Biology 2 Exam 3 Tom Holder SI
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
All animal cells share similarities in the ways in which they
-exchange materials with their surroundings
-obtain energy from organic nutrients
-synthesize complex molecules
-reproduce themselves
-detect and respond to signals in their immediate environment
Levels of animal organization
-cellular: phylum porifera
-tissue: phylum cnidara and ctenotophora
-organ: phylum platyhelminthes
-organ system: advanced animal groups;emphasis in vertebrates
Internal organization of animals
-cells with similar properties group to form tissues
-tissues combine together to form organs
-organs are linked to form organ systems
Tissue
an association of many cells that have a similar structure and function
Types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
Epethelial tissue
sheets of densely-packed cells that: cover the body or enclose organs or line the walls of the body cavities and organs
-specialized to protect and secrete/absorb ions and organic molecules
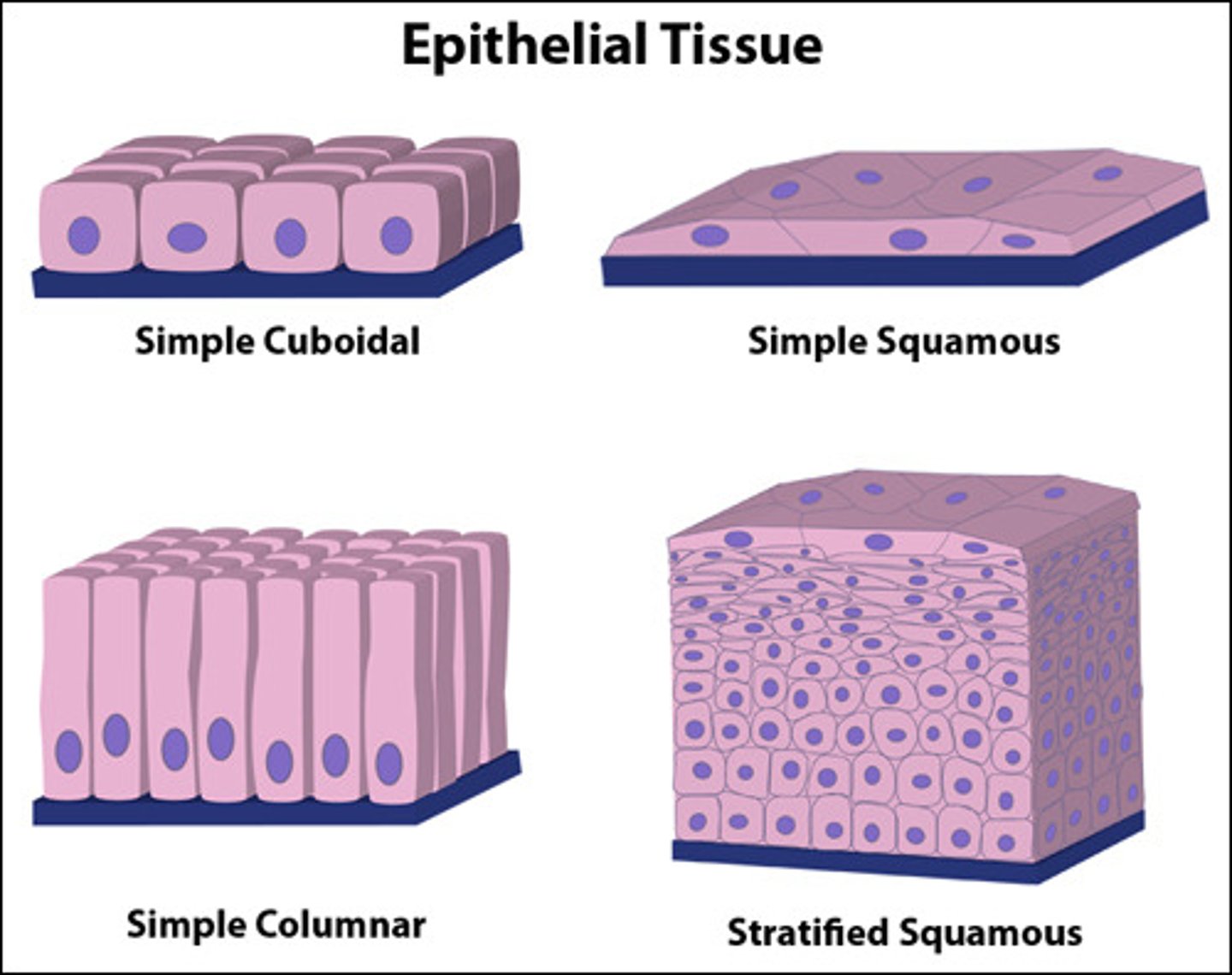
Shapes of epithelial cells
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
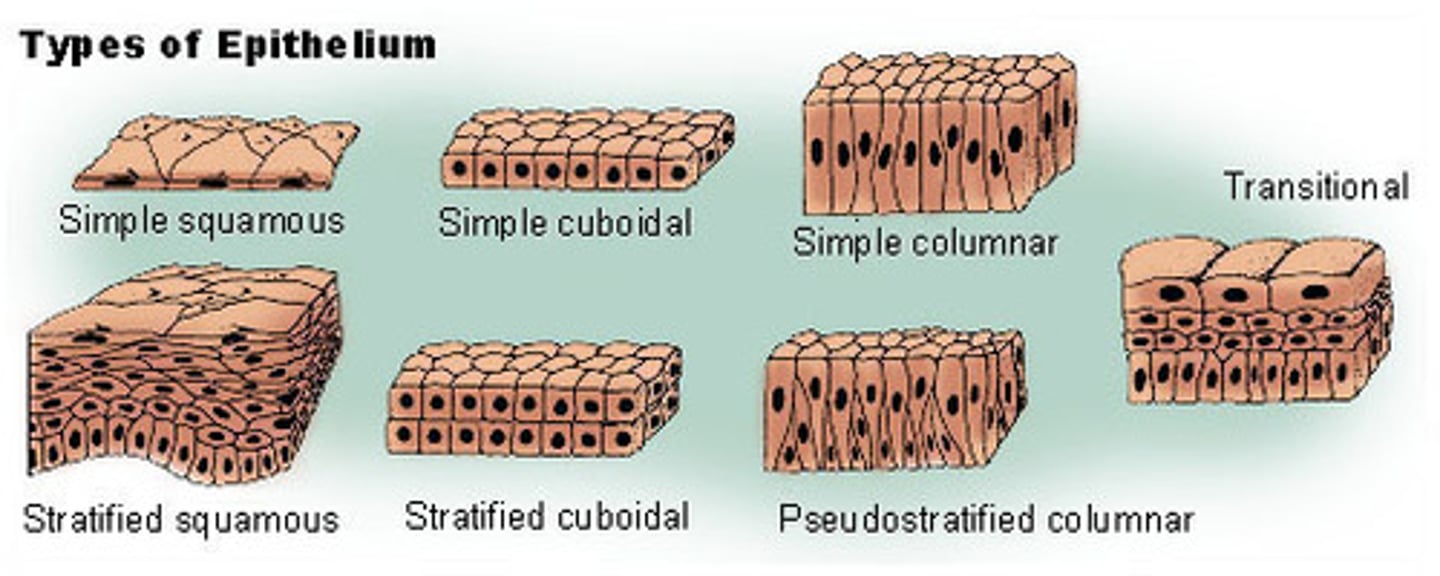
Epithelial cells are arranged to form different types of tissues by being:
simple: one layer
stratified: multiple layered
pseudostratified: one layer that appears to be stratified
epithelial tissue characteristics
all are asymmetrical or polarized
-one side rests on basal lamina (basement membrane) and the other faces environment
-can function as selective barriers
types of epithelial tissue
simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified columnar, stratified squamous, transitional: stretchable tissue
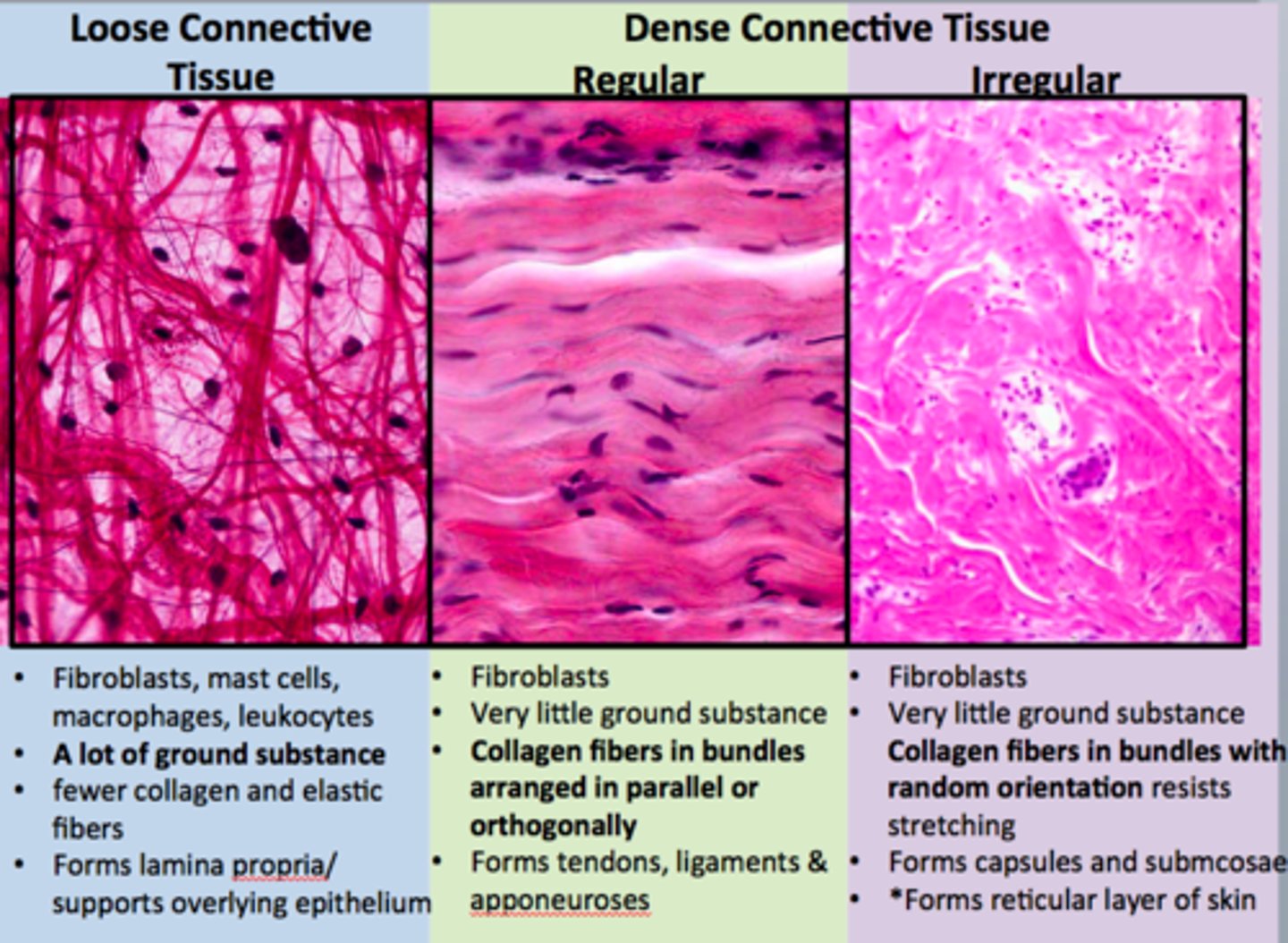
connective tissue
connect, surround, anchor, bind, transport, and support
-form extracellular matrix (ECM) around cells
-provides scaffold for attachment, protects and cushions, mechanical strength, and transmits information
types of connective tissue
-Blood: transport and protection
-Adipose: fat insulation, energy, support, and protection
-Bone: support and protection
-Cartilage: support and flexibility
-Loose: holds internal organs in place
-Dense: strength and support
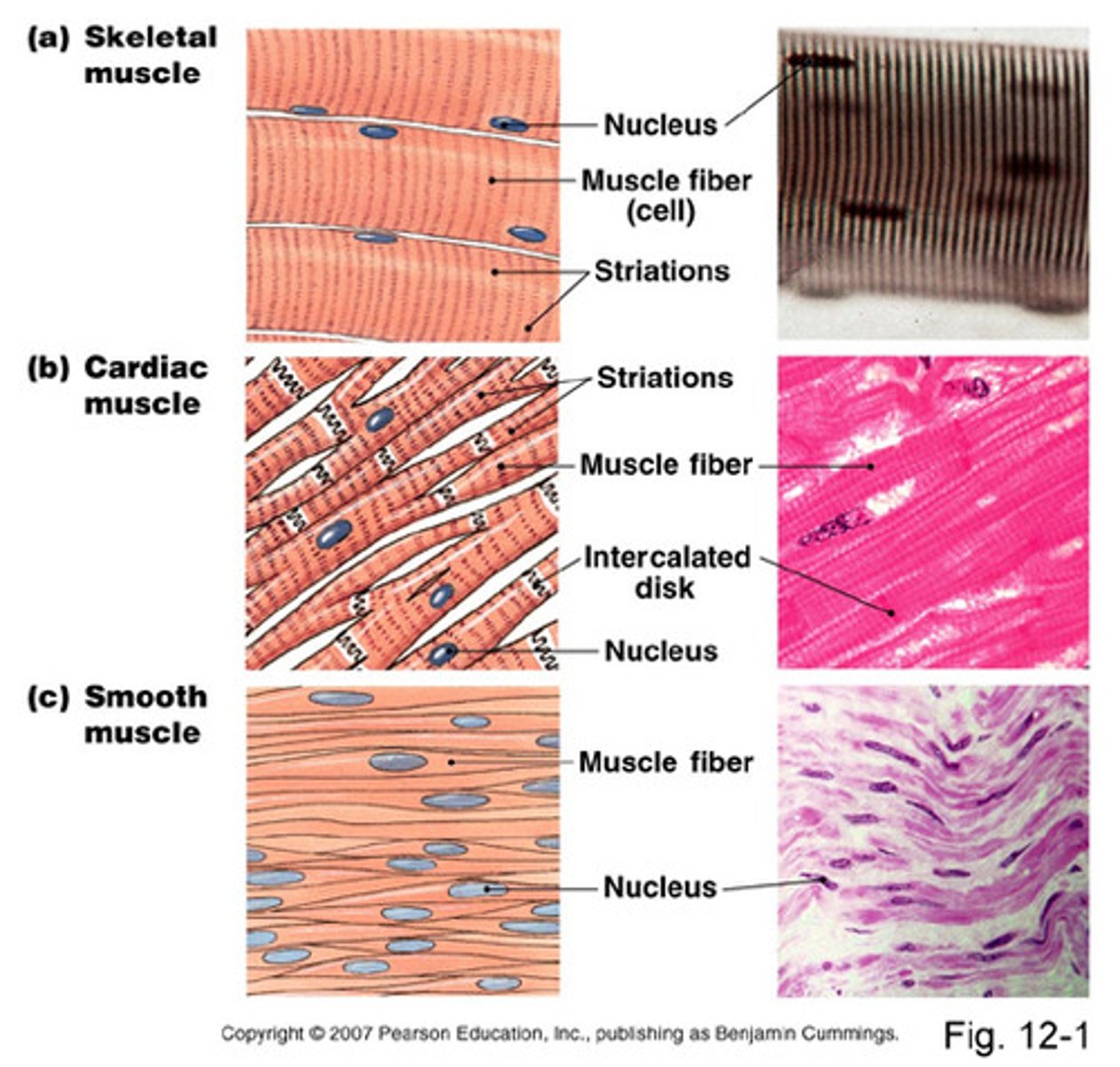
muscle tissue
cells specialized to contract (shorten), generating mechanical force
types of muscle tissue
-skeletal: attached to bone or exoskeleton for locomotion; elongate fibers; voluntary control; tubular cells
