Photosynthesis: Light Reactions and the Calvin Cycle
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Photosynthesis
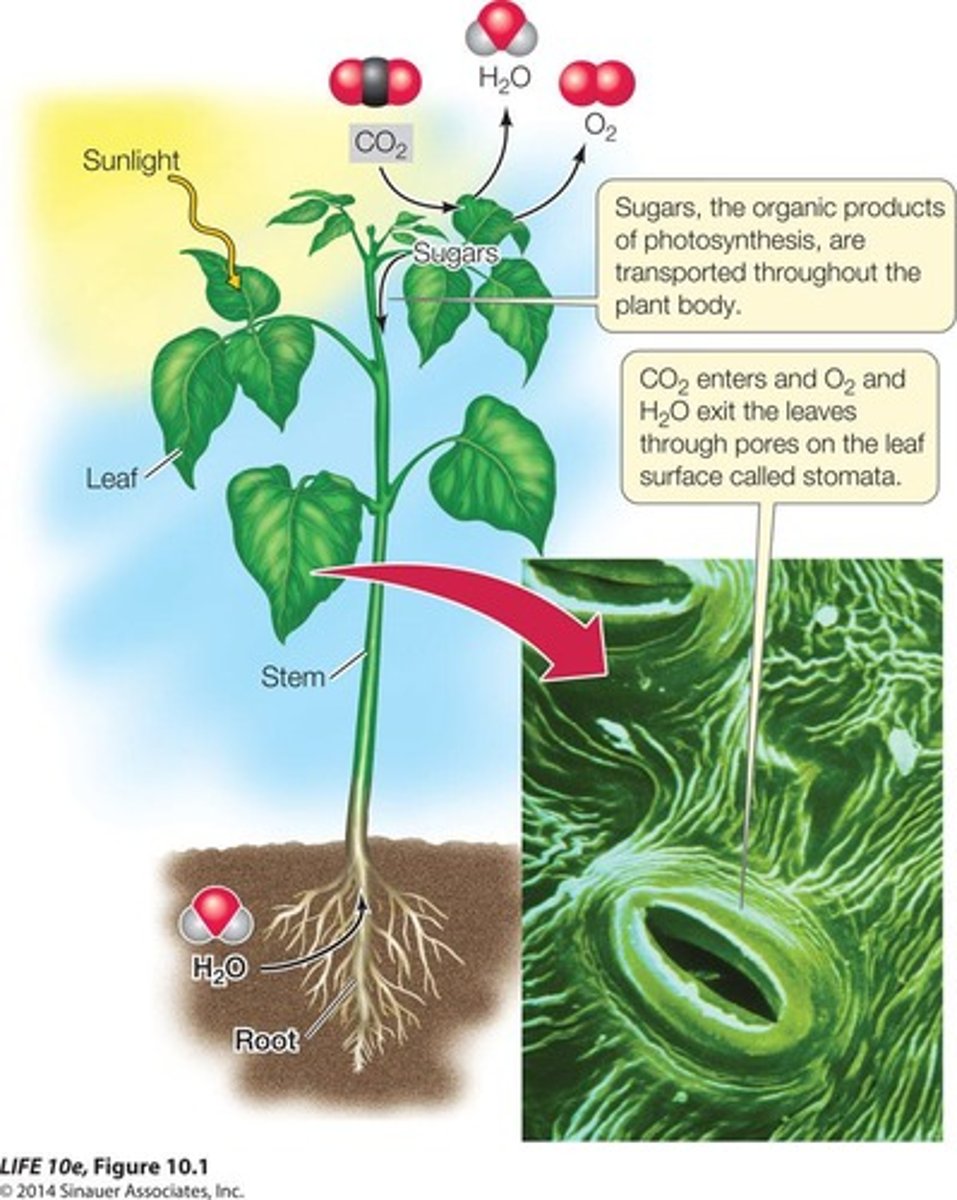
Process by which plants make their own food.
Anabolic Reaction
Builds complex molecules from simpler ones.
Endergonic Reaction
Requires energy input to proceed.
Water
Enters roots via osmosis for photosynthesis.
Stomata
Tiny openings for gas exchange in leaves.
