UGA Chem 1211L Lab Practical Spring 2022
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
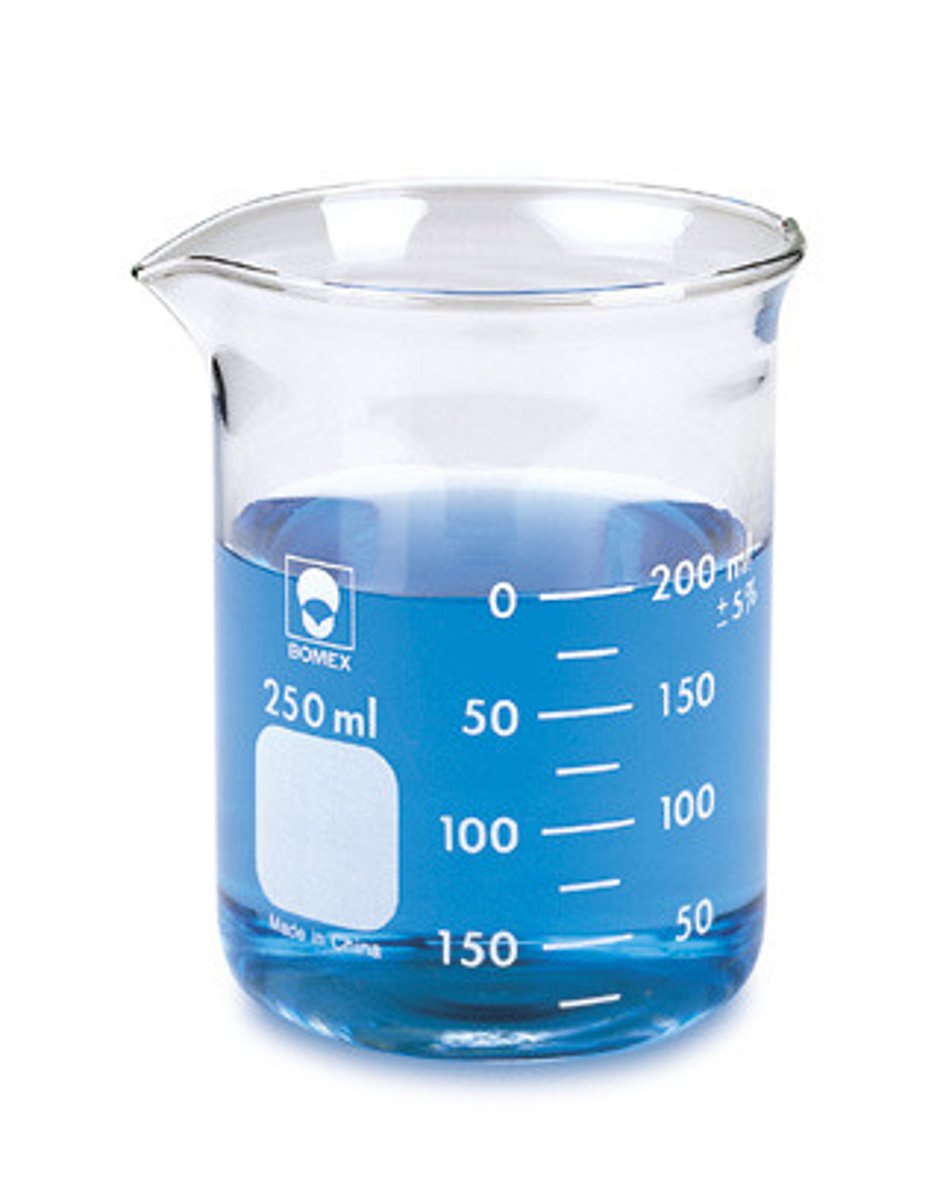
beaker
A lipped cylindrical glass container is used for holding or mixing liquids with a pouring spout; some have graduations indicating an APPROXIMATE volume of contents

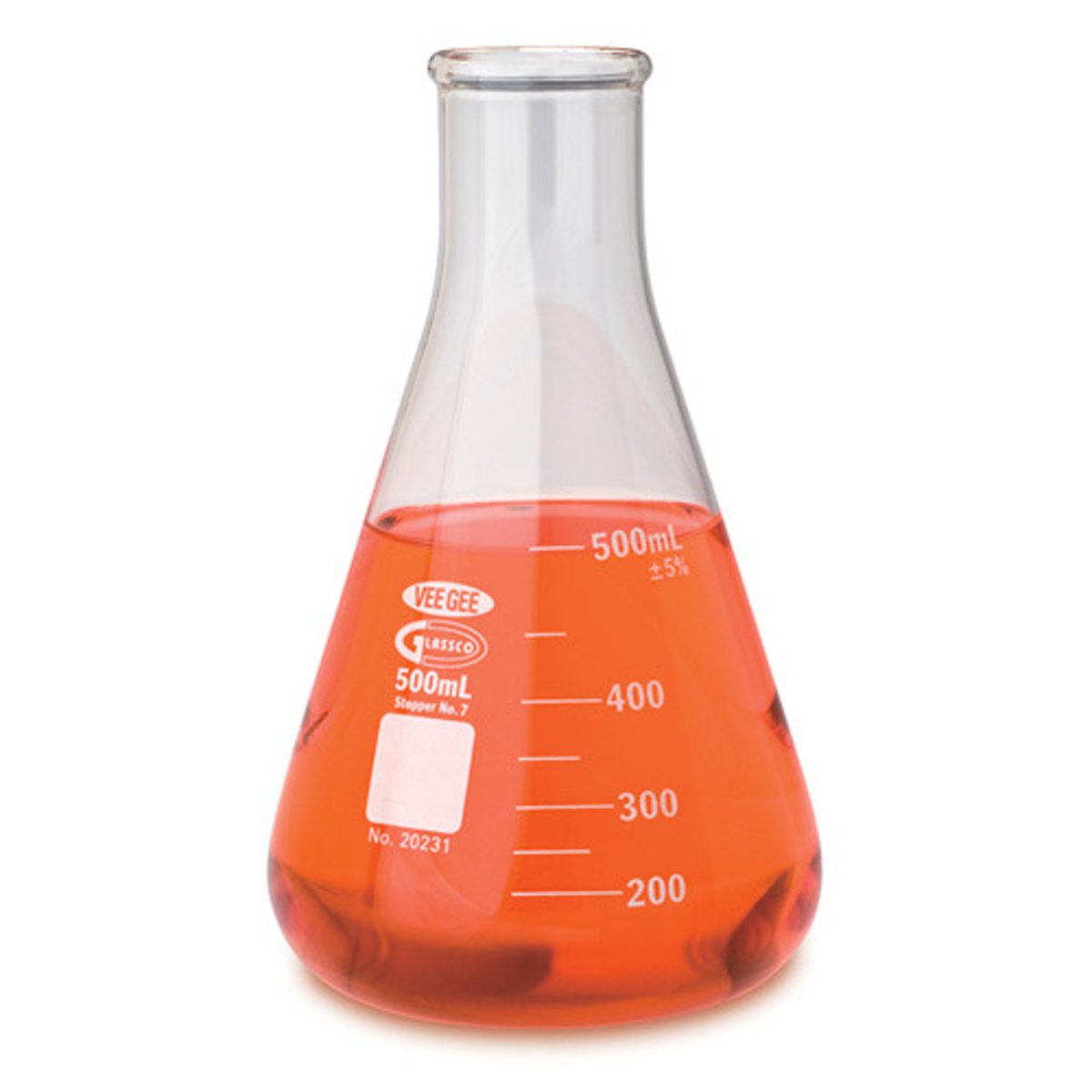
Erlenmeyer flask
A conical, flat-bottomed laboratory flask with a narrow neck used for holding or mixing liquids; some have graduations indicating APPROXIMATE volume of contents