-smooth: surrounds tubes and cavities for propulsion of contents; flattened cells; involuntary control
-cardiac: only in hear; elongate fibers; involuntary control; tubular cells
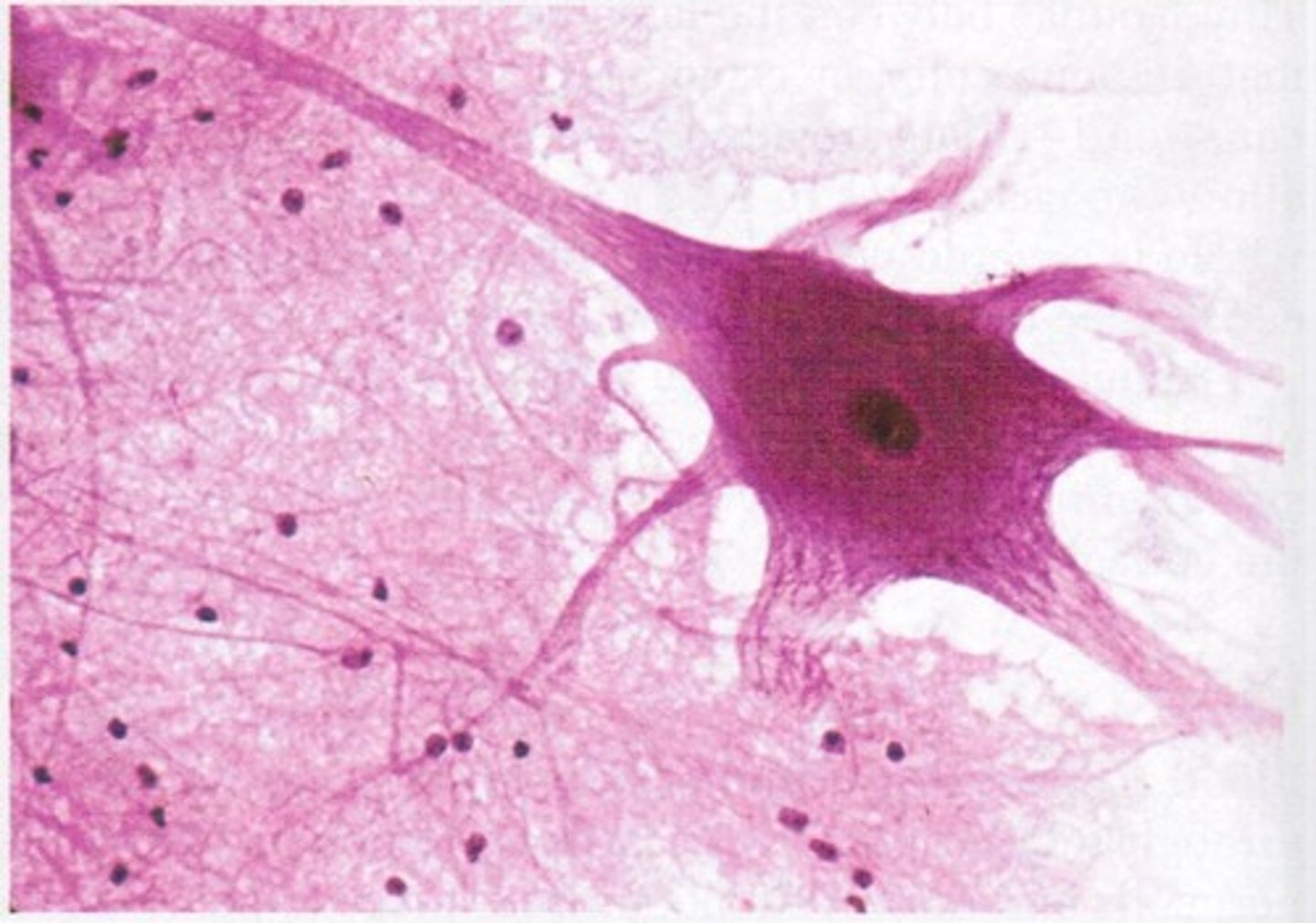
nervous tissue
complex networks of neurons and other cells
-initiate and conduct electrical signals from one part of the animal's body to another
-contains neuroglial cells: more numerous than neurons and provide metabolic support. maintenance, ion balance, and cleaning for neurons
electrical signals produced in one neuron may stimulate or inhibit other neurons to:
-initiate new electrical signals
-stimulate muscle cells to contract
-stimulate glandular cells to release chemicals
Organs
composed of 2 or more tissues
-may form sheets, tubes, layers, bundles, or strips
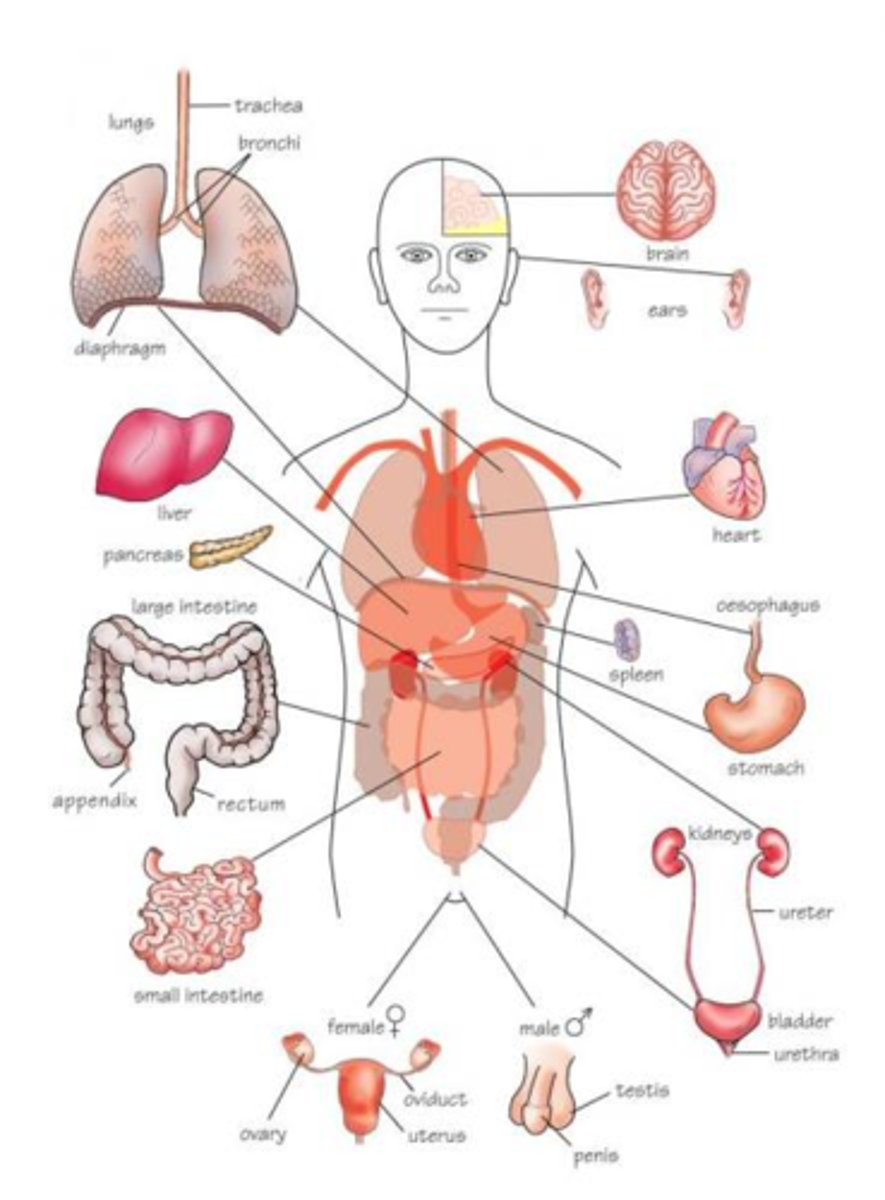