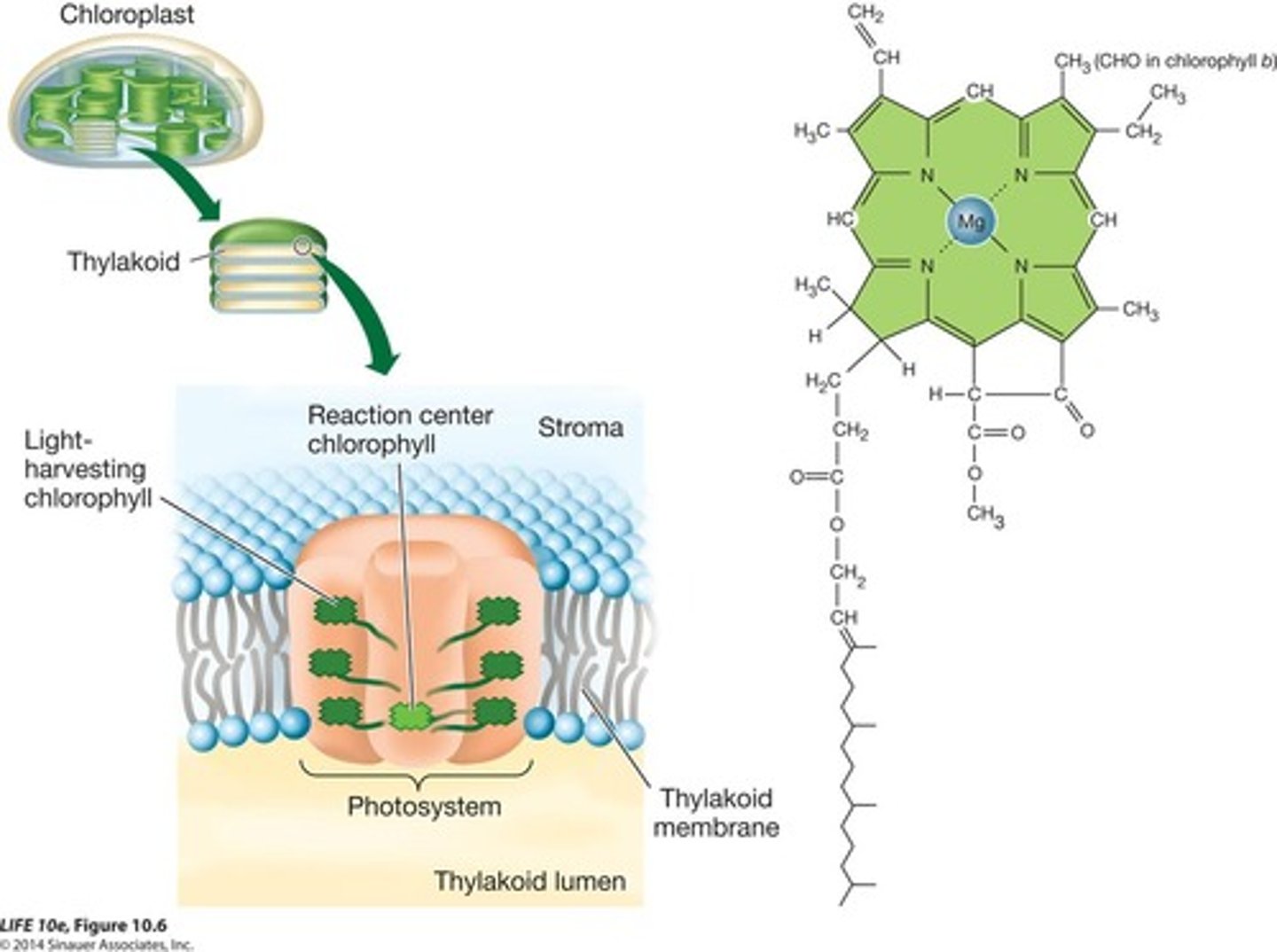
Chloroplasts
Organelles where photosynthesis occurs in plants.