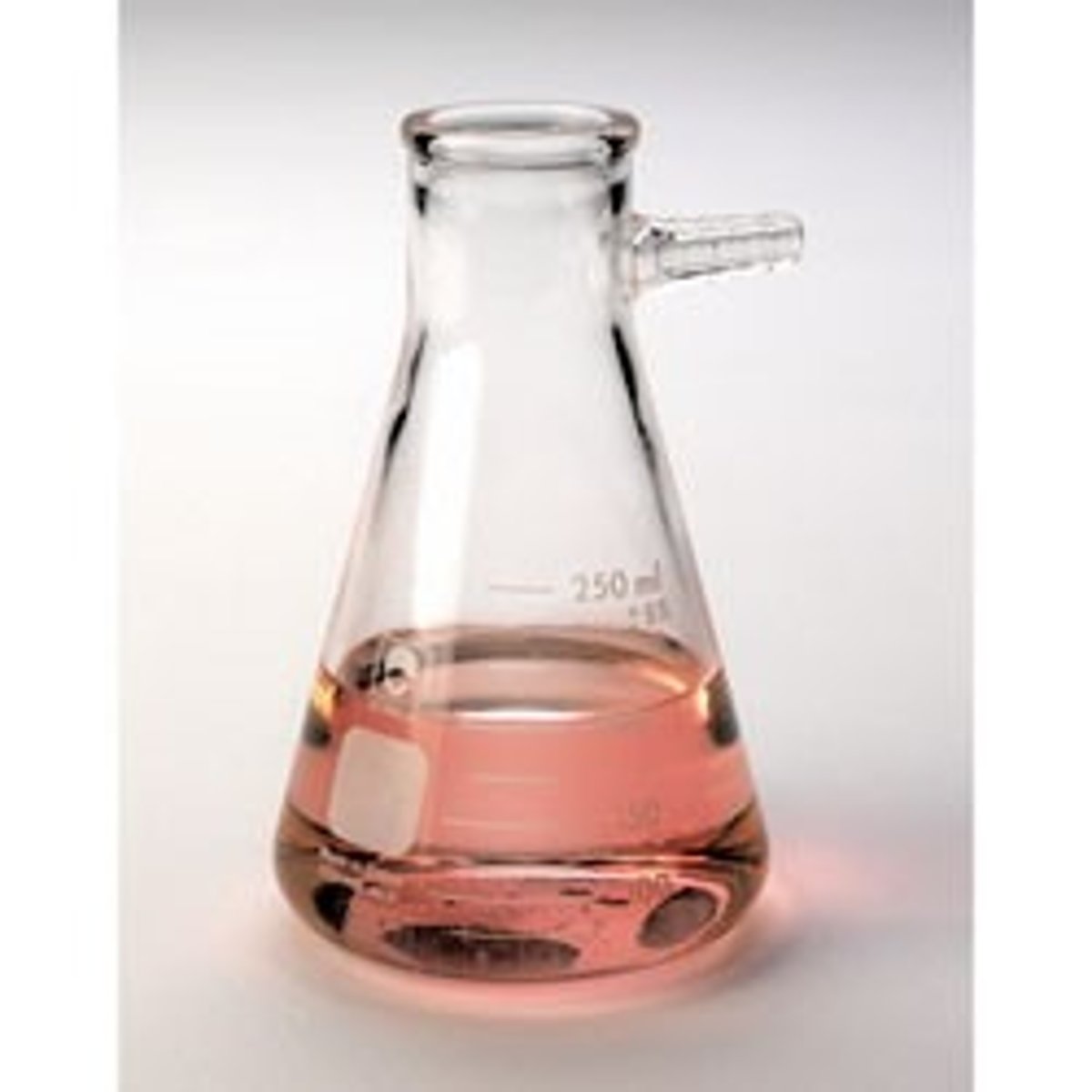
filtering flask
A heavy wall flask designed for use in suction (vacuum) filtration; has a side hose connection to attach vacuum tubing

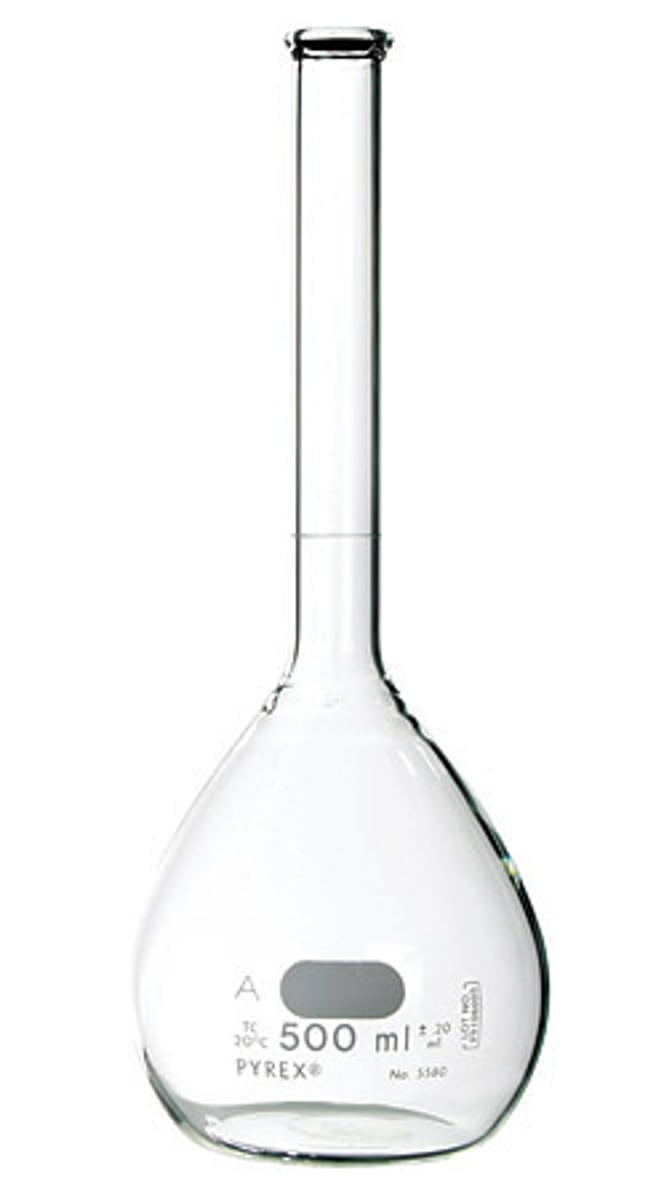
volumetric flask
A flask used for preparations of solutions, which are calibrated to contain a specific volume of liquid or solution

test tube
A round bottom glass tube used to contain or heat small amounts of material

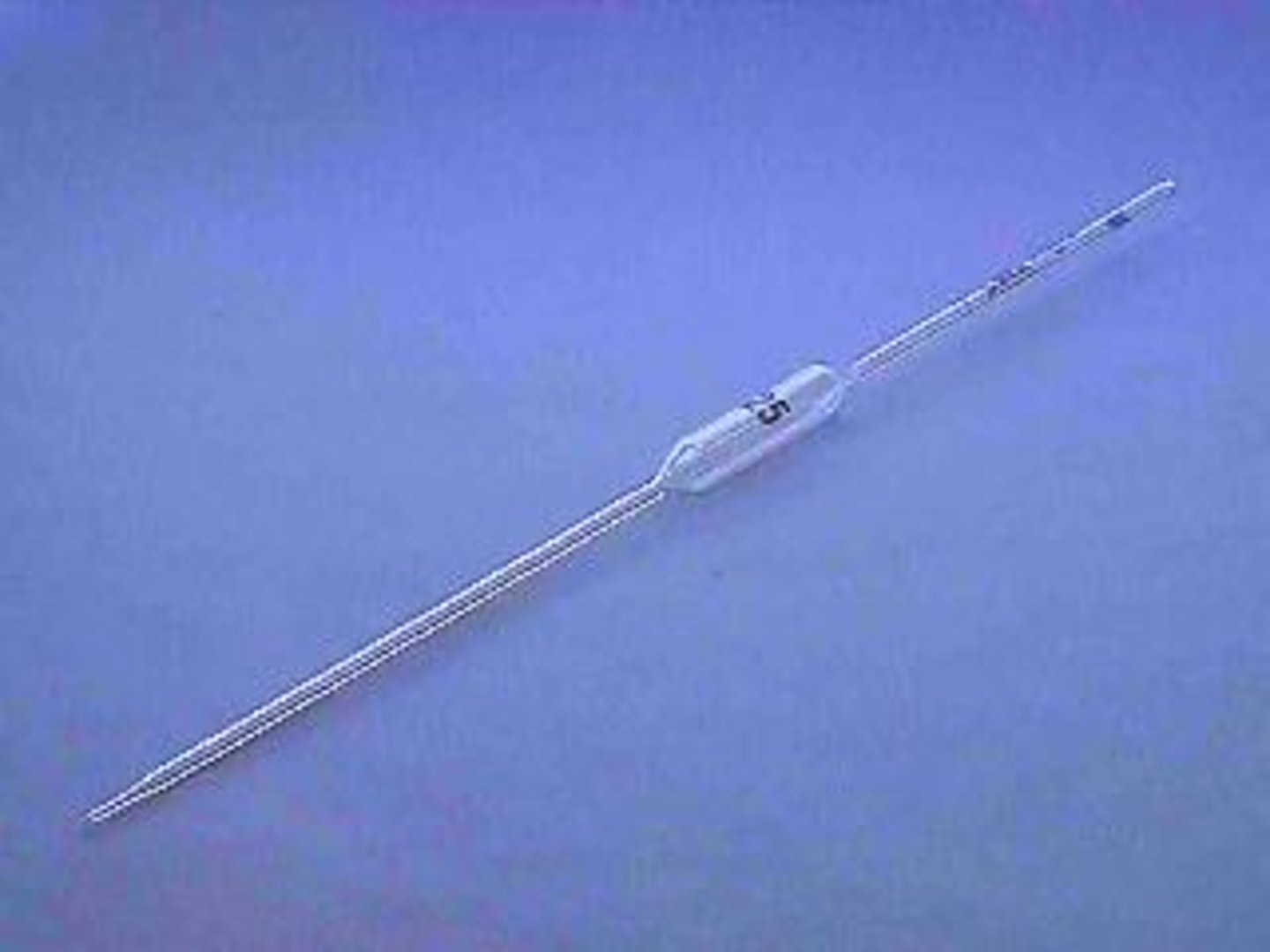
volumetric pipet
A pipet calibrated to deliver an EXACT amount of solvent or solution