organ system
different organs work together to perform an overall function
-organ systems typically work together
-arrangement of organs into organ systems part of overall body plan controlled by hox genes
Homeostasis
process of adjusting to the external environment and maintaining a stable internal environment
changing variables in environment (related to homeostasis)
-air temp
-water temp
-food supply
-water supply
-pH
-O2 concentration
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail
-integument and derivatives of vertebrates
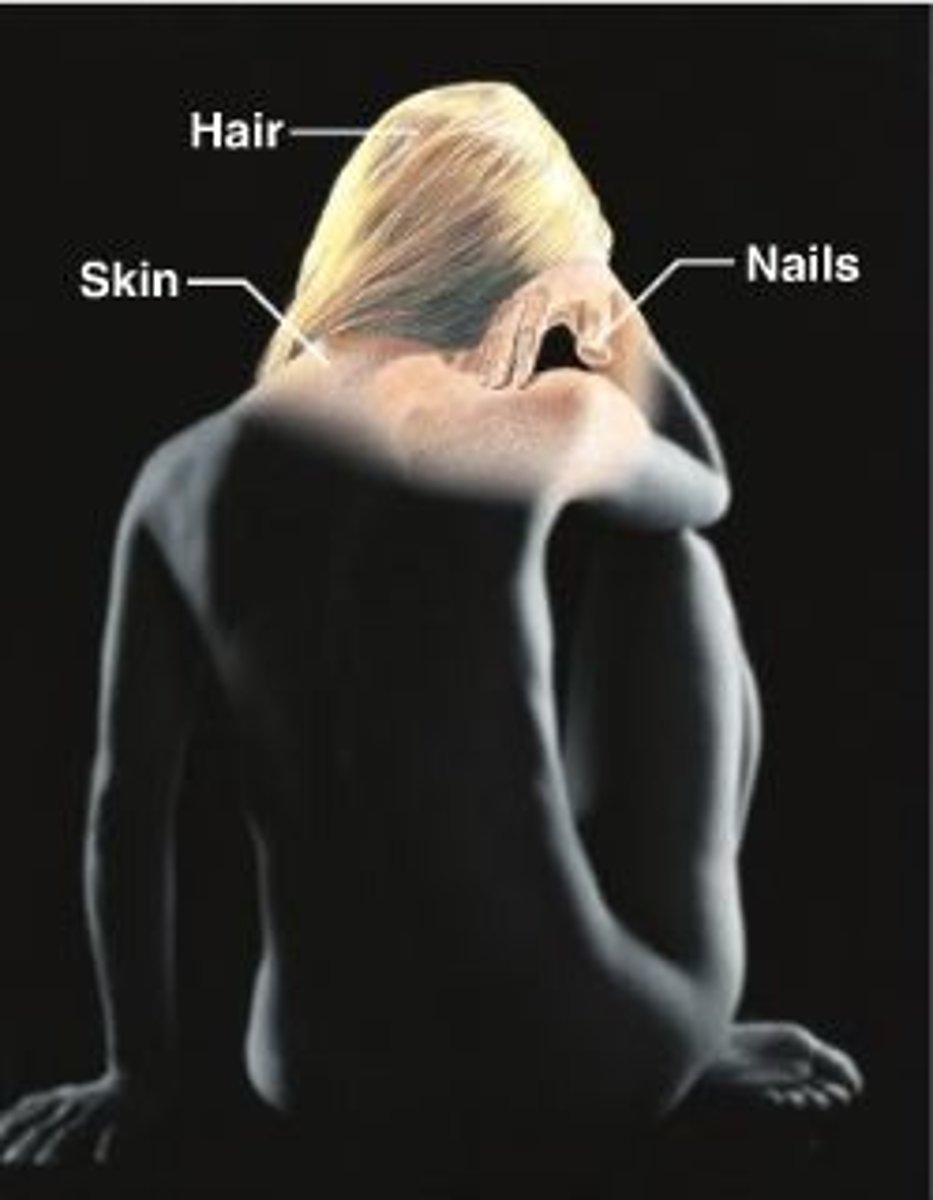
functions of integumentary system
-protection from abrasion
-protection against water loss
-barrier to disease causing pathogens
-protection from UV light
-temp regulation and excretion: evaporative cooling (sweating)
-contains sensory adapters