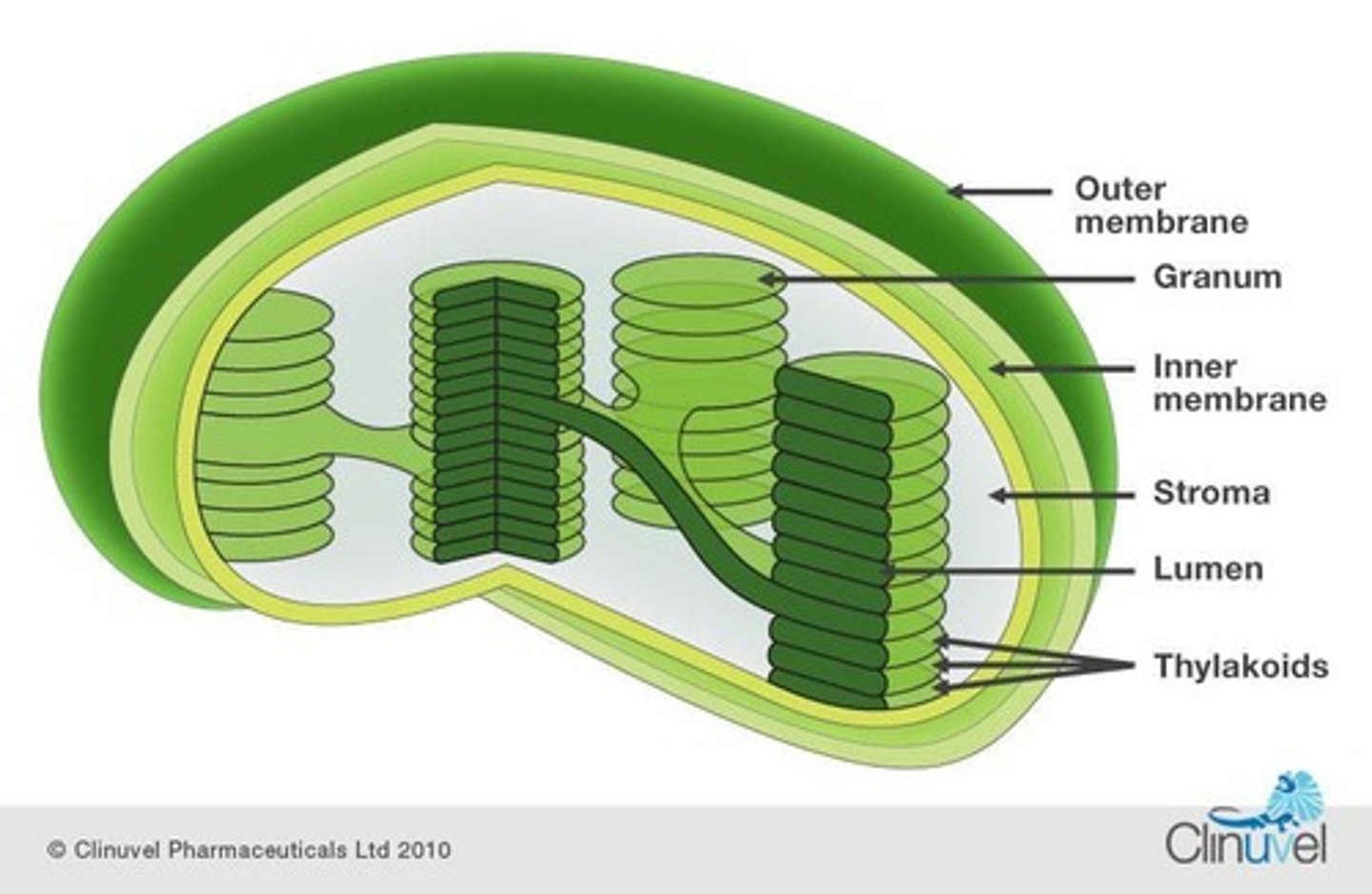
Thylakoids
Membrane-enclosed compartments within chloroplasts.
Stroma
Fluid-filled space surrounding thylakoids in chloroplasts.