Mohr pipet
A graduated pipet to deliver solution
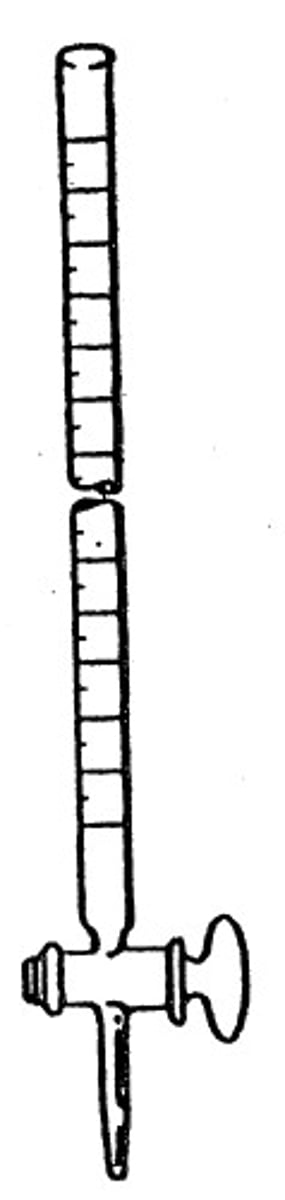
buret
A graduated glass tube with a tap at one end for delivering/dispensing known volumes of a liquid, especially in titrations through a stopcock
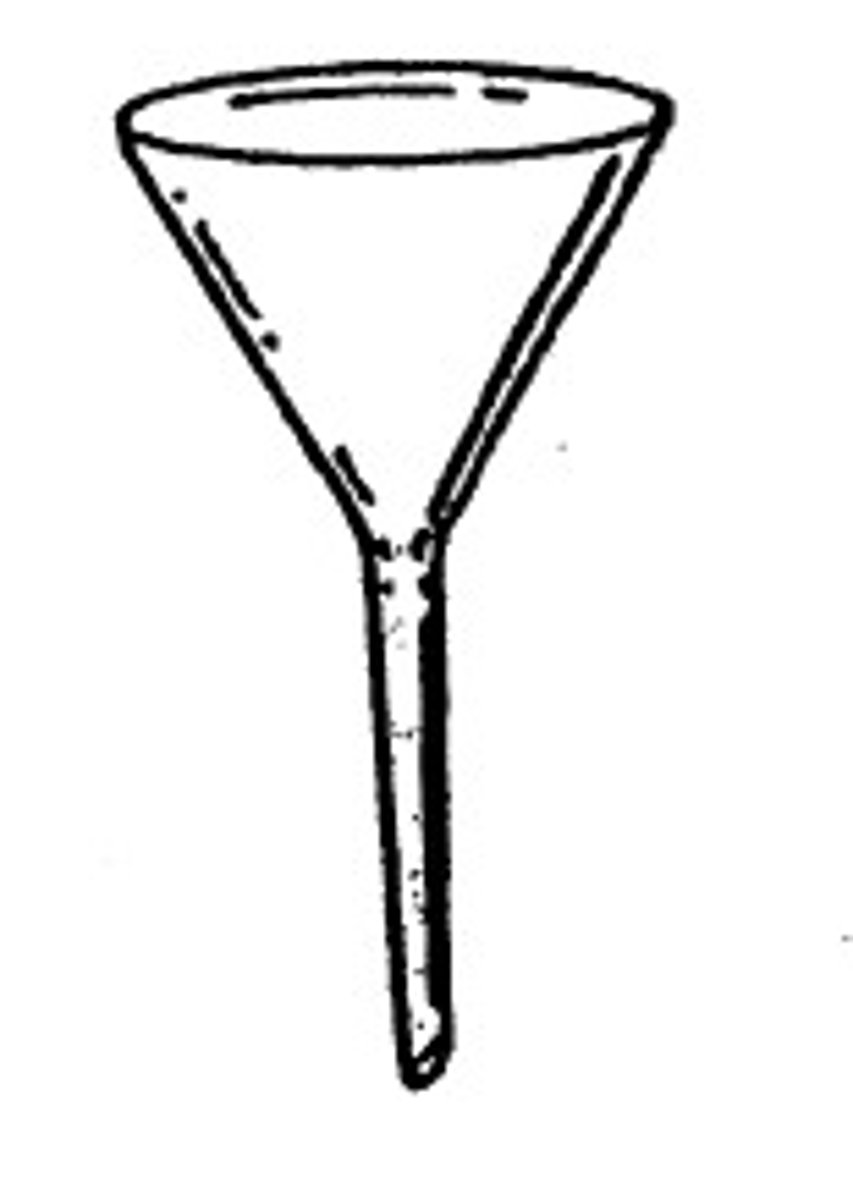
funnel
A pipe with a wide (often conical) mouth and a narrow stem is used to channel liquid or fine-grained substances into containers with a small opening
Buchner funnel
Used with vacuum filtration

Powder funnel
Funnell with a short, wide stem
rubber policeman
A rubber tip with a flattened end used on a glass rod for scraping solids from containers

spatula/scoopula
Labratory utensils used for handling small amounts of solid chemicals
graduated cylinder
A measuring device, graduated to contain liquids or solutions; tall versions are equipped with a plastic bumper to prevent shattering if it is knocked over

dropping pipet
A medicine dropper used to dispense liquids in drop-wise amounts
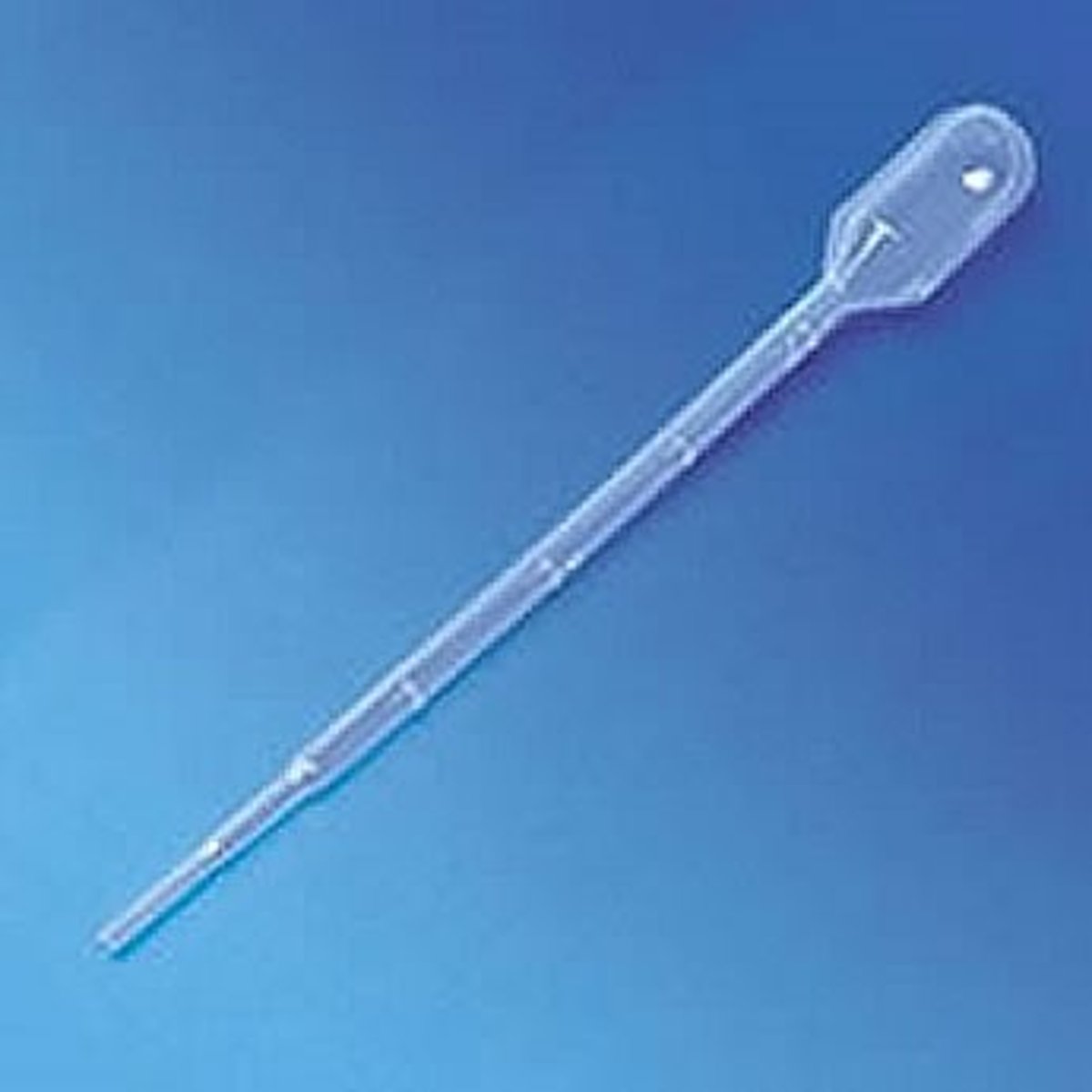
Pasteur Pipet
Small drops, usually disposable
watch glass
A glass dish that can be used for evaporation of small amounts of liquids, for studying small amounts of solids (weighing, etc.), or covers for beakers

