ib econ- 4.4: economic integration
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/global-economy/4-4-economic-integration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is economic integration?
the process of nations becoming more interdependent and economically unified with each other
what is a preferential trade agreement?
forms of economic integration that involve multiple countries committing trade treaties with each othee, ensuring that each side receive favourable conditions
what re the three levels of trade agreement?
bilateral trade agreements: ones between two countries in order to reduce barriers to trade
regional trade agreements: ones between more than two countries but often confined to a certain region.
multilateral trade agreements: ones between more than two countries, but under supervision and guidance by the world trade organisation
what is a trading bloc?
a group of countries that integrate economically, by reducing trade barriers. they can also sometimes collectively impose tariffs and other barriers to outside countries. therefore to varying extents, they can be considered singular economic entities.
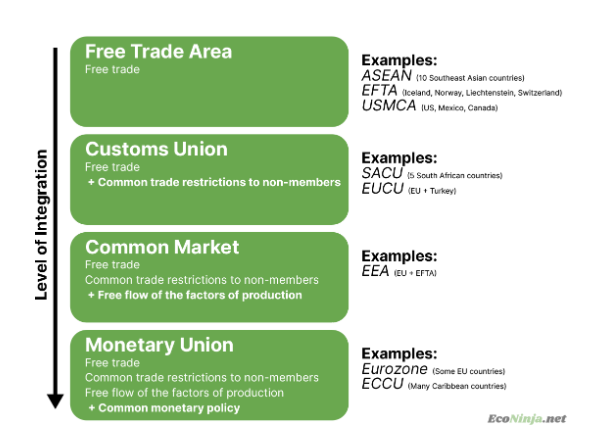
what are the three levels of trading blocks?
free trade areas: a trading block with free trade between member countries, but they can still impose different trade restrictions to non-member countries
customs unions: a trading block with free trade within member countries, member countries impose the same trade restrictions on non-member countries
common markets: a customs union but the four factors of production can move freely between member countries
what are advantages of trading blocs?
greater access to markets offers the potential for economies of scale
with freedom of labour, there may be greater employment opportunities
membership in a trading bloc may allow for stringer bargaining power in multilateral negotiations
greater political stability and cooperation as interdependence between countries encourages cooperation for the greater good
what are the disadvantages of trading blocs?
loss of sovereignty; countries can no longer do exactly as they please (big driving force behind Brexit)
challenge to multilateral trading negotiations as so many ocuntries are involved and negotiation is difficult
what is a monetary union?
a common market with added collective monetary policy (currency)
what is the world trade organisation (wto)?
an intergovernmental organisation that exists to promote trade liberalisation, facilitate and regulate multilateral trade agreements and handle trade disputes between member countries
what are the objectives and functions of the wto?
set and enforce rules for international trade
facilitate and promote trade liberalisation
resolve trade disputes
increase transparency of trade agreement decision making
cooperate with other international economic institutions
help developing countries benefit from global trading
what are the factors affecting the influence of the wto?
difficulties in reaching agreement on services/primary products: many countries enable protectionism to sustain a domestic industry in areas where it would be more economic to trade (e.g. Scandinavia places high tariffs on agricultural products from abroad whilst highly subsidising its own farmers). this is against wto principles but it is difficult for them to make countries give up their sovereignty
unequal bargaining power of members: countries with the largest amount of consumers tend to have more bargaining power