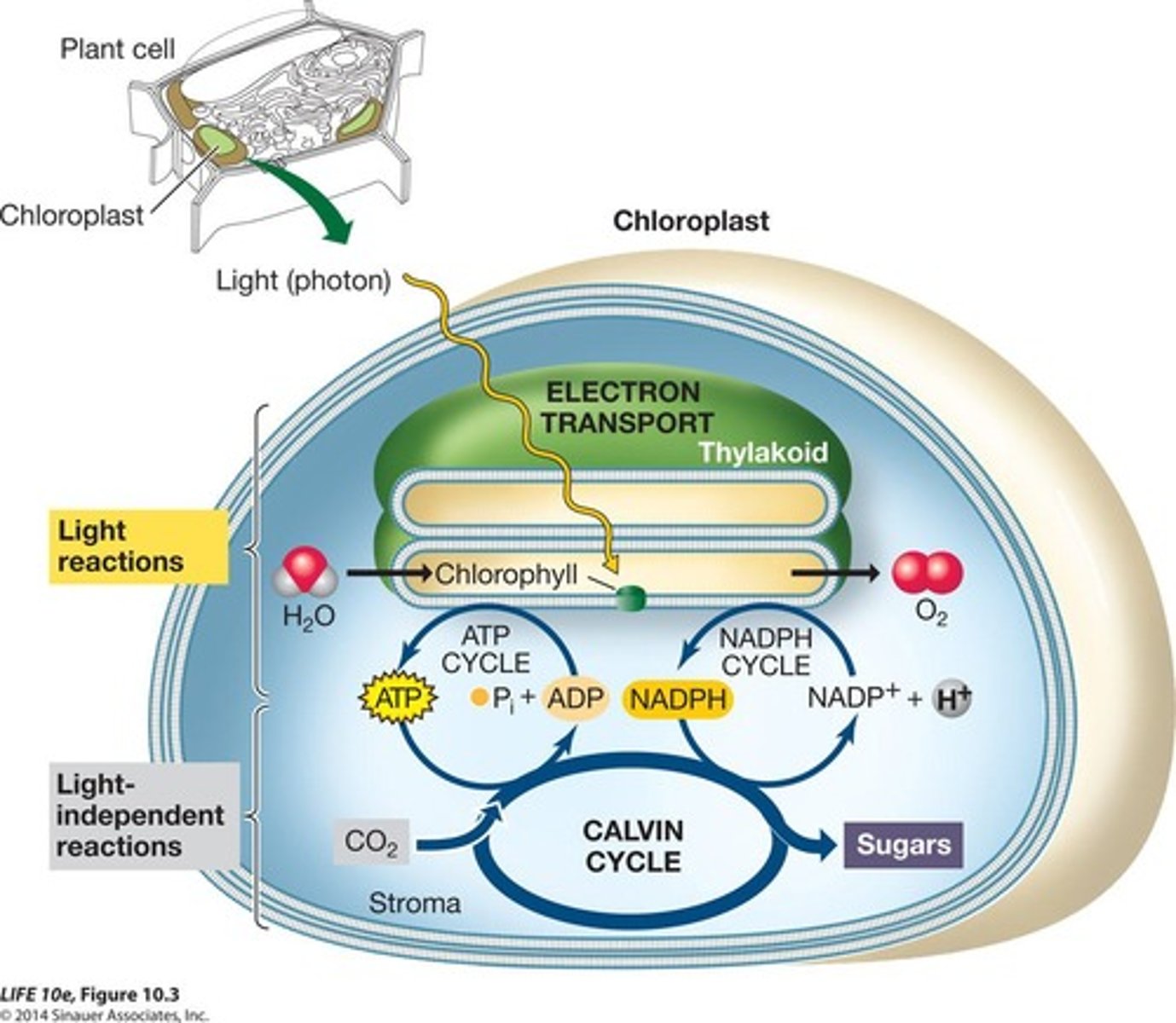
Light Reactions
Convert light energy into ATP and NADPH.
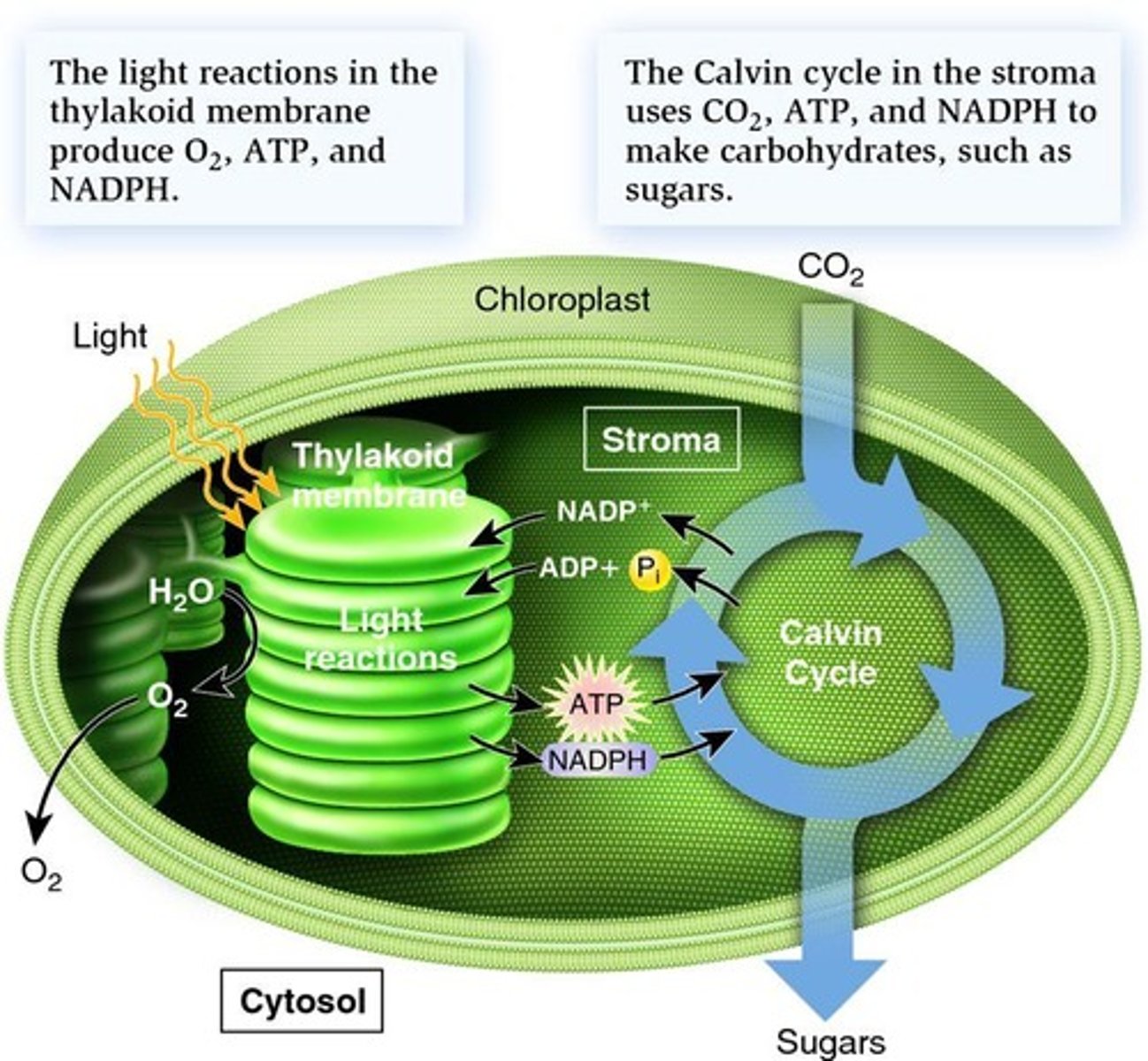
Calvin Cycle