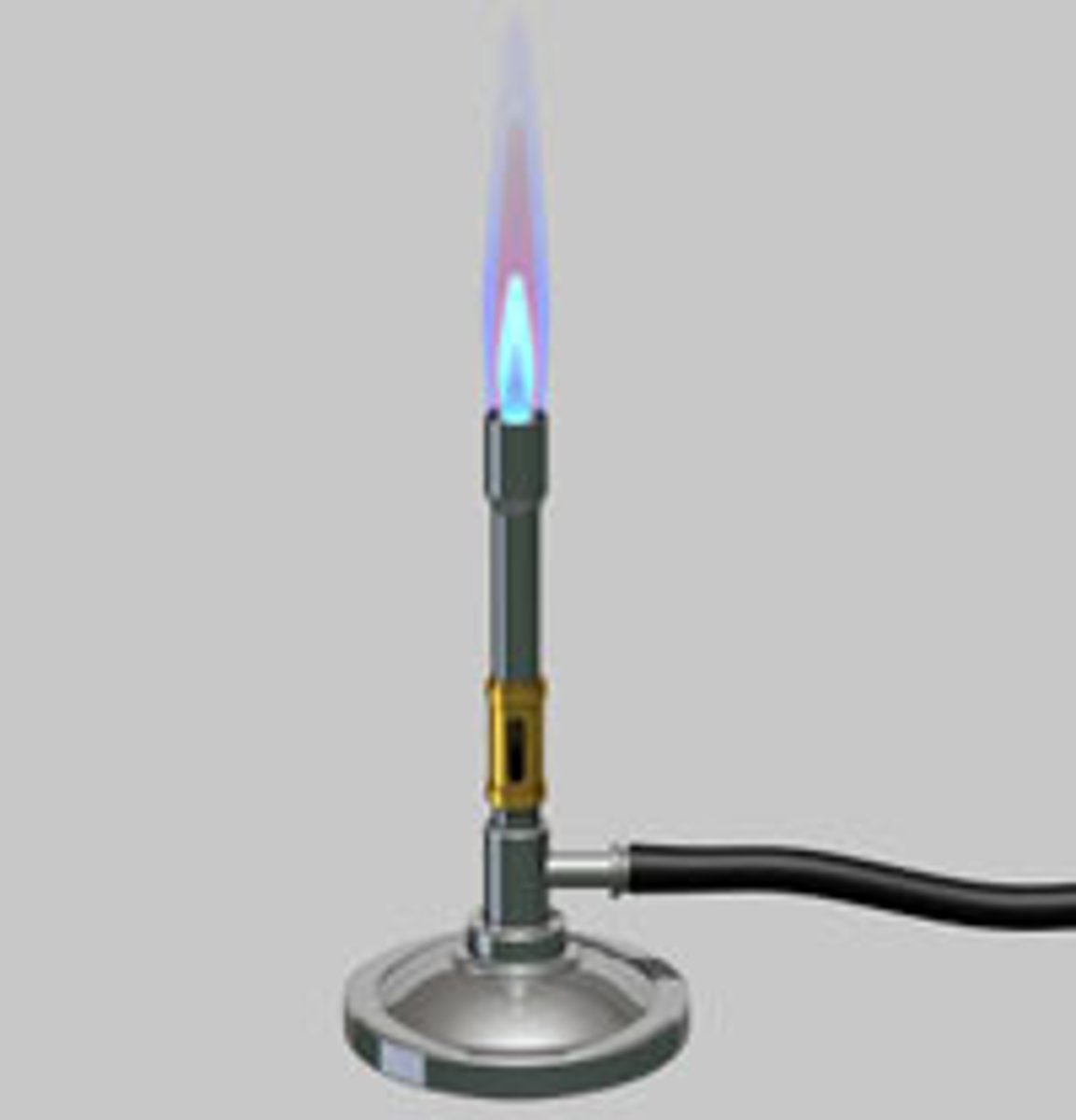
bunsen burner
A burner that contains a needle valve for gas flow regulation

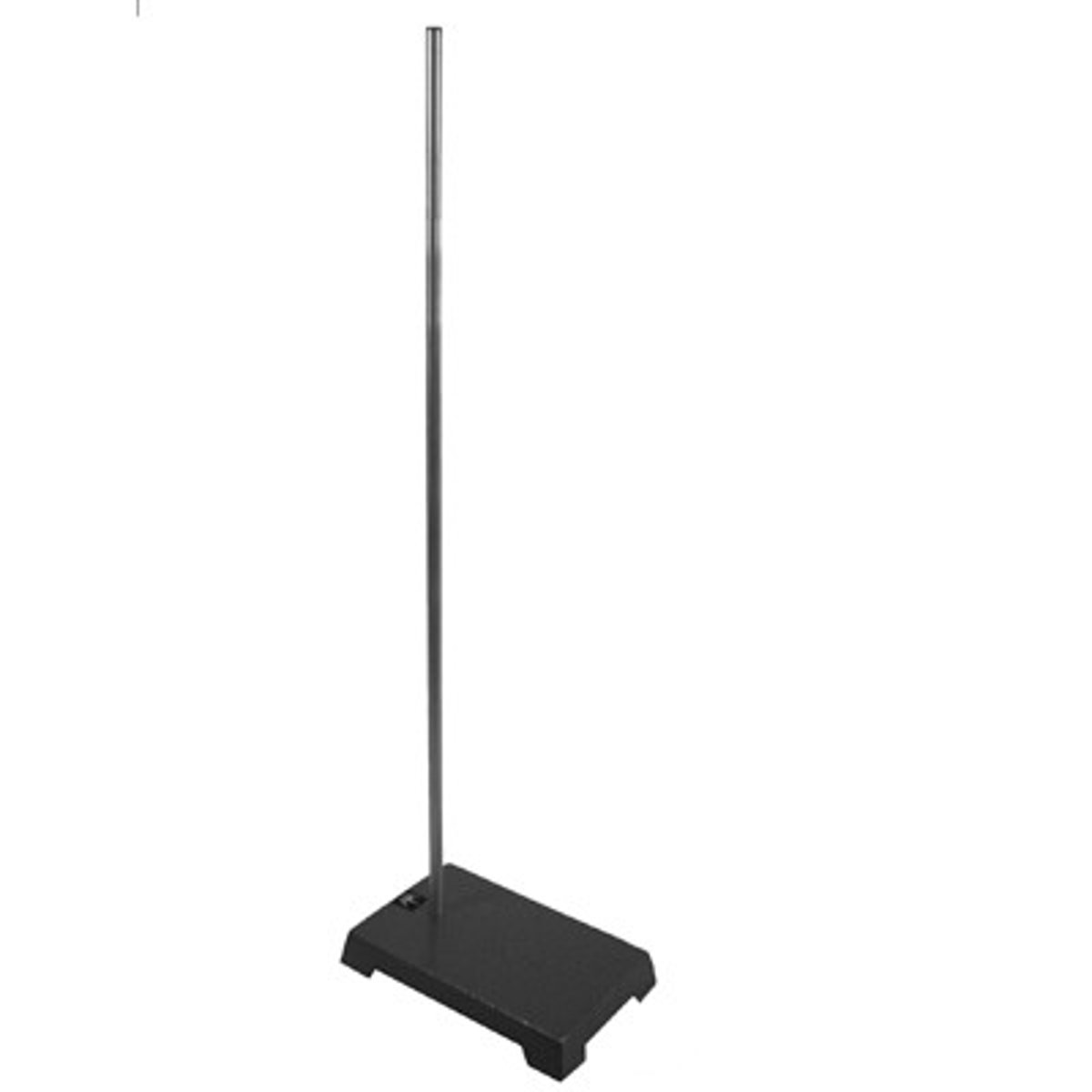
ring stand support
Consists of a heavy base with a metal rod for supporting apparatus for a variety of laboratory operations

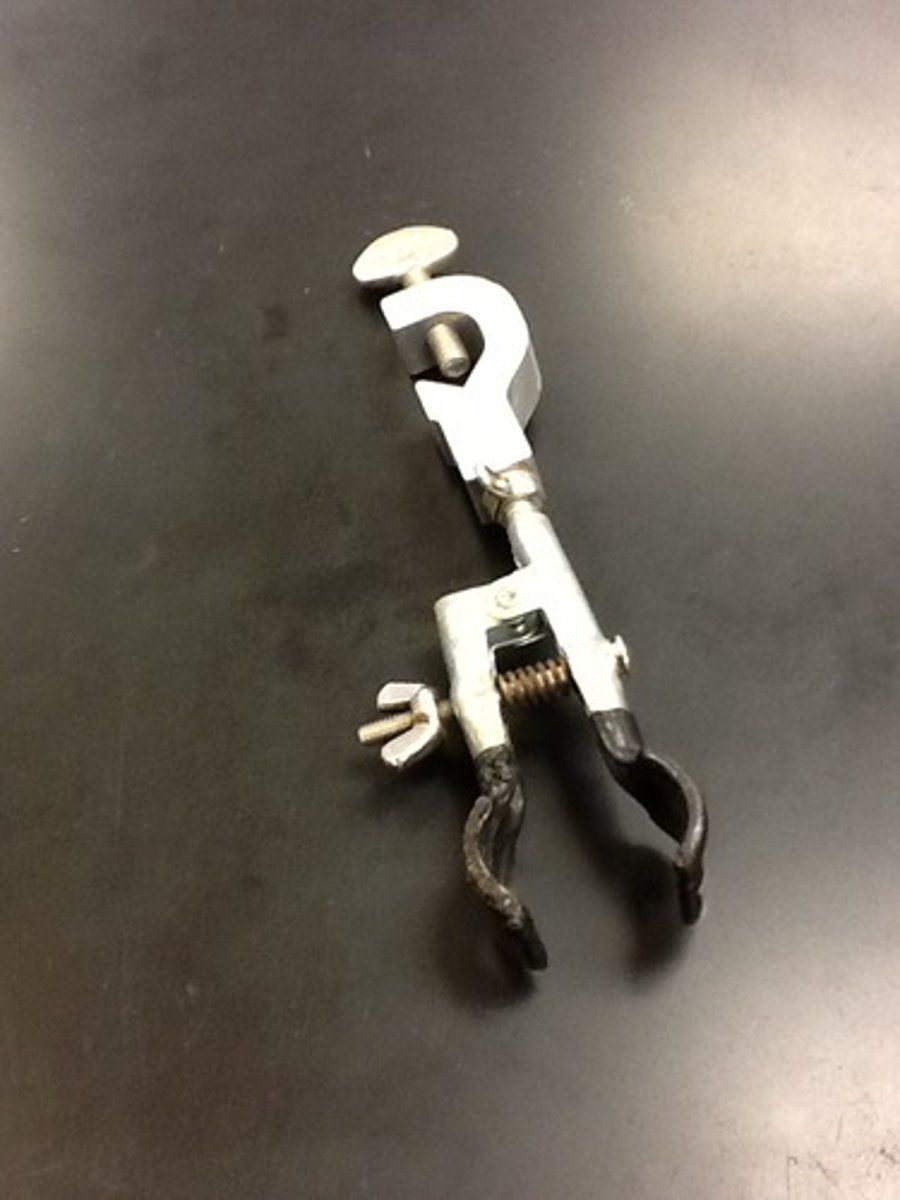
utility clamp
Adjustable clamp for holding a test tube, buret, or other apparatus