integument
skin and all other accessories (scales, heathers, hair)
-skin is largest organ of vertebrates
Skin
consists of 2 layers:
-Epidermis: outside of dermis
-Dermis
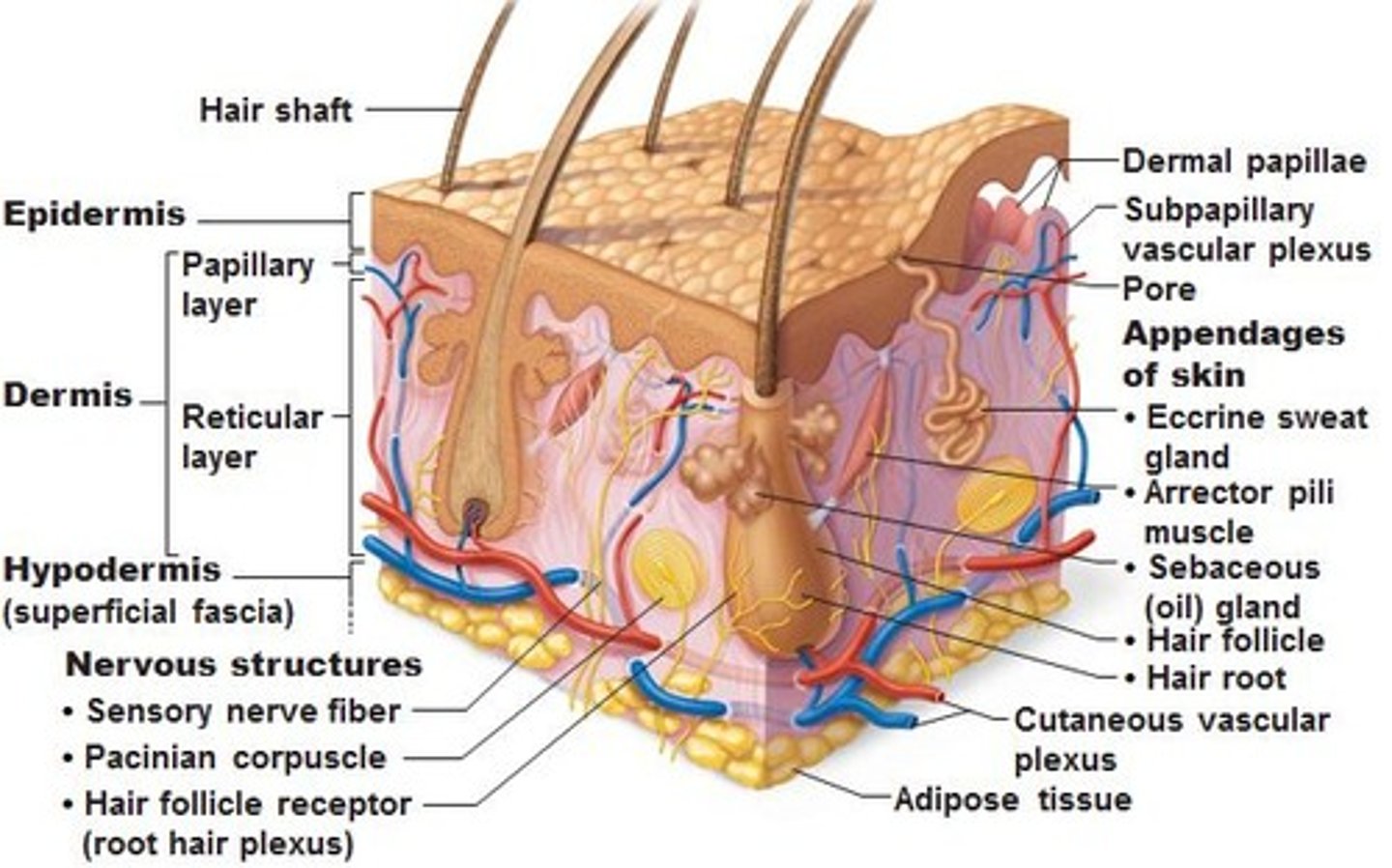
Epidermis
outer layer, thinner
-nutrients diffuse into this from the dermis
-stratified squamous epithelium
cell types of epidermis
Langerhans cells: defensive cells
Melanocytes: produce pigment melanin, skin coloration, and protection from UV light
Merkel cells: touch receptors
Keratinocytes
primary cell type
-produce insoluble protein, keratin
-amount of keratin increases from inside to outside
-keratin fills cytoplasm and impairs nutrient diffusion
dermis
inner layer; thicker than epidermis
-highly vascularized ((vessels)
-contains sensory structures, vessels, nerves, glands
-origin of hair, feathers, scales, etc.