Uses ATP and NADPH to synthesize glucose.
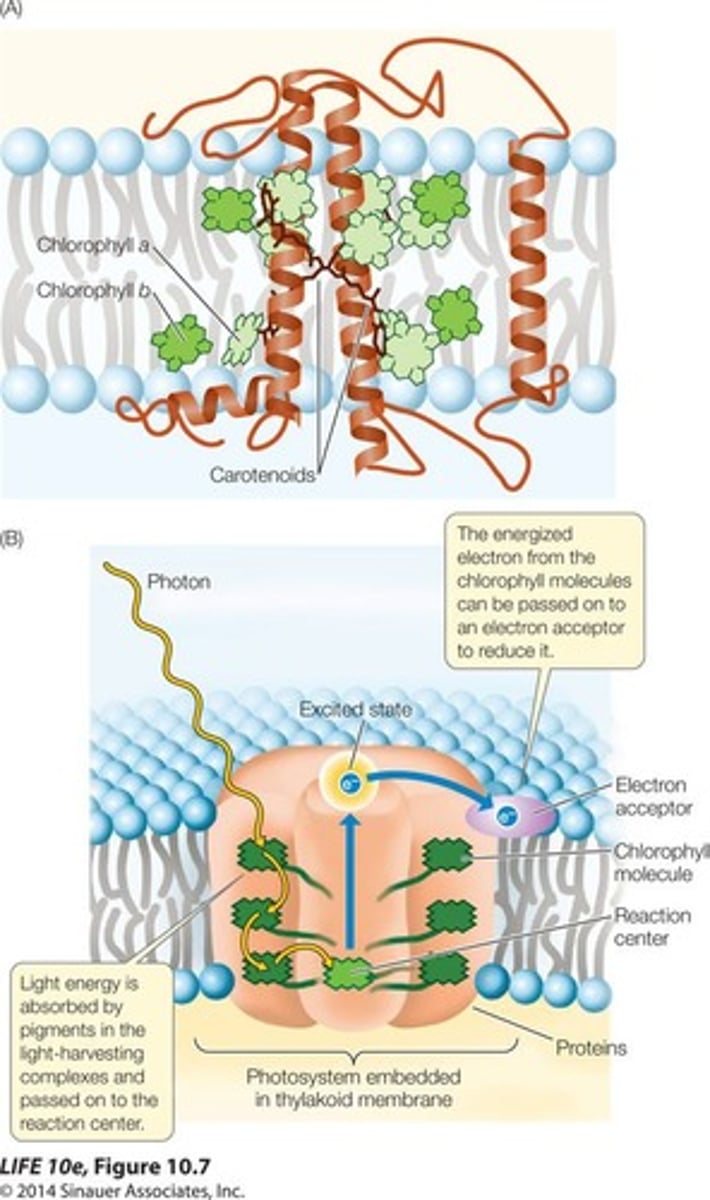
Photons
Packets of light energy that drive photosynthesis.