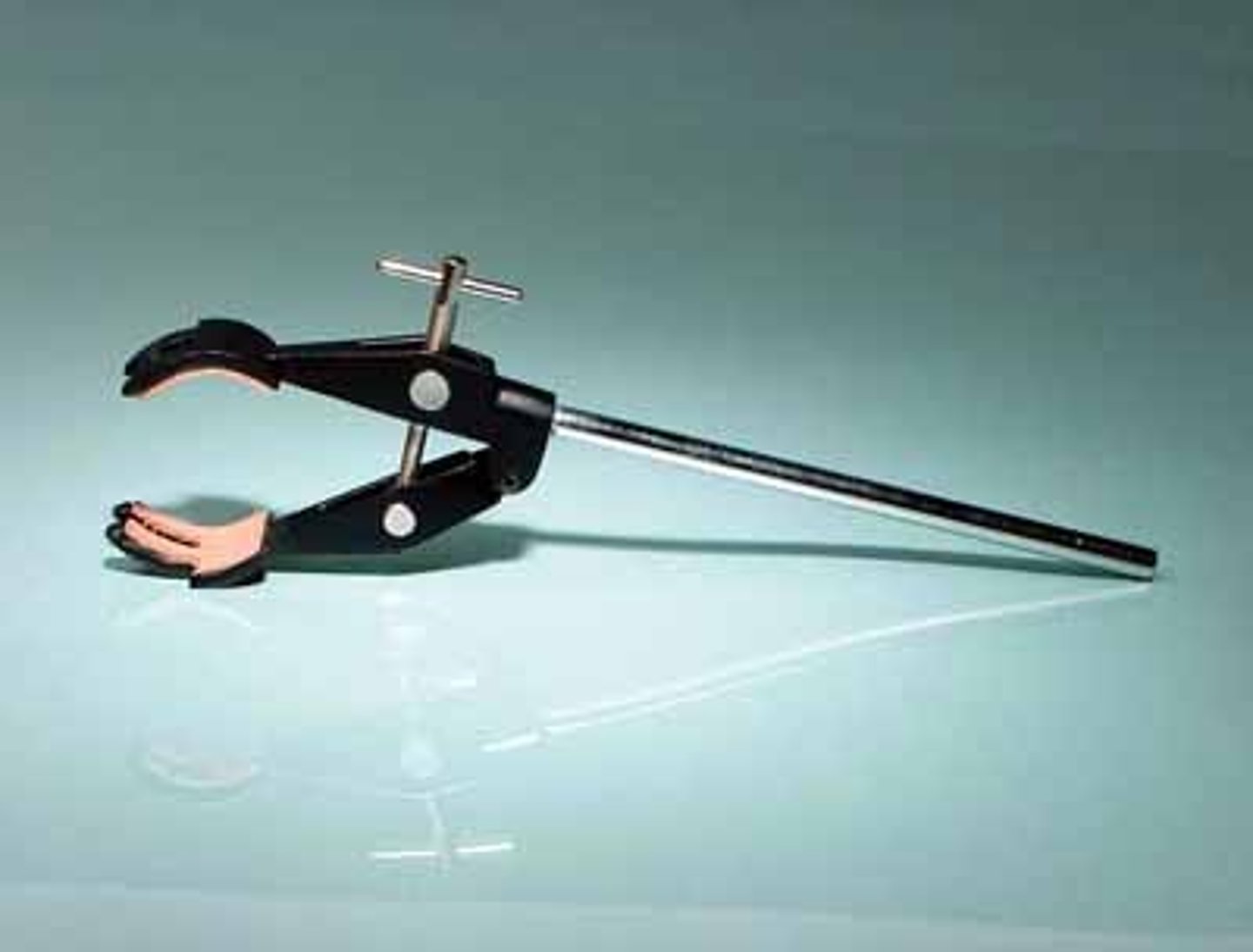
extension clamp
Used with a clamp holder, allows for more varaition in positioning than a utility clamp

3-prong clamp
Used with a clamp holder, allows for more versatility in holding different types of apparatus

extension clamp holder
Used to attach an a extension clamp to a ring stand support or support frame
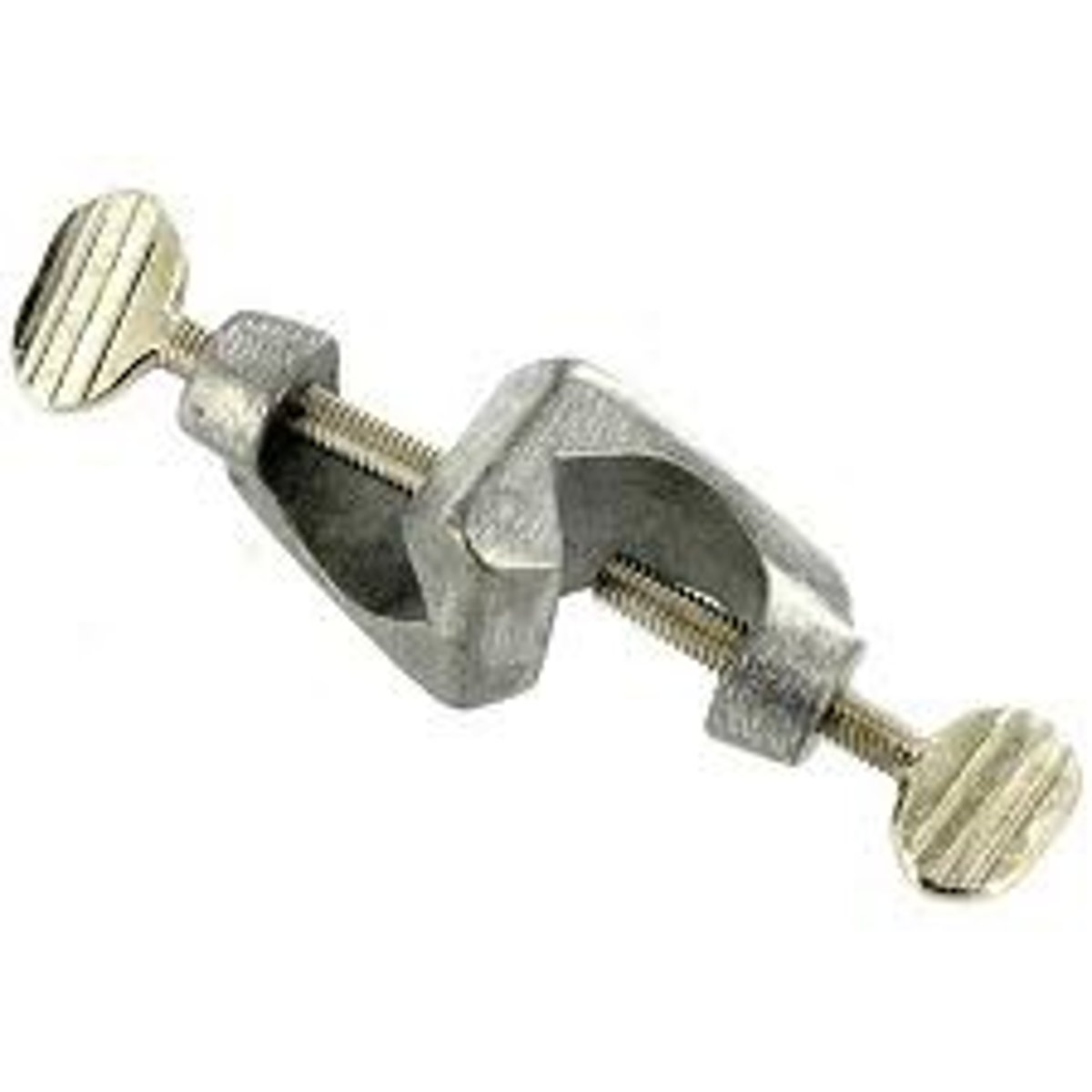