sensory structures
Meissner's corpuscles: light touch
Pachinian Courpuscles: deep pressure, vibration
sweat glands
temperature regulation
-produce sweat (primarily water)
-2.2 million in body
-release of heat
sebaceous glands
produce sebum: lubricates and softens hair and skin
-all over body except for palms and soles
-large on face, neck, and upper chest
Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer)
lies beneath dermis
-NOT LAYER OF SKIN
-contains much adipose (fat) tissue
Functions: body contour, insulation, supports skin
-females have thicker layer of adipose than males
digestive system
body system the breaks down food and absorbs nutrients
nutrient
any substance taken in by an organism that is needed for survival, growth, development, tissue repair, or reproduction
nutrition
process of consuming and using food and nutrients
Hetertrophs
can not make their own food
-require already synthesized organic compounds of plants or animals to supply materials for: survival, maintenance, growth, and reproduction
Two types of gut tracts
1. Blind gut: no cavity between gut and body wall; one opening, primitive form
2. Tube-within-a-tube: flow through digestive system, body cavity between gut and body wall; separate openings and advances
digestive enzymes
-Hydrolases: require water
-Carbohydrase
-proteases
-Lipases
-Nucleases
Food Processing in Animals (5 phases)
1. Ingestion
2. Digestion
3. Transport
4. Absorption
5. Egestion
Ingestion
food is taken into body and moves into a digestive cavity (alimentary canal)
Digestion
food is broken down into smaller molecules (chemical/mechanical)
Absorption
ions, waters, vitamins, minerals, hormones, diffuse or are transported into circulatory system
Egestion
undigested materials and other wastes are passed from the body
alimentary canal
digestive tract/tube with opening at both ends and 5 regions:
1. region of reception
2. region of conduction
3. region of storage and more digestion
4. region of terminal digestion and absorption
5. region of water absorption/concentration of solids
characteristics of alimentary canal
-contains smooth muscle in walls
-lined by epithelial cells
-synthesize and secrete digestive enzymes
-secrete hormones
-transport digested material
-storage area
Structure of GI tract
same general structure from midpoint of esophagus to anus
cloaca: lumen lines by epithelial and glandular cells
-secretory cells releases a protective layer of mucus
-other cells release hormones '-glands release acid, enzymes, water, and ions
Epithelial cells are linked by tight junctions and surrounded by layers of tissue made of smooth muscles, neurons, connective tissue and blood vessels; neurons activated by sight and smell of food
region of reception
Buccal Cavity (mouth and accessory structures)
-ingestion site and digestion site
-jaws, teeth, cheek muscles, tongue, salivary glands
-saliva: enzymes like amylase
-Pharynx: back of mouth cavity and point that digestive and respiratory cross paths
Region of Conduction
Esophagus: tube carrying materials from mouth cavity to of the alimentary canal "neck-region"
-conducts food from pharynx to stomach
Peristalsis: rhythmic wave-like contractions which propel food forward in GI tract; digestion continues here
region of storage and more digestion
Stomach: saclike organ evolved for storing food; muscular nature helps break up food-partial digestion
-regulates rate of emptying into small intestine
Secretions:
-Hydrochloric Acid: kills microbes, dissolves particulate matter, secreted by parietal cells
-Pepsinogen: converted to pepsin to begin protein digestion (chief cells); breaks peptide bonds
-epithelium coated with alkaline mucus
Lumen (cavity) stomach
Region of Terminal Digestion and Absorption
Small Intestine
-nearly all digestion of food, and nearly all absorption of food
-hydrolytic enzymes found on apical surface of epithelial cells or secreted by pancreas into lumen
-products of digestion absorbed across epithelial cells and enter blood; vitamins, minerals, and water absorbed
-simple epithelium; MOST ABSORPTION
small intestine surface area specializations
because small intestine carries out the bulk of digestion and absorption they have:
-Mucosal Infoldings
-Villi: finger-like projections; epithelial cells with microvilli create brush border
These specializations increase surface area 600-fold
-increases likelihood of food particle encountering digestive enzyme and being absorbed
Small intestine regions
1. Duodenum
2. Jejunum
3. Ileum
plicae circulares
large folds of the epithelial lining
-increase surface area 2-3 times
Villi
finger-like projections lined with simple epithelium
-increase surface area 10 time
Microvilli
folding of the plasma membrane of cells lining the villi
-increases surface area 20 times
region of water absorption and concentration of solids
Large Intestine
-conserve and package water
-mammals have intestine of about 1.5 meters
-lack plicae, villi, and microvilli
-water absorbed through epithelium
Function: compacts and elimination of feces
waste (feces)
75% water
5% Inorganic substances
8% Roughage
5% Fat
2% Undigested protein, dead cell, bile
-limited vitamin synthesis by resident bacteria
anus
end of large intestine; opening at posterior end of alimentary canal for the release of waste material
Cloaca: some vertebrates; chamber receiving contents of digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts; vent opening to the outside (Birds, Reptiles)
accessory digestive organs
NOT PART OF ALIMENTARY CANAL
-Pancreas: secrete enzymatic juices through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum of the GI
-Liver: produces bile (assist enzymes in breakdown of large fat globules into smaller forms )
-Gallbladder: storage of bile; secreted bile into GI as needed
-Biomolecules
-Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, and Nucleic Acids
nervous system
consists of CNS (brain and spinal chord) and PNS (neurons and their projections that are outside of CNS)
Types of cells in nervous system
neurons and glial cells
Neurons
cells that send and receive electrical and chemical signals to and from each other and other cells throughout the body
-structural and functional units
-present in all animals but sponges
-number varies widely as a function of size and behavioral complexity
Neuron Structure
Cell body: contains nucleus and organelles
Dendrites: extensions of cell body that RECEIVE incoming signals
Axon: extensions of cell body that CARRIES signals AWAY to other cells; typically single and vary in length
--Axon hillock: near cell body
--Axon terminals: convey electrical or chemical signals to other cells
Wrapper in Myelin Sheath
Glia
surround neurons and perform numerous functions
