, Promissory Notes
True or False: once a federal treasury note or bond with longer maturities has only 1 year left to maturity, it is considered a money market instrument
True
Characteristics of money market securities:
highly liquid
hard to sell
very safe
very volatile
short-term
long-term
low rate of return
high rate of return
highly liquid, very safe, short-term, low rate of return
True or False: Interest on treasury bonds is tax-free at the federal, state, and local levels
False: interest on treasury bonds is taxed at the federal level but not the state nor local levels
True or False: Interest owned from Agency Securities such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac is tax-free
False; interest for these securities is taxed at both the federal and state levels
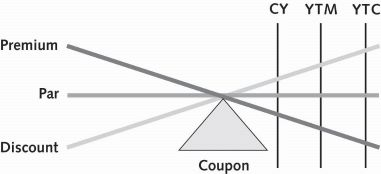
For a callable bond trading at a discount, the yields in ascending order are:
coupon (nominal), current, yield to maturity, yield to call
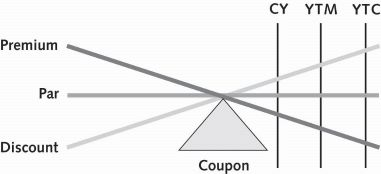
For a bond trading at par, the yields will be the same but will fall in this order:
coupon, current, ytm, and yield to call
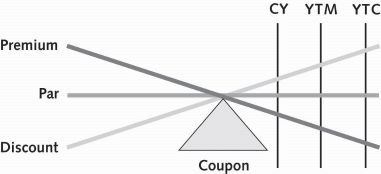
when trading at a premium, bond yields will descend in this order
coupon, current, ytm, and yield to call
unsecured promissory note issued by banks
negotiable CD
unsecured promissory notes issued by corporations
commercial or prime paper
an issuer in default would be rated this by Moody’s
C
an issuer in default would be rated this by S&P
D
True or False: GNMA securities are backed by the full faith and credit of the US government
True
True or False: FNMA and FHLMC securities are backed by the full faith and credit of the US government
False; they are backed by the implied backing but not full faith and credit