support ring
A ring designed as a base support for beakers and flasks when heated on a ring stand support
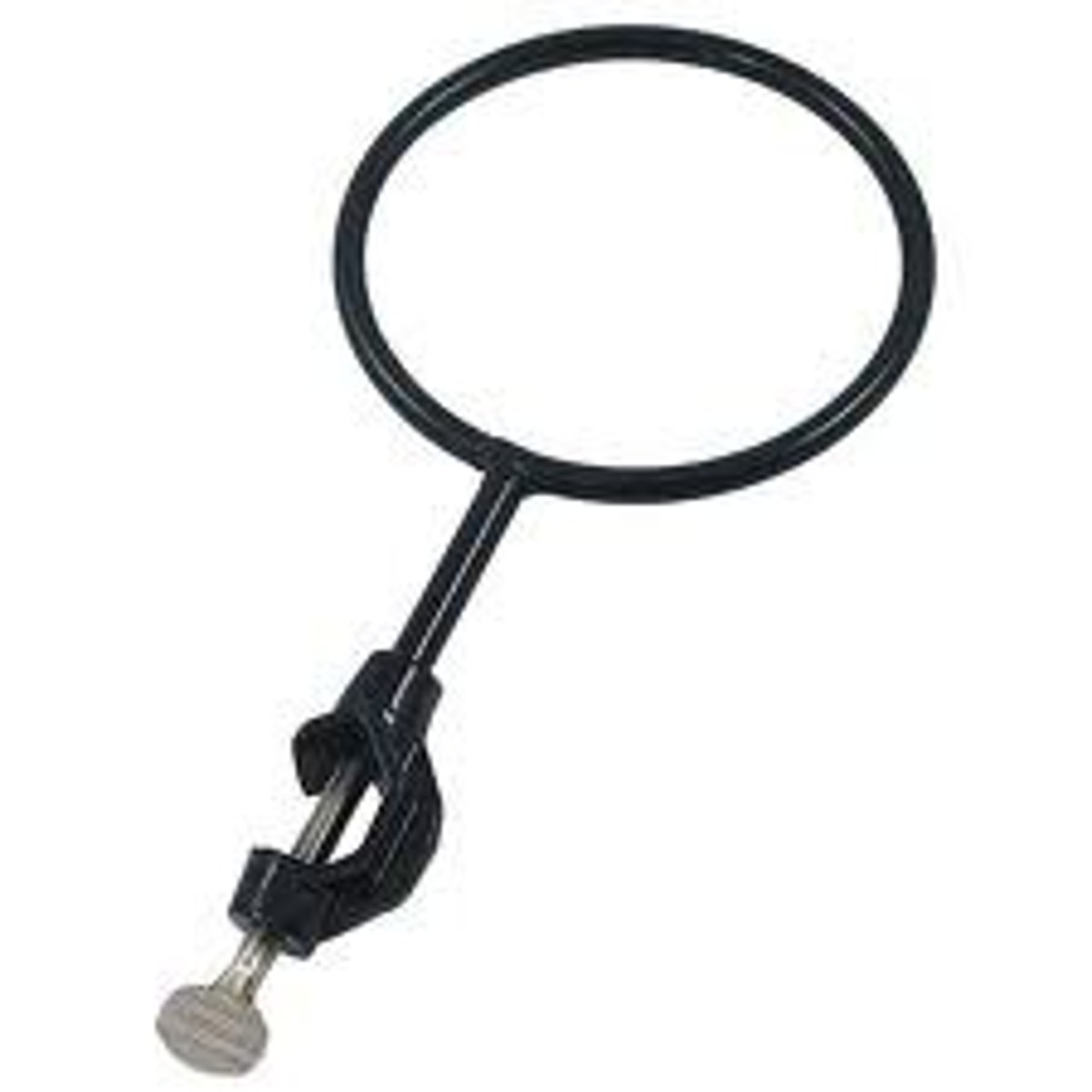

double buret holder
A double clamp for holding burets

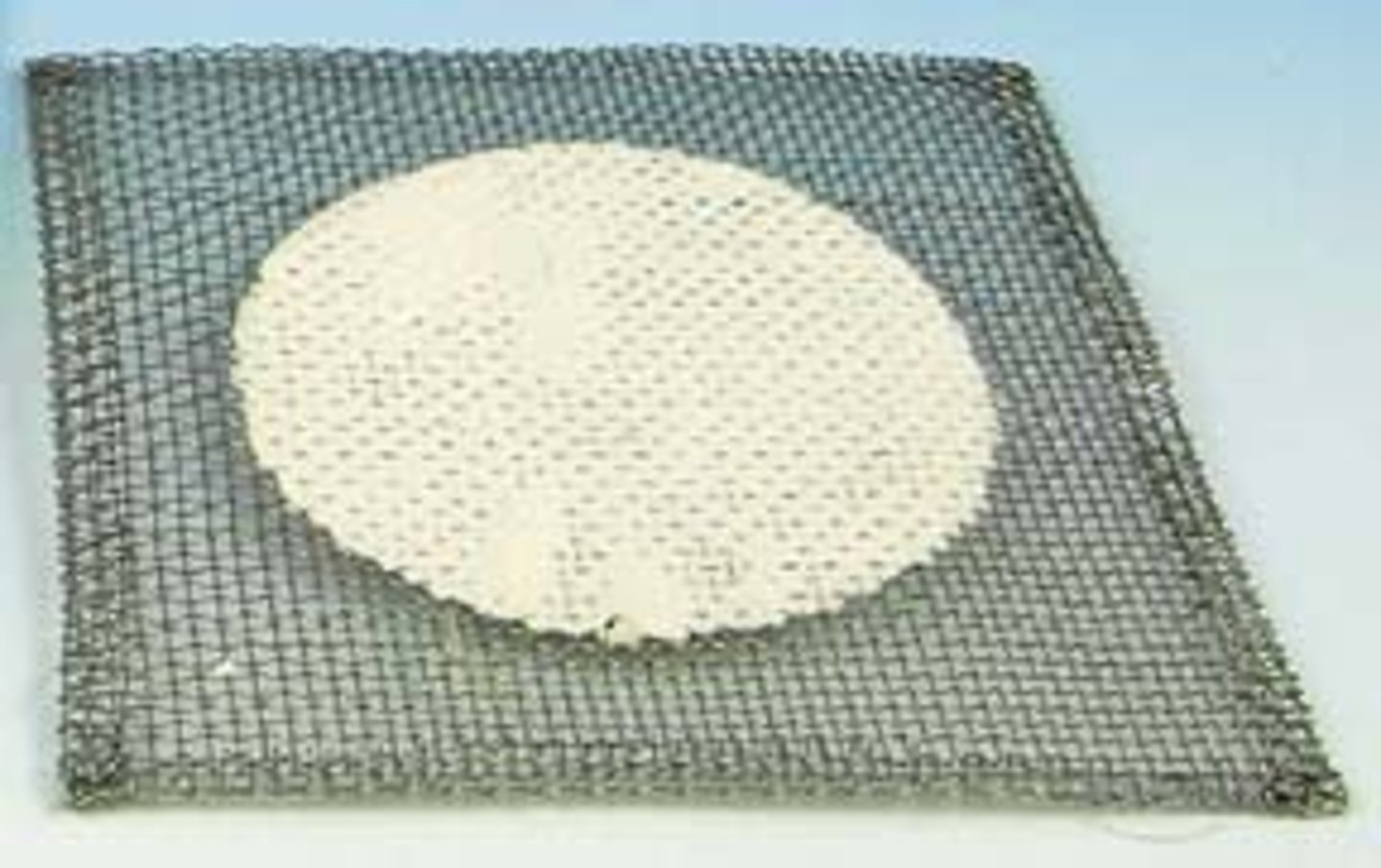
Wire gauze (ceramic center)
a support surface to be used with a ring support or tripod to provide uniform heat distribution

stir bar
A teflon coated magnet used for mixing reactions
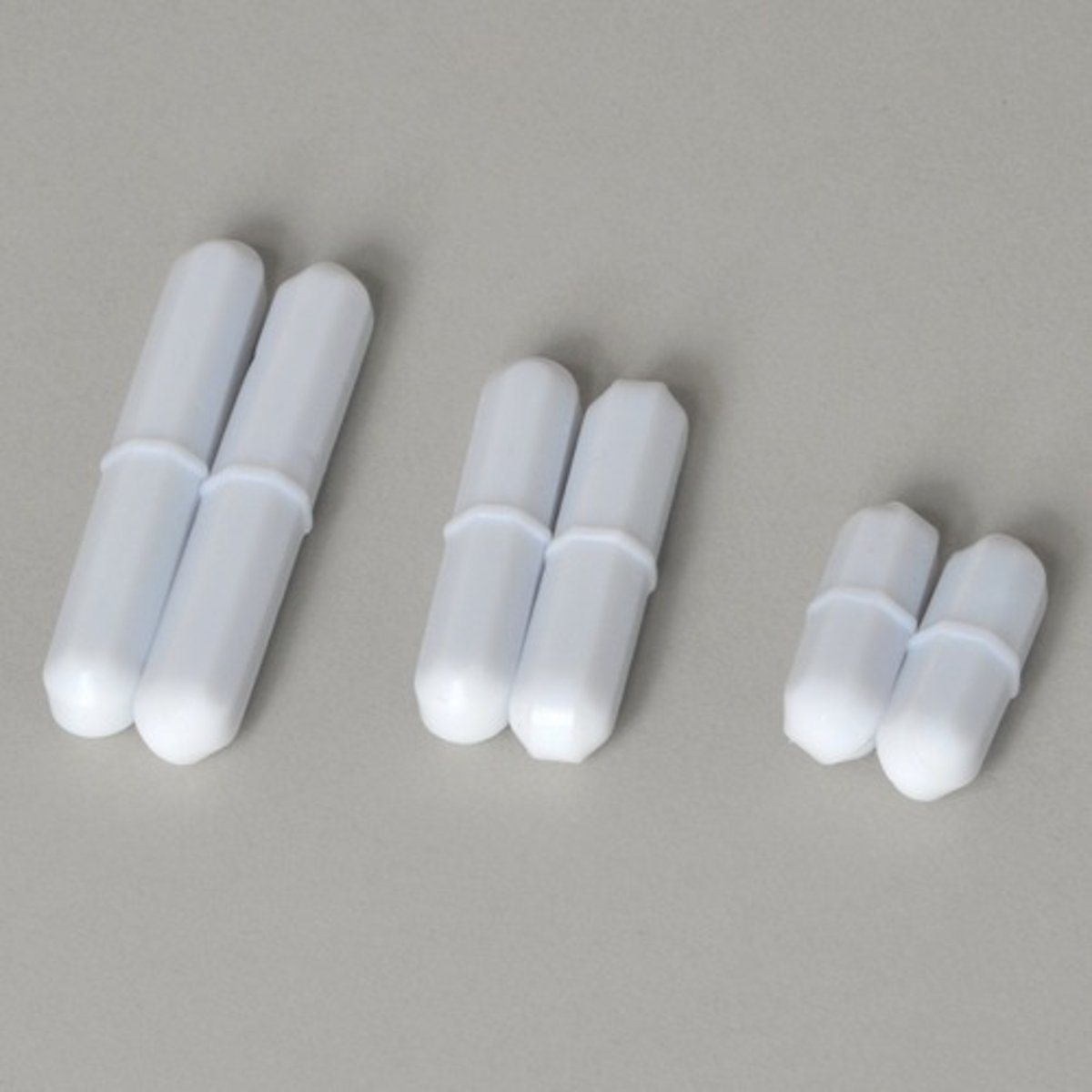
boiling chip
A tiny, unevenly shaped piece of calcium carbonate or silicon carbide added to liquids to make them boil more calmly