Pigments
Molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light.
Chlorophyll A
Most abundant pigment in plants, absorbs light.
Photosystems
Complexes of pigments that initiate light reactions.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Series of reactions transferring electrons in thylakoids.
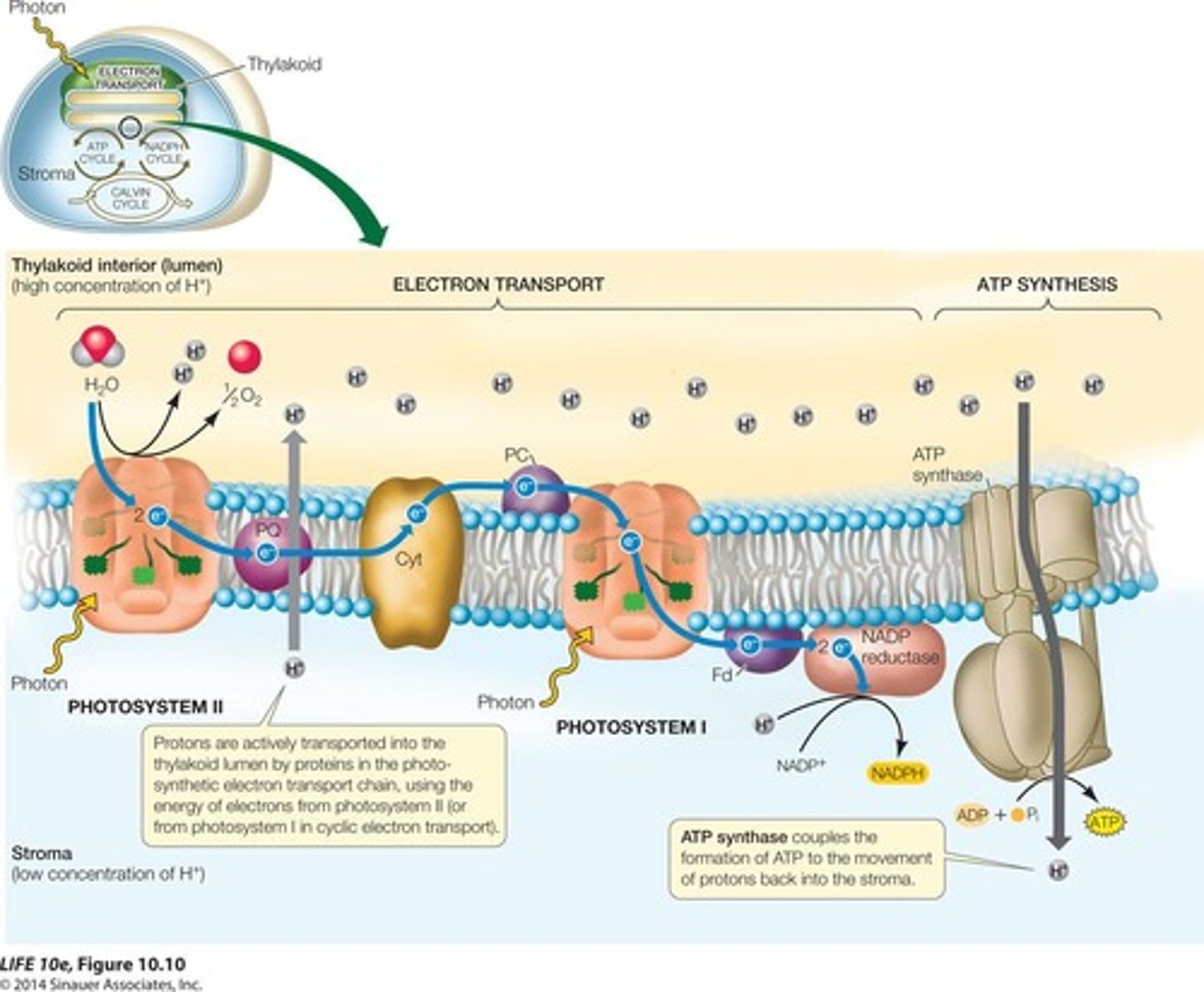
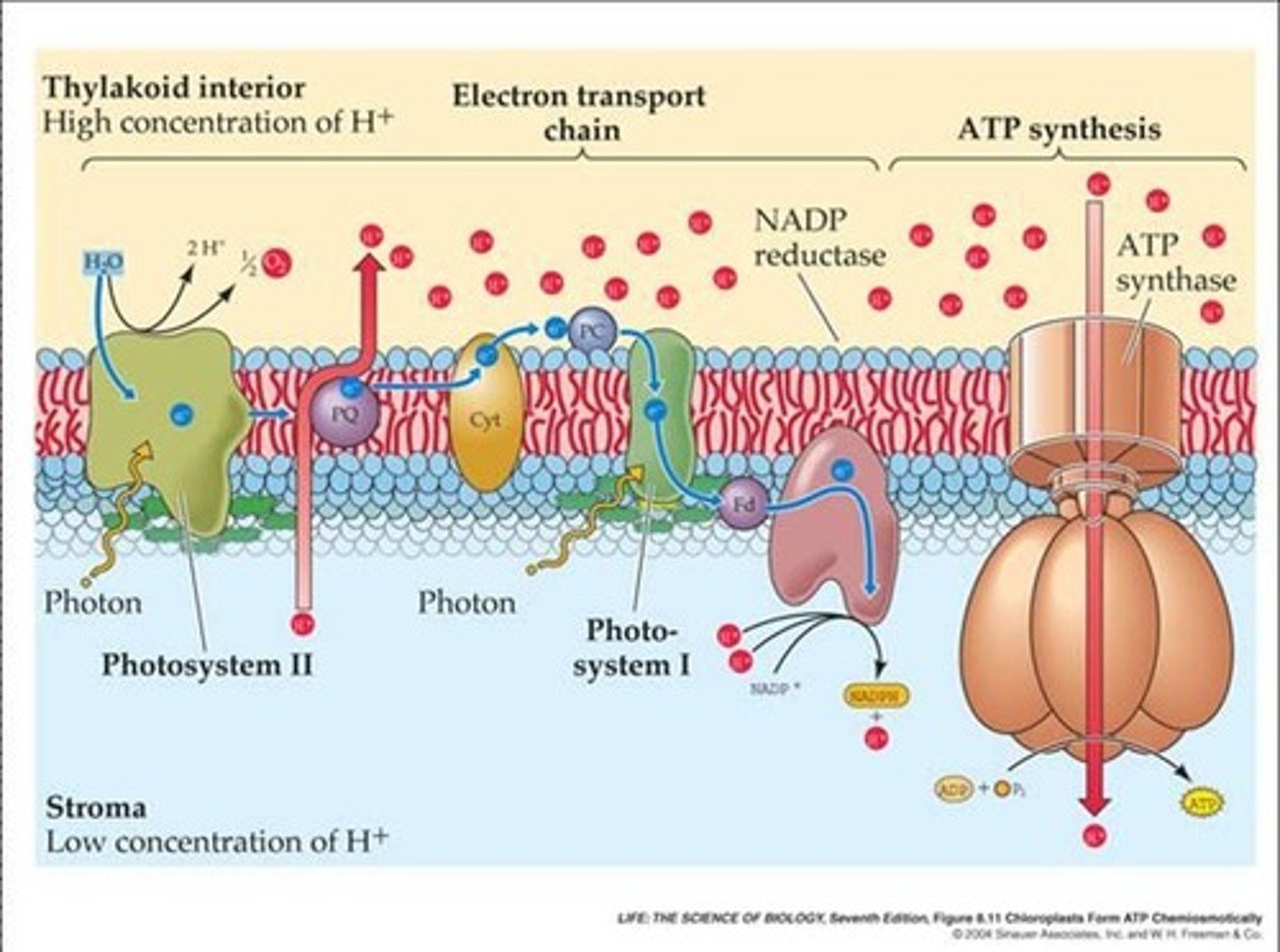
Concentration Gradient
Difference in proton concentration across thylakoid membrane.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme that produces ATP using proton flow.
NADP+
Oxidized form, final electron acceptor in photosynthesis.