-Astrocytes: metabolic support, form the blood-brain barrier, and maintain stable concentration of ions in extracellular fluid
-Microglia: participate in immune functions and remove cellular debris
1000x more numerous than neurons
Myelin Sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
-Nodes of Ranvier
-Oligodendrocytes
-Schwann Cells
-Radial Glial Cells
types of neurons
1. Sensory: detect info from outside world or internal body conditions; transmit signal to CNS; AKA afferent neurons
2. Motor: send signals away from CNS (efferent neurons) to elicit response
3. Interneurons: form connections between other neurons; critical in interpretation of info and elicited response
reflex arc
stimulus from sensory neurons sent to CNS, little or no interpretation, signal transmitted to motorneurons to elicit response
QUICK AND AUTOMATIC RESPONSE
-stimulus to receptor (effector to response)
Electrical Properties of Neurons
- membrane potential- "gatekeeper" (selectively permeable)
-ONLY neurons and muscle cell generate electrical signals
-cell is POLARIZED due to membrane's permeability
-> difference in ions between inside/outside of neuron- causes both chemical and electrical differences
resting membrane potential
state where neuron is not sending a signal
-selectively permeable to cations and anions; inside is more negative and outside is more positive
-anions inside are drawn to the cations outside so most ions are near the edge of the membrane
electro-chemical gradient
imbalance due to differences inside/outside of neuron
-chemicals: K+, Na+, Cl-
-charge: + or -
3 factors contributing to resting potential
1) sodium-potassium pump: ATP; pumps 3 Na for every 2 K; pumps from LOW to HIGH concentration
2) Ion specific channels allow passive movement: membrane is more permeable to K; K channels more frequently open at resting potential
3) Polarity: more negative inside neuron
gated ion channels
-voltage-gated: open/close in response to voltage changes
-chemical-gated: open/close in response to chemicals
nerve impulse
the message carried by a neuron
-higher the frequency, greater the excitation level (faster reaction)
1.RESTING POTENTIAL
2.ACTION POTENTIAL
3.SODIUM-POTASSIUM PUMP
resting potential
imbalance between K+ and Na+ inside/outside
-membrane selectively permeable to K but channels close for Na and Cl
-outside neuron: 10x more Na, 5x more Cl
-inside neuron: 30x more K
action potential
a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
-electric potential of the impulse
-self-propagating
-after passing a given point, membrane returns to resting
-at given impulse point, channels for Na open and Na diffuses in
-K already diffusing out, but is increased
sodium-potassium pump
complex of proteins in membrane
-pump out Na and carry in K
-returns the imbalance
-requires ATP: low --> high
nerve impulse rate
variable dependent on complexity of system and organism
Ex: sea anemones (0.1 m/s), mammal (120 m/s)
Invertebrate speed relevant to axon diameter
Vertebrate speed combo of axon diameter and layer of myelin sheath
-every jump picks up speed
evolution of nervous system
1. phylum cnidaria (jellyfish): nerve net, simplest organization, simple primitive cells
2.phylum Platyhelminthes(flatworms): 2 anterior ganglia, weak PNS and no brain or spinal chord
3.phylum Annelida(segmented worms): brain, ventral nerve chord, simpler motor/sensory neurons
4. phylum Mollusca(mollusks): complex except for squid and octopus which may be close but not quite
5. phylum Arthropoda: similar to annelids and most mollusks EXCEPT SOCIAL INSECTS. social insects have well developed brain, complex social behaviors, learning, etc
6. vertebrates: CNS-brain and spinal chord; most complex
Meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
-outer: Duramater
-middle: Arachnoid
-inner: Piamater
between these and in canal of spinal chord is cerebrospinal fluid
spinal chord
enclosed within vertebral column
always dorsal and hollow
brain
increase in size with complexity and vertebrate evolution
3 divisions: Hindbrain, Midbrain, Forebrain
Brain:Spinal cord ratio
fish 2:1
amphibians 10:1
reptiles 25:1
birds 35:1
humans 55:1
Thalamus
signal and relay station between midbrain and higher brain regions
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
-homeostasis regulation
"house keeping center"
pituitary gland
tiny hormonal gland
corpus callosum
thick band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
Ex; thinking, communication, learning
largest overall part
Midbrain
Region between the hindbrain and the forebrain; it is important for hearing and sight.
spinal chord function
transmit signals to and from the brain and the rest of the body, acts independently of the brain to produce local reflexes
Medulla
an extension of the spinal cord into the skull that coordinates heart rate, circulation, and respiration
skeleton
a structure that functions in support, protection, locomotion (movement from one place to another)
Three types of skeletons
exoskeleton, endoskeleton, hydroskeleton: found in some soft-bodies invertebrate that use water
-use water pressure for propulsion
exoskeleton
external skeleton that surrounds and protects body surface
-arthropod skeleton(crayfish): made of chitin, tough and durable, segmented for movement, growth requires molting
-vary in complexity, thickness, and durability; muscles are attached
endoskeleton
internal structures; do not protect body surface, only internal organs
-found in echinoderms and vertebrates
-minerals provide firmness
-echinoderm skeletons composed of spiky networks of proteins and minerals or mineralized plate-like structures
-vertebrate skeletons composed entirely of cartilage or of cartilage and bone; living structure that grows and allows growth of animal
other functions of skeleton
- blood cells and platelets are formed in marrow
- calcium and mineral storage
- provides attachment sites for skeletal muscle
bone
living, dynamic, connective tissue
-organic components:
--osteoblasts and osteocytes: cells of bone
--collagen: provides strength and flexibility
--osteoclasts: breakdown bone
mineral component: mix of Ca2+, PO4-, and other ions that provide rigidity
-continuously formed, broken down, and reformed
formation of bone
1. endochondral (bone replacing cartilage)
2. intramembranous (bone forms with tissue membranes) skull plates
-1in^3 of bone can sustain 1900 lbs
-1mm diameter of collagen can hold 19 lbs
Types of bone tissue
Compact: composed of osteons; AKA ground-bone
Spongy: lack osteons, lots of air spaces; "bony spikes: (trabeculae)
Osteon
structural unit of compact bone
osteonic canal
Supports and protects from damage while providing space for arteriole, venules, and nerves