magnetic stirrer/hot plate
A device used to stir and heat reactions sat on top of it

pH and mV meter / thermometer
Used to measure

Test tube holder
a clamp secures the test tubes in place
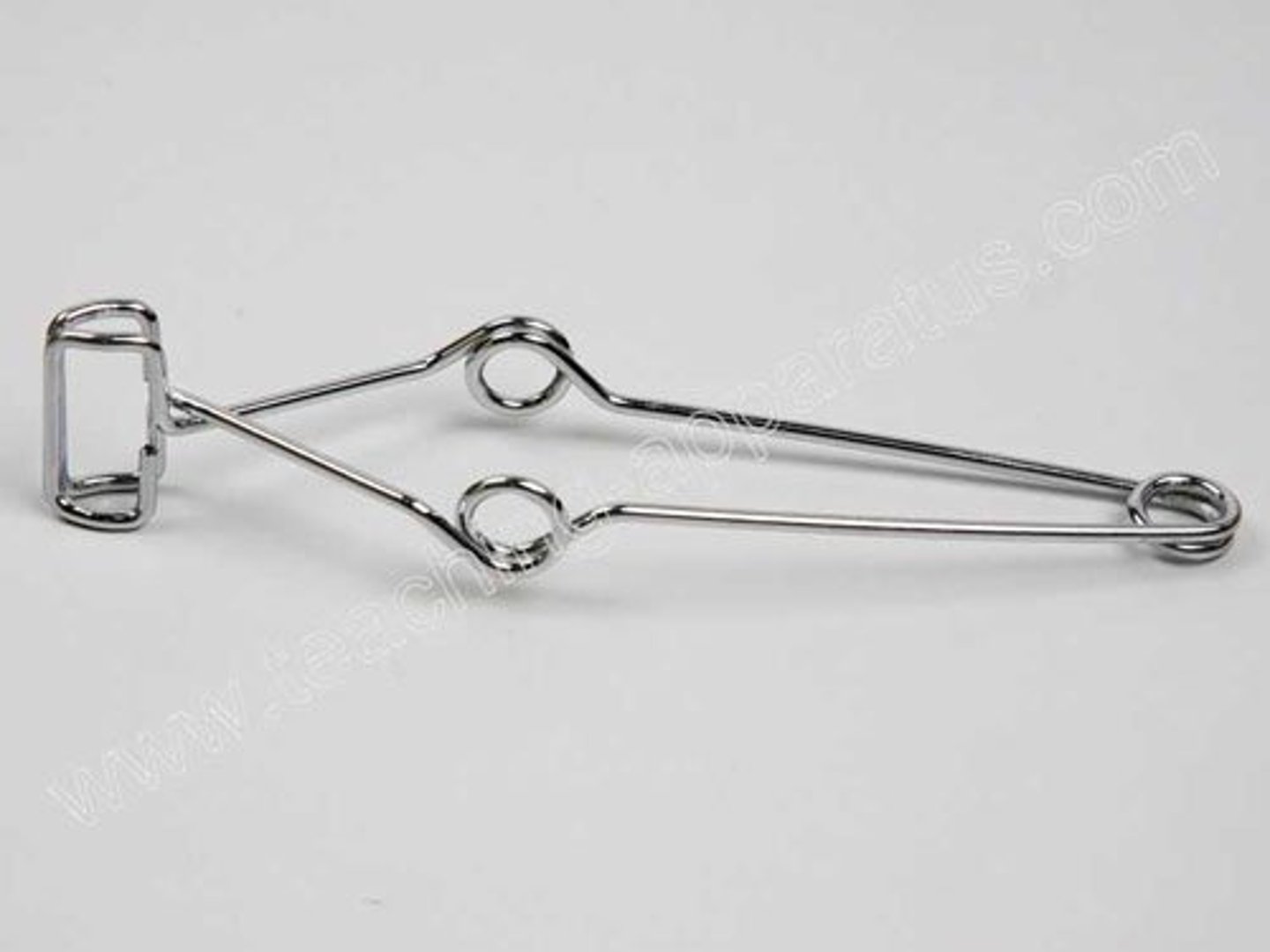
beaker tongs
Wide-jaw tongs for holding beakers
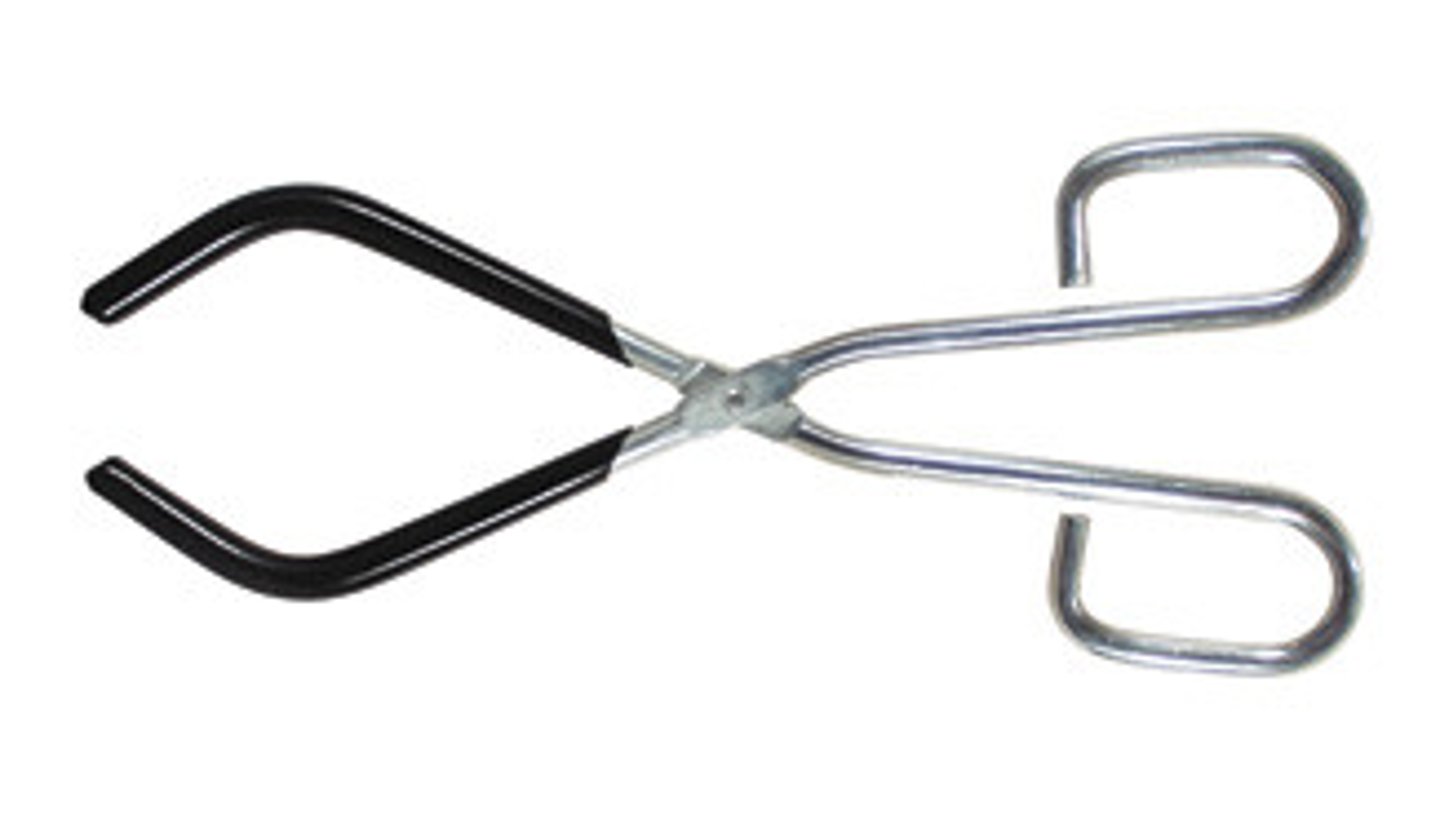
crucible tongs
Tongs with oval opening in jaws for holding crucibles; tips used for handling crucible covers

stirring rod
A piece of laboratory equipment used to mix chemicals and liquids for laboratory purposes; usually made of solid glass

evaporating dish
A small ceramic dish in which liquids are heated over a flame so that they evaporate, leaving a solid residue