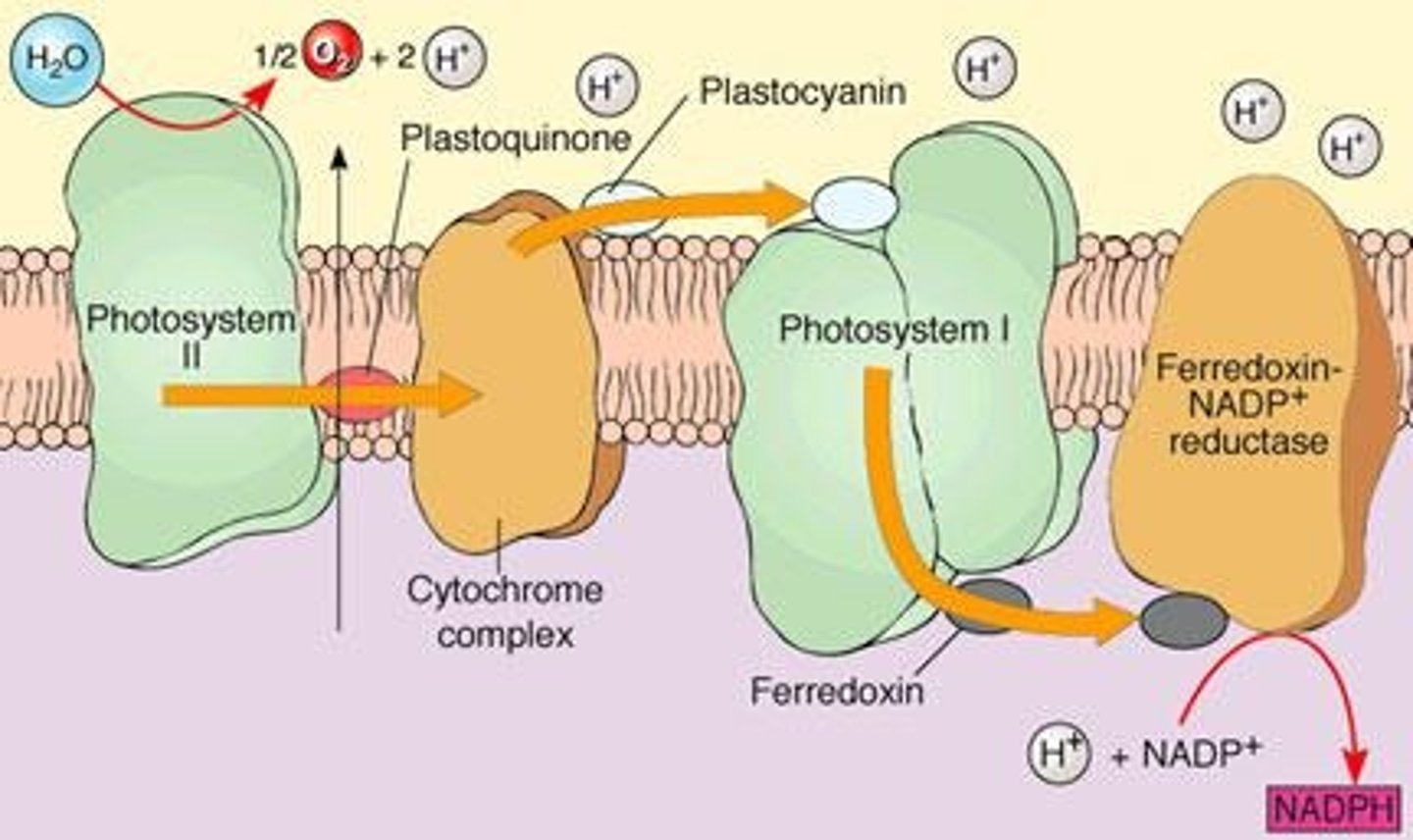
NADPH
Reduced form, carries electrons for Calvin cycle.
Carbon Fixation
Incorporation of CO2 into organic compounds.
3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG)
First stable product of carbon fixation.
Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate (G3P)
Intermediate formed from 3PG, can become glucose.
Rubisco
Enzyme that catalyzes CO2 fixation in Calvin cycle.
RuBP
5-carbon molecule that reacts with CO2.
Photorespiration
Process where Rubisco uses O2 instead of CO2.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from others.
Efficiency of Photosynthesis
Only about 5% of sunlight converted to sugars.
Climate Change Impact
High temperatures affect CO2/O2 balance in plants.
Oxygen Release
Byproduct of water splitting during light reactions.