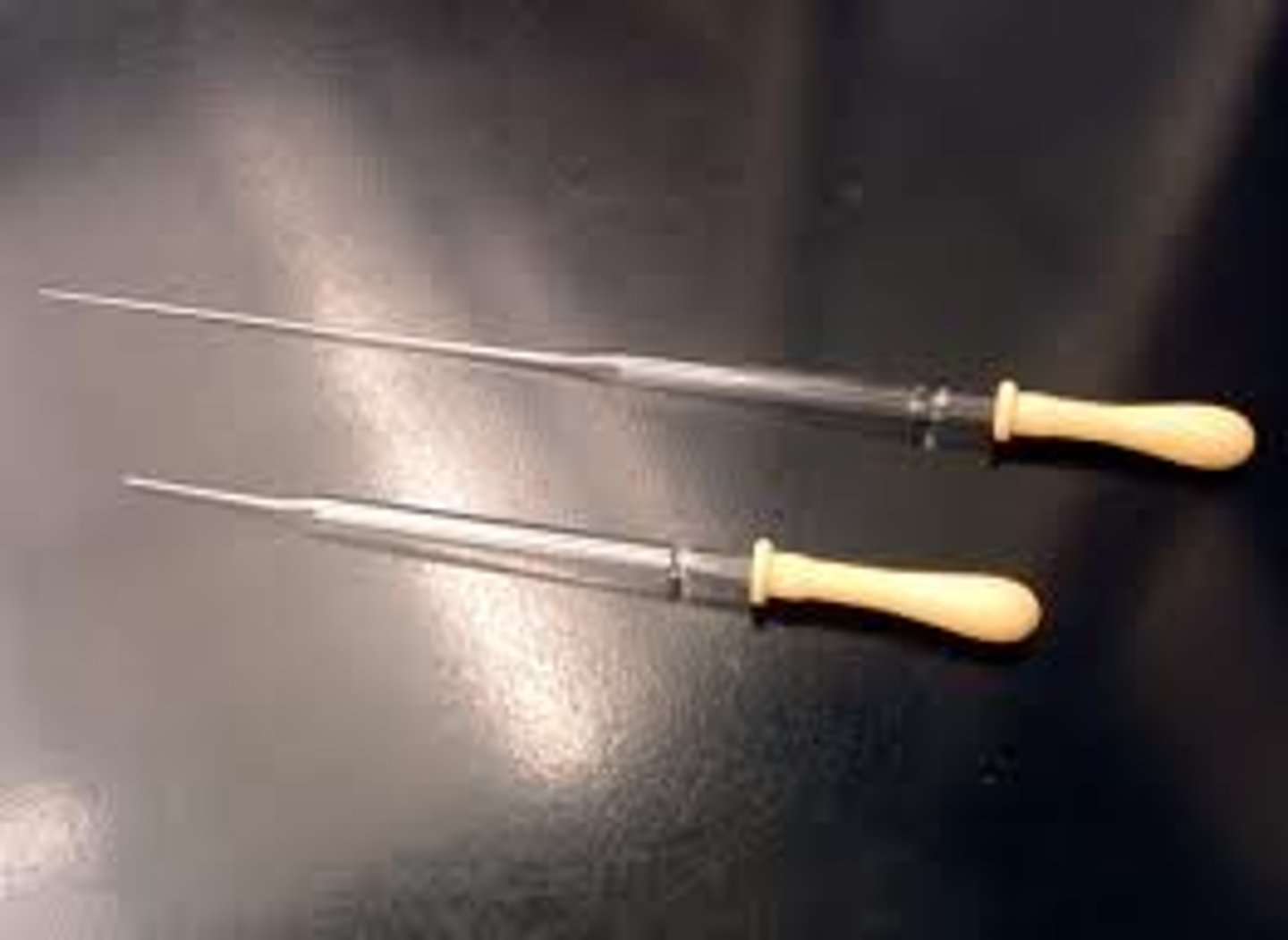
tweezers
Small metal instruments that are usually held between the thumb and index finger, are used for plucking, holding, or manipulating, and consist of two legs joined at one end

spectrophotometer
An apparatus for measuring the intensity of light in a part of the spectrum, especially as transmitted or emitted by particular substances.

T
T/F: Volumetric glassware have been calculated to be precise in their volume.
F- approximate
T/F: Beakers are accurate tools to measure volumes.
n+1 decimal place
If a laboratory instrument is marked to nth decimal place, record data to the ___________.
1
1 ml = ______ cm³
1.00g/mL
Density of pure water at STP
standard solution
A solution containing a precisely known concentration of an element or a substance
5.000%
If using a 100mL of water (solvent) and 5.000 grams of sugar (solute), a __________ sugar solution would be prepared.
law of conservation of mass
The mass of the reactants consumed must equal the mass of the products generated
law of definite proportions
A given chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio (by mass) and does not depend on its source and method of preparation
atomic theory
Matter is composed of discrete units called atoms and combine in a ratio of small whole numbers
electrolysis
Chemical decomposition produced by passing an electric current through a liquid or solution containing ions, which would otherwise not happen
decant
To gradually pour (liquid or a solution) from one container into another, especially without disturbing the sediment at the bottom
filtration
One component dissolves in water. Mixture is separated by filter funnel and filter paper. Solid is collected on paper. Liquid flows through paper and becomes filtrate.
sedimentation
When solid particles settle out; heavier solids fall to the bottom of the slurry or suspension
centrifugation
Use of centrifugal force for the sedimentation of heterogeneous mixtures
distillation
Process of separating components from liquid mixtures through vaporization and condensation, based on different boiling points of components in the mixture
evaportation
Used when the solid present in the liquid is non-volatile. Solution is heated. Solvent evaporates and solid is left as residue
chromatography
Different constituents when dissolved in a solvent will travel at different rates on the paper and become separated; has a mobile phase and a stationary phase
coagulant
A substance that causes a liquid to change to a solid or semisolid state
molar absorptivity
The measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs light at a given a wavelength (ε in the equation for the Lambert-Beer law)
Lambert-Beer law
The absorption of light as it passes through a solution is proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species, the length of the light path, and the fundamental property of the material (the molar absorptivity)
A=εlc
Equation for Lambert-Beer law
light path length
l in Lambert-Beer law
concentration
c in Lambert-Beer law
transmittance
The fraction of light that passes through the sample in spectophotometry
T=I/Io
Equation for transmittance
absorbance
A logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at particular wavelength) as the light passes through a sample or substance
A=log(1/T) or A=-log(I/Io)
Equation for absorbance
calorie
The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water through 1°C
law of conservation of energy
In a closed system, i.e., a system that isolated from its surroundings, the total energy of the system is conserved
percent yield
The percentage of actual to theoretical
(actual/theoretical)×100
Equation for percent yield
percent error
The difference between the estimated number and the actual number when compared to the actual number expressed in percent format
(theoretical-actual)/actual)×100
Equation for percent error
r^2
Symbol for the linear regression of data
The precision of a measurement is
a measure of the reproducibility of a set of measurements
Absolute error is the difference between
measured value and actual value
standard deviation
a measure of the amount of variation within a set of values, how close are they to the mean?
density of penny = (density of copper 8.92g/cm3 * % of Cu [x] ) + (density of zinc 7.14 g/cm3 * % of Zn [1-x] )
percent composition of the penny
Density
Intensive, doesnt depend on quantity of material, M/V
When HCl reacts with new penny, whats chemical equaiton?
2 HCl (aq) + Zn (S) yields ZnCl2 (s) + H2 (aq)
Calculate percent sugar in cola using linear regression
y = density x = percent sugar concentration
Filtration is
one component dissolves in a solvent and others remain in the solid-state, separated with a filter funnel and filter paper, solid is on paper and liquid flows through paper to be filtrate
Sedimentation
Solids will settle to bottom of solid-liquid heterogeneous mixture
Evaporation is
separation of homogeneous mixtures, like sodium chloride can be isolated from salt water by evaporating the water. SOlution is heated and solvent evaporates, solid residue is left
Centrifugaiton
use of centrifugal forces for the sedimentation of heterogeneous mixtures
Distillaiton
seperation through vaporization and condensation, based on different boiling points of liquids
Paper chromotography
Dissolved consituents will travel at different rates on paper and separate in mobile phase till stationary phase
Separation of mixture experiment
1. Iron fillings by magnet
2a. Vacuum filtration system separates solid calcium carbonate and silicon dioxide from watered down solution.
2b. Add HCl to disolve the CaCO3, then vacuum filtrate the silicon dioxide again
3. Erwin meyer glass moves to hotplate to evaporate water from NaCl.
Found the masses of 3/4, subtract from initial mass to find SiO2. Find mass percent
Mass percent of CaCO3
Mass of CaCO3 / Mass on unknown x 100
Percent composition of Si
MM of Si / total mass of SiO2 = percent comp of Si then multiply by mass percent of SiO2 then by 100 for percentage
Ethanol disolves
Sodium Chloride but not sodium bicarbonate
Coagulation
removes dirt and other particles in water
Potassium Alum, an inorganic coagulent used to remove negatively charged particles that are in suspension in water because they nutrilize them and metal hydroxide precipitates of the aluminum ion formed, trapping the suspended particles and settle to the bottom, not filtration can be used for sedimentation
KAl (SO4)2 * 12H2O
Aluminum metal is oxidized to
Al 3+ via strong base, forming Al(OH)4-1, with K to neutralize and hydrogen gas.
Add more H2SO4 to form
Al3+ solutions in water. aluminum ions combine with potassium and sulfate to crystalize
Then a strong acid (H2SO4) is used to form
aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3)
Percent yield is
actual / theoretical x 100
Sulfate is in our product because
SO4 2- (aq) + Ba 2+ (aq) → Ba SO4
The greater the amount of phosphate ions in water analysis, the more intense yellow color and then
the spectrophotometer determines the absorbtion
Lambert-Beer Law
Absorbtivity= molar absorbivity x light path length x concentration, a direct relationship is shown
Absorbance is inverse of transmittence
A = log (1/T)
Cuvette
goes in a spectrophotometer